Immunopathology

On this page
🛡️ Immunopathology: The Body's Defense Network Under Siege
Your immune system orchestrates an elegant defense network, but when this precision machinery misfires-attacking self, overreacting to harmless triggers, or failing to respond-disease emerges. You'll explore how immune architecture establishes normal function, dissect the mechanisms behind hypersensitivity, autoimmunity, and immunodeficiency, then master the clinical patterns, diagnostic strategies, and targeted therapies that transform immunopathology from abstract concept into actionable clinical insight across every organ system.
🛡️ Immunopathology: The Body's Defense Network Under Siege
🏗️ The Immune Architecture: Foundation Blueprints
Cellular Defense Architecture
-
Innate Immunity Components
- Neutrophils: 60-70% of circulating leukocytes, lifespan 6-8 hours
- Macrophages: Tissue residence weeks to months, phagocytic capacity 100+ pathogens
- Natural killer cells: 5-15% of lymphocytes, cytotoxic within 4-6 hours
- Perforin release: <30 minutes after target recognition
- Granzyme activation: Apoptosis induction in 2-4 hours
-
Adaptive Immunity Framework
- B lymphocytes: 10-15% of circulating lymphocytes, antibody production 10^3-10^4 molecules/second
- T helper cells (CD4+): 60-70% of T cells, activation threshold 100-1000 peptide-MHC complexes
- Cytotoxic T cells (CD8+): 20-30% of T cells, target killing within 2-6 hours
- Memory formation: 10-15% of activated cells become memory cells
- Secondary response: 100-1000x faster than primary response
📌 Remember: MAIN - Macrophages Activate, Innate responds, Neutrophils arrive first (<4 hours), followed by adaptive immunity (3-5 days)
| Cell Type | Percentage | Lifespan | Primary Function | Activation Time | Key Markers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neutrophils | 60-70% | 6-8 hours | Phagocytosis | <30 minutes | CD16+, CD66b+ |
| Lymphocytes | 20-30% | Days-years | Adaptive immunity | 3-5 days | CD3+, CD19+ |
| Monocytes | 3-8% | 1-3 days | Antigen presentation | 2-4 hours | CD14+, CD68+ |
| Eosinophils | 1-4% | 8-12 days | Parasitic/allergic | 4-6 hours | CD125+, CCR3+ |
| Basophils | <1% | 60-70 hours | Immediate hypersensitivity | <15 minutes | CD123+, FcεRI+ |
Molecular Recognition Systems
The immune system employs sophisticated pattern recognition through Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. TLR activation occurs within minutes of pathogen encounter, while MHC-peptide presentation requires 2-6 hours for optimal T cell recognition.
-
Pattern Recognition Receptors
- TLR4: Recognizes lipopolysaccharide, activation within 5-15 minutes
- TLR2: Peptidoglycan recognition, inflammatory response in 30-60 minutes
- TLR9: CpG DNA detection, interferon production within 2-4 hours
-
MHC Class I Pathway
- Present on all nucleated cells (>99% of body cells)
- Peptide loading: 8-10 amino acids, processing time 30-90 minutes
- CD8+ T cell recognition threshold: 1-10 peptide-MHC complexes per cell
-
MHC Class II Pathway
- Restricted to antigen-presenting cells (<5% of total cells)
- Peptide length: 12-25 amino acids, processing time 2-6 hours
- CD4+ T cell activation: 100-1000 peptide-MHC complexes required
💡 Master This: MHC Class I presents intracellular peptides to CD8+ cells (think "1 goes with 8"), while MHC Class II presents extracellular peptides to CD4+ cells (think "2 goes with 4")

📌 Remember: CLIP for MHC Class II - Class II-associated Invariant chain Peptide blocks peptide binding until HLA-DM removes it, allowing foreign peptide loading in 2-4 hours
Understanding this immune architecture reveals why immunopathological conditions follow predictable patterns. Connect these foundational principles through cellular dysfunction mechanisms to understand how immune system failures manifest as clinical disease.
🏗️ The Immune Architecture: Foundation Blueprints
⚙️ Immune Dysfunction Mechanisms: When Defense Systems Fail
Primary Immunodeficiency Mechanisms
Primary immunodeficiencies result from genetic defects affecting specific immune components. These disorders demonstrate Mendelian inheritance patterns and typically manifest within the first 2 years of life with recurrent infections.
-
B Cell Defects
- X-linked agammaglobulinemia: BTK gene mutation, <2% normal B cells
- Common variable immunodeficiency: IgG <400 mg/dL, IgA <10 mg/dL
- Selective IgA deficiency: 1:500-1:700 prevalence, IgA <7 mg/dL
- Associated conditions: 20-30% develop autoimmune disease
- Infection pattern: Sinopulmonary infections predominate
-
T Cell Defects
- DiGeorge syndrome: 22q11.2 deletion, <500 CD3+ cells/μL
- Severe combined immunodeficiency: <300 CD3+ cells/μL, <20% normal proliferation
- Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis: IL-17 pathway defects, persistent fungal infections
- Survival without treatment: <2 years for severe forms
- Bone marrow transplant success: >90% if performed <3.5 months
📌 Remember: SCID - Severe Combined Immunodeficiency affects both B and T cells, requires immediate isolation and bone marrow transplant within 3.5 months for >90% survival
| Deficiency Type | Gene/Pathway | Cell Count | Infection Pattern | Prognosis | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X-linked agammaglobulinemia | BTK | <2% B cells | Bacterial (encapsulated) | Good with IVIG | Lifelong IVIG |
| SCID | Multiple | <300 CD3+/μL | Opportunistic | Fatal <2 years | BMT <3.5 months |
| DiGeorge | 22q11.2 deletion | <500 CD3+/μL | Viral/fungal | Variable | Thymus transplant |
| CVID | Unknown | Normal counts | Sinopulmonary | Chronic complications | IVIG + monitoring |
| CGD | NADPH oxidase | Normal counts | Catalase+ bacteria | Reduced lifespan | Prophylactic antibiotics |
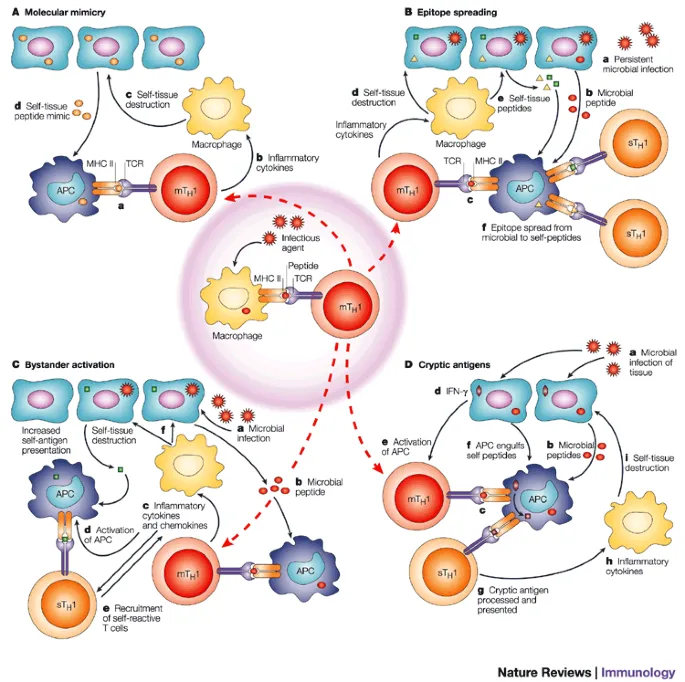
Autoimmunity develops when self-tolerance mechanisms fail, leading to immune attacks against normal tissues. This process involves molecular mimicry, epitope spreading, and regulatory T cell dysfunction with genetic susceptibility and environmental triggers.
-
Central Tolerance Breakdown
- Thymic selection defects: <95% of autoreactive T cells normally deleted
- AIRE gene mutations: Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy syndrome, >3 endocrine organs affected
- Bone marrow B cell selection: <10% of B cells normally reach periphery
-
Peripheral Tolerance Failure
- Regulatory T cell deficiency: <5% of CD4+ cells in autoimmune diseases
- Cytokine imbalance: Th1/Th17 predominance over Th2/Treg responses
- Molecular mimicry: Cross-reactive epitopes in >60% of autoimmune diseases
- Rheumatic fever: Streptococcal M protein mimics cardiac myosin
- Multiple sclerosis: Viral proteins cross-react with myelin basic protein
⭐ Clinical Pearl: HLA-B27 positivity increases ankylosing spondylitis risk by 100-fold, present in >90% of patients but only 8% of general population
💡 Master This: Autoimmune diseases follow epitope spreading - initial immune response against one self-antigen progressively expands to multiple epitopes within the same organ (intramolecular) then to different organs (intermolecular)
Hypersensitivity Reaction Mechanisms
Hypersensitivity reactions represent inappropriate immune responses to harmless antigens, classified by Gell and Coombs into four distinct types based on underlying mechanisms and temporal patterns.
-
Type I (Immediate)
- IgE-mediated: Mast cell degranulation within seconds to minutes
- Mediator release: Histamine peak at 5-10 minutes, leukotrienes at 30-60 minutes
- Anaphylaxis incidence: 1:1000-1:10,000 exposures to known allergens
-
Type II (Cytotoxic)
- Antibody-dependent: IgG/IgM binding to cell surface antigens
- Complement activation: C5a/C3a generation within 30-60 minutes
- Examples: Hemolytic transfusion reactions (1:76,000 units), drug-induced hemolysis
-
Type III (Immune Complex)
- Immune complex deposition: Antigen-antibody complexes in tissues
- Complement consumption: C3/C4 levels decrease >50% during active disease
- Serum sickness: 7-14 days after foreign protein exposure
-
Type IV (Delayed)
- T cell-mediated: 24-72 hours for maximal response
- Cytokine production: IFN-γ/TNF-α peak at 48-72 hours
- Contact dermatitis: >80% of population reactive to poison ivy upon re-exposure
📌 Remember: ACID for hypersensitivity types - Anaphylactic (I), Cytotoxic (II), Immune complex (III), Delayed (IV) with timing: minutes, hours, days, days
Understanding these dysfunction mechanisms reveals how single molecular defects cascade into complex clinical syndromes. Connect these pathophysiological principles through pattern recognition frameworks to understand how immune dysfunction manifests in clinical practice.
⚙️ Immune Dysfunction Mechanisms: When Defense Systems Fail
🎯 Clinical Pattern Recognition: Immune Dysfunction Signatures
Infection Pattern Recognition Matrix
-
Sinopulmonary Infections (Recurrent)
- B cell defects: >4 episodes/year of bacterial pneumonia
- Pathogens: Streptococcus pneumoniae (60%), Haemophilus influenzae (30%)
- Laboratory clues: IgG <400 mg/dL, poor vaccine responses (<4-fold titer increase)
- Diagnostic threshold: >2 pneumonias or >4 sinusitis episodes per year
- Associated findings: Bronchiectasis in 40-60% of untreated cases
-
Opportunistic Infections (Severe)
- T cell defects: Pneumocystis jirovecii, CMV, Candida infections
- CD4+ count correlation: <200 cells/μL for PCP risk, <50 cells/μL for CMV
- Timing: First 6 months of life for severe combined immunodeficiency
- Failure to thrive: <5th percentile weight/height by 6 months
- Chronic diarrhea: >14 days duration with negative bacterial cultures
-
Catalase-Positive Bacterial Infections
- Phagocyte defects: Staphylococcus aureus, Serratia, Aspergillus
- Chronic granulomatous disease: Nitroblue tetrazolium test <5% positive
- Infection sites: Lymph nodes (80%), liver abscesses (60%), pneumonia (70%)
- Diagnostic clue: Catalase-positive organisms cause >90% of infections
- Granuloma formation: Non-caseating granulomas in affected tissues
📌 Remember: SLIPAD for CGD infections - Staphylococcus, Listeria, Invasive fungi, Pseudomonas, Aspergillus, Discrete granulomas with catalase-positive organisms
| Immune Defect | Infection Pattern | Key Pathogens | Laboratory Findings | Diagnostic Test | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B cell deficiency | Sinopulmonary bacterial | S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae | Low IgG/IgA | Poor vaccine response | Good with IVIG |
| T cell deficiency | Opportunistic | PCP, CMV, Candida | Low CD4+ count | <200 cells/μL | Variable |
| Phagocyte defect | Catalase+ bacteria | S. aureus, Aspergillus | Normal counts | NBT test <5% | Reduced lifespan |
| Complement deficiency | Neisseria infections | N. meningitidis, N. gonorrhoeae | Low C3/C4 | CH50 <10% | Good with vaccination |
| Combined deficiency | Multiple patterns | All above | Pancytopenia | Multiple abnormal | Poor without BMT |
Autoimmune diseases demonstrate characteristic organ involvement sequences and autoantibody patterns that enable early diagnosis and targeted therapy. Recognition of initial presentations prevents irreversible organ damage in >80% of cases.
-
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patterns
- "4 of 11" criteria: >95% sensitivity for diagnosis
- ANA positivity: >95% of cases, titer >1:160 significant
- Anti-dsDNA: 60-70% of cases, correlates with nephritis (r=0.7)
- Renal involvement: 50-60% of patients, leading cause of morbidity
- CNS lupus: 15-20% prevalence, anti-ribosomal P in 90% of psychosis cases
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis Progression
- Rheumatoid factor: 70-80% positive, IgM anti-IgG antibodies
- Anti-CCP antibodies: 95% specificity, present years before clinical disease
- Joint destruction: >50% erosions within 2 years if untreated
- Morning stiffness: >1 hour duration in >90% of active cases
- Symmetric involvement: Small joints of hands/feet in 80%
-
Antiphospholipid Syndrome Recognition
- Triple positivity: Lupus anticoagulant + anti-cardiolipin + anti-β2GP1
- Thrombosis risk: >50% with triple positivity vs <10% with single positivity
- Pregnancy complications: >90% fetal loss without anticoagulation
- Laboratory paradox: Prolonged PTT but increased thrombosis risk
- Diagnostic requirement: Positive tests on 2 occasions >12 weeks apart
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Anti-CCP antibodies predict rheumatoid arthritis development 2-5 years before clinical symptoms in >80% of cases, with 95% specificity for RA diagnosis
💡 Master This: "SOAP BRAIN MD" for SLE criteria - Seizures, Oral ulcers, Arthritis, Photosensitivity, Blood disorders, Renal disease, ANA, Immunologic tests, Neurologic disorders, Malar rash, Discoid rash
Hypersensitivity Reaction Recognition
-
Type I Hypersensitivity (Immediate)
- Timing: Seconds to minutes after allergen exposure
- Tryptase elevation: >11.4 ng/mL confirms mast cell activation
- Biphasic reactions: 10-20% of anaphylaxis cases, second phase at 4-12 hours
- Epinephrine timing: <15 minutes for optimal outcomes
- Observation period: Minimum 4-6 hours for biphasic risk assessment
-
Type IV Hypersensitivity (Delayed)
- Timing: 48-72 hours for maximal response
- Patch testing: 96-hour reading for contact allergens
- Drug reactions: DRESS syndrome onset 2-8 weeks after drug initiation
- Eosinophilia: >1500 cells/μL in >80% of DRESS cases
- Organ involvement: Liver (90%), kidney (60%), lung (40%)
📌 Remember: "Minutes, Hours, Days, Days" for hypersensitivity timing - Type I (minutes), Type II (hours), Type III (days), Type IV (days), but Type IV has T cell involvement
Understanding these clinical patterns enables rapid recognition of immune dysfunction syndromes and guides targeted diagnostic workups. Connect these recognition frameworks through systematic evaluation approaches to understand how pattern recognition translates into clinical decision-making.
🎯 Clinical Pattern Recognition: Immune Dysfunction Signatures
🔬 Systematic Immunological Evaluation: Diagnostic Precision Tools
Primary Screening Laboratory Framework
-
Complete Blood Count with Differential
- Lymphocyte count: Normal 1500-4000/μL, <1000/μL suggests T cell deficiency
- Neutrophil morphology: Pelger-Huët anomaly in specific granule deficiency
- Platelet size: Giant platelets in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
- Eosinophilia: >500/μL suggests hyper-IgE syndrome or parasitic infection
- Lymphocyte morphology: Large granular lymphocytes in NK cell disorders
-
Quantitative Immunoglobulins
- IgG: Normal 700-1600 mg/dL, <400 mg/dL indicates hypogammaglobulinemia
- IgA: Normal 70-400 mg/dL, <7 mg/dL defines selective IgA deficiency
- IgM: Normal 40-230 mg/dL, elevated in hyper-IgM syndrome
- Age-specific ranges: IgG reaches adult levels by 6-8 years
- IgE levels: >2000 IU/mL suggests hyper-IgE syndrome (Job syndrome)
-
Complement Screening
- CH50: Total hemolytic complement, normal >60 units
- C3/C4 levels: C3 normal 90-180 mg/dL, C4 normal 10-40 mg/dL
- Alternative pathway: AH50 assesses properdin pathway function
- C1 esterase inhibitor: <50% activity in hereditary angioedema
- Factor H/I deficiency: Uncontrolled C3 consumption, <10% normal levels
📌 Remember: "GAMED" for immunoglobulin evaluation - Gamma globulin levels, Age-appropriate ranges, Maternal antibody interference (<6 months), Elevated IgE (>2000), Deficiency patterns (IgA most common)
| Test Category | Normal Range | Critical Values | Associated Conditions | Follow-up Tests | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lymphocytes | 1500-4000/μL | <1000/μL | SCID, DiGeorge | Flow cytometry | T cell deficiency |
| IgG | 700-1600 mg/dL | <400 mg/dL | CVID, XLA | Vaccine responses | B cell dysfunction |
| IgA | 70-400 mg/dL | <7 mg/dL | Selective IgA deficiency | IgG subclasses | Mucosal immunity |
| CH50 | >60 units | <10 units | Complement deficiency | Individual components | Classical pathway |
| NBT test | >95% positive | <10% positive | CGD | DHR flow cytometry | Phagocyte function |
-
Lymphocyte Proliferation Studies
- Mitogen responses: PHA, ConA, PWM stimulation >50,000 cpm
- Antigen-specific responses: Tetanus, Candida recall >10-fold over baseline
- Mixed lymphocyte reaction: Allogeneic stimulation >20,000 cpm
- Stimulation index: >10 indicates normal T cell function
- IL-2 production: >100 pg/mL after PHA stimulation
-
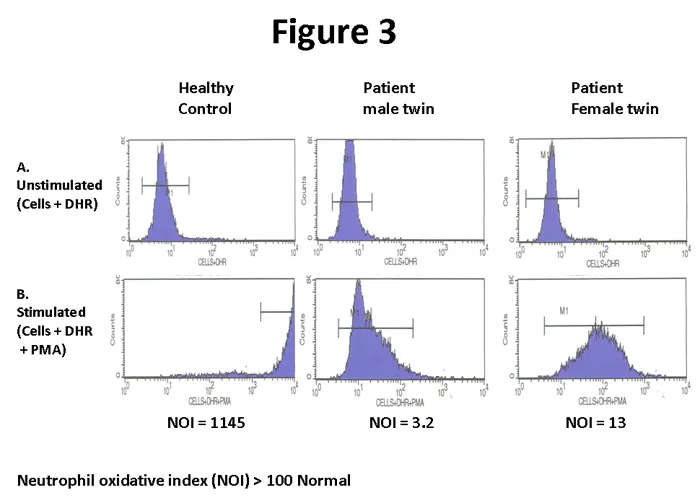
Phagocyte Function Assessment
- Nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT): >95% of neutrophils reduce dye normally
- Dihydrorhodamine (DHR): Flow cytometry shows >95% oxidative burst
- Chemotaxis assays: >80% of normal control migration
- Killing assays: >90% bacterial killing at 60 minutes
- Adhesion molecules: CD11/CD18 expression >80% of normal
-
Natural Killer Cell Function
- Chromium release assay: >20% specific lysis at 40:1 effector:target ratio
- CD107a degranulation: >15% of NK cells positive after stimulation
- Perforin/granzyme: Intracellular staining >80% of NK cells positive
- NK cell percentage: 5-15% of total lymphocytes normally
- Cytotoxicity defects: <10% specific lysis indicates dysfunction
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Dihydrorhodamine flow cytometry has >99% sensitivity for chronic granulomatous disease and can detect female carriers with mosaic patterns due to X-inactivation
💡 Master This: Functional assays are essential because normal cell counts don't guarantee normal function - >30% of primary immunodeficiencies have normal screening labs but abnormal functional tests
Autoimmune Disease Laboratory Evaluation
-
Autoantibody Screening Panels
- Antinuclear antibodies (ANA): >1:160 significant, pattern interpretation crucial
- Extractable nuclear antigens: Anti-Sm (99% specific for SLE)
- Antiphospholipid antibodies: Lupus anticoagulant, anti-cardiolipin, anti-β2GP1
- Anti-dsDNA: 60-70% of SLE patients, correlates with nephritis
- Anti-centromere: >95% specific for limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis
-
Inflammatory Markers
- ESR: >100 mm/hr suggests active systemic disease
- CRP: <3 mg/L normal, >10 mg/L indicates significant inflammation
- Complement consumption: Low C3/C4 in active lupus (80% of flares)
- Ferritin levels: >10,000 ng/mL in macrophage activation syndrome
- Lactate dehydrogenase: >1000 U/L suggests tissue destruction
-
Organ-Specific Autoantibodies
- Thyroid: Anti-TPO (>95% in Hashimoto's), TSI (>95% in Graves')
- Pancreatic: Anti-GAD (80% in Type 1 DM), anti-IA2 (60%)
- Liver: Anti-mitochondrial (>95% in PBC), anti-smooth muscle (80% in AIH)
- Tissue transglutaminase: >98% sensitivity for celiac disease
- Anti-CCP: 95% specificity for rheumatoid arthritis
📌 Remember: "SPAM" for ANA patterns - Speckled (anti-Sm, anti-RNP), Peripheral (anti-dsDNA), Anti-centromere (CREST), Mitochondrial (PBC)
Understanding systematic evaluation approaches enables efficient diagnosis of complex immunological disorders while minimizing unnecessary testing. Connect these diagnostic frameworks through evidence-based treatment algorithms to understand how systematic evaluation guides targeted therapeutic interventions.
🔬 Systematic Immunological Evaluation: Diagnostic Precision Tools
⚕️ Evidence-Based Immunomodulation: Therapeutic Precision
Immunosuppressive Therapy Algorithms
-
Conventional Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
- Methotrexate: 15-25 mg weekly, >70% response rate in RA
- Hydroxychloroquine: 5 mg/kg/day, retinal toxicity <1% with proper monitoring
- Sulfasalazine: 2-3 g daily, >60% response in inflammatory arthritis
- Monitoring requirements: CBC, LFTs every 4-8 weeks initially
- Folic acid supplementation: 5 mg weekly reduces MTX toxicity by >50%
-
Biologic Therapy Selection
- TNF-α inhibitors: 60-70% ACR20 response in RA, 40-50% remission rates
- IL-6 receptor antagonists: >80% response in tocilizumab-treated RA
- B cell depletion: Rituximab achieves >90% B cell depletion for 6-9 months
- Infection risk: 2-3x increased with TNF inhibitors
- Malignancy screening: Required before and during biologic therapy
-
Targeted Small Molecule Inhibitors
- JAK inhibitors: Tofacitinib >60% ACR20 response, oral administration
- Calcineurin inhibitors: Tacrolimus 0.1-0.2 mg/kg/day, nephrotoxicity monitoring
- mTOR inhibitors: Sirolimus 1-5 mg daily, wound healing impairment
- Therapeutic drug monitoring: Trough levels guide dosing adjustments
- Drug interactions: CYP3A4 inhibitors increase levels 2-3x
📌 Remember: "BIMARC" for biologic MOA - B-cell depletion (rituximab), IL-6 blockade (tocilizumab), Migration inhibition (natalizumab), Activation blockade (abatacept), Receptor antagonism (anakinra), Cytokine neutralization (TNF inhibitors)
| Drug Class | Mechanism | Response Rate | Monitoring | Major Toxicities | Contraindications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MTX | Folate antagonist | 70% RA response | CBC, LFTs q4-8wk | Hepatotoxicity, pneumonitis | Pregnancy, renal disease |
| TNF inhibitors | Cytokine blockade | 60-70% ACR20 | TB screening, CBC | Infections, malignancy | Active infection, CHF |
| Rituximab | B cell depletion | >90% depletion | Ig levels, infections | Hypogammaglobulinemia | Active hepatitis B |
| JAK inhibitors | Signal transduction | >60% ACR20 | CBC, lipids | Cytopenias, thrombosis | Active infection |
| Calcineurin inhibitors | T cell suppression | Variable | Creatinine, levels | Nephrotoxicity, HTN | Renal dysfunction |
-
Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG)
- Standard dosing: 400-600 mg/kg every 3-4 weeks
- Trough IgG targets: >500 mg/dL for most patients, >800 mg/dL for severe disease
- Infusion rates: Start 0.5 mg/kg/min, increase to 4 mg/kg/min if tolerated
- Premedication: Acetaminophen/antihistamines reduce reactions by >50%
- IgA-deficient patients: Risk of anaphylaxis, require IgA-depleted products
-
Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin (SCIG)
- Weekly dosing: 100-150 mg/kg weekly achieves steady-state levels
- Bioavailability: >90% compared to IVIG
- Injection sites: 2-4 sites, <25 mL per site, abdomen/thighs preferred
- Patient preference: >80% prefer SCIG for convenience
- Systemic reactions: <5% vs >20% with IVIG
-
Hyperimmune Globulins
- CMV-IVIG: 150 mg/kg for high-risk transplant recipients
- Hepatitis B immunoglobulin: 0.06 mL/kg within 24 hours of exposure
- Varicella-zoster immunoglobulin: 125 units/10 kg within 96 hours
- RSV prophylaxis: Palivizumab 15 mg/kg monthly during RSV season
- Rabies immunoglobulin: 20 IU/kg infiltrated around wound
⭐ Clinical Pearl: SCIG therapy achieves more stable IgG levels with fewer systemic reactions (<5% vs >20% with IVIG) and higher patient satisfaction (>80% prefer SCIG)
💡 Master This: Trough IgG levels should be measured before the next infusion and maintained >500 mg/dL for infection prevention, with higher targets (>800 mg/dL) for patients with chronic lung disease
Cellular and Gene Therapy Innovations
-
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- SCID survival: >95% with HLA-matched sibling, >85% with matched unrelated donor
- Conditioning regimens: Reduced intensity preserves >90% of organ function
- Graft-versus-host disease: 20-40% incidence with matched unrelated donors
- Timing critical: <3.5 months for optimal SCID outcomes
- Gene therapy: >90% success in ADA-SCID with lentiviral vectors
-
CAR-T Cell Therapy
- CD19 CAR-T: >80% complete remission in refractory B-ALL
- Cytokine release syndrome: >90% of patients, severe in 10-20%
- Neurotoxicity: 30-50% incidence, reversible in >95%
- Manufacturing time: 2-4 weeks from apheresis to infusion
- Bridging therapy: Required in >70% of patients
-
Regulatory T Cell Therapy
- Expanded Tregs: >100-fold expansion achievable ex vivo
- GVHD prevention: >50% reduction with Treg infusion
- Autoimmune applications: Phase I/II trials show >60% response rates
- Stability concerns: <50% maintain Foxp3 expression long-term
- Combination approaches: Low-dose IL-2 enhances Treg survival
📌 Remember: "CART" for CAR-T complications - Cytokine release syndrome (>90%), Aphasia/neurotoxicity (30-50%), Refractory disease (10-20%), Tumor lysis syndrome (rare)
Understanding evidence-based immunomodulation enables precision therapy selection that maximizes efficacy while minimizing toxicity. Connect these therapeutic principles through multi-system integration approaches to understand how targeted immunotherapy impacts complex disease networks.
⚕️ Evidence-Based Immunomodulation: Therapeutic Precision
🌐 Multi-System Immunological Integration: Network Medicine
Immune-Endocrine Network Integration
-
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis
- Cortisol circadian rhythm: Peak 8 AM (15-25 μg/dL), nadir midnight (<5 μg/dL)
- Stress response: 3-5x cortisol increase within 30 minutes of acute stress
- Immunosuppressive effects: >50% reduction in T cell proliferation at physiologic levels
- Autoimmune flares: >70% occur during periods of stress or cortisol withdrawal
- Adrenal insufficiency: Increased infection risk due to impaired stress response
-
Thyroid-Immune Interactions
- Autoimmune thyroiditis: >90% have anti-TPO antibodies
- Thyroid hormone effects: T3/T4 modulate >200 immune-related genes
- Polyglandular syndromes: >80% develop multiple endocrine autoimmunity
- AIRE gene mutations: >95% develop ≥2 endocrine autoimmune diseases
- Thyroid dysfunction: Present in >40% of SLE patients
-
Insulin-Immune Network
- Type 1 diabetes: >95% have ≥1 autoantibody at diagnosis
- Metabolic inflammation: Obesity increases CRP >3x and IL-6 >2x
- Insulin resistance: >50% of RA patients develop metabolic syndrome
- Adipokine dysregulation: Leptin >50 ng/mL promotes Th1/Th17 responses
- Metformin effects: >30% reduction in autoimmune disease risk
📌 Remember: "HATS" for immune-endocrine integration - HPA axis (cortisol), Adrenal insufficiency (infections), Thyroid autoimmunity (TPO), Sugar metabolism (insulin resistance)
| Endocrine System | Immune Effects | Autoimmune Associations | Biomarkers | Clinical Implications | Treatment Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPA axis | T cell suppression | Stress-induced flares | Cortisol rhythm | Infection susceptibility | Steroid replacement |
| Thyroid | Gene expression | Hashimoto's, Graves' | Anti-TPO, TSI | Multi-glandular disease | Hormone replacement |
| Pancreas | Metabolic inflammation | Type 1 DM, LADA | Anti-GAD, IA2 | Cardiovascular risk | Insulin therapy |
| Gonads | Sex hormone effects | PCOS, fertility | Testosterone, estradiol | Reproductive health | Hormone modulation |
| Parathyroid | Calcium homeostasis | Hypoparathyroidism | PTH, calcium | Bone metabolism | Calcium/vitamin D |
-
Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction
- Tight junction proteins: Claudin-5 decreased >50% in neuroinflammation
- Permeability markers: S100β >0.5 μg/L indicates BBB disruption
- Immune cell infiltration: >10-fold increase in activated microglia during MS flares
- Cytokine penetration: IL-1β, TNF-α cross disrupted BBB within hours
- Therapeutic implications: BBB-penetrating drugs required for CNS autoimmunity
-
Microglial Activation Patterns
- M1 polarization: Pro-inflammatory, >5x IL-1β production
- M2 polarization: Anti-inflammatory, >10x IL-10 production
- Chronic activation: >6 months leads to neurodegeneration in >80%
- PET imaging: TSPO ligands detect activated microglia with >90% sensitivity
- CSF biomarkers: YKL-40 >200 ng/mL indicates microglial activation
-
Autonomic-Immune Integration
- Vagal anti-inflammatory pathway: Acetylcholine reduces TNF-α by >70%
- Sympathetic activation: Norepinephrine enhances Th2 responses >3x
- Heart rate variability: Reduced HRV correlates with increased inflammation (r=-0.6)
- Vagal stimulation: >50% reduction in inflammatory markers
- Beta-blocker effects: Propranolol reduces autoimmune flares by >30%
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Reduced heart rate variability (RMSSD <20 ms) predicts autoimmune flares with >80% sensitivity and correlates with elevated inflammatory markers (CRP, IL-6)
💡 Master This: Neuroinflammation creates positive feedback loops where BBB disruption → immune cell infiltration → microglial activation → further BBB damage, explaining progressive neurological deterioration in >60% of CNS autoimmune diseases
Gut-Immune-Microbiome Axis
-
Intestinal Barrier Function
- Tight junction integrity: Zonulin levels >3 ng/mL indicate increased permeability
- Microbial translocation: LPS >50 pg/mL suggests barrier dysfunction
- Immune sampling: >10^11 bacteria interact with gut-associated lymphoid tissue daily
- Peyer's patches: >200 follicles contain >10^8 B cells for IgA production
- Lamina propria: >10^9 plasma cells produce >3g IgA daily
-
Microbiome-Immune Crosstalk
- Bacterial diversity: Shannon index <2.5 associated with autoimmune disease
- Short-chain fatty acids: Butyrate >10 mM promotes Treg development >5x
- Pathobiont expansion: >50% reduction in beneficial bacteria during inflammation
- Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio: >4:1 correlates with metabolic inflammation
- Segmented filamentous bacteria: Induce Th17 cells within 2-3 weeks
-
Molecular Mimicry Networks
- Cross-reactive epitopes: >60% of autoimmune diseases show microbial mimicry
- Klebsiella pneumoniae: Shares epitopes with HLA-B27 in ankylosing spondylitis
- Campylobacter jejuni: GM1 ganglioside mimicry triggers Guillain-Barré syndrome
- Epitope spreading: Initial microbial response expands to >5 self-antigens
- Bystander activation: Microbial adjuvants activate autoreactive T cells
📌 Remember: "GALT" for gut immunity - Gut-associated lymphoid tissue (>60% of immune system), Antigen sampling (M cells), Lamina propria (plasma cells), Tolerance induction (Tregs)
Understanding multi-system integration reveals how immune dysfunction propagates through biological networks to produce complex clinical syndromes. Connect these integration principles through rapid mastery frameworks to understand how systems thinking transforms clinical decision-making.
🌐 Multi-System Immunological Integration: Network Medicine
🎯 Immunopathology Mastery: Clinical Command Center
Essential Clinical Arsenal
-
High-Yield Diagnostic Thresholds
- ANA >1:160: >95% sensitivity for systemic autoimmune disease
- IgG <400 mg/dL: Defines hypogammaglobulinemia, requires IVIG therapy
- CD4+ <200/μL: High-risk for opportunistic infections
- Complement CH50 <10: >90% probability of complement deficiency
- NBT <10% positive: Pathognomonic for chronic granulomatous disease
-
Critical Timing Windows
- SCID treatment: <3.5 months for >90% survival with bone marrow transplant
- Anaphylaxis intervention: Epinephrine <15 minutes for optimal outcomes
- Autoimmune flare: Treatment <48 hours prevents irreversible damage
- Lupus nephritis: Treatment <6 months preserves >80% renal function
- Giant cell arteritis: Steroids <24 hours prevent permanent vision loss
-
Therapeutic Monitoring Parameters
- MTX toxicity: ALT >3x normal requires dose reduction or discontinuation
- TNF inhibitor screening: Tuberculin >5 mm or IGRA positive contraindicated
- Rituximab monitoring: IgG <400 mg/dL requires IVIG supplementation
- JAK inhibitor safety: ANC <1000/μL requires dose adjustment
- Calcineurin inhibitors: Creatinine >30% increase indicates nephrotoxicity
📌 Remember: "TIMERS" for immunopathology urgency - Time-sensitive interventions, Irreversible damage prevention, Monitoring parameters, Emergency protocols, Rapid recognition, Systemic complications
| Clinical Scenario | Recognition Pattern | Critical Threshold | Intervention Window | Success Rate | Monitoring Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCID | Opportunistic infections <6 months | CD3+ <300/μL | <3.5 months BMT | >90% survival | Engraftment markers |
| Anaphylaxis | Rapid onset, multi-system | Tryptase >11.4 ng/mL | Epinephrine <15 min | >95% recovery | Biphasic monitoring |
| Lupus nephritis | Proteinuria, hematuria | Cr >1.5 mg/dL | Treatment <6 months | >80% preservation | Renal function |
| GCA | Headache, vision changes | ESR >50 mm/hr | Steroids <24 hours | >90% vision saved | Visual assessment |
| CGD | Catalase+ infections | NBT <10% positive | Prophylaxis lifelong | >80% infection-free | Infection monitoring |
-
"See This, Think That" Algorithms
- Recurrent sinopulmonary + low IgG → B cell deficiency → IVIG therapy
- Opportunistic infections + low CD4+ → T cell deficiency → Isolation + workup
- Catalase+ bacteria + normal counts → Phagocyte defect → NBT testing
- Neisseria infections + family history → Complement deficiency → CH50/AH50
- Multi-organ autoimmunity + ANA positive → Systemic lupus → Organ assessment
-
Red Flag Recognition Matrix
- Age <2 years + severe infections → Primary immunodeficiency (>90% probability)
- Multiple autoimmune diseases → Polyglandular syndrome (>80% genetic)
- Granulomas + immunodeficiency → CGD or CVID (>70% association)
- Eosinophilia + recurrent infections → Hyper-IgE syndrome (Job syndrome)
- Thrombocytopenia + eczema + infections → Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
-
Therapeutic Response Patterns
- IVIG response: >50% infection reduction within 3-6 months
- Biologic efficacy: >60% improvement by 12-16 weeks
- Immunosuppression: >70% response to combination therapy
- Steroid response: >80% improvement within 2-4 weeks in responsive diseases
- Rituximab depletion: >90% B cell reduction for 6-9 months
⭐ Clinical Pearl: "Rule of 3s" for immunodeficiency - 3 serious infections, 3 months of antibiotics, or 3 family members affected warrant immunological evaluation
💡 Master This: Immunopathology mastery requires systems thinking - recognize that >60% of patients have multi-system involvement requiring coordinated subspecialty care and long-term monitoring
Clinical Integration Commandments
-
Diagnostic Precision Principles
- Function over numbers: Normal cell counts don't guarantee normal function
- Pattern recognition: Infection patterns reveal specific immune defects
- Timing matters: Age of onset distinguishes primary from secondary defects
- Family history: >50% of primary immunodeficiencies have genetic patterns
- Geographic factors: Endemic infections modify clinical presentations
-
Therapeutic Optimization Strategies
- Personalized dosing: Trough levels guide IVIG optimization
- Combination approaches: >80% of refractory cases respond to multi-drug regimens
- Monitoring intensity: High-risk patients require monthly assessments
- Preventive strategies: Vaccination protocols reduce infection burden by >70%
- Quality of life: Patient-reported outcomes guide treatment decisions
-
Long-term Management Framework
- Complication surveillance: >40% develop secondary complications over 10 years
- Transition planning: Pediatric to adult care requires structured protocols
- Emergency preparedness: Action plans reduce hospitalization by >50%
- Genetic counseling: >90% of families benefit from reproductive guidance
- Research participation: Clinical trials offer >30% of breakthrough therapies
📌 Remember: "MASTER" immunopathology - Multi-system thinking, Algorithmic approach, Systemic monitoring, Timing optimization, Evidence-based therapy, Rapid recognition patterns
Understanding immunopathology mastery transforms complex immune dysfunction into manageable clinical algorithms that optimize patient outcomes through precision medicine approaches. This comprehensive framework enables expert-level clinical decision-making in challenging immunological cases.
🎯 Immunopathology Mastery: Clinical Command Center
Practice Questions: Immunopathology
Test your understanding with these related questions
A scientist in Chicago is studying a new blood test to detect Ab to EBV with increased sensitivity and specificity. So far, her best attempt at creating such an exam reached 82% sensitivity and 88% specificity. She is hoping to increase these numbers by at least 2 percent for each value. After several years of work, she believes that she has actually managed to reach a sensitivity and specificity much greater than what she had originally hoped for. She travels to China to begin testing her newest blood test. She finds 2,000 patients who are willing to participate in her study. Of the 2,000 patients, 1,200 of them are known to be infected with EBV. The scientist tests these 1,200 patients' blood and finds that only 120 of them tested negative with her new exam. Of the patients who are known to be EBV-free, only 20 of them tested positive. Given these results, which of the following correlates with the exam's specificity?













