Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
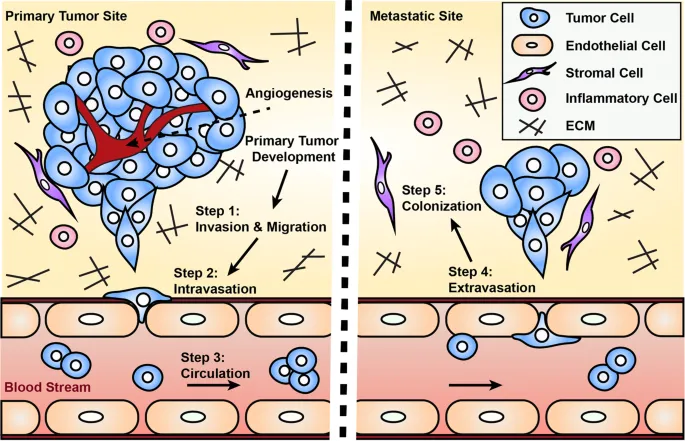
Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors US Medical PG Question 1: A researcher is studying the ability of breast cancer cells to metastasize. Neoplastic cells obtained from 30 patients with stage IV ductal carcinoma of the breast are tagged with a fluorescent antibody. The cells are then inserted into a medium resembling normal human tissue. After 2 weeks, all samples show in vitro hematogenous invasion and migration away from the original site of insertion. Which of the following properties is most likely responsible for the ability of these neoplastic cells to metastasize?
- A. Loss of cellular polarity
- B. Presence of fibrous tissue capsule
- C. Overexpression of HER2/neu
- D. Increase in N:C ratio
- E. Release of matrix metalloproteinase (Correct Answer)
Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors Explanation: ***Release of matrix metalloproteinase***
- **Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)** degrade components of the **extracellular matrix (ECM)** and **basement membrane**, allowing cancer cells to invade surrounding tissues and metastasize [1].
- The in vitro observation of **hematogenous invasion** and **migration** confirms the ability to break down barriers critical for metastasis [2].
*Loss of cellular polarity*
- While **loss of polarity** is a feature of malignant transformation, it primarily contributes to disorganized growth and invasion rather than the active breakdown of the physical barriers required for long-distance metastasis.
- It does not directly explain the enzymatic degradation of the **ECM** necessary for transmural passage into blood vessels [2].
*Presence of fibrous tissue capsule*
- A **fibrous tissue capsule** typically indicates a **benign tumor** or a well-demarcated malignant tumor with limited invasiveness, restricting spread.
- Its presence would hinder, rather than promote, the ability of cancer cells to metastasize.
*Overexpression of HER2/neu*
- **HER2/neu overexpression** is a marker of aggressive breast cancer and can promote cell proliferation and survival.
- However, it does not directly facilitate the enzymatic degradation of the **extracellular matrix** required for active invasion and migration [2].
**References:**
[1] Cross SS. Underwood's Pathology: A Clinical Approach. 6th ed. (Basic Pathology) introduces the student to key general principles of pathology, both as a medical science and as a clinical activity with a vital role in patient care. Part 2 (Disease Mechanisms) provides fundamental knowledge about the cellular and molecular processes involved in diseases, providing the rationale for their treatment. Part 3 (Systematic Pathology) deals in detail with specific diseases, with emphasis on the clinically important aspects., pp. 232-233.
[2] Kumar V, Abbas AK, et al.. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. 9th ed. Neoplasia, pp. 314-316.
Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors US Medical PG Question 2: A 56-year-old woman presents to a physician for evaluation of a lump in her left breast. She noticed the lump last week while taking a shower. She says that the lump seemed to be getting larger, which worried her. The lump is not painful. The medical history is unremarkable. She has smoked cigarettes for the last 30 years. On examination, bilateral small nodules are present that are non-tender and immobile. A mammography confirms the masses and fine needle aspiration cytology of the lesions reveals malignant cells arranged in a row of cells. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Fibroadenoma
- B. Mucinous carcinoma
- C. Inflammatory carcinoma
- D. Invasive lobular carcinoma (Correct Answer)
- E. Invasive ductal carcinoma
Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors Explanation: ***Invasive lobular carcinoma***
- The classic presentation of **invasive lobular carcinoma** includes **bilateral, non-tender, immobile masses** and malignant cells arranged in a **single-file pattern** on FNA, often described as "**Indian files**".
- This type of cancer frequently presents with subtle thickening or diffuse induration rather than well-defined masses due to its infiltrative growth pattern.
*Fibroadenoma*
- **Fibroadenomas** are typically **benign, mobile, well-defined** masses, often described as "rubbery" or "slippery," unlike the immobile nodules described.
- While they can be firm, they do not show malignant cells on FNA or the classic "Indian file" arrangement.
*Mucinous carcinoma*
- **Mucinous carcinoma** is characterized by the presence of tumor cells floating in abundant **extracellular mucin**, which would be evident on FNA.
- This typically presents as a **soft, gelatinous mass**, which doesn't align with the description of firm, immobile nodules.
*Inflammatory carcinoma*
- **Inflammatory carcinoma** presents with characteristic inflammatory signs like **redness, warmth, swelling, and peau d'orange** (orange peel skin appearance) due to dermal lymphatic invasion.
- These prominent skin changes are not mentioned in the patient's presentation.
*Invasive ductal carcinoma*
- **Invasive ductal carcinoma** usually presents as a **solitary, firm, irregular mass** and on FNA typically shows malignant cells in **duct-like structures** or disorganized clusters, not characteristically in single-file lines.
- While it is the most common type of breast cancer, the specific "Indian file" arrangement points more strongly to lobular carcinoma.
Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors US Medical PG Question 3: A research team develops a new monoclonal antibody checkpoint inhibitor for advanced melanoma that has shown promise in animal studies as well as high efficacy and low toxicity in early phase human clinical trials. The research team would now like to compare this drug to existing standard of care immunotherapy for advanced melanoma. The research team decides to conduct a non-randomized study where the novel drug will be offered to patients who are deemed to be at risk for toxicity with the current standard of care immunotherapy, while patients without such risk factors will receive the standard treatment. Which of the following best describes the level of evidence that this study can offer?
- A. Level 1
- B. Level 3 (Correct Answer)
- C. Level 5
- D. Level 4
- E. Level 2
Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors Explanation: ***Level 3***
- A **non-randomized controlled trial** like the one described, where patient assignment to treatment groups is based on specific characteristics (risk of toxicity), falls into Level 3 evidence.
- This level typically includes **non-randomized controlled trials** and **well-designed cohort studies** with comparison groups, which are prone to selection bias and confounding.
- The study compares two treatments but lacks randomization, making it Level 3 evidence.
*Level 1*
- Level 1 evidence is the **highest level of evidence**, derived from **systematic reviews and meta-analyses** of multiple well-designed randomized controlled trials or large, high-quality randomized controlled trials.
- The described study is explicitly stated as non-randomized, ruling out Level 1.
*Level 2*
- Level 2 evidence involves at least one **well-designed randomized controlled trial** (RCT) or **systematic reviews** of randomized trials.
- The current study is *non-randomized*, which means it cannot be classified as Level 2 evidence, as randomization is a key criterion for this level.
*Level 4*
- Level 4 evidence includes **case series**, **case-control studies**, and **poorly designed cohort or case-control studies**.
- While the study is non-randomized, it is a controlled comparative trial rather than a case series or retrospective case-control study, placing it at Level 3.
*Level 5*
- Level 5 evidence is the **lowest level of evidence**, typically consisting of **expert opinion** without explicit critical appraisal, or based on physiology, bench research, or animal studies.
- While the drug was initially tested in animal studies, the current human comparative study offers a higher level of evidence than expert opinion or preclinical data.
Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors US Medical PG Question 4: An investigator studying the molecular characteristics of various malignant cell lines collects tissue samples from several families with a known mutation in the TP53 tumor suppressor gene. Immunohistochemical testing performed on one of the cell samples stains positive for desmin. This sample was most likely obtained from which of the following neoplasms?
- A. Squamous cell carcinoma
- B. Rhabdomyosarcoma (Correct Answer)
- C. Prostate cancer
- D. Endometrial carcinoma
- E. Melanoma
Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors Explanation: ***Rhabdomyosarcoma***
- **Desmin** is an intermediate filament present in **muscle cells**, and its positive staining is a definitive marker for tumors of muscle origin
- A **rhabdomyosarcoma** is a malignant tumor of **skeletal muscle** differentiation, thus explaining the positive desmin staining.
*Squamous cell carcinoma*
- **Squamous cell carcinomas** are epithelial tumors that typically stain positive for **cytokeratin**, not desmin, as they originate from epithelial cells.
- They are characterized by features such as **intercellular bridges** and **keratinization**.
*Prostate cancer*
- **Prostate cancer** is an adenocarcinoma, meaning it's derived from glandular epithelial cells, and would stain positive for markers like **PSA (prostate-specific antigen)**, not desmin.
- This tumor type is characterized by glandular differentiation.
*Endometrial carcinoma*
- **Endometrial carcinomas** are adenocarcinomas of the uterine lining, derived from glandular epithelial cells, and would express **cytokeratins**, not desmin.
- Histologically, they show glandular structures and atypical endometrial cells.
*Melanoma*
- **Melanomas** are malignant tumors of melanocytes and would stain positive for markers such as **S-100**, **HMB-45**, and **Mart-1**, not desmin.
- These tumors originate from neural crest cells and are not muscle-derived.
Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors US Medical PG Question 5: A 65-year-old man with a 40-pack-year smoking history presents with hemoptysis and a persistent cough. Chest CT shows a 3.5 cm centrally located mass in the right main bronchus. Positron emission tomography confirms a malignant nodule. Bronchoscopy with transbronchial biopsy is performed and a specimen sample of the nodule is sent for frozen section analysis. The tissue sample is most likely to show which of the following tumor types?
- A. Carcinoid tumor
- B. Metastasis of colorectal cancer
- C. Small cell lung carcinoma
- D. Large cell carcinoma
- E. Squamous cell carcinoma (Correct Answer)
Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors Explanation: ***Squamous cell carcinoma***
- This is the most likely diagnosis given the **central location** in the main bronchus, **heavy smoking history**, and presentation with **hemoptysis**.
- **Squamous cell carcinoma** accounts for 25-30% of lung cancers and characteristically arises in **central/proximal airways**, making it readily accessible by **bronchoscopy**.
- Histologically, it shows **keratin pearls** and **intercellular bridges** on biopsy.
- The **central endobronchial location** and ability to obtain tissue via transbronchial biopsy strongly favor squamous cell over peripheral tumors.
*Carcinoid tumor*
- **Carcinoid tumors** are **neuroendocrine tumors** that can present as central endobronchial masses and cause hemoptysis.
- However, they are typically **slow-growing** with more indolent presentation, and PET scans show **variable uptake** (often less intense than aggressive carcinomas).
- They represent only **1-2% of lung tumors** and occur more commonly in **younger, non-smoking patients**.
*Metastasis of colorectal cancer*
- While lung is a common site for **colorectal metastases**, these typically present as **multiple peripheral nodules** rather than a solitary central endobronchial mass.
- The clinical presentation strongly suggests **primary lung cancer** rather than metastatic disease.
- Without history of colorectal cancer, this is unlikely.
*Small cell lung carcinoma*
- **Small cell lung carcinoma** (SCLC) represents 15% of lung cancers and typically presents as a **large central mass** with early mediastinal involvement.
- However, SCLC is usually **too extensive at presentation** for transbronchial biopsy alone and often requires mediastinoscopy or CT-guided biopsy.
- Histology shows **small cells with scant cytoplasm**, **salt-and-pepper chromatin**, and **oat-cell morphology**.
- While possible, the single accessible endobronchial mass is more characteristic of squamous cell.
*Large cell carcinoma*
- **Large cell carcinoma** is a **diagnosis of exclusion** made when tumors lack features of adenocarcinoma, squamous cell, or small cell differentiation.
- It typically presents as **large peripheral masses** rather than central endobronchial lesions.
- It represents only **10% of lung cancers** and is less common than squamous cell carcinoma in this clinical scenario.
Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors US Medical PG Question 6: A 53-year-old farmer presents to the clinic for evaluation of a pigmented lesion on his arm. He states that he first noticed the lesion last year, but he believes that it has been slowly growing in size. He otherwise does not have any complaints and is generally healthy. Which of the following findings on physical exam would suggest a malignant diagnosis?
- A. Symmetrical ovoid lesion
- B. Flat lesion with symmetric hyperpigmentation
- C. Tenderness to palpation
- D. Hyperpigmented lesion with smooth borders
- E. Different pigmentation throughout the lesion (Correct Answer)
Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors Explanation: ***Different pigmentation throughout the lesion***
- **Malignant melanoma** often presents with **multicolor variegation** or areas of differing pigmentation within the same lesion, which is a key indicator for malignancy (the "C" in ABCDE).
- This **uneven coloration** reflects the uncontrolled proliferation of melanocytes producing melanin in varying amounts and patterns, a hallmark of dysplastic changes.
*Symmetrical ovoid lesion*
- **Benign nevi** (moles) typically maintain **symmetry** in their shape and border, meaning that if you were to draw a line through the middle of the lesion, both halves would largely match.
- While some melanomas can be ovoid, **asymmetry** is a more concerning feature for malignancy, unlike the description provided here.
*Flat lesion with symmetric hyperpigmentation*
- A **benign lesion** often has **symmetric pigmentation** and a uniform color distribution, with a flat appearance.
- **Irregular pigmentation** (color variegation) within the lesion is a more concerning sign for **melanoma**, falling under the "C" (color) criteria of the ABCDEs.
*Tenderness to palpation*
- **Tenderness** is not a typical characteristic of early or even advanced **melanoma**; pain or tenderness is often associated with inflammation, infection, or trauma rather than primary skin cancer.
- While ulcerated or infected tumors can be painful, tenderness alone without other suspicious features is **not a primary diagnostic criterion** for melanoma.
*Hyperpigmented lesion with smooth borders*
- **Benign moles** typically have **smooth, regular, and well-defined borders**, making them appear round or oval.
- In contrast, **malignant melanoma** often presents with **irregular, notched, or poorly defined borders (the "B" in ABCDE),** which would be more indicative of malignancy.
Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors US Medical PG Question 7: A 76-year-old woman comes to the physician for evaluation of a 3-month history of vulvar itching and pain. She was diagnosed with lichen sclerosus 4 years ago. She has smoked 1 pack of cigarettes daily for 35 years. Physical examination shows a 2.5-cm nodular, ulcerative lesion on the vaginal introitus and left labia minora with surrounding erythema. Punch biopsy shows squamous cell carcinoma. A CT scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis shows enlarged lymph nodes concerning for metastatic disease. Which of the following lymph node regions is the most likely primary site of metastasis?
- A. Superficial inguinal (Correct Answer)
- B. Internal iliac
- C. External iliac
- D. Inferior mesenteric
- E. Para-aortic
Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors Explanation: ***Superficial inguinal***
- The **vulva** drains primarily into the **superficial inguinal lymph nodes**, making them the most likely first site for metastatic spread from vulvar squamous cell carcinoma.
- The lesion's location on the **vaginal introitus** and **labia minora** directly correlates with this lymphatic drainage pathway.
*Internal iliac*
- **Internal iliac nodes** receive drainage mainly from deep pelvic structures like the cervix, upper vagina, and uterus, not directly from the vulva.
- Metastasis to these nodes usually occurs after involvement of more superficial nodes or in advanced disease with deeper invasion.
*External iliac*
- **External iliac nodes** generally drain the lower extremities and deeper pelvic structures (e.g., bladder, distal ureter), not the vulva as a primary site.
- Involvement here would typically indicate more advanced local spread or secondary metastasis from other pelvic nodes.
*Inferior mesenteric*
- **Inferior mesenteric nodes** drain the hindgut and its derivatives, including the distal colon and rectum, which are distant from the vulva.
- This region is not involved in the lymphatic drainage of the vulva.
*Para-aortic*
- **Para-aortic nodes** drain structures like the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and upper uterus; they are too superior for primary vulvar lymphatic drainage.
- Metastasis to these nodes from vulvar cancer would signify widespread, very advanced disease and not a primary site of spread.
Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors US Medical PG Question 8: A 26-year-old nulligravid woman presents to her gynecologist after noticing a lump in her right breast while showering. She states that she first noticed the lump approximately 2 weeks ago, when the mass was slightly tender to touch. Since then, the lump has gotten slightly smaller and is now non-tender. The patient is otherwise healthy. She does not take oral contraceptives. Her last menses was approximately 2 weeks ago. There is no family history of cancer. On exam, the patient's temperature is 98.3°F (36.8°C), blood pressure is 116/84 mmHg, pulse is 65/min, and respirations are 12/min. In her right breast, there is a small 1.5 cm mass that is mobile, well-circumscribed, and firm. Which of the following is most likely on histological examination of the mass?
- A. Large, pleomorphic cells with associated central necrosis and microcalcifications
- B. Cysts with “leaf-like” projections
- C. Terminal duct lobular units surrounded by dense stroma
- D. Hypercellular stroma with overgrowth of fibrous and glandular tissues (Correct Answer)
- E. Dilated glands with 2 cell layers present
Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors Explanation: ***Hypercellular stroma with overgrowth of fibrous and glandular tissues***
- The clinical presentation of a **mobile, well-circumscribed, firm breast mass** in a young nulligravid woman, which slightly decreased in tenderness and size, is highly characteristic of a **fibroadenoma**.
- Histologically, fibroadenomas are benign tumors composed of both **fibrous and glandular tissue**, with a characteristic **hypercellular stroma** surrounding compressed ducts.
*Large, pleomorphic cells with associated central necrosis and microcalcifications*
- This histological description is characteristic of **ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)** or **invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC)**, particularly the **comedo type DCIS**.
- The patient's clinical presentation with a mobile, non-tender lump that improved and her young age make **malignancy less likely**.
*Cysts with “leaf-like” projections*
- This describes the histological appearance of a **phyllodes tumor**, which can be benign, borderline, or malignant.
- While phylloides tumors can present as mobile masses, they tend to **grow rapidly** and often become quite large, unlike the description of the mass in this patient.
*Terminal duct lobular units surrounded by dense stroma*
- This description is characteristic of **fibrocystic changes** in the breast, a common benign condition.
- While fibrocystic changes can cause lumps and tenderness, the presence of a distinct, mobile, well-circumscribed mass is more indicative of a **fibroadenoma**.
*Dilated glands with 2 cell layers present*
- This describes **sclerosing adenosis** or other types of **adenosis**, which are benign proliferative lesions within the breast.
- While these can present as masses, the classic presentation of a fibroadenoma with its distinct encapsulation and mobility is a more precise fit.
Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors US Medical PG Question 9: A 70-year-old man comes to the physician because of right-sided back pain, red urine, and weight loss for the last 4 months. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 40 years. A CT scan of the abdomen shows a large right-sided renal mass. Biopsy of the mass shows polygonal clear cells filled with lipids. Which of the following features is necessary to determine the tumor grade in this patient?
- A. Invasion of surrounding structures
- B. Response to chemotherapy
- C. Nuclear pleomorphism and nucleolar prominence (Correct Answer)
- D. Involvement of regional lymph nodes
- E. Size of malignant proliferation
Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors Explanation: ***Nuclear pleomorphism and nucleolar prominence***
- The **Fuhrman nuclear grading system** (and newer WHO/ISUP grading system) for renal cell carcinoma is based on **nuclear morphologic features**: nuclear size, nuclear contour irregularity, and most importantly, **nucleolar prominence**.
- **Grade 1**: Small uniform nuclei with inconspicuous nucleoli
- **Grade 2**: Slightly irregular nuclei with small nucleoli visible at 400× magnification
- **Grade 3**: Moderately irregular nuclei with prominent nucleoli visible at 100× magnification
- **Grade 4**: Marked nuclear pleomorphism, multilobated nuclei, and prominent nucleoli
- Higher nuclear grades correlate with more aggressive tumor behavior and worse prognosis.
*Invasion of surrounding structures*
- This feature is crucial for **tumor staging (T stage)**, specifically T3 disease when perinephric fat, renal vein, or IVC is invaded, and T4 when beyond Gerota's fascia.
- **Invasion** determines surgical approach and prognosis related to local spread but does not define histological grade.
*Response to chemotherapy*
- **Response to chemotherapy** is evaluated after treatment and is not a feature used for grading at diagnosis.
- Clear cell RCC is **chemoresistant**; treatment typically involves targeted therapy (VEGF inhibitors, mTOR inhibitors) or immunotherapy, not traditional chemotherapy.
*Involvement of regional lymph nodes*
- **Lymph node involvement** is a component of **tumor staging (N stage)**: N0 (no nodes), N1 (regional nodes positive).
- It indicates metastatic spread and significantly worsens prognosis but does not contribute to **histological grade**, which assesses cellular differentiation.
*Size of malignant proliferation*
- **Tumor size** is the primary criterion for **T staging**: T1a (≤4 cm), T1b (>4-7 cm), T2a (>7-10 cm), T2b (>10 cm), all confined to kidney.
- Size is a prognostic factor but does not determine **histological grade**, which is based exclusively on nuclear microscopic features.
Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors US Medical PG Question 10: A 62-year-old man seeks evaluation at a local walk-in clinic for mid-low back pain of several weeks. He has tried different rehabilitation therapies and medications with no improvement. He was prescribed some pain medications and sent home last week, but the patient presents today with difficulty walking and worsening of his back pain. He was referred to the ER, where he was examined and found to have hypoesthesia from T12 to S4–S5, significant muscle weakness in both lower limbs, and reduced knee and ankle deep tendon reflexes. A hypotonic anal sphincter with conserved deep anal pressure was demonstrated on digital rectal examination, as well as a multinodular, asymmetric prostate. Imaging studies showed multiple sclerotic bone lesions along the spine. Subsequently, a prostate core biopsy was obtained which confirmed the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Which of the following characteristics would you expect in the specimen?
- A. Well-formed glands with an increase in interglandular stroma
- B. Fat invasion
- C. Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia
- D. Small, closely-packed, well-formed glands
- E. Perineural invasion (Correct Answer)
Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors Explanation: ***Perineural invasion***
- **Perineural invasion** is a common finding in prostate adenocarcinoma, indicating that cancer cells have invaded the nerves surrounding the prostatic glands. This feature is often associated with a higher Gleason score and increased likelihood of extraprostatic extension and metastasis.
- While not visible on gross examination, its presence on biopsy can influence staging and treatment decisions for prostate cancer, particularly regarding the risk of recurrence and spread to other tissues.
*Well-formed glands with an increase in interglandular stroma*
- This description is more indicative of **benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)**, a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate, characterized by an increase in both glandular and stromal components.
- In BPH, the glands typically remain well-formed, and the stroma often proliferates, but these features do not represent malignancy.
*Fat invasion*
- **Fat invasion** is not a typical characteristic of prostate cancer within the prostate gland itself, as the prostate is not primarily composed of fat.
- While prostate cancer can invade periprostatic fatty tissue if it extends beyond the prostatic capsule, fat invasion within the biopsy specimen from the prostate proper is not a diagnostic feature of adenocarcinoma.
*Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia*
- **Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN)** is a pre-malignant lesion where the prostatic ductal and acinar cells show cytologic atypia but remain confined within the basement membrane.
- While PIN (especially high-grade PIN) can be associated with prostate cancer and may precede its development, it is not cancer itself and is not the definitive diagnosis in this case where prostate cancer has been confirmed.
*Small, closely-packed, well-formed glands*
- This description could represent a **low-grade prostate adenocarcinoma** (Gleason pattern 3), where the glands are still relatively well-formed but are more numerous and crowded than in benign tissue.
- However, compared to perineural invasion, which is a more definitive sign of aggressive behavior and advanced disease in a patient presenting with metastatic features (sclerotic bone lesions, neurologic symptoms), this histological finding alone is less specific for the advanced cancer described.
More Characteristics of benign vs malignant tumors US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.