Inflammation

On this page
🔥 The Inflammatory Arsenal: Your Body's Defense Command Center
Inflammation is your body's most fundamental survival response, yet its dysregulation underlies conditions from septic shock to autoimmune disease. You'll master how vascular changes, cellular armies, and chemical mediators coordinate defense, then learn to recognize when this protective cascade becomes pathologic. By integrating hemodynamic shifts, leukocyte behavior, and therapeutic targets, you'll build the clinical judgment to assess inflammatory states rapidly and intervene effectively across organ systems.
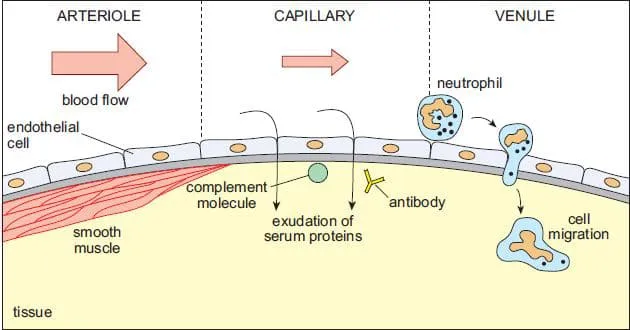
Inflammation represents the body's first-line defense mechanism, activated within seconds of tissue injury. This complex biological response involves 5 cardinal signs: rubor (redness), tumor (swelling), calor (heat), dolor (pain), and functio laesa (loss of function). The inflammatory response can be triggered by 4 major categories of stimuli: infectious agents, tissue necrosis, foreign bodies, and immune reactions.
📌 Remember: SHARP - Swelling, Heat, Ache (pain), Redness, Poor function. These 5 cardinal signs appear in >95% of acute inflammatory responses within 2-6 hours of initial tissue injury.
The inflammatory process follows a biphasic pattern: an initial vascular phase lasting 15-30 minutes, followed by a cellular phase extending 6-48 hours. During the vascular phase, arteriolar vasodilation increases blood flow by 300-400%, while increased vascular permeability allows plasma proteins to extravasate at rates 10-20 times normal levels.
- Acute Inflammation Timeline
- 0-15 minutes: Immediate vasoconstriction followed by vasodilation
- 15-30 minutes: Peak vascular permeability and plasma extravasation
- Histamine release peaks at 5-10 minutes
- Prostaglandin synthesis increases 50-100 fold
- 2-6 hours: Neutrophil recruitment and extravasation
- >90% of circulating neutrophils mobilized
- Tissue neutrophil concentration increases 1000-fold
- 12-48 hours: Monocyte/macrophage infiltration and tissue repair initiation
| Parameter | Normal State | Acute Inflammation | Peak Response Time | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood Flow | 100% baseline | 300-400% increase | 15-30 minutes | 2-6 hours |
| Vascular Permeability | 1x normal | 10-20x increase | 5-15 minutes | 30-60 minutes |
| Neutrophil Count | 4,000-11,000/μL | >15,000/μL | 4-6 hours | 24-48 hours |
| Temperature | 98.6°F (37°C) | >100.4°F (38°C) | 1-4 hours | Variable |
| ESR | <20 mm/hr | >50 mm/hr | 24-48 hours | Days-weeks |
The complement cascade amplifies inflammatory responses through 3 distinct pathways: classical (antibody-mediated), alternative (direct pathogen recognition), and lectin (mannose-binding). All pathways converge at C3 convertase, generating C3a and C5a anaphylatoxins that increase vascular permeability by 500-1000% and recruit neutrophils with chemotactic gradients effective over 100-200 μm distances.
💡 Master This: C-reactive protein (CRP) rises 6-12 hours after inflammatory stimulus, peaks at 24-48 hours, and has a half-life of 19 hours. CRP levels >100 mg/L suggest bacterial infection with 90% specificity, while levels <20 mg/L make serious bacterial infection unlikely in 95% of cases.
Understanding inflammatory kinetics predicts clinical presentations and guides therapeutic timing. The transition from acute to chronic inflammation occurs when resolution mechanisms fail after 7-14 days, leading to persistent tissue damage and systemic complications.
🔥 The Inflammatory Arsenal: Your Body's Defense Command Center
⚡ Vascular Command Center: The Hemodynamic Response Engine
Vasodilation occurs through dual mechanisms: neurogenic (immediate, lasting 5-10 minutes) and chemical mediator-induced (sustained, lasting hours to days). Neurogenic vasodilation results from axon reflexes releasing substance P and CGRP, causing immediate arteriolar relaxation within seconds. Chemical mediators including histamine, prostaglandin E2, and nitric oxide maintain sustained vasodilation with peak effects at 15-30 minutes.
📌 Remember: HPNO - Histamine (immediate), Prostaglandins (sustained), Nitric oxide (potent), Other mediators. These 4 categories control >90% of inflammatory vasodilation, with histamine dominating the first 15 minutes and prostaglandins maintaining response for hours.
Increased vascular permeability follows 3 distinct patterns: immediate transient (histamine-mediated, 5-30 minutes), immediate sustained (severe injury, hours to days), and delayed prolonged (cytokine-mediated, 2-12 hours onset). The immediate transient pattern accounts for 60-70% of acute inflammatory responses and involves endothelial cell contraction creating intercellular gaps of 0.1-0.4 μm.
- Vascular Permeability Mechanisms
- Endothelial Contraction: Histamine, leukotrienes, substance P
- Gap formation: 0.1-0.4 μm diameter
- Duration: 15-30 minutes
- Affects: Venules 20-60 μm diameter
- Endothelial Injury: Direct cytotoxic damage
- Gap size: >1 μm (allows cell passage)
- Duration: Hours to days
- Affects: All vessel types
- Leukocyte-Mediated: Neutrophil adhesion and transmigration
- Mechanism: Toxic oxygen species and enzymes
- Onset: 4-6 hours after stimulus
- Duration: Days to weeks
- Endothelial Contraction: Histamine, leukotrienes, substance P
| Mediator | Onset Time | Peak Effect | Duration | Primary Target | Potency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histamine | <1 minute | 5-10 minutes | 15-30 minutes | Venules | 100x baseline |
| Prostaglandin E2 | 5-15 minutes | 30-60 minutes | 2-6 hours | Arterioles | 50x baseline |
| Nitric Oxide | <30 seconds | 2-5 minutes | 10-30 minutes | All vessels | 1000x baseline |
| Complement C3a/C5a | 2-5 minutes | 15-30 minutes | 1-2 hours | Venules | 200x baseline |
| Bradykinin | 1-2 minutes | 10-15 minutes | 30-60 minutes | Venules | 300x baseline |
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Pulmonary edema develops when pulmonary capillary wedge pressure exceeds 18-20 mmHg in normal lungs, but inflammatory increased permeability can cause edema with pressures as low as 12-15 mmHg. This explains why ARDS patients develop edema despite normal cardiac function.
Lymphatic drainage increases 10-20 fold during inflammation, removing excess interstitial fluid and inflammatory mediators. Normal lymphatic flow of 2-4 L/day can increase to 20-40 L/day, but when filtration exceeds lymphatic capacity, clinical edema develops. Lymphatic obstruction reduces this safety valve, causing edema with minimal increases in vascular permeability.
💡 Master This: Pitting edema requires >2.5-3 L of excess interstitial fluid accumulation, representing failure of lymphatic compensation. The absence of pitting doesn't exclude inflammation-non-pitting edema occurs when protein concentration in interstitial fluid exceeds 3-4 g/dL, creating gel-like consistency.
Understanding vascular dynamics enables prediction of inflammatory complications and guides therapeutic interventions targeting specific hemodynamic abnormalities.
⚡ Vascular Command Center: The Hemodynamic Response Engine
🎯 Cellular Strike Force: The Leukocyte Recruitment Engine
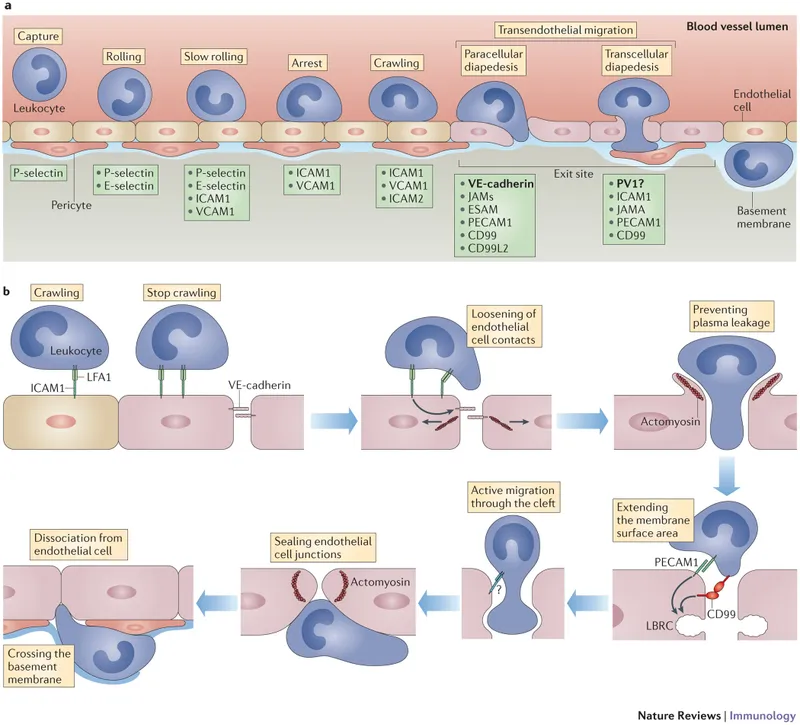
Leukocyte extravasation follows the 4-step paradigm: rolling, activation, firm adhesion, and transmigration. This process occurs primarily in post-capillary venules (20-50 μm diameter) where blood flow velocity decreases to 0.1-0.5 mm/second, allowing selectin-mediated interactions to initiate rolling behavior at velocities 100-1000 times slower than free-flowing blood.
📌 Remember: RAFT - Rolling (selectins), Activation (chemokines), Firm adhesion (integrins), Transmigration (PECAM-1). This sequence occurs in >95% of leukocyte extravasation events, with each step requiring specific molecular interactions and taking 2-5 minutes to complete.
Selectin-mediated rolling involves 3 selectin types: P-selectin (stored in Weibel-Palade bodies, mobilized within minutes), E-selectin (synthesized de novo, peaks at 4-6 hours), and L-selectin (constitutively expressed on leukocytes). P-selectin mediates immediate rolling within 2-5 minutes of inflammatory stimulus, while E-selectin sustains prolonged recruitment for 12-24 hours.
- Leukocyte Recruitment Timeline
- 0-5 minutes: P-selectin mobilization and initial rolling
- >90% of immediate rolling mediated by P-selectin
- Rolling velocity: 5-20 μm/second
- 15-60 minutes: L-selectin shedding and firm adhesion
- ADAM17 cleaves L-selectin from activated neutrophils
- Firm adhesion efficiency: >80% of rolling cells
- 2-6 hours: E-selectin expression peak
- TNF-α and IL-1β induce maximal E-selectin synthesis
- Sustained recruitment: 6-12 hours
- 12-48 hours: Monocyte recruitment dominance
- CCR2 and CX3CR1 mediate monocyte-specific trafficking
- >70% of recruited cells are monocytes/macrophages
- 0-5 minutes: P-selectin mobilization and initial rolling
| Cell Type | Recruitment Peak | Primary Selectins | Key Integrins | Chemokine Receptors | Tissue Half-life |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neutrophils | 4-6 hours | P-selectin, E-selectin | CD11b/CD18 | CXCR1, CXCR2 | 6-12 hours |
| Monocytes | 24-48 hours | P-selectin, E-selectin | CD11b/CD18, VLA-4 | CCR2, CX3CR1 | 2-3 days |
| Eosinophils | 24-72 hours | P-selectin, E-selectin | VLA-4, CD11b/CD18 | CCR3, CCR5 | 3-5 days |
| Lymphocytes | 48-96 hours | L-selectin, E-selectin | LFA-1, VLA-4 | CCR7, CXCR3 | Days-weeks |
| Basophils | 6-24 hours | P-selectin, E-selectin | VLA-4 | CCR2, CCR3 | 1-2 days |
Integrin activation transforms low-affinity (Kd ~10⁻⁴ M) to high-affinity (Kd ~10⁻⁸ M) binding states through inside-out signaling. Chemokine binding to G-protein coupled receptors triggers rapid integrin conformational changes within seconds, increasing adhesion strength by 1000-10,000 fold. LFA-1 (CD11a/CD18) and Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18) represent the dominant integrins mediating >80% of neutrophil firm adhesion.
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Leukocyte adhesion deficiency (LAD) results from CD18 mutations affecting β2-integrin function. Patients present with recurrent infections, delayed wound healing, and neutrophil counts >50,000/μL due to impaired extravasation. Absence of pus formation despite high neutrophil counts is pathognomonic.
Transmigration occurs through 2 pathways: paracellular (>90% of cases) via endothelial junctions and transcellular (<10%) through endothelial cell bodies. PECAM-1 (CD31) mediates homophilic interactions during paracellular transmigration, while CD99 and JAM proteins facilitate junction navigation. Complete transmigration requires 5-15 minutes and involves sequential engagement of >10 adhesion molecules.
💡 Master This: Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) form when >80% of neutrophils undergo NETosis in severe inflammation. NET formation requires 2-4 hours and involves chromatin decondensation with antimicrobial protein binding. Excessive NET formation contributes to thrombosis and tissue damage in sepsis and autoimmune diseases.
Understanding leukocyte recruitment patterns enables prediction of inflammatory resolution versus chronicity, guiding targeted therapeutic interventions.
🎯 Cellular Strike Force: The Leukocyte Recruitment Engine
🧬 Mediator Command Network: The Chemical Orchestration Matrix
Arachidonic acid metabolites represent the most potent inflammatory mediators, with prostaglandins and leukotrienes active at nanomolar concentrations (10⁻⁹ M). Phospholipase A2 liberates arachidonic acid from membrane phospholipids within seconds of inflammatory stimulus. Cyclooxygenase (COX) and lipoxygenase pathways generate >20 bioactive metabolites with distinct temporal profiles and tissue-specific effects.
📌 Remember: PILL - Prostaglandins (vasodilation, pain), Interleukins (cellular communication), Leukotrienes (bronchoconstriction, chemotaxis), Lipoxins (resolution signals). These 4 mediator families control >80% of inflammatory responses, with prostaglandins dominating acute vascular changes and leukotrienes mediating cellular recruitment.
Prostaglandin synthesis peaks 15-30 minutes after stimulus, with PGE2 causing vasodilation and hyperalgesia, PGI2 (prostacyclin) providing potent vasodilation and platelet inhibition, and TXA2 promoting vasoconstriction and platelet aggregation. COX-2 induction increases prostaglandin production by 10-100 fold compared to constitutive COX-1 activity.
- Mediator Temporal Profiles
- Immediate Release (0-5 minutes): Preformed mediators
- Histamine: Mast cell degranulation, peak at 2-5 minutes
- Serotonin: Platelet release, duration 10-15 minutes
- Complement C3a/C5a: Cascade activation, peak at 5-10 minutes
- Early Synthesis (5-60 minutes): Enzyme-dependent production
- Prostaglandins: COX pathway, peak at 15-30 minutes
- Leukotrienes: 5-LOX pathway, peak at 30-60 minutes
- Nitric oxide: NOS induction, sustained for hours
- Late Phase (2-24 hours): Transcriptional responses
- Cytokines: TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, peak at 4-8 hours
- Chemokines: IL-8, MCP-1, peak at 6-12 hours
- Acute phase proteins: CRP, fibrinogen, peak at 24-48 hours
- Immediate Release (0-5 minutes): Preformed mediators
| Mediator Class | Onset Time | Peak Effect | Duration | Primary Actions | Therapeutic Targets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histamine | <1 minute | 2-5 minutes | 15-30 minutes | Vasodilation, permeability | H1/H2 antagonists |
| Prostaglandins | 5-15 minutes | 15-30 minutes | 2-6 hours | Vasodilation, pain, fever | COX inhibitors |
| Leukotrienes | 15-30 minutes | 30-60 minutes | 4-8 hours | Bronchoconstriction, chemotaxis | 5-LOX inhibitors |
| TNF-α | 30-60 minutes | 2-4 hours | 8-24 hours | Endothelial activation, fever | Anti-TNF biologics |
| IL-1β | 1-2 hours | 4-6 hours | 12-24 hours | Fever, acute phase response | IL-1 antagonists |
Cytokine networks exhibit redundancy and pleiotropy, with single cytokines affecting multiple cell types and multiple cytokines producing similar effects. TNF-α represents the master inflammatory cytokine, inducing endothelial activation, leukocyte recruitment, fever, and acute phase responses within 2-4 hours. IL-1β synergizes with TNF-α, amplifying inflammatory responses by 5-10 fold.
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Cytokine storm occurs when TNF-α levels exceed 100 pg/mL (normal <8.1 pg/mL) and IL-6 levels exceed 1000 pg/mL (normal <7 pg/mL). This syndrome carries >40% mortality and requires immediate cytokine blockade with anti-TNF agents or tocilizumab (anti-IL-6 receptor).
Resolution mediators including lipoxins, resolvins, and protectins actively terminate inflammation through specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs). Lipoxin A4 switches neutrophil recruitment to monocyte recruitment, promotes neutrophil apoptosis, and enhances macrophage phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. Resolution failure leads to chronic inflammation when SPM production is insufficient or delayed.
💡 Master This: Aspirin-triggered lipoxins (ATL) form when low-dose aspirin (75-100 mg) acetylates COX-2, converting it from prostaglandin synthase to lipoxin synthase. This mechanism explains why low-dose aspirin provides anti-inflammatory benefits without significant COX-1 inhibition, reducing cardiovascular events by 20-25%.
Understanding mediator networks enables rational drug selection, optimal dosing strategies, and prediction of therapeutic responses across different inflammatory conditions.
🧬 Mediator Command Network: The Chemical Orchestration Matrix
⚖️ Therapeutic Command Center: Evidence-Based Intervention Strategies
NSAID selection depends on COX selectivity, half-life, and tissue penetration. Non-selective NSAIDs inhibit both COX-1 (constitutive, GI protection) and COX-2 (inducible, inflammation), while selective COX-2 inhibitors reduce GI toxicity by 50-70% but increase cardiovascular risk by 15-25%. Ibuprofen provides optimal safety profile with 4-6 hour dosing, while naproxen offers 12-hour duration with lower cardiovascular risk.
📌 Remember: NSAID toxicity follows RENAL pattern - Renal dysfunction, Edema/hypertension, Nausea/GI bleeding, Asthma exacerbation, Liver dysfunction. GI bleeding risk increases 3-5 fold with non-selective NSAIDs, 10-15 fold with concurrent anticoagulation, and 20-30 fold in patients >65 years with prior GI bleeding.
Corticosteroid therapy requires dose-response optimization balancing anti-inflammatory efficacy with systemic toxicity. Prednisone 0.5-1 mg/kg/day provides maximal anti-inflammatory effect for most conditions, while doses >1.5 mg/kg/day increase toxicity without additional benefit. Pulse therapy with methylprednisolone 1000 mg IV daily × 3 days achieves rapid immunosuppression for severe inflammatory conditions.
- Anti-inflammatory Drug Categories
- NSAIDs: COX inhibition, rapid onset
- Ibuprofen: 400-800 mg q6-8h, GI-sparing profile
- Naproxen: 250-500 mg q12h, CV-protective effects
- Celecoxib: 100-200 mg q12h, COX-2 selective
- Corticosteroids: Broad immunosuppression
- Prednisone: 0.5-1 mg/kg/day, oral maintenance
- Methylprednisolone: 1-2 mg/kg/day IV, acute severe
- Dexamethasone: 0.1-0.2 mg/kg/day, CNS penetration
- DMARDs: Disease-modifying agents
- Methotrexate: 15-25 mg weekly, folate antagonist
- Sulfasalazine: 2-3 g daily, anti-TNF effects
- Hydroxychloroquine: 400 mg daily, lysosomal inhibition
- Biologics: Targeted cytokine inhibition
- Adalimumab: 40 mg q2 weeks SC, anti-TNF-α
- Tocilizumab: 8 mg/kg q4 weeks IV, anti-IL-6R
- Rituximab: 1000 mg × 2 doses, B-cell depletion
- NSAIDs: COX inhibition, rapid onset
| Drug Class | Onset Time | Peak Effect | Duration | Efficacy Rate | Major Toxicities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSAIDs | 30-60 minutes | 2-4 hours | 4-12 hours | 70-80% | GI bleeding, renal dysfunction |
| Corticosteroids | 2-6 hours | 24-48 hours | Days-weeks | 85-95% | Infection, osteoporosis, diabetes |
| Methotrexate | 2-6 weeks | 8-12 weeks | Months | 60-70% | Hepatotoxicity, bone marrow suppression |
| Anti-TNF biologics | 2-4 weeks | 12-16 weeks | Months | 70-80% | Infection, malignancy |
| Rituximab | 4-8 weeks | 16-24 weeks | 6-12 months | 60-80% | Infection, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy |
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Tuberculosis screening is mandatory before biologic therapy due to 3-8 fold increased reactivation risk. Latent TB affects 25-30% of anti-TNF candidates and requires 4-week anti-TB treatment before biologic initiation. Interferon-gamma release assays have 85-90% sensitivity for latent TB detection.
Combination therapy strategies optimize efficacy while minimizing toxicity. Methotrexate + anti-TNF combinations achieve remission rates of 40-50% compared to 20-30% with monotherapy. Triple therapy (methotrexate + sulfasalazine + hydroxychloroquine) provides equivalent efficacy to biologics in early rheumatoid arthritis with significantly lower cost.
💡 Master This: Therapeutic drug monitoring optimizes biologic dosing by measuring drug levels and anti-drug antibodies. Low adalimumab levels (<5 μg/mL) predict treatment failure, while anti-drug antibodies develop in 10-30% of patients, requiring drug switching or immunosuppressive augmentation.
Evidence-based treatment algorithms enable personalized therapy selection, optimal monitoring strategies, and proactive complication management across inflammatory disease spectrum.
⚖️ Therapeutic Command Center: Evidence-Based Intervention Strategies
🌐 Systems Integration Hub: Multi-Organ Inflammatory Networks
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) develops when local inflammatory mediators enter systemic circulation at concentrations exceeding physiological buffering capacity. SIRS criteria require ≥2 of the following: temperature >38°C or <36°C, heart rate >90 bpm, respiratory rate >20/min, WBC >12,000 or <4,000/μL. SIRS progression to sepsis occurs when infectious source is identified, with mortality increasing from 5-10% (SIRS) to 20-30% (sepsis).
📌 Remember: SIRS criteria use THRW - Temperature abnormal, Heart rate >90, Respiratory rate >20, WBC abnormal. ≥2 criteria define SIRS with 85% sensitivity for systemic inflammation, but only 40% specificity for sepsis. qSOFA score (altered mental status, SBP ≤100, RR ≥22) better predicts sepsis mortality.
Acute phase response represents coordinated hepatic protein synthesis triggered by IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β. Positive acute phase proteins increase 2-1000 fold: CRP (100-1000×), serum amyloid A (100-1000×), fibrinogen (2-5×), ferritin (2-5×). Negative acute phase proteins decrease 20-50%: albumin, transferrin, prealbumin. Peak response occurs 24-48 hours after inflammatory stimulus.
- Multi-System Inflammatory Effects
- Cardiovascular System: Hemodynamic instability
- Vasodilation: NO-mediated, SVR decreases 40-60%
- Increased permeability: Capillary leak, third-spacing
- Myocardial depression: Cytokine-mediated, EF decreases 20-40%
- Pulmonary System: Gas exchange impairment
- ARDS development: P/F ratio <300, bilateral infiltrates
- Pulmonary edema: Non-cardiogenic, protein-rich
- V/Q mismatch: Shunt fraction >20%
- Renal System: Acute kidney injury
- Prerenal azotemia: Hypoperfusion, FENa <1%
- Acute tubular necrosis: Cytokine-mediated, FENa >2%
- Glomerular dysfunction: Proteinuria, hematuria
- Hepatic System: Metabolic dysfunction
- Cholestasis: Bilirubin elevation, alkaline phosphatase ↑
- Synthetic dysfunction: Albumin ↓, coagulation abnormalities
- Drug metabolism: CYP450 inhibition, altered clearance
- Cardiovascular System: Hemodynamic instability
| System | Early Changes (0-6 hours) | Intermediate (6-24 hours) | Late Changes (>24 hours) | Mortality Predictor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular | Tachycardia, hyperdynamic | Hypotension, ↓SVR | Shock, myocardial depression | Lactate >4 mmol/L |
| Pulmonary | Tachypnea, mild hypoxemia | V/Q mismatch, ↑A-a gradient | ARDS, respiratory failure | P/F ratio <150 |
| Renal | Oliguria, ↑BUN/Cr | AKI, electrolyte abnormalities | Anuria, dialysis requirement | Creatinine >3 mg/dL |
| Hepatic | ↑Transaminases | Cholestasis, ↓synthetic function | Hepatic failure | Bilirubin >6 mg/dL |
| Hematologic | Leukocytosis/leukopenia | Thrombocytopenia, ↑PT/PTT | DIC, bleeding | Platelets <50,000 |
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Procalcitonin levels distinguish bacterial from viral inflammation with 85% accuracy. PCT >0.5 ng/mL suggests bacterial infection, >2 ng/mL indicates severe sepsis, and >10 ng/mL predicts septic shock. PCT-guided antibiotic therapy reduces antibiotic duration by 25-30% without increasing mortality.
Neuroendocrine integration involves hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis activation through IL-1β and TNF-α. Cortisol levels increase 5-10 fold during acute inflammation, providing negative feedback and resolution signals. Relative adrenal insufficiency develops when cortisol response is inadequate for inflammatory stress, requiring hydrocortisone supplementation in septic shock.
💡 Master This: Immunoparalysis occurs in 40-60% of sepsis survivors, characterized by HLA-DR expression <30% on monocytes and reduced TNF-α production upon ex vivo stimulation. This state predicts secondary infections, prolonged ICU stay, and increased mortality at 6-12 months.
Understanding multi-system integration enables early recognition of systemic inflammation, appropriate monitoring strategies, and targeted interventions to prevent organ dysfunction and improve outcomes.
🌐 Systems Integration Hub: Multi-Organ Inflammatory Networks
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Rapid Assessment and Decision Tools
Rapid inflammatory assessment follows the INFLAME protocol: Infection source identification, Neurologic status, Fever pattern, Laboratory markers, Acute phase response, Multi-organ involvement, Evidence of complications. This 7-component framework achieves >90% diagnostic accuracy when systematically applied within 15 minutes of presentation.
📌 Remember: Laboratory inflammatory markers follow CEPIL pattern - CRP (6-12 hour rise), ESR (24-48 hour rise), Procalcitonin (bacterial specific), IL-6 (early cytokine), Lactate (tissue hypoperfusion). CRP >100 mg/L suggests bacterial infection with 90% specificity, while PCT >2 ng/mL indicates severe sepsis with 85% sensitivity.
Severity stratification uses validated scoring systems with mortality prediction accuracy >85%. qSOFA score (mental status change, SBP ≤100 mmHg, RR ≥22/min) predicts ICU mortality with AUROC 0.81. SOFA score incorporates 6 organ systems with mortality increasing 15-20% per point increase. APACHE II provides 24-48 hour mortality prediction with calibration accuracy >90%.
- Clinical Assessment Framework
- Vital Sign Patterns: Hemodynamic stability assessment
- SIRS criteria: ≥2 abnormal parameters
- Shock index: HR/SBP >0.9 predicts severe illness
- Modified early warning score: ≥5 points requires ICU evaluation
- Laboratory Integration: Multi-marker approach
- Complete blood count: Left shift, thrombocytopenia
- Comprehensive metabolic panel: Anion gap, lactate
- Inflammatory markers: CRP, PCT, ESR
- Coagulation studies: PT/PTT, D-dimer, fibrinogen
- Imaging Correlation: Source identification
- Chest X-ray: Pneumonia, ARDS pattern
- CT abdomen/pelvis: Abscess, perforation
- Echocardiogram: Cardiac function, volume status
- Microbiologic Evidence: Pathogen identification
- Blood cultures: 2 sets before antibiotics
- Source cultures: Urine, sputum, wound
- Rapid diagnostics: PCR, antigen testing
- Vital Sign Patterns: Hemodynamic stability assessment
| Assessment Tool | Time to Complete | Sensitivity | Specificity | Mortality Prediction | Clinical Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qSOFA | 2-3 minutes | 65% | 85% | AUROC 0.81 | Sepsis screening |
| SOFA | 5-10 minutes | 80% | 75% | AUROC 0.85 | ICU mortality |
| APACHE II | 15-20 minutes | 85% | 80% | AUROC 0.90 | 24-48h mortality |
| SAPS III | 10-15 minutes | 82% | 78% | AUROC 0.88 | ICU outcomes |
| CRP + PCT | Laboratory dependent | 90% | 85% | N/A | Bacterial infection |
Treatment decision algorithms integrate severity assessment with evidence-based interventions. Sepsis bundles require completion within 1 hour: lactate measurement, blood cultures, broad-spectrum antibiotics, 30 mL/kg crystalloid if hypotensive or lactate ≥4 mmol/L. Bundle compliance >80% reduces mortality by 25-30%.
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Antibiotic timing is critical in sepsis management. Each hour delay in appropriate antibiotic administration increases mortality by 7.6% in septic shock. Empirical broad-spectrum coverage should target likely pathogens based on infection source and local resistance patterns.
Monitoring parameters guide therapeutic adjustments and complication detection. Lactate clearance >10% in 6 hours predicts improved survival. Central venous oxygen saturation >70% indicates adequate oxygen delivery. Urine output >0.5 mL/kg/hr suggests adequate renal perfusion. Mean arterial pressure >65 mmHg maintains organ perfusion in most patients.
💡 Master This: Biomarker-guided therapy optimizes treatment duration and reduces complications. PCT-guided antibiotic discontinuation when levels decrease >80% or <0.25 ng/mL reduces antibiotic exposure by 2-3 days without increasing mortality. CRP monitoring guides anti-inflammatory therapy tapering in chronic conditions.
Complication prediction enables proactive intervention before irreversible organ damage. Acute kidney injury develops when creatinine increases >0.3 mg/dL in 48 hours or urine output <0.5 mL/kg/hr for 6 hours. ARDS manifests as P/F ratio <300 with bilateral infiltrates and PCWP <18 mmHg. DIC presents with platelet count <100,000, fibrinogen <150 mg/dL, and D-dimer >500 ng/mL.
This clinical mastery arsenal enables systematic inflammatory disease assessment, evidence-based treatment selection, and proactive complication management across emergency, inpatient, and outpatient settings.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Rapid Assessment and Decision Tools
Practice Questions: Inflammation
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 56-year-old postmenopausal woman comes to the physician because of a 6-month history of worsening pain and swelling in her left knee. She has a history of peptic ulcer disease for which she takes cimetidine. Examination shows palpable crepitus and limited range of motion of the left knee. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy for this patient’s symptoms?











