Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV). These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) US Medical PG Question 1: A 25-year-old woman presents to an urgent care center following a bee sting while at a picnic with her friends. She immediately developed a skin rash and swelling over her arm and face. She endorses diffuse itching over her torso. Past medical history is significant for a mild allergy to pet dander and ragweed. She occasionally takes oral contraceptive pills and diphenhydramine for her allergies. Family history is noncontributory. Her blood pressure is 119/81 mm Hg, heart rate is 101/min, respiratory rate is 21/min, and temperature is 37°C (98.6°F). On physical examination, the patient has severe edema over her face and severe stridor with inspiration at the base of both lungs. Of the following options, this patient is likely experiencing which of the following hypersensitivity reactions?
- A. Type 2 - cytotoxic hypersensitivity reaction
- B. Type 1 - anaphylactic hypersensitivity reaction (Correct Answer)
- C. Both A & B
- D. Type 4 - cell mediated (delayed) hypersensitivity reaction
- E. Type 3 - immune complex mediated hypersensitivity reaction
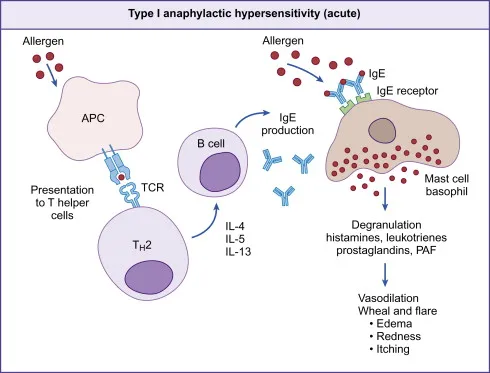
Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) Explanation: ***Type 1 - anaphylactic hypersensitivity reaction***
- The rapid onset of symptoms like **skin rash**, **swelling (angioedema)**, **diffuse itching (pruritus)**, and **stridor** immediately following a **bee sting** is characteristic of an immediate, IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reaction.
- This type of reaction involves the release of **histamine** and other mediators from **mast cells** and **basophils**, leading to systemic symptoms, including potential airway obstruction.
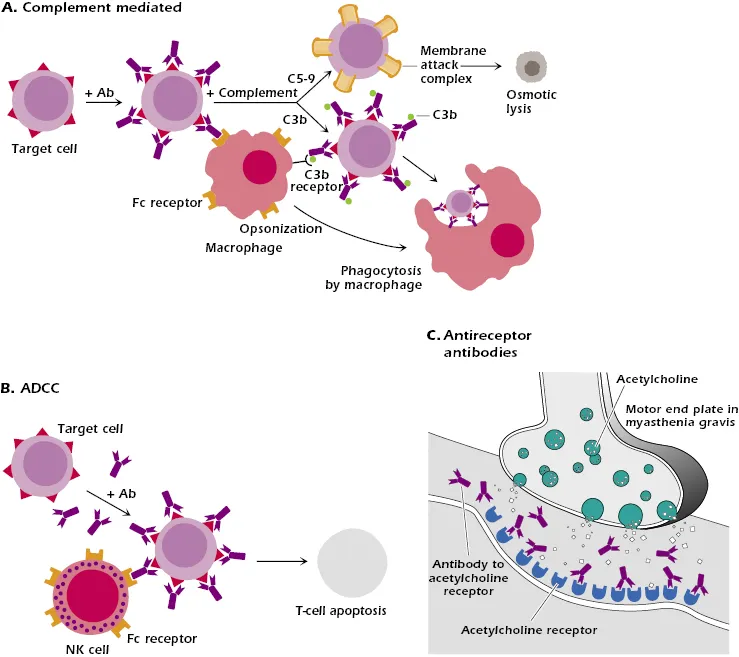
*Type 2 - cytotoxic hypersensitivity reaction*
- Type 2 hypersensitivity involves **antibodies** (IgG or IgM) binding to antigens on the surface of **target cells**, leading to cell destruction.
- Examples include **hemolytic anemia** or **transfusion reactions**, which do not match the presented symptoms of allergic rash and angioedema.
*Both A & B*
- This option is incorrect because the patient's symptoms are highly consistent with a **Type 1 reaction** and do not align with the mechanisms or clinical manifestations of a Type 2 reaction.
- The immediate and widespread allergic response points specifically to IgE-mediated anaphylaxis.
*Type 4 - cell mediated (delayed) hypersensitivity reaction*
- Type 4 hypersensitivity is a **delayed reaction** mediated by **T cells**, typically appearing 24-72 hours after exposure.
- Examples include **contact dermatitis** or the **tuberculin skin test**, which are much slower in onset and different in presentation than the immediate, severe reaction described.
*Type 3 - immune complex mediated hypersensitivity reaction*
- Type 3 hypersensitivity involves the formation of **immune complexes** (antigen-antibody complexes) that deposit in tissues, causing inflammation.
- Conditions like **serum sickness** or **lupus nephritis** are examples and typically have a slower onset and different clinical presentation (e.g., vasculitis, glomerulonephritis) compared to acute anaphylaxis.
Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) US Medical PG Question 2: A 60-year-old man who recently immigrated from South America schedules an appointment with a physician to complete his pre-employment health clearance form. According to company policy, a skin test for tuberculosis must be administered to all new employees. Thus, he received an intradermal injection of purified protein derivative (PPD) on his left forearm. After 48 hours, a 14-mm oval induration is noticed. The type of cells most likely present and responsible for the indurated area will have which of the following characteristic features?
- A. They are rich in myeloperoxidase enzyme.
- B. They need thymus for their maturation. (Correct Answer)
- C. They play an important part in allergic reactions.
- D. They have multiple-lobed nucleus.
- E. Their half-life is 24–48 hours.
Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) Explanation: ***They need thymus for their maturation.***
- The induration in a **PPD test** is mediated by **T-helper cells (CD4+)**, which are a type of **T lymphocyte**.
- **T lymphocytes** mature in the **thymus**, where they undergo positive and negative selection.
*They are rich in myeloperoxidase enzyme.*
- Cells rich in **myeloperoxidase enzyme** are primarily **neutrophils**, which are involved in acute inflammation and bacterial killing.
- The PPD induration is a **Type IV hypersensitivity reaction**, characterized by a delayed, cell-mediated immune response, not an acute neutrophil-driven one.
*They play an important part in allergic reactions.*
- Cells primarily involved in allergic reactions (**Type I hypersensitivity**) are **mast cells** and **basophils**, which release mediators like histamine.
- The PPD test is a **Type IV, delayed-type hypersensitivity**, involving T-cells and macrophages, not allergic reactions.
*They have multiple-lobed nucleus.*
- Cells with a **multiple-lobed nucleus** are characteristic of **neutrophils**, as well as other granulocytes like eosinophils and basophils.
- **T lymphocytes** typically have a large, round nucleus that fills most of the cytoplasm.
*Their half-life is 24–48 hours.*
- Cells with a short half-life of 24-48 hours are characteristic of some granulocytes, like **neutrophils**, which have a relatively short lifespan.
- **Memory T lymphocytes**, which are crucial for the PPD response, can persist for many years, providing long-term immunity.
Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) US Medical PG Question 3: A 55-year-old man with a history of fatigue and exertional dyspnea presents to the urgent care clinic following an acute upper respiratory illness. On physical examination, his pulses are bounding, his complexion is very pale, and scleral icterus is apparent. The spleen is moderately enlarged. Oxygen saturation is 79% at rest, with a new oxygen requirement of 9 L by a non-rebreather mask. Laboratory analysis results show a hemoglobin level of 6.8 g/dL. Of the following options, which hypersensitivity reaction does this condition represent?
- A. Type III–immune complex-mediated hypersensitivity reaction
- B. Type I–anaphylactic hypersensitivity reaction
- C. Type IV–cell-mediated (delayed) hypersensitivity reaction
- D. Type II–cytotoxic hypersensitivity reaction (Correct Answer)
- E. Type II and III–mixed cytotoxic and immune complex hypersensitivity reaction
Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) Explanation: ***Type II–cytotoxic hypersensitivity reaction***
- The patient's symptoms, including **fatigue**, **exertional dyspnea**, **pale complexion**, **scleral icterus**, and **splenomegaly**, along with a **low hemoglobin** of 6.8 g/dL, strongly suggest **hemolytic anemia**.
- Following an **upper respiratory illness**, this presentation is consistent with **autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA)**, where antibodies (mainly IgG or IgM) mistakenly target and destroy red blood cells, which is a classic example of a **Type II hypersensitivity reaction**.
*Type III–immune complex-mediated hypersensitivity reaction*
- This reaction involves the formation of **immune complexes** that deposit in tissues, leading to inflammation and damage, as seen in conditions like **serum sickness** or **lupus nephritis**.
- The patient's primary symptoms of **hemolysis** and **anemia** are not characteristic of immune complex deposition.
*Type I–anaphylactic hypersensitivity reaction*
- This type involves **IgE-mediated mast cell degranulation**, leading to rapid onset symptoms like **urticaria**, **angioedema**, **bronchospasm**, and **hypotension**.
- The patient's presentation of gradual onset fatigue, anemia, and icterus does not align with the acute, systemic allergic reaction seen in Type I hypersensitivity.
*Type IV–cell-mediated (delayed) hypersensitivity reaction*
- This reaction is mediated by **T cells** and **macrophages**, with a delayed onset (24-72 hours), as seen in **contact dermatitis** or **tuberculosis skin tests**.
- The patient's rapid development of severe anemia and an acute hemolytic picture is not consistent with a T-cell-mediated delayed reaction.
*Type II and III–mixed cytotoxic and immune complex hypersensitivity reaction*
- While some autoimmune conditions can involve elements of both Type II and Type III reactions, the overwhelming clinical picture in this patient points to direct **antibody-mediated destruction of red blood cells (Type II)**.
- There are no specific features mentioned, such as vasculitis or nephritis, that would strongly suggest **immune complex deposition** in addition to the prominent hemolytic anemia.
Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) US Medical PG Question 4: A 31-year-old woman presents to her primary care provider to discuss the results from a previous urine analysis. She has no new complaints and feels well. Past medical history is significant for systemic lupus erythematosus. She was diagnosed 5 years ago and takes hydroxychloroquine every day and prednisone when her condition flares. Her previous urine analysis shows elevated protein levels (4+) and blood (3+). The urine sediment contained red blood cells (6 RBCs/high-power field). The treating physician would like to perform a renal biopsy to rule out lupus nephritis. What type of hypersensitivity is suggestive of lupus nephritis?
- A. Type IV, mediated by IgG and IgM antibodies
- B. Type IV, mediated by CD4+ T cells
- C. Type III, mediated by IgG antibodies (Correct Answer)
- D. Type I, mediated by IgE antibodies
- E. Type II, mediated by IgG and IgM antibodies
Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) Explanation: ***Type III, mediated by IgG antibodies***
- Lupus nephritis is a classic example of a **Type III hypersensitivity reaction**, characterized by the formation of **immune complexes** (combinations of antibodies and antigens) in the circulation.
- These circulating **autoantibody-antigen complexes** deposit in the glomeruli of the kidneys, activating complement and initiating an inflammatory response that damages renal tissue.
*Type IV, mediated by IgG and IgM antibodies*
- **Type IV hypersensitivity** is a **delayed-type reaction** mediated by T cells, not antibodies.
- IgG and IgM antibodies are involved in Type II and Type III hypersensitivity, not Type IV.
*Type IV, mediated by CD4+ T cells*
- While **Type IV hypersensitivity** is indeed mediated by **CD4+ T cells** (and CD8+ T cells), lupus nephritis is primarily an **immune complex-mediated (Type III)** disease.
- T cells do play a role in the pathogenesis of SLE, but the direct kidney damage in lupus nephritis is driven by antibody-antigen complex deposition.
*Type I, mediated by IgE antibodies*
- **Type I hypersensitivity** is an **immediate allergic reaction** mediated by **IgE antibodies** binding to mast cells and basophils, leading to histamine release.
- This type of reaction is responsible for conditions like asthma, allergies, and anaphylaxis, and is not involved in lupus nephritis.
*Type II, mediated by IgG and IgM antibodies*
- **Type II hypersensitivity** involves **antibodies directly targeting antigens on cell surfaces or extracellular matrix components**, leading to cell lysis or dysfunction.
- While IgG and IgM are involved, the defining feature is direct binding to fixed tissue antigens rather than deposition of circulating immune complexes as seen in lupus nephritis.
Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) US Medical PG Question 5: An 18-year-old man is known to be allergic to peanuts, and he mistakenly eats biscuits containing some traces of peanuts. Within 15 minutes, he develops generalized redness of the skin and urticaria, associated with shortness of breath and diffuse wheezing. His blood pressure is 80/55 mm Hg and heart rate is 124/min. He is given intramuscular epinephrine and transported emergently to the local hospital. This patient’s presentation is an example of which of the following hypersensitivity reactions?
- A. Delayed hypersensitivity
- B. Immediate hypersensitivity (Correct Answer)
- C. Type II hypersensitivity
- D. Contact dermatitis
- E. Serum sickness
Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) Explanation: ***Immediate hypersensitivity***
- The rapid onset (within 15 minutes) of symptoms like **generalized redness**, **urticaria**, **shortness of breath**, **wheezing**, and **hypotension** after exposure to peanuts is characteristic of an **anaphylactic reaction**, which is a severe form of immediate (Type I) hypersensitivity.
- This reaction involves **IgE-mediated mast cell and basophil degranulation**, leading to the rapid release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators.
*Delayed hypersensitivity*
- This type of hypersensitivity, also known as **Type IV hypersensitivity**, typically manifests 24 to 72 hours after antigen exposure.
- It is mediated by **T-cells** and macrophages, not antibodies, and is commonly seen in reactions like **tuberculin skin tests** or contact dermatitis.
*Type II hypersensitivity*
- This reaction involves **antibody-mediated cytotoxicity**, where antibodies (IgG or IgM) bind to antigens on cell surfaces, leading to cell destruction.
- Examples include **hemolytic transfusion reactions** and **autoimmune hemolytic anemia**, which do not match the presented symptoms.
*Contact dermatitis*
- This is a form of **Type IV hypersensitivity** that results from direct contact of the skin with an allergen, leading to a localized rash.
- It presents with **localized skin inflammation** and typically has a delayed onset, usually days after exposure, unlike the rapid systemic reaction described.
*Serum sickness*
- This is a **Type III hypersensitivity reaction** characterized by the formation of **immune complexes** that deposit in tissues, causing symptoms like fever, rash, and arthralgia.
- It typically occurs days to weeks after exposure to certain drugs or foreign proteins, which does not align with the immediate, severe systemic symptoms.
Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) US Medical PG Question 6: A 7-year-old girl is brought to the physician with complaints of erythema and rashes over the bridge of her nose and on her forehead for the past 6 months. She also has vesiculobullous and erythematous scaly crusted lesions on the scalp and around the perioral areas. Her parents report a history of worsening symptoms during exposure to sunlight, along with a history of joint pain and oral ulcers. Her temperature is 38.6°C (101.4°F), pulse is 88/min, and respirations are 20/min. On physical examination, pallor and cervical lymphadenopathy are present. On cutaneous examination, diffuse hair loss and hyperpigmented scaly lesions are present. Her laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 7.9 mg/dL
Total leukocyte count 6,300/mm3
Platelet count 167,000/mm3
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate 30 mm/h
ANA titer 1:520 (positive)
Which of the following most likely explains the mechanism of this condition?
- A. Type II hypersensitivity
- B. Type IV hypersensitivity
- C. Type V hypersensitivity
- D. Type I hypersensitivity
- E. Type III hypersensitivity (Correct Answer)
Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) Explanation: ***Type III hypersensitivity***
- This condition describes **Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)**, characterized by the formation of **immune complexes** that deposit in various tissues and trigger inflammation.
- The positive **ANA titer**, along with clinical features like **malar rash**, photosensitivity, arthritis, oral ulcers, and hematologic abnormalities (anemia, lymphadenopathy), are all consistent with SLE, which is a classic example of **Type III hypersensitivity**.
*Type II hypersensitivity*
- Involves **antibodies directly attacking antigens on cell surfaces**, leading to cell lysis or dysfunction.
- While SLE can have Type II features (e.g., hemolytic anemia), the broad systemic inflammation and diverse organ involvement are primarily driven by immune complex deposition.
*Type IV hypersensitivity*
- This is a **delayed-type hypersensitivity** reaction mediated by **T cells** and macrophages, not antibodies.
- Examples include contact dermatitis and tuberculin skin tests, which do not align with the multi-organ, immune complex-mediated pathology seen here.
*Type V hypersensitivity*
- A rare subtype of Type II hypersensitivity where antibodies **stimulate or inhibit cell function** by binding to cell surface receptors (e.g., Grave's disease, Myasthenia Gravis).
- It does not explain the widespread immune complex deposition and systemic inflammation characteristic of SLE.
*Type I hypersensitivity*
- Involves **IgE antibodies** binding to mast cells, leading to immediate release of histamine and other mediators upon antigen exposure.
- This type causes allergic reactions like hay fever or anaphylaxis and does not explain the chronic autoimmune manifestations of SLE.
Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) US Medical PG Question 7: A 5-year-old African American female has experienced recurrent respiratory infections. To determine how well her cell-mediated immunity is performing, a Candida skin injection is administered. After 48 hours, there is no evidence of induration at the injection site. Of the following cell types, which one would normally mediate this type of immune reaction?
- A. Plasma cells
- B. Fibroblasts
- C. T-cells (Correct Answer)
- D. Mast cells
- E. Basophils
Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) Explanation: ***T-cells***
- The **Candida skin injection** tests for **delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH)**, also known as **Type IV hypersensitivity**, which is a classic example of **cell-mediated immunity**.
- **CD4+ Th1 helper T-cells** are the primary mediators of DTH responses. Upon re-exposure to Candida antigens, these memory T-cells release **IFN-γ and other cytokines** that recruit and activate **macrophages**, causing **induration** at the injection site within **48-72 hours**.
- The absence of induration in this patient suggests **impaired cell-mediated immunity**, which explains her recurrent infections.
*Plasma cells*
- **Plasma cells** are responsible for producing and secreting **antibodies**, which are part of the **humoral immune response** (Type II and III hypersensitivity), not cell-mediated immunity.
- While antibodies can play a role in fighting infections, they do not mediate the DTH reaction observed in a skin test.
*Fibroblasts*
- **Fibroblasts** are connective tissue cells involved in wound healing and structural support in tissues, producing **collagen** and other extracellular matrix components.
- They do not directly participate in the initiation or mediation of immune responses like cell-mediated hypersensitivity.
*Mast cells*
- **Mast cells** are primarily involved in **allergic reactions** and defense against parasites through the release of **histamine** and other inflammatory mediators.
- They mediate **immediate-type hypersensitivity reactions (Type I)**, which occur within minutes, not the delayed-type hypersensitivity response tested by a Candida skin injection that peaks at 48-72 hours.
*Basophils*
- **Basophils** are granulocytes that release **histamine** and other mediators, similar to mast cells, and are involved in **allergic reactions** and **parasitic infections**.
- Like mast cells, they primarily contribute to **Type I immediate hypersensitivity**, not the cell-mediated response of DTH.
Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) US Medical PG Question 8: You are working in the emergency room of a children's hospital when a 4-year-old girl is brought in by ambulance due to "difficulty breathing." The patient had been eating lunch on a school field trip when she suddenly complained of abdominal pain. Shortly thereafter, she was noted to have swelling of the lips, a rapidly developing red rash and difficulty breathing. In the ambulance her blood pressure was persistently 80/50 mmHg despite intramuscular epinephrine. In the course of stabilization and work up of the patient, you note an elevated tryptase level. What is the mechanism behind this elevated tryptase level?
- A. IgM mediated complement activation
- B. Cross-linking of IgE on mast cells (Correct Answer)
- C. IgG production by plasma cells
- D. Antibody-antigen immune complexes
- E. Cross-linking of IgG on mast cells
Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) Explanation: **Cross-linking of IgE on mast cells**
- The rapid onset of symptoms like **lip swelling**, **rash**, and **difficulty breathing** after eating, along with **hypotension** despite epinephrine, points to **anaphylaxis**, which is primarily mediated by **IgE**.
- **Tryptase** is a serine protease selectively stored in the secretory granules of **mast cells** and is released upon mast cell activation, making it a reliable marker for **anaphylaxis**.
*IgM mediated complement activation*
- **IgM-mediated complement activation** is primarily involved in host defense against infections and in autoimmune conditions, but not typically in acute allergic reactions like anaphylaxis.
- While complement activation can occur in severe allergic reactions, the direct trigger and primary mechanism for tryptase release in anaphylaxis is **IgE cross-linking**.
*IgG production by plasma cells*
- **IgG production by plasma cells** is part of the adaptive immune response, responsible for long-term immunity and neutralizing toxins and pathogens.
- It is not the immediate mechanism for **mast cell degranulation** and **tryptase release** in an acute allergic reaction such as anaphylaxis.
*Antibody-antigen immune complexes*
- **Antibody-antigen immune complexes** are typically associated with Type III hypersensitivity reactions, which involve deposition of complexes in tissues, leading to inflammation (e.g., lupus, serum sickness).
- These reactions generally have a delayed onset and a different clinical presentation, not the acute, systemic symptoms of **anaphylaxis** seen here.
*Cross-linking of IgG on mast cells*
- While **IgG** can play a role in some immune responses, the primary immunoglobulin involved in immediate hypersensitivity reactions like anaphylaxis, leading to mast cell degranulation, is **IgE**, not IgG.
- Mast cells have **Fc receptors** for IgE, not IgG, that, when cross-linked by allergen, trigger the release of mediators including **tryptase**.
Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) US Medical PG Question 9: A 45-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician for knee pain. She states that she has been experiencing a discomfort and pain in her left knee that lasts for several hours but tends to improve with use. She takes ibuprofen occasionally which has been minimally helpful. She states that this pain is making it difficult for her to work as a cashier. Her temperature is 98.6°F (37.0°C), blood pressure is 117/58 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, respirations are 14/min, and oxygen saturation is 97% on room air. Physical exam reveals a stable gait that the patient claims causes her pain. The patient has a non-pulsatile, non-erythematous, palpable mass over the posterior aspect of her left knee that is roughly 3 to 4 cm in diameter and is hypoechoic on ultrasound. Which of the following is associated with this patient's condition?
- A. Venous valve failure
- B. Herniated nucleus pulposus
- C. Inflammation of the pes anserinus bursa
- D. Artery aneurysm
- E. Baker's cyst (Correct Answer)
Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) Explanation: ***Baker's cyst***
- The patient's presentation of a **palpable, non-pulsatile, non-erythematous mass** in the posterior knee that is **hypoechoic on ultrasound** is highly suggestive of a Baker's cyst.
- A Baker's cyst (popliteal cyst) is often associated with **underlying knee joint pathology**, such as osteoarthritis or meniscal tears, which can cause knee pain that improves with use and is worse with activity like standing for a cashier.
*Venous valve failure*
- **Venous valve failure** leads to **chronic venous insufficiency**, presenting as varicose veins, edema, skin changes (hyperpigmentation, lipodermatosclerosis), and ulcers, typically in the lower leg and ankle.
- While it can cause leg discomfort, it does not typically manifest as a discreet, non-pulsatile mass in the posterior knee or be hypoechoic on ultrasound.
*Herniated nucleus pulposus*
- A **herniated nucleus pulposus** (slipped disc) causes **radicular pain** (sciatica) that radiates down the leg, numbness, tingling, and weakness, often exacerbated by sitting, coughing, or sneezing.
- It would not present with a palpable mass in the posterior knee and is a spinal condition, not a direct knee pathology.
*Inflammation of the pes anserine bursa*
- **Pes anserine bursitis** causes pain and tenderness specifically on the **medial aspect of the knee**, about 2-3 inches below the joint line, where the pes anserinus tendons insert.
- It would not cause a mass in the posterior knee and the pain location is distinct.
*Artery aneurysm*
- An **artery aneurysm**, particularly a popliteal artery aneurysm, would present as a **pulsatile mass** in the popliteal fossa.
- Its pulsatile nature and the risk of rupture or thrombus formation distinguish it from the described non-pulsatile mass.
Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) US Medical PG Question 10: A 55-year-old woman presents with pain in both hands and wrists for several years. It is associated with morning stiffness that lasts for almost an hour. She has a blood pressure of 124/76 mm Hg, heart rate of 71/min, and respiratory rate of 14/min. Physical examination reveals tenderness and swelling in both hands and wrists. Laboratory investigations reveal the presence of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide. Which of the following immune-mediated processes is responsible for this patient’s condition?
- A. Self-tolerance
- B. Type IV hypersensitivity
- C. IgE-mediated immune responses only
- D. Both type II and III hypersensitivities
- E. Type III hypersensitivity (Correct Answer)
Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) Explanation: ***Type III hypersensitivity***
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), suggested by **symmetric joint pain**, **morning stiffness >1 hour**, and **positive anti-CCP antibodies**, is primarily mediated by **Type III hypersensitivity** (immune complex-mediated).
- **Immune complexes** (rheumatoid factor-IgG complexes, anti-CCP complexes) deposit in the **synovium**, activate **complement**, and recruit inflammatory cells causing **chronic synovitis** and joint destruction.
- Note: Type IV hypersensitivity (T cell-mediated) also contributes significantly to RA pathogenesis, though this option is not provided.
*Self-tolerance*
- **Self-tolerance** is the immune system's ability to recognize and not attack self-antigens.
- RA represents a **breakdown of self-tolerance** (an autoimmune disease), not a mechanism of tissue damage itself.
*Type IV hypersensitivity*
- **Type IV hypersensitivity** (delayed-type, T cell-mediated) does play an important role in RA pathogenesis, with CD4+ T cells driving chronic inflammation.
- However, the **primary mechanism** involves immune complex deposition (Type III), making Type III the more complete answer when Type IV is not combined with it.
*IgE-mediated immune responses only*
- **IgE-mediated responses** (Type I hypersensitivity) cause **allergic reactions** like anaphylaxis, asthma, and hay fever.
- This involves IgE binding to mast cells/basophils with histamine release, which is **not characteristic of RA**.
*Both type II and III hypersensitivities*
- While **Type III hypersensitivity** is central to RA, **Type II hypersensitivity** (antibody-mediated cytotoxicity against cell surface antigens) is **not a primary mechanism** in RA.
- Type II occurs in diseases like Goodpasture syndrome, Graves' disease, and myasthenia gravis, where antibodies directly target cell surface receptors or tissue antigens.
- In RA, autoantibodies (RF, anti-CCP) primarily form **immune complexes** (Type III), not direct cell targeting (Type II).
More Hypersensitivity reactions (types I-IV) US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.