Systemic autoimmune diseases US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Systemic autoimmune diseases. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Systemic autoimmune diseases US Medical PG Question 1: A 47-year-old woman comes to the physician because of progressive pain and stiffness in her hands and wrists for the past several months. Her hands are stiff in the morning; the stiffness improves as she starts her chores. Physical examination shows bilateral swelling and tenderness of the wrists, metacarpophalangeal joints, and proximal interphalangeal joints. Her range of motion is limited by pain. Laboratory studies show an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate. This patient's condition is most likely associated with which of the following findings?
- A. IgM antibodies against the Fc region of IgG (Correct Answer)
- B. HLA-B27 protein on white blood cells
- C. HLA-A3 proteins on white blood cells
- D. HLA-DQ2 proteins on white blood cells
- E. IgG antibodies with a TNF-α binding domain on the Fc region
Systemic autoimmune diseases Explanation: ***IgM antibodies against the Fc region of IgG***
- The patient's symptoms of symmetric **polyarthritis** affecting the **small joints of the hands and wrists**, morning stiffness that improves with activity, and elevated ESR are highly suggestive of **rheumatoid arthritis (RA)**.
- The finding described, **rheumatoid factor (RF)**, is an IgM antibody directed against the Fc portion of IgG and is a hallmark of RA.
*HLA-B27 protein on white blood cells*
- **HLA-B27** is strongly associated with **seronegative spondyloarthropathies**, such as **ankylosing spondylitis** and **reactive arthritis**.
- These conditions typically involve the **axial skeleton** (spine) and large joints, which differs from the presentation of small joint polyarthritis seen here.
*HLA-A3 proteins on white blood cells*
- **HLA-A3** is associated with **hereditary hemochromatosis**, a disorder of iron overload.
- While hemochromatosis can cause arthropathy, it typically affects the **second and third metacarpophalangeal joints** and does not present with the classic features of rheumatoid arthritis described.
*HLA-DQ2 proteins on white blood cells*
- **HLA-DQ2** is strongly associated with **celiac disease** and, to a lesser extent, type 1 diabetes.
- These conditions are not directly linked to the inflammatory polyarthritis presented by this patient.
*IgG antibodies with a TNF-α binding domain on the Fc region*
- This description refers to **therapeutic monoclonal antibodies** (biologics) used to treat inflammatory conditions like RA, such as **infliximab** or **adalimumab**, which are designed to bind TNF-α.
- These are **pharmacological interventions**, not diagnostic markers or naturally occurring antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis.
Systemic autoimmune diseases US Medical PG Question 2: A 47-year-old woman comes to the physician because of body aches for the past 9 months. She also has stiffness of the shoulders and knees that is worse in the morning and tingling in the upper extremities. Examination shows marked tenderness over the posterior neck, bilateral mid trapezius, and medial aspect of the left knee. A complete blood count and erythrocyte sedimentation rate are within the reference ranges. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Systemic lupus erythematosus
- B. Fibromyalgia (Correct Answer)
- C. Rheumatoid arthritis
- D. Polymyositis
- E. Major depressive disorder
Systemic autoimmune diseases Explanation: ***Fibromyalgia***
- The patient's presentation of widespread **body aches for 9 months**, morning **stiffness**, and **multiple tender points** (posterior neck, bilateral mid trapezius, medial aspect of the knee) in the absence of inflammatory markers (normal ESR, normal CBC) is highly characteristic of **fibromyalgia**.
- **Paresthesias** (tingling in the upper extremities) are a common associated feature in fibromyalgia.
- Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain syndrome diagnosed clinically based on widespread pain and tender points, with normal laboratory findings.
*Systemic lupus erythematosus*
- SLE typically presents with **systemic inflammation**, often involving joints, skin, and kidneys, along with abnormalities in inflammatory markers (e.g., elevated ESR, positive ANA, cytopenias).
- The widespread tender points and completely normal inflammatory markers make SLE very unlikely.
*Rheumatoid arthritis*
- RA primarily affects the **synovial joints** symmetrically, leading to joint swelling, warmth, and morning stiffness, typically accompanied by elevated ESR and CRP.
- The examination findings show specific **tender points** rather than objective joint swelling, and the normal ESR rules against active RA.
*Polymyositis*
- Polymyositis is characterized by **proximal muscle weakness** (not diffuse body aches) and is associated with elevated muscle enzymes (CK, aldolase) and inflammatory changes on muscle biopsy.
- This patient has pain and tenderness without weakness, and her laboratory tests are normal.
*Major depressive disorder*
- While **fatigue**, body aches, and sleep disturbances can be symptoms of major depressive disorder, the presence of specific, well-defined **tender points on examination** points towards a primary pain syndrome.
- Fibromyalgia often coexists with depression, but the objective physical findings of multiple tender points are more consistent with fibromyalgia as the primary diagnosis.
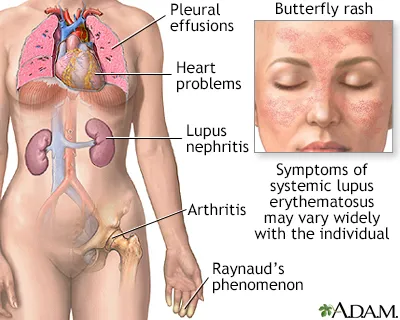
Systemic autoimmune diseases US Medical PG Question 3: A 25-year-old woman presents into the clinic complaining of worsening malaise, hair loss, and a rash on her face. The patient states that she has been avoiding daylight because the rash becomes painful, and she has not been able to go to classes because of debilitating arthralgia in her fingers and ankles. No significant past medical history. She takes no medication. At the time of the consult, the patient has a fever of 39.0°C (102.2 °F). The presence of which of the following is most commonly seen on diagnostic labs in this patient’s most likely condition?
- A. Anti-smith antibody
- B. Anti-dsDNA
- C. Anti-Ro antibody
- D. Antinuclear antibody (Correct Answer)
- E. Anti-histone antibody
Systemic autoimmune diseases Explanation: ***Antinuclear antibody***
- The patient's symptoms (malaise, hair loss, photosensitive malar rash, arthralgia, fever) are highly suggestive of **Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)**.
- An **antinuclear antibody (ANA)** test is the **most sensitive screening test** for SLE and is present in over 95% of patients with the condition.
*Anti-dsDNA*
- While **anti-dsDNA antibodies** are highly specific for SLE and often correlate with disease activity, particularly **lupus nephritis**, they are present in only about 70-80% of SLE patients, making them less common than ANA.
- This antibody is more specific than ANA but **not as sensitive** as ANA for initial diagnosis.
*Anti-smith antibody*
- **Anti-Smith antibodies** are highly specific for SLE (pathognomonic), meaning their presence strongly indicates SLE, but they are found in only about 20-30% of SLE patients, making them relatively uncommon.
- Their presence is **not as common** as ANA or even anti-dsDNA in the general SLE population.
*Anti-Ro antibody*
- **Anti-Ro/SSA antibodies** are associated with specific manifestations of SLE, such as **subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus**, neonatal lupus, and Sjögren's syndrome, but are not present in all SLE patients.
- This antibody is present in approximately 25-30% of SLE patients, and its diagnostic significance is more often for specific subsets rather than overall disease presence.
*Anti-histone antibody*
- **Anti-histone antibodies** are primarily associated with **drug-induced lupus (DIL)**, although they can also be present in a small percentage of idiopathic SLE cases.
- Given that the patient takes no medication and her symptoms are more consistent with idiopathic SLE, this antibody is **less likely to be the most commonly seen** diagnostic marker.
Systemic autoimmune diseases US Medical PG Question 4: A 42-year-old woman presents complaining of pain in her hands. She reports that the pain is in both hands, and that it is usually worse in the morning. She reports that her hands are also stiff in the morning, but that this gradually improves throughout the morning. She notes, however, that her symptoms seem to be getting worse over the last three months. What is the most likely pathogenesis of her disease process?
- A. Production of antibodies against smooth muscle
- B. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody production
- C. Production of antibodies against antibodies (Correct Answer)
- D. Type 1 hypersensitivity reaction
- E. Repetitive microtrauma
Systemic autoimmune diseases Explanation: ***Production of antibodies against antibodies***
- The patient's symptoms of **bilateral hand pain and morning stiffness** improving with activity, worsening over three months, are classic for **Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)**.
- RA is characterized by the production of **rheumatoid factor (RF)**, an antibody (typically IgM) directed against the Fc portion of IgG, which is essentially an antibody against an antibody.
*Production of antibodies against smooth muscle*
- This describes the presence of **anti-smooth muscle antibodies (ASMA)**, which are characteristic of **Autoimmune Hepatitis type 1**.
- Autoimmune hepatitis primarily affects the liver, leading to symptoms like fatigue, jaundice, and elevated liver enzymes, not primarily joint pain.
*Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody production*
- This refers to **ANCA (anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies)**, which are associated with various forms of **vasculitis**, such as Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Wegener's), Microscopic Polyangiitis, and Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss).
- While vasculitis can cause systemic symptoms, the patient's presentation of symmetric, inflammatory arthritis is not typical for primary ANCA-associated vasculitis.
*Type 1 hypersensitivity reaction*
- A **type I hypersensitivity reaction** involves IgE-mediated mast cell degranulation, leading to immediate allergic reactions like asthma, anaphylaxis, or hives.
- This mechanism is completely unrelated to the pathogenesis of an autoimmune, chronic inflammatory arthritis like Rheumatoid Arthritis.
*Repetitive microtrauma*
- Repetitive microtrauma is more consistent with **osteoarthritis** or **occupational overuse injuries**.
- Osteoarthritis typically presents with pain that worsens with activity and improves with rest, **morning stiffness lasting less than 30 minutes**, and often affects weight-bearing joints or specific joints due to trauma or wear and tear, rather than the inflammatory pattern described.
Systemic autoimmune diseases US Medical PG Question 5: A 33-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician for gradually worsening pain in both wrists that began several months ago. The pain originally did not bother her, but it has recently begun to affect her daily functioning. She states that the early morning stiffness in her hands is severe and has made it difficult to tend to her rose garden. She occasionally takes ibuprofen for the pain, but she says this does not really help. Her medical history is significant for diabetes mellitus and major depressive disorder. She is currently taking insulin, sertraline, and a daily multivitamin. The vital signs include: blood pressure 126/84 mm Hg, heart rate 82/min, and temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F). On physical exam, her wrists and metacarpophalangeal joints are swollen, tender, erythematous, and warm to the touch. There are no nodules or vasculitic lesions. Which of the following antibodies would be most specific to this patient’s condition?
- A. c-ANCA
- B. Anti-Ro
- C. Anti-Scl-70
- D. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (Correct Answer)
- E. Rheumatoid factor
Systemic autoimmune diseases Explanation: ***Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide***
- **Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP)** antibodies are highly specific for **rheumatoid arthritis (RA)** and are often present early in the disease course.
- The patient's presentation with **symmetric polyarthritis**, particularly affecting the **wrists and metacarpophalangeal joints**, with severe **morning stiffness**, is classic for RA.
*c-ANCA*
- **c-ANCA (cytoplasmic antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies)** are primarily associated with **granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener's)**, a systemic vasculitis.
- This condition typically presents with symptoms such as **upper and lower respiratory tract involvement**, **renal disease**, and constitutional symptoms, which are not described here.
*Anti-Ro*
- **Anti-Ro (SS-A)** antibodies are strongly associated with **Sjögren's syndrome**, a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by dry eyes and mouth, and also with **systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)**.
- While Sjögren's can present with arthritis, the prominent joint inflammation and morning stiffness described are more characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis.
*Anti-Scl-70*
- **Anti-Scl-70 (anti-topoisomerase I)** antibodies are highly specific for **systemic sclerosis (scleroderma)**, particularly the diffuse cutaneous form.
- Scleroderma presents with **skin thickening**, **Raynaud's phenomenon**, and potential involvement of internal organs like the lungs and esophagus, which are absent in this patient's presentation.
*Rheumatoid factor*
- **Rheumatoid factor (RF)** is often positive in **rheumatoid arthritis**, but it is less specific than anti-CCP antibodies.
- RF can also be elevated in other autoimmune diseases, chronic infections, and even in healthy individuals, making it a less specific diagnostic marker.
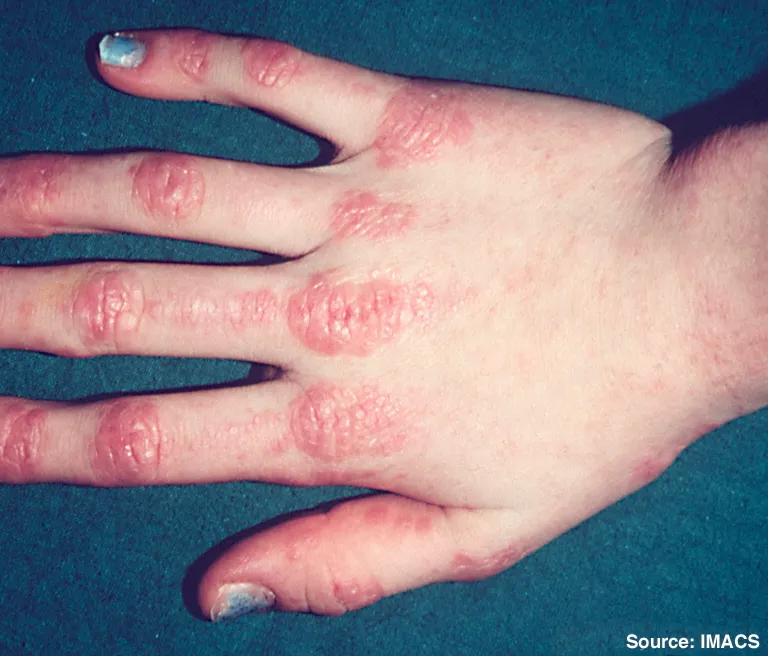
Systemic autoimmune diseases US Medical PG Question 6: A 33-year-old woman comes to the clinic for a follow-up visit after recently starting high dose corticosteroids for a newly diagnosed autoimmune condition. She was first evaluated a month ago due to fatigue, muscle weakness, and a scaly rash on both hands. On examination, muscle strength was rated 2 out of 5 in the upper extremities. Creatine kinase-MB was elevated, and anti-Jo-1 antibodies were observed. A muscle biopsy later showed perimysial inflammation and treatment was initiated. Today, the patient says that her symptoms have not improved despite treatment with corticosteroids. It is agreed upon to initiate methotrexate with the hopes of achieving better symptom control. Which of the following is most often associated with this patient’s condition?
- A. Ovarian cancer
- B. Arthritis
- C. Lung cancer
- D. Raynaud's phenomenon
- E. Interstitial lung disease (Correct Answer)
Systemic autoimmune diseases Explanation: ***Interstitial lung disease***
- The patient's condition, characterized by **fatigue**, **muscle weakness**, **scaly rash** (likely **Gottron's papules** or **heliotrope rash**), **elevated CK-MB**, and **anti-Jo-1 antibodies**, strongly suggests **dermatomyositis**, which is frequently associated with **interstitial lung disease (ILD)**.
- Approximately 70% of patients with **anti-Jo-1 antibodies** develop **ILD**, which can manifest as chronic cough and dyspnea.
*Ovarian cancer*
- While dermatomyositis is associated with an **increased risk of malignancy**, particularly in older patients, **ovarian cancer** is not the *most common* or *most frequently associated* manifestation of the disease overall, especially given the patient's age (33).
- The risk of malignancy is higher in adults with dermatomyositis and polymyositis, with various cancers observed, but no single cancer type predominates as a universal association.
*Arthritis*
- **Arthritis** can occur in dermatomyositis and polymyositis, but it is typically **non-erosive** and **non-deforming**, affecting small and large joints.
- While a possible feature, it is less specific and less frequently highlighted as a major systemic complication compared to interstitial lung disease in the context of anti-Jo-1 antibodies.
*Lung cancer*
- Similar to ovarian cancer, **lung cancer** is a potential malignancy associated with dermatomyositis, especially in older patients and smokers.
- However, for a 33-year-old woman with anti-Jo-1 antibodies, **interstitial lung disease** is a more direct and prevalent associated complication than **lung cancer**.
*Raynaud's phenomenon*
- **Raynaud's phenomenon** (episodic digital ischemia) is observed in a subset of patients with dermatomyositis, often those with features of overlap syndromes.
- While present in some cases, it is not as highly prevalent or as clinically significant as **interstitial lung disease** in patients with anti-Jo-1 antibodies.
Systemic autoimmune diseases US Medical PG Question 7: A 32-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 4-day history of low-grade fever, joint pain, and muscle aches. The day before the onset of her symptoms, she was severely sunburned on her face and arms during a hike with friends. She also reports being unusually fatigued over the past 3 months. Her only medication is a combined oral contraceptive pill. Her temperature is 37.9°C (100.2°F). Examination shows bilateral swelling and tenderness of the wrists and metacarpophalangeal joints. There are multiple nontender superficial ulcers on the oral mucosa. The detection of antibodies directed against which of the following is most specific for this patient's condition?
- A. Nuclear Sm proteins (Correct Answer)
- B. Fc region of IgG
- C. Single-stranded DNA
- D. Cell nucleus
- E. Histones
Systemic autoimmune diseases Explanation: ***Nuclear Sm proteins***
- Antibodies to **Sm proteins** (anti-Sm antibodies) are highly specific for **Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)**, although present in only a minority of patients.
- The patient's symptoms, including **photosensitivity (exacerbation by sunburn)**, **arthritis**, **oral ulcers**, and **fatigue**, are classic manifestations of SLE.
*Fc region of IgG*
- Antibodies directed against the **Fc region of IgG** are known as **rheumatoid factor (RF)**.
- While RF can be positive in a small percentage of SLE patients, it is most characteristic of **rheumatoid arthritis** and is not specific for SLE.
*Single-stranded DNA*
- Antibodies to **single-stranded DNA (anti-ssDNA antibodies)** are found in various autoimmune diseases, including SLE, but are **less specific** than anti-dsDNA or anti-Sm antibodies for SLE diagnosis.
- These antibodies can also be seen in drug-induced lupus and other conditions, making them a less definitive marker.
*Cell nucleus*
- Antibodies directed against the **cell nucleus** (antinuclear antibodies or **ANA**) are present in nearly all patients with SLE and are highly sensitive for the disease.
- However, ANA can also be positive in many other autoimmune conditions, infections, and even healthy individuals, making it **not specific** enough for a definitive diagnosis without other criteria.
*Histones*
- Antibodies to **histones** are most commonly associated with **drug-induced lupus erythematosus**.
- While they can be present in some cases of SLE, the patient's presentation does not strongly suggest drug-induced lupus, and anti-histone antibodies are not the most specific marker for typical SLE.
Systemic autoimmune diseases US Medical PG Question 8: A 27-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician with a chief complaint of pain in her hands, shoulders, and knees. She states that the pain has lasted for several months but seems to have worsened recently. Any activity such as opening jars, walking, or brushing her teeth is painful. The patient has a past medical history of a suicide attempt in college, constipation, anxiety, depression, and a sunburn associated with surfing which was treated with aloe vera gel. Her temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 137/78 mmHg, pulse is 92/min, respirations are 14/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Laboratory values are obtained and shown below.
Hemoglobin: 9 g/dL
Hematocrit: 33%
Leukocyte count: 2,500/mm^3 with normal differential
Platelet count: 107,000/mm^3
Serum:
Na+: 139 mEq/L
Cl-: 102 mEq/L
K+: 4.4 mEq/L
HCO3-: 24 mEq/L
BUN: 21 mg/dL
Glucose: 90 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1.0 mg/dL
Ca2+: 10.2 mg/dL
AST: 12 U/L
ALT: 10 U/L
Which of the following is the most likely to be found in this patient?
- A. Anti-dsDNA antibodies (Correct Answer)
- B. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies
- C. IgM against parvovirus B19
- D. Anti-histone antibodies
- E. Degenerated cartilage in weight bearing joints
Systemic autoimmune diseases Explanation: ***Anti-dsDNA antibodies***
- The patient's presentation with **polyarthralgia**, **anemia**, **leukopenia**, and **thrombocytopenia** is highly suggestive of **systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)**.
- **Anti-dsDNA antibodies** are highly specific for SLE and are often associated with **lupus nephritis** and disease activity.
*Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies*
- These antibodies are highly specific for **rheumatoid arthritis**, which primarily causes **inflammatory arthritis** but does not typically present with the **heme abnormalities** (anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia) seen in this patient.
- The patient's symptoms of pain in hands, shoulders, and knees are broad and not specifically localized to the **small joints** in a symmetric pattern typical of rheumatoid arthritis.
*IgM against parvovirus B19*
- **Parvovirus B19 infection** can cause **arthralgia** and some hematological abnormalities, particularly **transient aplastic crisis**, but it typically does not cause the persistent **pancytopenia** or the broad systemic features seen here.
- IgM antibodies indicate an **acute infection**, and while it could cause joint pain, it is less likely to explain the constellation of symptoms including chronic multi-joint pain and significant cytopenias over several months.
*Anti-histone antibodies*
- **Anti-histone antibodies** are most commonly associated with **drug-induced lupus**, which typically develops after exposure to certain medications (e.g., **hydralazine**, **procainamide**).
- There is no mention of such drug exposure in the patient's history, and while they can be present in SLE, anti-dsDNA antibodies are more specific for idiopathic SLE.
*Degenerated cartilage in weight bearing joints*
- **Degenerated cartilage** in weight-bearing joints is characteristic of **osteoarthritis**, which is a **degenerative joint disease**.
- Osteoarthritis typically does not present with **systemic symptoms** like fatigue or the **hematological abnormalities** (anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia) observed in this patient.
Systemic autoimmune diseases US Medical PG Question 9: A 44-year-old woman comes to her primary care physician with complaints of irritation and a gritty sensation in her eyes for the past few months. She denies any discharge from her eyes. She has no significant past medical or surgical history. She takes multivitamins occasionally but denies use of any other medication. On further questioning, she expresses her concerns about frequent dental caries for the past 2 years. On examination, her temperature is 37.1°C (98.8°F), blood pressure is 110/80 mm Hg, pulse rate is 74/min, and respiratory rate is 16/min. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
- A. Sjögren's syndrome (Correct Answer)
- B. Fibromyalgia
- C. Rheumatoid arthritis
- D. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- E. Scleroderma
Systemic autoimmune diseases Explanation: ***Sjögren's syndrome***
- The patient's complaints of **irritation and gritty sensation in her eyes** (suggesting **dry eyes**), along with **frequent dental caries** (suggesting **dry mouth**), are classic symptoms of **Sjögren's syndrome**, an autoimmune disorder characterized by destruction of exocrine glands.
- The absence of ocular discharge further supports dry eyes rather than infection or allergy.
*Fibromyalgia*
- **Fibromyalgia** is characterized by widespread **musculoskeletal pain**, fatigue, and sleep disturbances.
- It does not explain the specific symptoms of dry eyes and increased dental caries due to xerostomia.
*Rheumatoid arthritis*
- **Rheumatoid arthritis** primarily involves chronic **symmetrical polyarthritis**, particularly affecting small joints.
- While it can be associated with secondary Sjögren's, the primary symptoms presented here are not joint-related.
*Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)*
- **SLE** is a systemic autoimmune disease with diverse manifestations, including joint pain, skin rashes, and kidney involvement.
- While **dry eyes** can occur, **dental caries** due to dry mouth are not a primary diagnostic feature of SLE, and other SLE-specific symptoms are absent.
*Scleroderma*
- **Scleroderma** is characterized by **skin thickening** and fibrosis affecting various organs.
- Symptoms like dry eyes and dental caries are not typical presenting features; instead, patients often experience **Raynaud's phenomenon**, dysphagia, and skin changes.
Systemic autoimmune diseases US Medical PG Question 10: A 47-year-old woman presents to her physician for difficulty swallowing. She states that she intentionally delayed seeing a physician for this issue. She says her primary issue with swallowing is that her mouth always feels dry so she has difficulty chewing food to the point that it can be swallowed. On physical examination, her oral mucosa appears dry. Both of her eyes also appear dry. Several enlarged lymph nodes are palpated. Which of the following patterns of reactive lymphadenitis is most commonly associated with this patient’s presentation?
- A. Sinus hyperplasia
- B. Follicular hyperplasia (Correct Answer)
- C. Diffuse hyperplasia
- D. Mixed B and T cell hyperplasia
- E. Paracortical hyperplasia
Systemic autoimmune diseases Explanation: ***Follicular hyperplasia***
- The patient's symptoms of **dry mouth (xerostomia)** and **dry eyes (xerophthalmia)** strongly suggest **Sjögren syndrome**. This autoimmune disease selectively affects **exocrine glands**, particularly the salivary and lacrimal glands.
- Lymphoid hyperplasia, especially **follicular hyperplasia**, is a common feature in Sjögren syndrome due to chronic B-cell activation, which is linked to a higher risk of developing **MALT lymphoma**.
*Sinus hyperplasia*
- **Sinus hyperplasia**, also known as **reticular hyperplasia**, is characterized by an increase in the number and size of macrophages within the subcapsular and medullary sinuses of lymph nodes.
- It is typically associated with **lymph nodes draining a site of malignancy** or conditions involving histiocytic proliferation.
*Diffuse hyperplasia*
- **Diffuse hyperplasia** involves a generalized expansion of all lymphoid components within the lymph node, without a predominance of any specific area.
- This pattern is less specific and can be seen in various **chronic inflammatory conditions** or reactive processes, but it is not the most characteristic pattern for Sjögren syndrome.
*Mixed B and T cell hyperplasia*
- While both B and T cells are involved in immune responses, **mixed B and T cell hyperplasia** refers to the expansion of both populations in a less defined pattern than follicular or paracortical types.
- Conditions like **toxoplasmosis** can present with mixed hyperplasia, but it is not the classic pattern seen in Sjögren syndrome.
*Paracortical hyperplasia*
- **Paracortical hyperplasia** involves the expansion of the paracortical areas of the lymph node, which are rich in T-lymphocytes.
- This pattern is typically seen in response to **viral infections** (e.g., infectious mononucleosis) or certain drug reactions, where T-cell activation is a prominent feature.
More Systemic autoimmune diseases US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.