AIDS pathology US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for AIDS pathology. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
AIDS pathology US Medical PG Question 1: A 26-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. He was diagnosed with HIV infection 2 weeks ago. His CD4+ T-lymphocyte count is 162/mm3 (N ≥ 500). An interferon-gamma release assay is negative. Prophylactic treatment against which of the following pathogens is most appropriate at this time?
- A. Cytomegalovirus
- B. Toxoplasma gondii
- C. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- D. Aspergillus fumigatus
- E. Pneumocystis jirovecii (Correct Answer)
AIDS pathology Explanation: ***Pneumocystis jirovecii***
- This patient's **CD4+ T-lymphocyte count of 162/mm3** is below the threshold of 200/mm3, indicating a significant risk for **Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP)**, an opportunistic infection in HIV.
- Prophylaxis with **trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX)** is highly effective and recommended for HIV patients with CD4 counts less than 200/mm3.
*Cytomegalovirus*
- **CMV prophylaxis** is generally not recommended for all HIV patients, even with low CD4 counts, unless there is evidence of active disease or extremely low CD4 counts (e.g., <50/mm3) with high viral loads.
- While CMV can cause end-organ disease in advanced HIV, routine primary prophylaxis is not standard for this CD4 level.
*Toxoplasma gondii*
- **Toxoplasma prophylaxis** is indicated for HIV patients with **CD4 counts less than 100/mm3** who are also seropositive for *Toxoplasma gondii*.
- The patient's CD4 count is 162/mm3, and there's no mention of *Toxoplasma* serostatus, making it less appropriate than PCP prophylaxis.
*Mycobacterium tuberculosis*
- The patient's **interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA) is negative**, which suggests no **latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI)**, thus making primary prophylaxis unnecessary at this time.
- While HIV patients are at high risk for TB, prophylaxis is typically given for LTBI or as secondary prophylaxis for those who have completed treatment for active TB.
*Aspergillus fumigatus*
- **Aspergillus infections** are typically seen in patients with severe **neutropenia** or those receiving high-dose corticosteroids, not primarily in HIV patients based solely on CD4 count.
- Routine prophylaxis for Aspergillus is not recommended for HIV patients, even with low CD4 counts, unless there is a specific risk factor.
AIDS pathology US Medical PG Question 2: A 32-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination 1 week after being admitted to the hospital for oral candidiasis and esophagitis. His CD4+ T lymphocyte count is 180 cells/μL. An HIV antibody test is positive. Genotypic resistance assay shows the virus to be susceptible to all antiretroviral therapy regimens and therapy with dolutegravir, tenofovir, and emtricitabine is initiated. Which of the following sets of laboratory findings would be most likely on follow-up evaluation 3 months later?
$$$ CD4 +/CD8 ratio %%% HIV RNA %%% HIV antibody test $$$
- A. ↓ ↓ negative
- B. ↑ ↑ negative
- C. ↓ ↑ negative
- D. ↑ ↓ positive (Correct Answer)
- E. ↓ ↑ positive
AIDS pathology Explanation: ***↑ ↓ positive***
- With effective **antiretroviral therapy (ART)**, the **CD4+/CD8 ratio** would increase as **CD4+ T cell counts rise** and **CD8+ T cell counts decrease**.
- **HIV RNA (viral load)** would significantly decrease (ideally to undetectable levels) due to the suppression of viral replication, but HIV antibodies would remain positive indefinitely.
*↓ ↓ negative*
- A decrease in the **CD4+/CD8 ratio** and **HIV RNA** (viral load) along with a negative **HIV antibody test** is inconsistent with successful ART.
- A negative HIV antibody test would mean the patient was never infected, which contradicts the initial positive result and symptoms.
*↑ ↑ negative*
- An increase in the **CD4+/CD8 ratio** is expected with ART, but an increase in **HIV RNA** (viral load) indicates treatment failure.
- A negative **HIV antibody test** is impossible after a confirmed positive result, regardless of treatment success.
*↓ ↑ negative*
- A decrease in the **CD4+/CD8 ratio** would suggest worsening immune function, while an increase in **HIV RNA** indicates treatment failure.
- A negative **HIV antibody test** is not possible once a patient has developed antibodies to HIV.
*↓ ↑ positive*
- A decrease in the **CD4+/CD8 ratio** would indicate immune decline, contrary to the expected improvement with effective ART.
- An increase in **HIV RNA (viral load)** would signify treatment failure, even if HIV antibodies remain positive.
AIDS pathology US Medical PG Question 3: A 52-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of headaches, vertigo, and changes to his personality for the past few weeks. He was diagnosed with HIV 14 years ago and was started on antiretroviral therapy at that time. Medical records from one month ago indicate that he followed his medication schedule inconsistently. Since then, he has been regularly taking his antiretroviral medications and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. His vital signs are within normal limits. Neurological examination shows ataxia and apathy. Mini-Mental State Examination score is 15/30. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 12.5 g/dL
Leukocyte count 8400/mm3
Segmented neutrophils 80%
Eosinophils 1%
Lymphocytes 17%
Monocytes 2%
CD4+ T-lymphocytes 90/μL
Platelet count 328,000/mm3
An MRI of the brain with contrast shows a solitary ring-enhancing lesion involving the corpus callosum and measuring 4.5 cm in diameter. A lumbar puncture with subsequent cerebrospinal fluid analysis shows slight pleocytosis, and PCR is positive for Epstein-Barr virus DNA. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. CNS lymphoma (Correct Answer)
- B. AIDS dementia
- C. Glioblastoma
- D. Bacterial brain abscess
- E. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
AIDS pathology Explanation: ***CNS lymphoma***
- The patient's **immunosuppressed state (CD4 count 90/µL)** and the **solitary ring-enhancing lesion in the corpus callosum** are highly suggestive of CNS lymphoma.
- The **positive Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA in CSF** is a strong indicator, as primary CNS lymphoma in HIV-positive patients is often associated with EBV infection.
*AIDS dementia*
- Characterized by **widespread cortical atrophy** and demyelination rather than a solitary, well-defined mass.
- While associated with cognitive decline, it doesn't typically present with a **mass lesion** or **EBV DNA in CSF**.
*Glioblastoma*
- More commonly presents as an **irregularly enhancing mass** in immunocompetent individuals and is less common in HIV patients with low CD4 counts.
- **EBV DNA in CSF** is not a feature of glioblastoma.
*Bacterial brain abscess*
- Usually presents with **fever, seizures, and focal neurological deficits**, and often multiple lesions.
- There is no mention of fever or a clear source of bacterial infection, and **EBV DNA in CSF** is not typical.
*Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy*
- Typically presents with **non-enhancing white matter lesions** without mass effect.
- Caused by the **JC virus (JCV)**, not EBV, and does not show ring enhancement.
AIDS pathology US Medical PG Question 4: A physician scientist is looking for a more efficient way to treat HIV. Patients infected with HIV mount a humoral immune response by producing antibodies against the HIV envelope proteins. These antibodies are the same antibodies detected by the ELISA and western blot assays used to diagnose the disease. The physician scientist is trying to generate a new, more potent antibody against the same HIV envelope proteins targeted by the natural humoral immune response. Of the following proteins, which is the most likely target of the antibody he is designing?
- A. p24
- B. CXCR4
- C. CCR5
- D. p17
- E. gp120 (Correct Answer)
AIDS pathology Explanation: ***gp120***
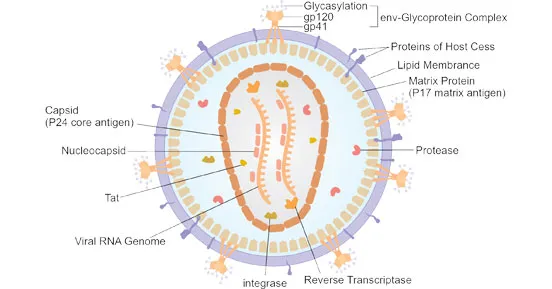
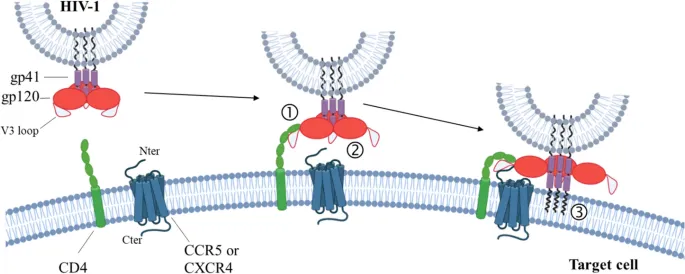
- **gp120** is an **envelope glycoprotein** on the surface of HIV, responsible for binding to CD4 receptors on host cells.
- Antibodies against **gp120** are generated during natural infection and are detected by diagnostic assays, making it a primary target for therapeutic antibody development.
*p24*
- **p24** is a **capsid protein** of HIV, forming the conical core of the virus, but it is not an envelope protein.
- While antibodies against **p24** are produced during infection and are detectable, it's an internal protein, not exposed on the viral surface for direct neutralization.
*CXCR4*
- **CXCR4** is a **chemokine co-receptor** found on the surface of host cells (e.g., T-lymphocytes), used by some HIV strains (T-tropic) for entry.
- It is a host cell protein, not an HIV viral protein, so it would not be a target for antibodies aiming to directly neutralize the virus.
*CCR5*
- **CCR5** is another **chemokine co-receptor** on host cells (e.g., macrophages, T-lymphocytes) used by other HIV strains (M-tropic) for viral entry.
- Similar to CXCR4, it is a host cell protein, not an HIV envelope protein, and therefore not a direct target for neutralizing antibodies against the virus itself.
*p17*
- **p17** is an HIV **matrix protein** located just beneath the viral envelope, playing a role in viral assembly and budding.
- Similar to p24, it is an internal structural protein, not an external envelope protein, making it less accessible for neutralizing antibodies.
AIDS pathology US Medical PG Question 5: A 41-year-old woman comes to the primary care physician’s office with a 7-day history of headaches, sore throat, diarrhea, fatigue, and low-grade fevers. The patient denies any significant past medical history, recent travel, or recent sick contacts. On review of systems, the patient endorses performing sex acts in exchange for money and recreational drugs over the last several months. You suspect primary HIV infection, but the patient refuses further evaluation. At a follow-up appointment 1 week later, she reports that she had been previously tested for HIV, and it was negative. Physical examination does not reveal any external abnormalities of her genitalia. Her heart and lung sounds are normal on auscultation. Her vital signs show a blood pressure of 123/82 mm Hg, heart rate of 82/min, and a respiratory rate of 16/min. Of the following options, which is the next best step in patient management?
- A. Retest with HIV antigen/antibody test in 1 year
- B. Perform VDRL
- C. Repeat rapid HIV at this office check-up
- D. Perform monospot test
- E. Retest with 4th generation HIV antigen/antibody test in 2-4 weeks and again in 3 months (Correct Answer)
AIDS pathology Explanation: ***Retest with 4th generation HIV antigen/antibody test in 2-4 weeks and again in 3 months***
- This patient presents with symptoms highly suggestive of **acute retroviral syndrome** (primary HIV infection), including headaches, sore throat, diarrhea, fatigue, and low-grade fevers in the context of high-risk behavior (sex work and recreational drug use).
- A previous negative HIV test was likely obtained during the **window period**, when the infection was too recent to be detected. The **4th generation antigen/antibody immunoassay** detects both HIV antibodies and p24 antigen, reducing the window period to approximately **2-4 weeks** post-exposure.
- **Follow-up testing at 3 months** is recommended to definitively rule out HIV, as rare cases may have delayed seroconversion.
- Current **CDC guidelines** recommend 4th generation testing as the initial screening test for HIV.
*Retest with HIV antigen/antibody test in 1 year*
- Waiting a full year to retest would result in significant delay in diagnosis and treatment, potentially allowing disease progression to AIDS and increasing transmission risk.
- The patient's acute symptoms warrant more immediate re-evaluation within weeks, not months.
*Perform VDRL*
- **VDRL** (Venereal Disease Research Laboratory) tests for syphilis, not HIV.
- While co-infection with syphilis is possible in high-risk patients, it does not explain the constellation of symptoms typical of **acute retroviral syndrome**.
- Syphilis testing may be appropriate as part of comprehensive STI screening but is not the priority given the clinical presentation.
*Repeat rapid HIV at this office check-up*
- While **4th generation rapid tests** have improved sensitivity, repeating the test only **1 week** after the previous negative result and during the likely window period may still yield a false negative.
- The patient needs time for antibodies and/or antigen to develop to detectable levels (typically 2-4 weeks from exposure).
*Perform monospot test*
- A **monospot test** diagnoses **infectious mononucleosis** caused by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).
- While EBV can cause fatigue, sore throat, and low-grade fevers, the patient's high-risk sexual behavior, diarrhea, and acute presentation are more consistent with **acute HIV infection** than mononucleosis.
- EBV mononucleosis typically presents with prominent lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly, which are not mentioned here.
AIDS pathology US Medical PG Question 6: A 44-year-old man with HIV comes to the physician for a routine follow-up examination. He has been noncompliant with his antiretroviral medication regimen for several years. He appears chronically ill and fatigued. CD4+ T-lymphocyte count is 180/mm³ (N ≥ 500). Further evaluation of this patient is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Multifocal demyelination on brain MRI
- B. Violaceous lesions on skin exam (Correct Answer)
- C. Ring-enhancing lesions on brain MRI
- D. Cotton-wool spots on fundoscopy
- E. Ground-glass opacities on chest CT
AIDS pathology Explanation: ***Violaceous lesions on skin exam***
- A CD4 count of 180/mm³ indicates severe **immunosuppression**, making the patient highly susceptible to **opportunistic infections** and cancers, such as Kaposi sarcoma.
- **Kaposi sarcoma** typically presents with violaceous (purple-blue) cutaneous lesions, which are often the initial manifestation of the disease in HIV-positive patients.
*Multifocal demyelination on brain MRI*
- This finding is characteristic of **progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)**, caused by the **JC virus**.
- PML typically occurs at **CD4 counts below 100/mm³**, lower than the patient's current count, although still possible with severe immunosuppression.
*Ring-enhancing lesions on brain MRI*
- **Ring-enhancing lesions** on brain MRI are often seen in cerebral **toxoplasmosis** or CNS **lymphoma** in HIV patients.
- Toxoplasmosis usually presents with focal neurological deficits and seizures, and is more common with CD4 counts below 100/mm³.
*Cotton-wool spots on fundoscopy*
- **Cotton-wool spots** are a common finding in **HIV retinopathy** due to retinal ischemia.
- While possible, they are non-specific and are usually asymptomatic, whereas the patient's presentation suggests a more prominent and diagnosable condition.
*Ground-glass opacities on chest CT*
- **Ground-glass opacities** on chest CT are characteristic of **Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP)**, a common opportunistic infection in HIV patients.
- While PJP is a strong possibility with a CD4 count <200/mm³, the question asks for a finding that is *most likely* given the patient's general appearance and the option of Kaposi sarcoma, which manifests directly on examination.
AIDS pathology US Medical PG Question 7: A 28-year-old G1P0 woman at 16 weeks estimated gestational age presents for prenatal care. Routine prenatal screening tests are performed and reveal a positive HIV antibody test. The patient is extremely concerned about the possible transmission of HIV to her baby and wants to have the baby tested as soon as possible after delivery. Which of the following would be the most appropriate diagnostic test to address this patient’s concern?
- A. CD4+ T cell count
- B. Viral culture
- C. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for HIV RNA (Correct Answer)
- D. Antigen assay for p24
- E. EIA for HIV antibody
AIDS pathology Explanation: ***Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for HIV RNA***
- **PCR for HIV RNA** directly detects the viral genetic material, providing a definitive diagnosis of HIV infection in an infant.
- Unlike antibody tests, PCR can distinguish between passively acquired maternal antibodies and actual infant infection, making it suitable for newborns.
*CD4+ T cell count*
- **CD4+ T cell count** is used to monitor the progression of HIV infection and immunosuppression, not for initial diagnosis, especially in neonates.
- While it's an important marker for HIV disease, it does not confirm the presence of the virus itself in a newborn.
*Viral culture*
- **Viral culture** is a highly specific method for detecting HIV, but it is expensive, time-consuming, and technically demanding.
- It is not routinely used for rapid early diagnosis in neonates due to its practical limitations and the availability of faster, reliable alternatives like PCR.
*Antigen assay for p24*
- The **p24 antigen test** can detect early HIV infection in adults, but its sensitivity is lower in neonates compared to PCR, especially immediately after birth.
- It may not reliably detect infection in newborns due to low viral loads or the presence of maternal antibodies that complex the antigen.
*EIA for HIV antibody*
- An **EIA for HIV antibody** will detect maternal antibodies that have crossed the placenta, meaning it will be positive in nearly all infants born to HIV-positive mothers, regardless of the infant's infection status.
- This test cannot distinguish between passive maternal antibody transfer and true infant infection.
AIDS pathology US Medical PG Question 8: An investigator is studying the mechanism of HIV infection in cells obtained from a human donor. The effect of a drug that impairs viral fusion and entry is being evaluated. This drug acts on a protein that is cleaved off of a larger glycosylated protein in the endoplasmic reticulum of the host cell. The protein that is affected by the drug is most likely encoded by which of the following genes?
- A. gag
- B. env (Correct Answer)
- C. tat
- D. pol
- E. rev
AIDS pathology Explanation: ***env***
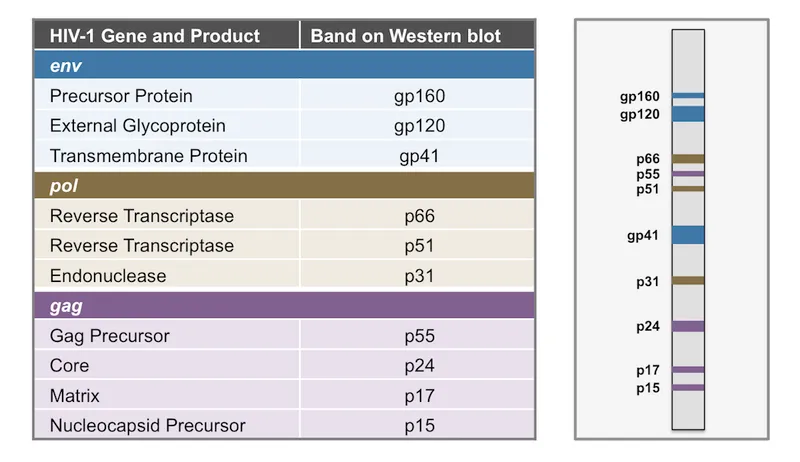
- The **env (envelope) gene** of HIV encodes for the precursor protein **gp160**, which is then cleaved by host cellular proteases into **gp120** and **gp41** within the endoplasmic reticulum.
- **gp120** and **gp41** together form the viral envelope glycoproteins responsible for viral binding to host cells and **fusion/entry**, making them the target of drugs that impair these processes.
*gag*
- The **gag (group-specific antigen) gene** encodes for structural proteins of the viral core, such as **p24 (capsid protein)**, p17 (matrix protein), and p7 (nucleocapsid protein).
- These proteins are primarily involved in the assembly of new virions and do not directly mediate viral fusion and entry.
*tat*
- The **tat (trans-activator of transcription) gene** encodes a regulatory protein that significantly enhances the transcription of viral genes.
- It plays a crucial role in the viral life cycle by increasing the efficiency of HIV gene expression, but it is not directly involved in viral fusion or entry.
*pol*
- The **pol (polymerase) gene** encodes for essential viral enzymes, including **reverse transcriptase**, integrase, and protease.
- These enzymes are critical for converting viral RNA into DNA, integrating viral DNA into the host genome, and cleaving viral polyproteins, respectively, but they are not involved in mediating viral entry.
*rev*
- The **rev (regulator of virion expression) gene** encodes a regulatory protein that facilitates the transport of unspliced and partially spliced viral RNAs from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
- This transport is crucial for the synthesis of structural and enzymatic proteins and for packaging viral RNA into new virions, but it does not directly participate in viral fusion and entry.
AIDS pathology US Medical PG Question 9: A 37-year-old woman presents to the occupational health clinic for a new employee health screening. She has limited medical records prior to her immigration to the United States several years ago. She denies any current illness or significant medical history. Purified protein derivative (PPD) is injected on the inside of her left forearm for tuberculosis (TB) screening. Approximately 36 hours later, the patient comes back to the occupational health clinic and has an indurated lesion with bordering erythema measuring 15 mm in diameter at the site of PPD injection. Of the following options, which is the mechanism of her reaction?
- A. Type III and IV–mixed immune complex and cell-mediated hypersensitivity reactions
- B. Type III–immune complex-mediated hypersensitivity reaction
- C. Type I–anaphylactic hypersensitivity reaction
- D. Type II–cytotoxic hypersensitivity reaction
- E. Type IV–cell-mediated (delayed) hypersensitivity reaction (Correct Answer)
AIDS pathology Explanation: ***Type IV–cell-mediated (delayed) hypersensitivity reaction***
- The **PPD test** for tuberculosis is a classic example of a **Type IV hypersensitivity reaction**, also known as **delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH)**. This reaction is orchestrated by **T lymphocytes** (specifically CD4+ T cells) that recognize antigens presented by antigen-presenting cells
- The **induration** at 36 hours is a hallmark of this type of reaction, as it typically peaks between **24 to 72 hours** after antigen exposure, reflecting the time required for T cells to migrate to the site and initiate an inflammatory response. The immune response involves the release of **cytokines** leading to macrophage accumulation and localized tissue damage.
*Type III and IV–mixed immune complex and cell-mediated hypersensitivity reactions*
- While immune complexes (Type III) and cell-mediated reactions (Type IV) can both lead to tissue damage, a PPD test is primarily a **cell-mediated response** and is not characterized by significant immune complex deposition.
- Mixed reactions are less common and usually involve a sustained presence of antigen leading to both types of responses, which is not the typical mechanism for an acute PPD skin test.
*Type III–immune complex-mediated hypersensitivity reaction*
- **Type III hypersensitivity** is characterized by the formation of **antigen-antibody immune complexes** that deposit in tissues, leading to inflammation and tissue damage, often seen in conditions like serum sickness or lupus nephritis.
- The PPD reaction is based on T-cell recognition of mycobacterial antigens, not the deposition of soluble antigen-antibody complexes.
*Type I–anaphylactic hypersensitivity reaction*
- **Type I hypersensitivity** is an **immediate allergic reaction** mediated by **IgE antibodies** binding to mast cells and basophils, leading to histamine release upon re-exposure to an allergen.
- This type of reaction typically occurs within minutes of exposure, not 36 hours later, and presents with symptoms like hives, angioedema, or anaphylaxis.
*Type II–cytotoxic hypersensitivity reaction*
- **Type II hypersensitivity** involves **antibodies (IgG or IgM)** binding to antigens on the surface of **host cells**, leading to cell lysis or dysfunction, often seen in transfusion reactions or autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
- The PPD test does not involve direct antibody-mediated destruction of host cells.
AIDS pathology US Medical PG Question 10: A 15-year-old girl comes to the physician because of a sore throat and subjective fevers for the past 2 weeks. She has been feeling lethargic and is unable to attend school. She has a history of multiple episodes of streptococcal pharyngitis treated with amoxicillin. She immigrated with her family to the United States from China 10 years ago. She appears thin. Her temperature is 37.8°C (100°F), pulse is 97/min, and blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg. Examination shows pharyngeal erythema and enlarged tonsils with exudates and palatal petechiae. There is cervical lymphadenopathy. The spleen is palpated 2 cm below the left costal margin. Her hemoglobin concentration is 12 g/dL, leukocyte count is 14,100/mm3 with 54% lymphocytes (12% atypical lymphocytes), and platelet count is 280,000/mm3. A heterophile agglutination test is positive. The underlying cause of this patient's symptoms is most likely to increase the risk of which of the following conditions?
- A. Kaposi sarcoma
- B. Glomerulonephritis
- C. Pneumonia
- D. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (Correct Answer)
- E. Necrotizing retinitis
AIDS pathology Explanation: ***Nasopharyngeal carcinoma***
- The patient's symptoms (sore throat, fatigue, pharyngeal erythema, enlarged tonsils with exudates, palatal petechiae, cervical lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, atypical lymphocytosis, and positive heterophile agglutination test) are classic for **infectious mononucleosis**, caused by the **Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)**.
- EBV infection is a significant risk factor for developing **nasopharyngeal carcinoma**, especially in individuals of Chinese descent, making this the most likely long-term complication.
*Kaposi sarcoma*
- **Kaposi sarcoma** is associated with **human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8)**, not EBV.
- It is typically seen in immunocompromised individuals, such as those with HIV/AIDS, or in specific endemic regions.
*Glomerulonephritis*
- **Glomerulonephritis** can be a complication of **Streptococcus pyogenes infections** (post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis) or other autoimmune diseases, but it is not directly linked to EBV infection.
- The patient's history of streptococcal pharyngitis is relevant for this, but her current presentation points to EBV.
*Pneumonia*
- While pneumonia can occur as a secondary complication in severely ill patients with infectious mononucleosis, it is not a direct long-term increased risk associated with the underlying EBV infection itself.
- EBV primarily affects lymphoid tissues.
*Necrotizing retinitis*
- **Necrotizing retinitis** is most commonly associated with **cytomegalovirus (CMV)** infection, particularly in immunocompromised patients (e.g., HIV/AIDS).
- It is not a typical complication or long-term risk of EBV infection.
More AIDS pathology US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.