Carcinogenic agents US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Carcinogenic agents. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Carcinogenic agents US Medical PG Question 1: A 45-year-old woman is found to have multiple masses in her liver while performing abdominal ultrasonography for recurrent right upper quadrant abdominal pain. Biopsy of one of the masses discloses large plates of adenoma cells, which are larger than normal hepatocytes and contain glycogen and lipid. Regular septa, portal tracts, and bile ductules are absent. Which of the following is associated with this patient's condition?
- A. Polyvinyl chloride
- B. Smoking
- C. Carbon tetrachloride
- D. Oral contraceptive pills (Correct Answer)
- E. Aflatoxin
Carcinogenic agents Explanation: ***Oral contraceptive pills***
- The description of **large plates of adenoma cells** containing **glycogen and lipid**, along with the absence of normal liver architecture (septa, portal tracts, bile ductules), points to a **hepatic adenoma**.
- **Hepatic adenomas** are strongly associated with **oral contraceptive pill (OCP)** use, especially in women aged 35-50.
*Polyvinyl chloride*
- Exposure to **polyvinyl chloride (PVC)** is mainly linked to **angiosarcoma of the liver**, a rare and aggressive vascular tumor, not hepatic adenomas.
- PVC exposure is typically found in occupational settings, which is not mentioned in this patient's history.
*Smoking*
- **Smoking** is a risk factor for various cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but it is **not directly associated** with the development of **hepatic adenomas**.
- While smoking can contribute to overall disease burden, it does not fit the specific liver tumor characteristics described.
*Carbon tetrachloride*
- Exposure to **carbon tetrachloride** is known to cause severe **hepatotoxicity**, leading to centrolobular necrosis and potentially cirrhosis.
- It is an industrial solvent and is not primarily linked to the formation of **hepatic adenomas**.
*Aflatoxin*
- **Aflatoxin** exposure, primarily from contaminated food products (e.g., peanuts, corn), is a well-established risk factor for **hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)**, especially in endemic areas.
- It is not associated with the development of benign **hepatic adenomas**, which have different histopathological features and risk factors.
Carcinogenic agents US Medical PG Question 2: While performing a Western blot, a graduate student spilled a small amount of the radiolabeled antibody on her left forearm. Although very little harm was done to the skin, the radiation did cause minor damage to the DNA of the exposed skin by severing covalent bonds between the nitrogenous bases and the deoxyribose sugar, leaving several apurinic/apyrimidinic sites. Damaged cells would most likely repair these sites by which of the following mechanisms?
- A. Nucleotide excision repair
- B. Nonhomologous end joining repair
- C. Homologous recombination
- D. Mismatch repair
- E. Base excision repair (Correct Answer)
Carcinogenic agents Explanation: **Base excision repair**
- This mechanism is specifically involved in correcting **single-base DNA damage** or **modified bases**, such as **apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) sites**.
- It involves removing the damaged base by a **DNA glycosylase**, creating an AP site, which is then processed by an **AP endonuclease** to cleave the phosphodiester backbone, followed by DNA polymerase and ligase.
*Nucleotide excision repair*
- Primarily repairs **bulky DNA lesions**, such as **thymine dimers** caused by UV radiation, or damage from chemical adducts that distort the DNA helix.
- It involves excising a larger oligonucleotide containing the damage, not just a single base.
*Nonhomologous end joining repair*
- This pathway is used to repair **double-strand DNA breaks**, where both strands of the DNA molecule are broken.
- It is a "quick-and-dirty" repair mechanism that ligates the broken ends together, often leading to small insertions or deletions.
*Homologous recombination*
- A repair mechanism for **double-strand DNA breaks** that uses a homologous DNA template (e.g., sister chromatid) to accurately repair the break.
- This process is highly accurate but occurs only when a homologous template is available, typically during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle.
*Mismatch repair*
- Corrects **base-pair mismatches** and **small insertions/deletions** that occur during DNA replication, which were not corrected by DNA polymerase proofreading.
- It targets newly synthesized DNA strands based on methylation patterns in the parental strand.
Carcinogenic agents US Medical PG Question 3: A 55-year old man living in Midwest USA comes in complaining of painless hematuria for the past week. He denies dysuria but complains of fatigue and lethargy at work. He has lost about 9.0 kg (20.0 lb) in the past 6 months. He drinks 1–2 beers on the weekends over the past 10 years but denies smoking. He has worked at a plastic chemical plant for the past 30 years and has never been out of the country. His father died of a heart attack at age 62 and his mother is still alive and well. There is a distant history of pancreatic cancer, but he can not remember the specifics. His vitals are stable and his physical exam is unremarkable. Urinary analysis is positive for RBCs. A cystoscopy is performed and finds a pedunculated mass projecting into the bladder lumen. A biopsy shows malignant cells. Which of the following is the most concerning risk factor for this patient’s condition?
- A. Aromatic amine exposure (Correct Answer)
- B. Alcohol
- C. Vinyl chloride exposure
- D. Genetic predisposition
- E. Schistosoma haematobium infection
Carcinogenic agents Explanation: ***Aromatic amine exposure***
- The patient's 30-year employment at a **plastic chemical plant** is a significant risk factor, as many chemicals used in such industries contain **aromatic amines**.
- Exposure to **aromatic amines** is a well-established cause of **transitional cell carcinoma** of the bladder, which is consistent with the painless hematuria and the finding of a malignant bladder mass.
*Alcohol*
- While heavy alcohol consumption can contribute to various health issues, it is **not considered a direct or strong risk factor** for bladder cancer.
- The patient's reported consumption of "1-2 beers on the weekends" over 10 years is relatively moderate and unlikely to be the primary cause of his severe presentation.
*Vinyl chloride exposure*
- **Vinyl chloride** exposure is primarily associated with **hepatic angiosarcoma** and, to a lesser extent, lung cancer and brain tumors.
- It is **not a significant risk factor** for bladder cancer, differentiating it from the patient's presentation of a bladder mass.
*Genetic predisposition*
- While there can be a genetic component to some cancers, the familial history mentioned (father died of heart attack, distant history of pancreatic cancer) does **not specifically point to a strong genetic predisposition** for bladder cancer.
- The powerful occupational exposure to chemicals is a much more direct and concerning risk factor in this case.
*Schistosoma haematobium infection*
- **Schistosoma haematobium** infection is a known cause of **squamous cell carcinoma** of the bladder, especially in endemic regions like parts of Africa and the Middle East.
- The patient has **never been out of the country** and lives in the Midwest USA, making this infection highly unlikely.
Carcinogenic agents US Medical PG Question 4: A 28-year-old male with a history of HIV infection is found to have a CD4+ T lymphocyte count of 68 cells per microliter. As a consequence of his HIV infection, this patient is at increased risk of malignancy due to which of the following?
- A. Pneumocystis jiroveci
- B. Actinomyces israelii
- C. Helicobacter pylori
- D. HHV-6
- E. Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) (Correct Answer)
Carcinogenic agents Explanation: ***Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)***
- **EBV** is a major cause of **AIDS-related malignancies**, particularly **B-cell lymphomas** including **non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL)** and **primary CNS lymphoma**, which are common in patients with CD4 counts below 100 cells/µL.
- The severe immunosuppression in **HIV/AIDS** allows for unchecked **EBV-driven lymphoproliferative disorders** due to impaired T-cell surveillance of EBV-infected B cells.
- Among the options listed, **EBV** is the only **oncogenic virus** and represents a significant cause of morbidity in advanced AIDS patients.
- **Note:** While HHV-8 (KSHV) causing Kaposi's sarcoma is also a major AIDS-related malignancy, it is not among the listed options.
*Pneumocystis jiroveci*
- **Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PCP)** is a common opportunistic **fungal infection** in HIV patients with CD4 < 200 cells/µL, causing severe respiratory illness.
- **PCP** is not oncogenic and does not increase malignancy risk; it causes acute infection, not cellular transformation.
*Actinomyces israelii*
- **Actinomyces israelii** is a gram-positive **bacterium** causing **actinomycosis**, a chronic suppurative infection with abscess formation and sinus tracts.
- While it can cause opportunistic infections in immunocompromised patients, it is **not oncogenic** and not associated with malignancy risk.
*Helicobacter pylori*
- **H. pylori** is a bacterium associated with **gastric adenocarcinoma** and **gastric MALT lymphoma** in the general population through chronic gastric inflammation.
- However, in the context of advanced HIV/AIDS with CD4 < 100, the predominant malignancy risk is from **oncogenic viruses** (EBV, HHV-8), not gastric pathology from **H. pylori**.
- **H. pylori** is not typically considered an AIDS-defining or AIDS-related malignancy.
*HHV-6*
- **Human Herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6)** causes roseola infantum in children and can reactivate in immunocompromised patients, potentially causing encephalitis or pneumonitis.
- **HHV-6** is **not established as oncogenic** and lacks strong evidence linking it to malignancy in HIV patients, unlike **EBV** (lymphomas) or **HHV-8** (Kaposi's sarcoma).
Carcinogenic agents US Medical PG Question 5: A 41-year-old man with HIV comes to the physician because of rectal bleeding and itching for 2 weeks. During this period, he has also had pain with defecation. Four months ago, he was diagnosed with anogenital warts that were treated with cryotherapy. Over the past year, he has been sexually active with 3 male partners. He uses condoms inconsistently. Current medications are zidovudine, emtricitabine, and efavirenz. Digital rectal examination and anoscopy show an exophytic mass on the anal margin that is protruding into the anal canal. The mass is tender to palpation and bleeds easily on contact. Laboratory studies show a leukocyte count of 7,600/mm3 and a CD4+ T-lymphocyte count of 410/mm3 (N ≥ 500). A biopsy specimen of the lesion shows a well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma. Which of the following cellular processes was most likely involved in the pathogenesis of this patient's malignancy?
- A. Activation of c-myc gene
- B. Inactivation of TP53 gene (Correct Answer)
- C. Activation of TAX gene
- D. Inactivation of VHL gene
- E. Inactivation of WT1 gene
Carcinogenic agents Explanation: ***Inactivation of TP53 gene***
- This patient's **squamous cell carcinoma** (SCC) of the anus is strongly associated with **human papillomavirus (HPV) infection**, which is common in HIV-positive sexually active men. HPV oncoproteins, particularly E6, promote the degradation of the **TP53 tumor suppressor protein**.
- Inactivating mutations or degradation of **TP53** remove a critical checkpoint in the cell cycle, allowing cells with DNA damage to proliferate uncontrollably and contributing to carcinogenesis.
*Activation of c-myc gene*
- The **c-myc proto-oncogene** is involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis, and its activation is commonly seen in lymphomas (e.g., Burkitt lymphoma) and other cancers.
- While *c-myc* activation can contribute to various malignancies, it is not the **primary molecular mechanism** linked to HPV-associated anal squamous cell carcinoma.
*Activation of TAX gene*
- The **TAX gene** is a transforming gene of **human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1)**, responsible for T-cell leukemia/lymphoma.
- This patient's presentation with anal squamous cell carcinoma, rather than a hematologic malignancy, makes HTLV-1 and TAX gene activation an unlikely cause.
*Inactivation of VHL gene*
- The **VHL (Von Hippel-Lindau) gene** is a tumor suppressor gene whose inactivation is strongly associated with **renal cell carcinoma** (clear cell type) and other tumors like pheochromocytoma and hemangioblastoma.
- Inactivation of **VHL** is not a primary mechanism in the development of anal squamous cell carcinoma.
*Inactivation of WT1 gene*
- The **WT1 (Wilms tumor 1) gene** is a tumor suppressor gene primarily associated with **Wilms tumor**, a kidney cancer that typically affects children.
- Inactivation of **WT1** is not a known pathogenic mechanism for anal squamous cell carcinoma in adults.
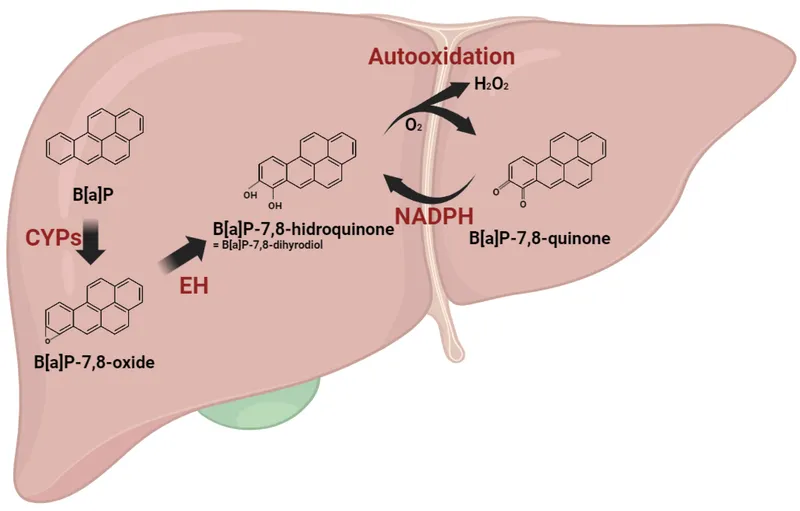
Carcinogenic agents US Medical PG Question 6: A previously healthy 48-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-month history of weight loss and yellowing of the skin. He works as a farmer and cultivates soybean and corn. He does not smoke, drink alcohol, or use illicit drugs. His vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows scleral icterus and tender hepatomegaly. Ultrasonography of the abdomen shows a 5-cm nodular lesion in the right lobe of the liver. Further evaluation of the lesion confirms hepatocellular carcinoma. The activity of which of the following enzymes most likely contributed to the pathogenesis of this patient's condition?
- A. Cytochrome P450 monooxygenases (Correct Answer)
- B. Nuclear glycosylases
- C. Lysosomal serine proteases
- D. Cytosolic cysteine proteases
- E. Peroxisomal catalases
Carcinogenic agents Explanation: ***Cytochrome P450 monooxygenases***
- This patient, a farmer exposed to agricultural products like soybean and corn, likely developed **hepatocellular carcinoma** due to exposure to **aflatoxins**, which are common contaminants of these crops.
- **Aflatoxins** are metabolized by **hepatic cytochrome P450 monooxygenases** into highly reactive **epoxide intermediates**, which can bind to DNA and cause mutations, leading to cancer.
*Nuclear glycosylases*
- **Nuclear glycosylases** are involved in **DNA repair**, specifically in the base excision repair pathway, removing damaged or incorrect bases from DNA.
- While important for maintaining genomic integrity, their activity is not typically implicated in the initial formation of carcinogenic metabolites like those from aflatoxins.
*Lysosomal serine proteases*
- **Lysosomal serine proteases** are involved in protein degradation within lysosomes and are not directly involved in the metabolic activation of procarcinogens or the initial steps of DNA damage leading to hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Their primary role is in cellular waste management and nutrient recycling.
*Cytosolic cysteine proteases*
- **Cytosolic cysteine proteases**, such as calpains and caspases, are crucial for various cellular processes including apoptosis, but they do not typically play a direct role in the metabolic activation of procarcinogens or the genotoxic events leading to chemical-induced liver cancer.
- Their functions are generally related to protein turnover and cell signaling.
*Peroxisomal catalases*
- **Peroxisomal catalases** are enzymes primarily responsible for decomposing **hydrogen peroxide** into water and oxygen, protecting the cell from oxidative damage.
- While managing reactive oxygen species is vital, catalases are not involved in the metabolic activation of procarcinogens like aflatoxins; their role is more in detoxification of harmful byproducts.
Carcinogenic agents US Medical PG Question 7: A 63-year-old man presents to his primary care physician because he has been having headaches and hearing loss. In addition, he says that he has been having difficulty opening his jaw to eat and recurrent middle ear infections. Physical exam reveals enlarged neck lymph nodes and a mass in the nasopharynx. Biopsy of the mass reveals undifferentiated squamous epithelial cells. The organism that is most likely associated with this patient's disease is also associated with which of the following disorders?
- A. Kaposi sarcoma
- B. Hepatocellular carcinoma
- C. Adult T-cell lymphoma
- D. Burkitt lymphoma (Correct Answer)
- E. Vulvar carcinoma
Carcinogenic agents Explanation: ***Burkitt lymphoma***
- The patient's symptoms (headaches, hearing loss, difficulty opening jaw, recurrent middle ear infections, nasopharyngeal mass, enlarged neck lymph nodes) and biopsy results (undifferentiated squamous epithelial cells) point to **nasopharyngeal carcinoma**.
- **Nasopharyngeal carcinoma** is strongly associated with the **Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)**. EBV is also a causative agent in **Burkitt lymphoma**.
*Kaposi sarcoma*
- **Kaposi sarcoma** is caused by **Human Herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8)**, not EBV.
- It typically presents as vascular skin lesions and can affect visceral organs, differing from the nasopharyngeal carcinoma described.
*Hepatocellular carcinoma*
- **Hepatocellular carcinoma** is primarily associated with **Hepatitis B virus (HBV)** and **Hepatitis C virus (HCV)** infection, as well as cirrhosis from other causes.
- There is no significant association between EBV and hepatocellular carcinoma.
*Adult T-cell lymphoma*
- **Adult T-cell lymphoma** is caused by the **Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1)**.
- This is a retrovirus distinct from EBV.
*Vulvar carcinoma*
- **Vulvar carcinoma** is most frequently associated with **Human Papillomavirus (HPV)** infection, especially high-risk strains like HPV 16 and 18.
- It is not typically linked to EBV.
Carcinogenic agents US Medical PG Question 8: A 54-year-old woman with breast cancer comes to the physician because of redness and pain in the right breast. She has been undergoing ionizing radiation therapy daily for the past 2 weeks as adjuvant treatment for her breast cancer. Physical examination shows erythema, edema, and superficial desquamation of the skin along the right breast at the site of radiation. Sensation to light touch is intact. Which of the following is the primary mechanism of DNA repair responsible for preventing radiation-induced damage to neighboring neurons?
- A. Homology-directed repair
- B. Base excision repair
- C. Nonhomologous end joining repair (Correct Answer)
- D. DNA mismatch repair
- E. Nucleotide excision repair
Carcinogenic agents Explanation: ***Nonhomologous end joining repair***
- This pathway is crucial for repairing **double-strand DNA breaks**, which are a major form of damage caused by **ionizing radiation**.
- It directly ligates the broken DNA ends without requiring a homologous template, making it an efficient but potentially error-prone repair mechanism.
*Homology-directed repair*
- This pathway is also used to repair **double-strand DNA breaks** but requires a **homologous DNA template** (usually a sister chromatid) for accurate repair.
- While highly accurate, it is typically active during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle and is generally slower and less dominant than NHEJ for immediate radiation-induced damage in non-dividing cells like neurons.
*Base excision repair*
- This mechanism primarily corrects damage to individual DNA bases, such as **oxidative damage**, alkylation, or deamination.
- It is not the primary mechanism for repairing the **double-strand breaks** induced by ionizing radiation.
*DNA mismatch repair*
- This pathway corrects errors that arise during **DNA replication**, specifically mismatched base pairs or small insertions/deletions.
- It is not involved in repairing radiation-induced DNA damage like **double-strand breaks**.
*Nucleotide excision repair*
- This pathway repairs bulky DNA lesions, such as those caused by **UV radiation** (e.g., pyrimidine dimers) or chemical mutagens.
- It removes a segment of DNA containing the damage but is not the primary repair mechanism for **double-strand breaks** caused by ionizing radiation.
Carcinogenic agents US Medical PG Question 9: A 67-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 4-month history of fatigue and weight loss. Physical examination shows jaundice. The liver is palpated 3 cm below the right costal margin. Serum studies show an elevated alpha-fetoprotein and a prolonged prothrombin time. Genetic analysis of a liver biopsy specimen shows a G:C to T:A transversion in codon 249 of the gene coding for the TP53 protein in affected cells. Which of the following risk factors is most specific to the patient's condition?
- A. Dietary aflatoxin exposure (Correct Answer)
- B. Alcoholism
- C. Schistosomiasis
- D. Hemochromatosis
- E. Hepatitis C infection
Carcinogenic agents Explanation: ***Dietary aflatoxin exposure***
- The **TP53 mutation** (G:C to T:A transversion at codon 249) is a **signature mutation** strongly associated with **aflatoxin B1 exposure**, particularly in hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Aflatoxins are potent **carcinogens produced by Aspergillus fungi**, often found in contaminated food storage in tropical regions.
*Schistosomiasis*
- This parasitic infection is a risk factor for **squamous cell carcinoma of the bladder** and, to a lesser extent, **cholangiocarcinoma**, but not typically hepatocellular carcinoma with this specific TP53 mutation signature.
- It primarily affects the **urinary bladder** and intestines, leading to chronic inflammation and fibrosis.
*Alcoholism*
- Chronic alcoholism is a major risk factor for **cirrhosis** and **hepatocellular carcinoma** due to continuous liver damage and regeneration.
- However, it does not typically cause the **specific TP53 codon 249 mutation** seen in this patient.
*Hemochromatosis*
- This genetic disorder causes **iron overload**, leading to liver damage, **cirrhosis**, and an increased risk of **hepatocellular carcinoma**.
- While it predisposes to liver cancer, it is not associated with the **specific G:C to T:A TP53 mutation** described.
*Hepatitis C infection*
- Chronic hepatitis C is a leading cause of **cirrhosis** and **hepatocellular carcinoma** worldwide due to chronic inflammation and hepatocyte turnover.
- Similar to alcoholism, it is a significant risk factor for liver cancer but does not specifically cause the **TP53 codon 249 mutation** linked to aflatoxin.
Carcinogenic agents US Medical PG Question 10: A 47-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 2-month history of a lump on her neck and a 1-week history of hoarseness. Examination shows a 3-cm, firm, non-tender nodule on the anterior neck. Further evaluation confirms a thyroid malignancy, and she undergoes thyroidectomy. Histopathologic examination of the surgical specimen shows lymphatic invasion. Genetic analysis shows an activating mutation in the RET/PTC genes. Microscopic examination of the surgical specimen is most likely to also show which of the following?
- A. Pleomorphic giant cells with numerous atypical mitotic figures
- B. Cuboidal cells arranged spherically around colloid lakes
- C. Hyperplastic epithelium with colloid scalloping
- D. Calcified spherules and large oval cells with empty-appearing nuclei (Correct Answer)
- E. Sheets of polygonal cells surrounding amyloid deposition
Carcinogenic agents Explanation: ***Calcified spherules and large oval cells with empty-appearing nuclei***
- The presence of an **activating mutation in RET/PTC genes**, **lymphatic invasion**, and a new neck lump with hoarseness (suggesting nerve involvement) are highly characteristic of **papillary thyroid carcinoma**.
- Microscopic features of papillary thyroid carcinoma include **Psammoma bodies (calcified spherules)**, **Orphan Annie eye nuclei (large oval cells with empty-appearing nuclei)**, and nuclear grooves.
*Pleomorphic giant cells with numerous atypical mitotic figures*
- This description typically refers to **anaplastic thyroid carcinoma**, a highly aggressive and undifferentiated tumor.
- While anaplastic carcinoma can present with rapid growth and hoarseness, it is less commonly associated with a **RET/PTC mutation** (BRAF mutations are more common) and typically has a much poorer prognosis, often presenting with a rapidly enlarging mass rather than a 2-month history suggestive of a more indolent tumor.
*Cuboidal cells arranged spherically around colloid lakes*
- This morphology is characteristic of **follicular thyroid carcinoma** or **follicular adenoma**.
- While follicular tumors can have RET/PTC mutations in some variants, the classic features described (empty-appearing nuclei and psammoma bodies) are absent here.
*Hyperplastic epithelium with colloid scalloping*
- This describes the histologic features seen in **Graves' disease** or **diffuse toxic goiter**, a benign condition.
- It is not indicative of malignancy, and the patient's presentation with a solitary nodule and hoarseness points to a malignant process.
*Sheets of polygonal cells surrounding amyloid deposition*
- This is the classic microscopic appearance of **medullary thyroid carcinoma**.
- Medullary thyroid carcinoma is also associated with **RET mutations**, but these are typically **germline or somatic RET point mutations** (e.g., RET M918T), not RET/PTC rearrangements, and it arises from parafollicular C cells, producing calcitonin, not thyroid hormones.
More Carcinogenic agents US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.