Amyloidosis types US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Amyloidosis types. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Amyloidosis types US Medical PG Question 1: A previously healthy 82-year-old man dies in a motor vehicle collision. At autopsy, the heart shows slight ventricular thickening. There are abnormal, insoluble aggregations of protein filaments in beta-pleated linear sheets in the ventricular walls and, to a lesser degree, in the atria and lungs. No other organs show this abnormality. Bone marrow examination shows no plasma cell dyscrasia. The abnormal protein aggregations are most likely composed of which of the following?
- A. Immunoglobulin light chain
- B. Normal transthyretin (Correct Answer)
- C. β-amyloid peptide
- D. Natriuretic peptide
- E. Serum amyloid A
Amyloidosis types Explanation: ***Normal transthyretin***
- The patient's age and the localization of the amyloid deposits primarily in the **heart (ventricular walls and atria)**, along with normal bone marrow and the absence of systemic involvement, are highly characteristic of **senile systemic amyloidosis** which is caused by wild-type (normal) transthyretin.
- **Transthyretin** is a transport protein for thyroid hormones and retinol; with aging, it can misfold and deposit as amyloid fibrils, particularly in the heart.
*Immunoglobulin light chain*
- This typically causes **primary amyloidosis (AL amyloidosis)**, which is associated with a **plasma cell dyscrasia** and multiorgan involvement, neither of which are present in this case.
- AL amyloidosis often affects the kidneys, liver, and nerves, in addition to the heart, which is not described here.
*β-amyloid peptide*
- This protein forms plaques primarily in the **brain** in **Alzheimer's disease** and cerebral amyloid angiopathy, not typically causing significant cardiac amyloidosis.
- While it can be found in some vascular structures, its primary association is with neurodegenerative disease.
*Natriuretic peptide*
- **Natriuretic peptides (ANP, BNP)** are hormones involved in cardiovascular homeostasis and do not form amyloid deposits.
- They are markers of heart failure, not the causative agents of amyloidosis.
*Serum amyloid A*
- This protein is associated with **secondary amyloidosis (AA amyloidosis)**, which develops as a complication of chronic inflammatory diseases or infections.
- The patient's history does not mention any such underlying conditions, and the deposition pattern is not typical for AA amyloidosis.
Amyloidosis types US Medical PG Question 2: A 48-year-old woman comes to the physician because of progressively worsening dyspnea on exertion and fatigue for the past 2 months. She had Hodgkin lymphoma as an adolescent, which was treated successfully with chemotherapy and radiation. Her father died from complications related to amyloidosis. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. Her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), pulse is 124/min, respirations are 20/min, and blood pressure is 98/60 mm Hg. Cardiac examination shows no murmurs. Coarse crackles are heard at the lung bases bilaterally. An ECG shows an irregularly irregular rhythm with absent P waves. An x-ray of the chest shows globular enlargement of the cardiac shadow with prominent hila and bilateral fluffy infiltrates. Transthoracic echocardiography shows a dilated left ventricle with an ejection fraction of 40%. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
- A. Postradiation fibrosis
- B. Coronary artery occlusion
- C. Amyloid deposition
- D. Acute psychological stress
- E. Chronic tachycardia (Correct Answer)
Amyloidosis types Explanation: ***Chronic tachycardia***
- The **irregularly irregular rhythm with absent P waves** on ECG is characteristic of **atrial fibrillation**, which can lead to **tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy** if sustained. The pulse of 124/min supports this.
- A sustained elevated heart rate like 124/min, especially in the context of atrial fibrillation, can cause **ventricular dilation** and reduced ejection fraction, leading to symptoms like dyspnea and fatigue observed in the patient.
*Postradiation fibrosis*
- While the patient has a history of radiation therapy for Hodgkin lymphoma, **radiation-induced cardiac damage** typically manifests as perivascular **fibrosis**, leading to **restrictive cardiomyopathy** or pericardial disease, not primarily dilated cardiomyopathy with an irregularly irregular rhythm.
- This condition is often associated with a **reduced diastolic filling** and **normal systolic function** initially, which contradicts the dilated left ventricle and reduced ejection fraction described.
*Amyloid deposition*
- The family history of amyloidosis is a red herring in this clinical picture. While **cardiac amyloidosis** can cause heart failure, it typically presents as **restrictive cardiomyopathy** with **thickened ventricular walls** and normal or reduced ventricular cavity size, not a dilated left ventricle.
- ECG findings in amyloidosis often include **low voltage QRS complexes** despite thickened walls, which is not described.
*Coronary artery occlusion*
- **Coronary artery occlusion** (e.g., myocardial infarction) can lead to dilated cardiomyopathy and reduced ejection fraction, but it usually presents with chest pain or specific ECG changes (e.g., ST elevation/depression, Q waves) that are not mentioned.
- The **irregularly irregular rhythm** (atrial fibrillation) and absence of murmurs make a primary ischemic event less likely as the sole explanation for the global cardiac changes.
*Acute psychological stress*
- **Acute psychological stress** can trigger **takotsubo cardiomyopathy** (stress-induced cardiomyopathy), which presents with left ventricular dysfunction and apical ballooning.
- However, this is typically an acute event with different ECG patterns (often ST elevation) and would not explain the chronic, sustained tachycardia and atrial fibrillation leading to dilated cardiomyopathy.
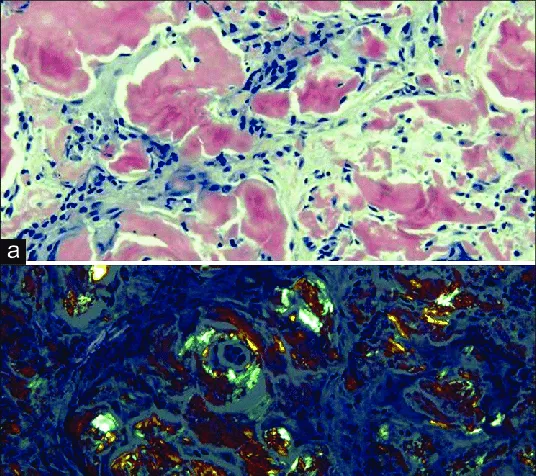
Amyloidosis types US Medical PG Question 3: A 62-year-old man comes to the physician because of fatigue and decreased urine output for 2 weeks. He has not been to the physician for many years and takes no medications. Serum studies show a urea nitrogen concentration of 42 mg/dL and a creatinine concentration of 2.3 mg/dL. Urinalysis shows heavy proteinuria. A photomicrograph of a section of a kidney biopsy specimen is shown. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Amyloidosis
- B. Diabetes mellitus (Correct Answer)
- C. Dyslipidemia
- D. Fibromuscular dysplasia
- E. Severe hypertension
Amyloidosis types Explanation: ***Diabetes mellitus***
- The kidney biopsy shows **diffuse glomerulosclerosis** with **Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules** (nodular mesangial sclerosis), which are pathognomonic for **diabetic nephropathy**.
- **Heavy proteinuria**, elevated BUN (42 mg/dL) and creatinine (2.3 mg/dL), along with the patient's age, are consistent with long-standing diabetes mellitus, even if previously undiagnosed.
- Diabetic nephropathy is the leading cause of end-stage renal disease in the United States.
*Amyloidosis*
- While amyloidosis can cause nephrotic syndrome and renal failure, the characteristic histology shows **extracellular amorphous deposits** that stain with **Congo red** and demonstrate apple-green birefringence under polarized light.
- The mesangial nodular pattern seen in diabetic nephropathy is distinct from the amyloid deposits seen in amyloidosis.
- Systemic amyloidosis typically presents with other organ involvement such as **cardiomyopathy**, **hepatosplenomegaly**, or **macroglossia**.
*Dyslipidemia*
- **Dyslipidemia** is a common comorbidity of nephrotic syndrome and diabetic nephropathy, but it is not a direct cause of the structural glomerular damage.
- It represents a metabolic consequence rather than the underlying etiology of the renal pathology.
*Fibromuscular dysplasia*
- **Fibromuscular dysplasia** affects the **renal arteries**, causing **renovascular hypertension** and renal ischemia.
- It typically presents with hypertension in young to middle-aged women and an abdominal bruit, not with heavy proteinuria and glomerular nodular sclerosis.
- The histology would show arterial wall changes, not glomerular pathology.
*Severe hypertension*
- **Severe hypertension** causes hypertensive nephrosclerosis with arteriolosclerosis and global glomerulosclerosis, but not the characteristic **nodular mesangial expansion** (Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules) seen in diabetic nephropathy.
- While hypertension commonly accompanies diabetic nephropathy, the specific histological findings of nodular glomerulosclerosis are pathognomonic for diabetes mellitus.
- Hypertensive nephrosclerosis shows arteriolar hyalinosis and ischemic changes, which differ from diabetic glomerular changes.
Amyloidosis types US Medical PG Question 4: A 63-year-old man presents to the emergency department with periorbital swelling. He states that he was gardening, came inside, looked in the mirror, and then noticed his eyelids were swollen. He denies pain, pruritus, or visual disturbances. He states that he was drinking “a lot of water" to prevent dehydration, because it was hot outside this morning. His medical history is significant for rheumatoid arthritis. He takes methotrexate and acetaminophen as needed. The patient’s temperature is 98°F (36.7°C), blood pressure is 168/108 mmHg, and pulse is 75/min. Physical examination is notable for periorbital edema, hepatomegaly, and bilateral 1+ pitting lower extremity edema. Labs and a urinalysis are obtained, as shown below:
Leukocyte count: 11,000/mm^3
Hemoglobin: 14 g/dL
Serum:
Na: 138 mEq/L
K+: 4.3 mEq/L
Cl-: 104 mEq/L
HCO3-: 25 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen: 26 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1.4 mg/dL
Glucose: 85 mg/dL
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST, GOT): 15 U/L
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT, GPT): 19 U/L
Albumin: 2.0 g/dL
Urine:
Protein: 150 mg/dL
Creatinine: 35 mg/dL
An abdominal ultrasound reveals an enlarged liver with heterogeneous echogenicity and enlarged kidneys with increased echogenicity in the renal parenchyma. A biopsy of the kidney is obtained. Which of the following biopsy findings is associated with the patient’s most likely diagnosis?
- A. Apple green birefringence with Congo red staining (Correct Answer)
- B. Subepithelial dense deposits
- C. Tubulointerstitial fibrosis
- D. Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules
- E. Glomerular basement membrane splitting
Amyloidosis types Explanation: ***Apple green birefringence with Congo red staining***
- The patient's presentation with **periorbital and pitting edema**, **hepatomegaly**, **renal dysfunction** (elevated creatinine, proteinuria), and **low serum albumin** in the setting of chronic **rheumatoid arthritis** suggests **AA amyloidosis**.
- **Congo red staining** followed by examination under polarized light revealing **apple green birefringence** is the classic diagnostic finding for amyloidosis on tissue biopsy.
*Subepithelial dense deposits*
- **Subepithelial dense deposits** are characteristic of **post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis** (PSGN) or other forms of immune-complex glomerulonephritis.
- PSGN typically presents with a recent history of infection and often hematuria, which is not described in this patient.
*Tubulointerstitial fibrosis*
- **Tubulointerstitial fibrosis** is a non-specific finding that can occur in various chronic kidney diseases, including those caused by long-term use of certain medications like **methotrexate** or chronic hypertension.
- While it might be present, it does not explain the widespread systemic findings or the specific cause of the present nephropathy in this case.
*Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules*
- **Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules** are pathognomonic for **diabetic nephropathy**, characterized by specific nodular glomerulosclerosis.
- The patient's glucose levels are normal, and there is no mention of diabetes mellitus in his history.
*Glomerular basement membrane splitting*
- **Glomerular basement membrane splitting** is a key feature of **Alport syndrome** and some forms of **membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis**.
- Alport syndrome is a genetic disorder typically presenting earlier in life with hematuria, hearing loss, and ocular abnormalities, none of which are detailed here.
Amyloidosis types US Medical PG Question 5: A 42-year-old man with systolic heart failure secondary to amyloidosis undergoes heart transplantation. The donor heart is obtained from a 17-year-old boy who died in a motor vehicle collision. Examination of the donor heart during the procedure shows a flat, yellow-white discoloration with an irregular border on the luminal surface of the aorta. A biopsy of this lesion is most likely to show which of the following?
- A. Apoptotic smooth muscle cells
- B. Necrotic cell debris
- C. Proteoglycan accumulation
- D. Collagen deposition
- E. Lipoprotein-laden macrophages (Correct Answer)
Amyloidosis types Explanation: ***Lipoprotein-laden macrophages***
- The description of a flat, yellow-white discolored lesion with an irregular border on the luminal surface of the aorta in a 17-year-old is classic for a **fatty streak**, the earliest lesion of **atherosclerosis**.
- Fatty streaks are histologically characterized by the accumulation of **macrophages that have ingested oxidized lipoproteins**, appearing as foam cells within the intima.
*Apoptotic smooth muscle cells*
- While apoptosis of various cell types, including smooth muscle cells, can occur in advanced atherosclerotic lesions, it is not the primary or defining feature of an early **fatty streak**.
- **Apoptosis** contributes to the necrotic core formation in later stages of plaque development, not the initial yellow-white discoloration of a fatty streak.
*Necrotic cell debris*
- **Necrotic cell debris** is a prominent feature of more advanced, **complicated atherosclerotic plaques**, forming the necrotic core.
- In a **fatty streak**, the cells are primarily viable foam cells, and significant necrosis is not yet present.
*Proteoglycan accumulation*
- **Proteoglycan accumulation** occurs in the arterial intima and is involved in the retention of lipoproteins, contributing to the development of atherosclerosis.
- However, the immediate and most characteristic histological finding of the **yellow-white discoloration** in a fatty streak is the lipid-laden macrophage.
*Collagen deposition*
- **Collagen deposition** is a key feature of the fibrous cap in **advanced atherosclerotic plaques**, laid down by migrating smooth muscle cells.
- It is not the primary histological characteristic of an early, flat, yellow-white **fatty streak**.
Amyloidosis types US Medical PG Question 6: A 55-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-day history of decreased urine output, progressively worsening bilateral pedal edema, and fatigue. He has a 4-month history of persistent lower back pain. He has hypercholesterolemia and stable angina pectoris. Current medications include atorvastatin, aspirin, and ibuprofen. His pulse is 80/min, respirations are 16/min, and blood pressure is 150/100 mm Hg. Examination shows periorbital and pedal edema and pallor. There is tenderness of the lumbar spinal vertebrae. Straight leg raise test is negative. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 8.9 g/dl
Serum
Urea nitrogen 20 mg/dl
Creatinine 2.4 mg/dl
Calcium 11.2 mg/dl
Alkaline phosphatase 140 U/L
X-ray of the spine shows diffuse osteopenia and multiple lytic lesions. Which of the following is most likely to confirm the diagnosis?
- A. Bone marrow biopsy (Correct Answer)
- B. Parathyroid hormone levels
- C. Congo red stain of renal tissue
- D. Peripheral blood smear
- E. Skeletal survey
Amyloidosis types Explanation: ***Bone marrow biopsy***
- This patient presents with signs highly suggestive of **multiple myeloma**, including **anemia**, **renal insufficiency**, **hypercalcemia**, and **lytic bone lesions** and diffuse osteopenia.
- A **bone marrow biopsy** is the most definitive test to confirm multiple myeloma by identifying an increased percentage of **plasma cells** and their clonality.
*Parathyroid hormone levels*
- While **hypercalcemia** is present, increased parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels would indicate **primary hyperparathyroidism**, which typically causes diffuse osteopenia but not multiple lytic lesions in this pattern.
- In multiple myeloma, hypercalcemia results from **bone destruction** by plasma cells, leading to **suppressed PTH levels**.
*Congo red stain of renal tissue*
- A Congo red stain of renal tissue is used to diagnose **amyloidosis**, which can cause renal failure, proteinuria, and sometimes edema.
- Although amyloidosis can be a complication of multiple myeloma, it is not the primary diagnostic test for the underlying myeloma itself, and this patient's presentation with prominent lytic lesions points more directly to myeloma.
*Peripheral blood smear*
- A peripheral blood smear might show **rouleaux formation** (RBCs stacked like coins) and occasionally **plasma cells**, which are suggestive of multiple myeloma.
- However, these findings are not specific or reliably present in all cases, and a bone marrow biopsy is required for definitive diagnosis.
*Skeletal survey*
- A skeletal survey (X-ray series) is crucial for identifying and characterizing the **lytic bone lesions** and diffuse osteopenia, as seen in this patient.
- While it provides strong evidence of bone involvement, it is an imaging study that supports the diagnosis but does not definitively confirm the underlying hematological malignancy like a bone marrow biopsy does.
Amyloidosis types US Medical PG Question 7: A 36-year-old man comes to the physician for a 4-week history of swollen legs. He has difficulty putting on socks because of the swelling. Two years ago, he was diagnosed with sleep apnea. He takes no medications. He emigrated from Guatemala with his family when he was a child. He is 171 cm (5 ft 6 in) tall and weighs 115 kg (253 lb); BMI is 39 kg/m2. His pulse is 91/min and blood pressure is 135/82 mm Hg. Examination shows periorbital and bilateral lower extremity edema.
Serum
Albumin 3.1 g/dL
Total cholesterol 312 mg/dL
Urine
Blood negative
Protein +4
RBC 1-2/hpf
RBC cast negative
Fatty casts numerous
A renal biopsy is obtained. Which of the following is most likely to be seen under light microscopy of the patient's renal biopsy specimen?
- A. Diffuse thickening of glomerular capillaries
- B. Amyloid deposition in the mesangium
- C. Eosinophilic nodules within the glomeruli
- D. Fibrin crescents within the glomerular space
- E. Segmental sclerosis of the glomeruli (Correct Answer)
Amyloidosis types Explanation: ***Segmental sclerosis of the glomeruli***
- The patient presents with **nephrotic syndrome** (edema, proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, hypercholesterolemia) and **obesity** (BMI 39 kg/m2), which are strong risk factors for **focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)**.
- **FSGS** is characterized by **segmental sclerosis** within some glomeruli, often affecting juxtamedullary glomeruli initially.
*Diffuse thickening of glomerular capillaries*
- **Diffuse thickening of glomerular capillaries** (due to subepithelial immune complex deposition causing SPIKES on silver stain) is characteristic of **membranous nephropathy**, which typically presents with nephrotic syndrome but is not directly linked to obesity in the way FSGS is.
- While membranous nephropathy could cause nephrotic syndrome, the association with **morbid obesity** makes FSGS a stronger consideration.
*Amyloid deposition in the mesangium*
- **Amyloid deposition** typically presents with nephrotic syndrome and is associated with chronic inflammatory conditions or plasma cell dyscrasias, not primarily with obesity or the specific presentation described.
- On light microscopy, amyloid appears as **acellular, eosinophilic congophilic deposits** in the mesangium and capillary walls, showing apple-green birefringence under polarized light, which is not suggested by the clinical picture.
*Eosinophilic nodules within the glomeruli*
- **Eosinophilic nodules within the glomeruli** (Kimmelstiel-Wilson lesions) are characteristic of **diabetic nephropathy**, which commonly causes nephrotic syndrome.
- While the patient is obese, there is no information about diabetes or hyperglycemia to suggest diabetic nephropathy as the primary cause.
*Fibrin crescents within the glomerular space*
- **Fibrin crescents within the glomerular space** are indicative of **rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (RPGN)**, which typically presents as nephritic syndrome (hematuria, hypertension, azotemia) rather than pure nephrotic syndrome.
- The patient's urine microscopic findings show only 1-2 RBC/hpf and no RBC casts, making RPGN unlikely.
Amyloidosis types US Medical PG Question 8: A 7-year-old girl is brought to her pediatrician by her mother because of puffiness under both eyes in the morning. The mother reports that the child has just recovered from a seasonal influenza infection a few days ago. Vital signs include: temperature 37°C (98.6°F), blood pressure 100/67 mm Hg, and pulse 95/min. On examination, there is facial edema and bilateral 2+ pitting edema over the legs. Laboratory results are shown:
Serum albumin 2.1 g/dL
Serum triglycerides 200 mg/dL
Serum cholesterol 250 mg/dL
Urine dipstick 4+ protein
Which of the following casts are more likely to be present in this patient’s urine?
- A. Waxy casts
- B. Fatty casts (Correct Answer)
- C. Red cell casts
- D. Granular casts
- E. White cell casts
Amyloidosis types Explanation: ***Fatty casts***
- The patient's presentation with **facial edema**, **pitting edema**, **hypoalbuminemia**, **hyperlipidemia** (increased triglycerides and cholesterol), and **heavy proteinuria** (4+ protein on urine dipstick) is highly suggestive of **nephrotic syndrome**.
- **Fatty casts** are pathognomonic for **nephrotic syndrome** because they are formed from renal tubular epithelial cells that have absorbed filtered lipids (cholesterol, triglycerides) and subsequently desquamated.
*Waxy casts*
- **Waxy casts** are typically associated with **chronic kidney disease** and indicate severe, longstanding tubular atrophy and dilation, often seen in end-stage renal disease.
- While they can be present in nephrotic syndrome if the kidney damage is severe and chronic, they are not the most characteristic cast *specifically* for the acute onset and hyperlipidemia seen here.
*Red cell casts*
- **Red cell casts** are indicative of **glomerulonephritis** (nephritic syndrome), where red blood cells leak through damaged glomerular capillaries into the renal tubules.
- This patient's presentation is characterized by **heavy proteinuria** and **edema** (nephrotic syndrome), without signs such as hematuria or hypertension that would typically suggest a nephritic picture.
*Granular casts*
- **Granular casts** are formed from degenerated cellular casts (e.g., granular breakdown products of renal tubular epithelial cells) or aggregated plasma proteins, and are non-specific indicators of **kidney damage** or **acute tubular necrosis**.
- While they can be seen in various kidney diseases, including nephrotic syndrome, they are not as specific as fatty casts for the constellation of symptoms presented.
*White cell casts*
- **White cell casts** are typically associated with **pyelonephritis** (kidney infection) or **interstitial nephritis**, indicating inflammation within the renal tubules or interstitium.
- There is no clinical or laboratory evidence of infection or inflammation suggesting pyelonephritis in this patient.
Amyloidosis types US Medical PG Question 9: A 52-year-old man presents with 2 months of diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fatigue. He reports a weight loss of 4 kg (8 lb). He also says his joints have been hurting recently, as well. Past medical history is unremarkable. Review of systems is significant for problems with concentration and memory. Physical examination is unremarkable. A GI endoscopy is performed with a biopsy of the small bowel. Which of the following histologic finding would most likely be seen in this patient?
- A. PAS positive macrophages (Correct Answer)
- B. Non-caseating granulomas in the small intestine
- C. Absence of nerves in the myenteric plexus
- D. Blunting of the villi
- E. Crypt hyperplasia with increased intraepithelial lymphocytes
Amyloidosis types Explanation: **PAS positive macrophages**
- The clinical presentation with **diarrhea**, abdominal pain, weight loss, joint pain, and **neurological symptoms** (problems with concentration and memory) is classic for **Whipple's disease**.
- **Whipple's disease** is caused by the bacterium **Tropheryma whipplei**, which is characterized histologically by **foamy macrophages** in the lamina propria that stain **positive with Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS)** due to undigested bacterial cell wall material.
*Non-caseating granulomas in the small intestine*
- **Non-caseating granulomas** are characteristic of **Crohn's disease**, which typically presents with abdominal pain, diarrhea, and weight loss, but **neurological symptoms** are not a primary feature.
- While Crohn's disease can cause joint pain (arthritis), the combination of GI and neurological symptoms points away from it.
*Absence of nerves in the myenteric plexus*
- An **absence of nerves in the myenteric plexus** is the hallmark of **Hirschsprung's disease**, which is a congenital disorder primarily affecting neonates and infants, causing intestinal obstruction and chronic constipation.
- This finding is inconsistent with the patient's age and presenting symptoms of diarrhea and neurological issues.
*Blunting of the villi*
- **Villi blunting** is characteristic of **celiac disease** (gluten-sensitive enteropathy), which presents with malabsorption symptoms like diarrhea, weight loss, and abdominal pain.
- However, **celiac disease** typically does not involve **neurological symptoms** like concentration and memory problems as a prominent feature, and the PAS-positive macrophages are specific to Whipple's.
*Crypt hyperplasia with increased intraepithelial lymphocytes*
- **Crypt hyperplasia** and **increased intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs)** are seen in various small bowel pathologies, including **celiac disease** and **microscopic colitis**.
- While these findings suggest intestinal inflammation, they are not specific to **Whipple's disease** and do not account for the characteristic neurological involvement.
Amyloidosis types US Medical PG Question 10: A 60-year-old woman comes to the physician because of lower back pain, generalized weakness, and weight loss that has occurred over the past 6 weeks. She also says that her urine has appeared foamy recently. Physical examination shows focal midline tenderness of the lumbar spine and conjunctival pallor. Her temperature is 100.5°F (38°C). A photomicrograph of a bone marrow biopsy specimen is shown. Further evaluation of this patient is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Myeloblasts with needle-shaped cytoplasmic inclusions
- B. Erythrocytes with cytoplasmic hemoglobin inclusions
- C. Neutrophils with hypersegmented nuclear lobes
- D. Grouped erythrocytes with stacked-coin appearance (Correct Answer)
- E. B-lymphocytes with radial cytoplasmic projections
Amyloidosis types Explanation: ***Grouped erythrocytes with stacked-coin appearance***
- The patient's presentation of **lower back pain** (lytic bone lesions), **foamy urine** (proteinuria from Bence Jones proteins), **weight loss**, and **fever** strongly suggests **multiple myeloma**.
- Bone marrow biopsy would show **increased plasma cells**, and further evaluation with **peripheral blood smear** would reveal **rouleaux formation** (stacked-coin appearance of RBCs).
- Rouleaux formation occurs due to **increased serum proteins** (M-protein/paraprotein) that decrease the negative charge between erythrocytes, causing them to stack.
- This finding, combined with **anemia** (conjunctival pallor) and **hypercalcemia** symptoms, is characteristic of multiple myeloma.
*Myeloblasts with needle-shaped cytoplasmic inclusions*
- This describes **Auer rods**, which are pathognomonic for **acute myeloid leukemia (AML)**.
- AML typically presents with **bleeding**, **infections**, and **pancytopenia**, rather than bone pain and foamy urine.
- The patient's clinical picture points to a **plasma cell dyscrasia**, not myeloid leukemia.
*Erythrocytes with cytoplasmic hemoglobin inclusions*
- This finding (Howell-Jolly bodies, Heinz bodies, or other inclusions) suggests **hemolytic anemia**, **thalassemia**, or **asplenia**.
- These conditions do not explain the **bone pain**, **proteinuria**, or **plasma cell proliferation** seen in this case.
- The patient's symptoms are better explained by **multiple myeloma**, not hemoglobinopathy.
*Neutrophils with hypersegmented nuclear lobes*
- Hypersegmented neutrophils (≥5 lobes) are characteristic of **megaloblastic anemia** due to **vitamin B12** or **folate deficiency**.
- While this could cause weakness and anemia, it does not explain the **bone pain**, **fever**, **foamy urine**, or **lumbar spine tenderness**.
- The complete clinical picture is consistent with **multiple myeloma**, not nutritional deficiency.
*B-lymphocytes with radial cytoplasmic projections*
- This describes **hairy cell leukemia**, a rare B-cell neoplasm with characteristic "hairy" projections.
- Hairy cell leukemia presents with **splenomegaly** and **pancytopenia**, not the bone lesions and proteinuria seen here.
- The patient's presentation aligns with **plasma cell myeloma**, not B-cell lymphoproliferative disorder.
More Amyloidosis types US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.