Primary immunodeficiencies US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Primary immunodeficiencies. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Primary immunodeficiencies US Medical PG Question 1: A 6-year-old child presents for evaluation of a medical condition associated with recurrent infections. After reviewing all of the medical history, gene therapy is offered to treat a deficiency in adenosine deaminase (ADA). ADA deficiency is the most common autosomal recessive mutation in which of the following diseases?
- A. Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome
- B. Bruton's Agammaglobulinemia
- C. Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (Correct Answer)
- D. DiGeorge Syndrome
- E. Hyper-IgM Syndrome
Primary immunodeficiencies Explanation: ***Severe Combined Immunodeficiency***
- **Adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency** leads to the accumulation of toxic metabolites that impair lymphocyte development and function, primarily affecting **T and B cells**, which is a common cause of SCID.
- Patients with SCID present with **recurrent, severe infections** due to profound immunodeficiency, making them candidates for treatments like gene therapy.
*Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome*
- This is an **X-linked recessive disorder** characterized by eczema, thrombocytopenia, and immunodeficiency, but it is caused by a mutation in the **WASP gene**, not ADA deficiency.
- While it involves immunodeficiency and recurrent infections, the underlying genetic defect and specific clinical triad are distinct from ADA deficiency.
*Bruton's Agammaglobulinemia*
- This is an **X-linked recessive disorder** caused by a defect in the **BTK gene**, leading to a lack of mature B cells and hence very low levels of immunoglobulins.
- While it results in recurrent bacterial infections due to absent antibodies, its genetic cause and primary immunological defect (B cell specific) differ from ADA deficiency.
*DiGeorge Syndrome*
- This is a developmental disorder caused by a **microdeletion on chromosome 22q11.2**, leading to abnormal development of the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches.
- It results in **T-cell deficiency** due to thymic aplasia/hypoplasia, hypocalcemia due to parathyroid hypoplasia, and congenital heart defects, but not ADA deficiency.
*Hyper-IgM Syndrome*
- This syndrome is characterized by normal or elevated IgM levels and deficiencies in other immunoglobulins (IgG, IgA, IgE), largely due to defects in **CD40-CD40L interaction** or other genes involved in isotype switching.
- Patients suffer from recurrent infections and opportunistic infections but the genetic basis and specific immunological defect are distinct from ADA deficiency.
Primary immunodeficiencies US Medical PG Question 2: A 7-month-old boy is brought in to his pediatrician’s office due to concern for recurrent infections. The parents state that over the last 3-4 months, the boy has had multiple viral respiratory infections, along with a fungal pneumonia requiring hospitalization. Currently he is without complaints; however, the parents are concerned that he continues to have loose stools and is falling off of his growth curve. Newborn screening is not recorded in the patient’s chart. On exam, the patient’s temperature is 98.4°F (36.9°C), blood pressure is 108/68 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 12/min. The patient is engaging appropriately and is able to grasp, sit, and is beginning to crawl. However, the patient is at the 20th percentile for length and weight, when he was previously at the 50th percentile at 3 months of age. Further screening suggests that the patient has an autosomal recessive immunodeficiency associated with absent T-cells. Which of the following is also associated with this disease?
- A. Accumulation of deoxyadenosine (Correct Answer)
- B. Nonfunctional common gamma chain
- C. Mutation in ATM DNA repair gene
- D. Dysfunctional cell chemotaxis
- E. Negative nitroblue-tetrazolium test
Primary immunodeficiencies Explanation: ***Accumulation of deoxyadenosine***
- The patient's presentation with **recurrent viral and fungal infections**, **failure to thrive**, and **absent T-cells** despite normal developmental milestones points towards **severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID)**.
- One of the most common causes of autosomal recessive SCID is **adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency**, which leads to an accumulation of **deoxyadenosine** and its toxic metabolites, particularly in lymphocytes, causing their destruction.
*Nonfunctional common gamma chain*
- A **nonfunctional common gamma chain** is associated with **X-linked SCID**, which is the most common form of SCID. However, the question specifies an **autosomal recessive** immunodeficiency.
- This defect affects signaling for several **cytokine receptors**, leading to impaired T-cell and NK-cell development.
*Mutation in ATM DNA repair gene*
- A **mutation in the ATM DNA repair gene** is characteristic of **ataxia-telangiectasia**, a primary immunodeficiency.
- While it can cause recurrent infections due to **T-cell defects** and IgA deficiency, it typically presents with **ataxia**, oculocutaneous telangiectasias, and increased risk of malignancy, which are not mentioned here.
*Dysfunctional cell chemotaxis*
- **Dysfunctional cell chemotaxis** is associated with disorders like **Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency (LAD)** or **Chédiak-Higashi syndrome**.
- These conditions primarily affect neutrophil function and lead to severe bacterial infections, rather than the prominent viral and fungal infections and T-cell absence seen in this case.
*Negative nitroblue-tetrazolium test*
- A **negative nitroblue-tetrazolium (NBT) test** is indicative of **chronic granulomatous disease (CGD)**, a phagocytic disorder.
- CGD is characterized by recurrent infections with catalase-positive organisms due to the inability of phagocytes to produce a **respiratory burst**, which is inconsistent with the patient's broad spectrum of infections and T-cell deficiency.
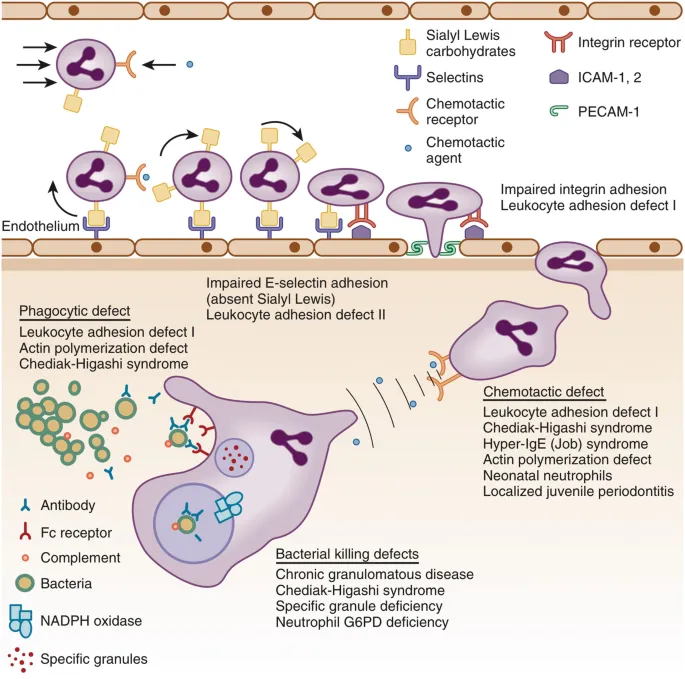
Primary immunodeficiencies US Medical PG Question 3: Which of the following patient presentations would be expected in an infant with defective LFA-1 integrin (CD18) protein on phagocytes, in addition to recurrent bacterial infections?
- A. Cardiac defects, hypoparathyroidism, palatal defects, and learning disabilities
- B. Chronic diarrhea, oral candidiasis, severe infections since birth, absent thymic shadow
- C. Progressive neurological impairment and cutaneous telangiectasia
- D. Skin infections with absent pus formation, delayed umbilicus separation (Correct Answer)
- E. Eczema and thrombocytopenia
Primary immunodeficiencies Explanation: ***Skin infections with absent pus formation, delayed umbilicus separation***
- A defect in **LFA-1 integrin (CD18)** prevents phagocytes from adhering to endothelial cells and migrating to sites of infection, leading to **absent pus formation** despite severe infections.
- **Delayed umbilical cord separation** (typically >30 days) is a classic sign due to impaired neutrophil recruitment at the site of cord detachment.
*Cardiac defects, hypoparathyroidism, palatal defects, and learning disabilities*
- This constellation of symptoms is characteristic of **DiGeorge syndrome**, which involves a defect in T-cell development due to thymic aplasia/hypoplasia.
- These specific defects are not directly caused by LFA-1 integrin deficiency.
*Chronic diarrhea, oral candidiasis, severe infections since birth, absent thymic shadow*
- These symptoms are highly suggestive of **Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID)**, which involves a profound defect in both B and T cell immunity.
- SCID presents with a broader spectrum of opportunistic infections and developmental issues not directly related to integrin function.
*Progressive neurological impairment and cutaneous telangiectasia*
- These are hallmark features of **Ataxia-Telangiectasia**, a genetic disorder affecting DNA repair and leading to immune deficiencies and cerebellar degeneration.
- This condition primarily involves T-cell dysfunction and increased cancer risk, not LFA-1 integrin deficiency.
*Eczema and thrombocytopenia*
- The combination of **eczema** (dermatitis) and **thrombocytopenia** (low platelet count), along with recurrent infections, is characteristic of **Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome**.
- This syndrome is caused by a defect in the WASP protein, affecting immune cell function and platelet formation, distinct from LFA-1 integrin deficiency.
Primary immunodeficiencies US Medical PG Question 4: You are seeing a 4-year-old boy in clinic who is presenting with concern for a primary immune deficiency. He has an unremarkable birth history, but since the age of 6 months he has had recurrent otitis media, bacterial pneumonia, as well as two episodes of sinusitis, and four episodes of conjunctivitis. He has a maternal uncle who died from sepsis secondary to H. influenza pneumonia. If you drew blood work for diagnostic testing, which of the following would you expect to find?
- A. Abnormally low number of T cells
- B. Abnormally high number of B cells
- C. Elevated immunoglobulin levels
- D. Abnormally low number of B cells (Correct Answer)
- E. Abnormally high number of T cells
Primary immunodeficiencies Explanation: ***Abnormally low number of B cells***
- The recurrent bacterial infections (otitis media, pneumonia, sinusitis, conjunctivitis) and the family history of death from *H. influenza* pneumonia suggest a **primary B-cell immunodeficiency**, such as **X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA)**.
- In XLA, there is a block in B-cell development, leading to a profound absence of mature B cells and immunoglobulins.
*Abnormally low number of T cells*
- This would point towards a **T-cell immunodeficiency** or a **combined immunodeficiency**, typically presenting with opportunistic infections, viral, or fungal infections, rather than predominantly bacterial infections.
- Examples include **Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID)**, which often presents earlier and more severely.
*Abnormally high number of B cells*
- This is not characteristic of a primary immunodeficiency with recurrent bacterial infections; rather, it might be seen in certain autoimmune conditions or lymphoproliferative disorders.
- **High B cell counts** generally imply a functioning humoral immune system, which contradicts the infectious history.
*Elevated immunoglobulin levels*
- This finding would generally indicate a **functioning humoral immune response**, possibly due to chronic infection or an inflammatory process, but not a primary B-cell immunodeficiency causing recurrent bacterial infections.
- In conditions like **Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID)**, some immunoglobulin levels might be normal, but often key classes (like IgG, IgA, or IgM) are low.
*Abnormally high number of T cells*
- This finding is generally not associated with the pattern of recurrent bacterial infections described, which strongly points to a **humoral (antibody) deficiency**.
- **Elevated T cells** could be seen in some autoimmune conditions or certain viral infections, but not typically in a primary immunodeficiency characterized by recurrent bacterial infections.
Primary immunodeficiencies US Medical PG Question 5: A 6-month-old baby boy presents to his pediatrician for the evaluation of recurrent bacterial infections. He is currently well but has already been hospitalized multiple times due to his bacterial infections. His blood pressure is 103/67 mm Hg and heart rate is 74/min. Physical examination reveals light-colored skin and silver hair. On examination of a peripheral blood smear, large cytoplasmic vacuoles containing microbes are found within the neutrophils. What diagnosis do these findings suggest?
- A. Leukocyte adhesion deficiency-1
- B. Common variable immunodeficiency
- C. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
- D. Chediak-Higashi syndrome (Correct Answer)
- E. Congenital thymic aplasia
Primary immunodeficiencies Explanation: **Chediak-Higashi syndrome**
- The presence of **recurrent bacterial infections**, **light-colored skin and silver hair**, and **large cytoplasmic vacuoles within neutrophils** is pathognomonic for Chediak-Higashi syndrome.
- This condition is an **autosomal recessive disorder** characterized by impaired lysosomal trafficking, affecting phagocyte function and melanosome formation.
*Leukocyte adhesion deficiency-1*
- This disorder is characterized by **recurrent bacterial infections** due to a defect in integrins, preventing neutrophils from adhering to endothelial cells and migrating to infection sites.
- However, it typically presents with **delayed umbilical cord separation** and lacks the distinctive features of light-colored skin/silver hair and giant cytoplasmic granules.
*Common variable immunodeficiency*
- This condition is characterized by **recurrent bacterial infections** due to low levels of immunoglobulins, leading to impaired B-cell function.
- It typically presents later in childhood or adulthood and does not involve abnormalities in skin pigmentation or neutrophil morphology.
*Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome*
- **AIDS** is caused by the **Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)** and leads to a progressive decline in CD4+ T cells, resulting in opportunistic infections.
- While it causes recurrent infections, the clinical presentation in a **6-month-old infant** with silver hair and giant neutrophil granules is not consistent with AIDS unless there's a strong perinatal exposure history, which is not mentioned.
*Congenital thymic aplasia*
- Also known as **DiGeorge syndrome**, this condition involves **T-cell immunodeficiency** due to hypoplasia or aplasia of the thymus, leading to recurrent viral, fungal, and parasitic infections.
- It is also associated with **hypocalcemia** and **congenital heart defects**, but it does not present with recurrent bacterial infections combined with light skin/silver hair and giant neutrophil granules.
Primary immunodeficiencies US Medical PG Question 6: A 5-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department by her mother with seizures. The blood glucose is 94 mg/dl and the serum calcium is 5.3 mg/dl; however, the PTH levels are low. The medical history includes a delay in achieving developmental milestones. Her mother also says she needs frequent hospital visits due to recurrent bouts with the flu. The cardiovascular examination is within normal limits. What is the most likely cause underlying this presentation?
- A. Deletion of the chromosome 22q11 (Correct Answer)
- B. Mutation in the WAS gene
- C. B cell development failure
- D. B cell maturation failure
- E. Lysosomal trafficking regulator gene defect
Primary immunodeficiencies Explanation: ***Deletion of the chromosome 22q11***
- The combination of **hypocalcemia with low PTH** (due to **parathyroid hypoplasia**), recurrent infections (due to **thymic hypoplasia** leading to T-cell deficiency), and developmental delay is classic for **DiGeorge syndrome**.
- **DiGeorge syndrome** is caused by a **microdeletion on chromosome 22q11.2**, affecting the development of structures derived from the **third and fourth pharyngeal pouches**.
*Mutation in the WAS gene*
- A mutation in the **WAS gene** causes **Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome**, characterized by **thrombocytopenia**, **eczema**, and **recurrent infections**.
- It does not directly explain the **hypocalcemia with low PTH** or developmental delay present in this patient.
*B cell development failure*
- **B-cell development failure**, as seen in conditions like **X-linked agammaglobulinemia**, leads to recurrent bacterial infections due to absent antibodies.
- However, it does not account for the **hypocalcemia** or developmental delay observed.
*B cell maturation failure*
- **B-cell maturation failure** results in impaired antibody production and recurrent infections but typically does not present with **hypocalcemia and low PTH** or developmental delay.
- Conditions like **Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID)** involve mature B cells failing to differentiate into plasma cells.
*Lysosomal trafficking regulator gene defect*
- A defect in the **lysosomal trafficking regulator gene (LYST)** is associated with **Chediak-Higashi syndrome**, which involves impaired lysosomal function, leading to immunodeficiency, **partial albinism**, and neurological abnormalities.
- This condition does not typically present with **hypocalcemia** or the specific constellation of symptoms seen in this case.
Primary immunodeficiencies US Medical PG Question 7: A 1-year-old infant is brought to the emergency department by his parents because of fever and rapid breathing for the past 2 days. He had a mild seizure on the way to the emergency department and developed altered sensorium. His mother states that the patient has had recurrent respiratory infections since birth. He was delivered vaginally at term and without complications. He is up to date on his vaccines and has met all developmental milestones. His temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse rate is 200/min, and respirations are 50/min. He is lethargic, irritable, and crying excessively. Physical examination is notable for a small head, an elongated face, broad nose, low set ears, and cleft palate. Cardiopulmonary exam is remarkable for a parasternal thrill, grade IV pansystolic murmur, and crackles over both lung bases. Laboratory studies show hypocalcemia and lymphopenia. Blood cultures are drawn and broad-spectrum antibiotics are started, and the child is admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit. The intensivist suspects a genetic abnormality and a fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis is ordered which shows 22q11.2 deletion. Despite maximal therapy, the infant succumbs to his illness. The parents of the child request an autopsy. Which of the following findings is the most likely to be present on autopsy?
- A. Aplastic thymus (Correct Answer)
- B. Hypercellular bone marrow
- C. Accessory spleen
- D. Hypertrophy of Hassall's corpuscles
- E. Absent follicles in the lymph nodes
Primary immunodeficiencies Explanation: ***Aplastic thymus***
- This infant's presentation with 22q11.2 deletion, recurrent respiratory infections, hypocalcemia, and congenital heart disease (parasternal thrill, pansystolic murmur) is classic for **DiGeorge syndrome**.
- **DiGeorge syndrome** is characterized by thymic aplasia or hypoplasia, leading to **T-cell immunodeficiency**, and parathyroid hypoplasia, resulting in **hypocalcemia**.
*Hypercellular bone marrow*
- **Hypercellular bone marrow** indicates increased hematopoietic activity and is not a characteristic finding in DiGeorge syndrome.
- In immunodeficiency states like DiGeorge, the bone marrow itself is often normal or may show lymphoid depletion.
*Accessory spleen*
- **Accessory spleen** is a common congenital anomaly and is not specifically associated with DiGeorge syndrome or its immunodeficiency.
- While it can occur in individuals with DiGeorge syndrome, it is not a direct pathological consequence of the 22q11.2 deletion.
*Hypertrophy of Hassall's corpuscles*
- **Hassall's corpuscles** are found in the medulla of the thymus, and their hypertrophy would indicate an active or hyperplastic thymus, which is contrary to the **thymic aplasia/hypoplasia** seen in DiGeorge syndrome.
- In DiGeorge syndrome, the thymus is either absent or severely underdeveloped.
*Absent follicles in the lymph nodes*
- **Absent follicles in the lymph nodes** would indicate a B-cell deficiency, as follicles are primarily composed of B lymphocytes.
- DiGeorge syndrome primarily affects **T-cell development** due to thymic abnormalities, not B-cell development or lymph node follicular formation directly.
Primary immunodeficiencies US Medical PG Question 8: An 8-year-old boy is brought to the pediatrician because his mother is concerned about recent behavioral changes. His mother states that she has started to notice that he is slurring his speech and seems to be falling more than normal. On exam, the pediatrician observes the boy has pes cavus, hammer toes, and kyphoscoliosis. Based on these findings, the pediatrician is concerned the child has a trinucleotide repeat disease. Which of the following trinucleotide repeats is this child most likely to possess?
- A. CTG
- B. GAA (Correct Answer)
- C. CGG
- D. CAG
- E. GCC
Primary immunodeficiencies Explanation: ***GAA***
- This trinucleotide repeat is associated with **Friedreich's ataxia**, an autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder.
- The presented symptoms of **ataxia** (slurred speech, falling), **pes cavus**, **hammer toes**, and **kyphoscoliosis** are classic features of Friedreich's ataxia.
*CTG*
- This trinucleotide repeat is associated with **myotonic dystrophy type 1**, an autosomal dominant disorder.
- While it causes muscle weakness, it is characterized by **myotonia** (delayed muscle relaxation), cataracts, and frontal baldness, which are not described here.
*CGG*
- This trinucleotide repeat is associated with **fragile X syndrome**, an X-linked dominant disorder.
- Fragile X syndrome primarily causes intellectual disability, behavioral issues (e.g., autism spectrum disorder), and characteristic facial features, but not the specific neurological and orthopedic findings seen in this patient.
*CAG*
- This trinucleotide repeat is associated with several neurodegenerative diseases, including **Huntington's disease**, spinocerebellar ataxias, and **dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy**.
- Huntington's disease, for example, presents with chorea, cognitive decline, and psychiatric symptoms, differing from the patient's presentation.
*GCC*
- This trinucleotide repeat is associated with **fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS)**.
- FXTAS typically affects older adult carriers of premutation alleles for fragile X, presenting with intention tremor and gait ataxia, not the early childhood onset and specific orthopedic deformities seen here.
Primary immunodeficiencies US Medical PG Question 9: A 5-year-old male is brought to his pediatrician after recurrent, prolonged upper respiratory infections over a period of several months. Physical exam reveals petechiae on the patient's legs and arms. Laboratory studies show hemoglobin: 10 g/dL, platelet count: 35,000/mm^3, leukocyte count: 6,600/mm^3. A bone marrow aspiration shows an abundance of lymphoblasts indicative of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Positive immunostaining for which of the following would support a diagnosis of precursor B-cell leukemia?
- A. CD2, CD8
- B. TdT, HER-2
- C. CD4, CD5
- D. CD19, CD10 (Correct Answer)
- E. CD30, CD15
Primary immunodeficiencies Explanation: ***CD19, CD10***
- **CD19** is a pan B-cell marker, expressed on almost all B-lymphocytes from early pre-B-cells through mature B-cells. Its presence, along with **CD10**, is highly characteristic of **precursor B-cell ALL (B-ALL)**.
- **CD10**, also known as common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CALLA), is typically expressed on **early B-cell progenitors** and is a reliable marker for differentiating B-ALL from other leukemias.
*CD2, CD8*
- **CD2** and **CD8** are markers primarily associated with **T-lymphocytes**. While CD2 is a pan T-cell marker, CD8 identifies cytotoxic T cells.
- Their positivity would suggest a **T-cell ALL (T-ALL)**, not the precursor B-cell type indicated by the clinical scenario.
*TdT, HER-2*
- **Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)** is an enzyme found in immature lymphocytes (both B and T cells) and is positive in most ALL cases, but it is not specific for B-cell lineage.
- **HER-2** is an oncogene and a growth factor receptor overexpressed in certain solid tumors (especially breast cancer) but is not a marker used for leukemia classification.
*CD4, CD5*
- **CD4** is a marker for helper T cells, while **CD5** is expressed on a subset of T cells and some B-cell malignancies (e.g., chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma).
- These markers are primarily associated with **T-cell lineages** and would not support a diagnosis of precursor B-cell leukemia in this context.
*CD30, CD15*
- **CD30** and **CD15** are classical markers for **Hodgkin lymphoma** (specifically the classical type).
- Their presence would point towards a lymphoproliferative disorder different from acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Primary immunodeficiencies US Medical PG Question 10: A 28-year-old man presents for severe abdominal pain and is diagnosed with appendicitis. He is taken for emergent appendectomy. During the procedure, the patient has massive and persistent bleeding requiring a blood transfusion. The preoperative laboratory studies showed a normal bleeding time, normal prothrombin time (PT), an INR of 1.0, and a normal platelet count. Postoperatively, when the patient is told about the complications during the surgery, he recalls that he forgot to mention that he has a family history of an unknown bleeding disorder. The postoperative laboratory tests reveal a prolonged partial thromboplastin time (PTT). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. von Willebrand disease
- B. Bernard-Soulier syndrome
- C. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
- D. Hemophilia A (Correct Answer)
- E. Glanzmann thrombasthenia
Primary immunodeficiencies Explanation: ***Hemophilia A***
- The patient's presentation with **severe, persistent bleeding** during surgery despite normal preoperative coagulation studies (PT, INR, platelet count) and a subsequent **prolonged PTT** strongly indicates a **factor deficiency in the intrinsic pathway**.
- **Hemophilia A**, an X-linked recessive disorder, is caused by a deficiency of **Factor VIII**, leading to a prolonged PTT and deep tissue bleeding, which fits the clinical picture and family history.
*von Willebrand disease*
- This condition typically presents with **mucocutaneous bleeding** (e.g., nosebleeds, menorrhagia) and can have a prolonged bleeding time, but the primary defect is in **platelet adhesion**, not usually massive operative bleeding with normal platelet count.
- While **von Willebrand factor (vWF)** carries Factor VIII, a primary deficiency of vWF would affect factor VIII levels but the presentation and normal bleeding time here make it less likely than direct factor VIII deficiency.
*Bernard-Soulier syndrome*
- This is a **platelet disorder** characterized by defective **glycoprotein Ib/IX/V complex**, leading to impaired platelet adhesion and often **thrombocytopenia** with unusually large platelets.
- The patient had a **normal platelet count** and a subsequent prolonged PTT, which points away from a primary platelet adhesion defect.
*Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura*
- This is a microangiopathic hemolytic anemia characterized by a **pentad of symptoms**: fever, neurologic symptoms, renal dysfunction, thrombocytopenia, and microangiopathic hemolytic anemia.
- It involves widespread **thrombosis** and **low platelet count**, which does not align with the patient's presentation of massive bleeding with normal platelet counts.
*Glanzmann thrombasthenia*
- This is a rare **platelet aggregation disorder** caused by a defect in **glycoprotein IIb/IIIa**, leading to impaired fibrinogen binding and platelet aggregation.
- While it causes severe bleeding, it would be associated with a **prolonged bleeding time** and normal PTT, which contradicts the patient's normal bleeding time and prolonged PTT.
More Primary immunodeficiencies US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.