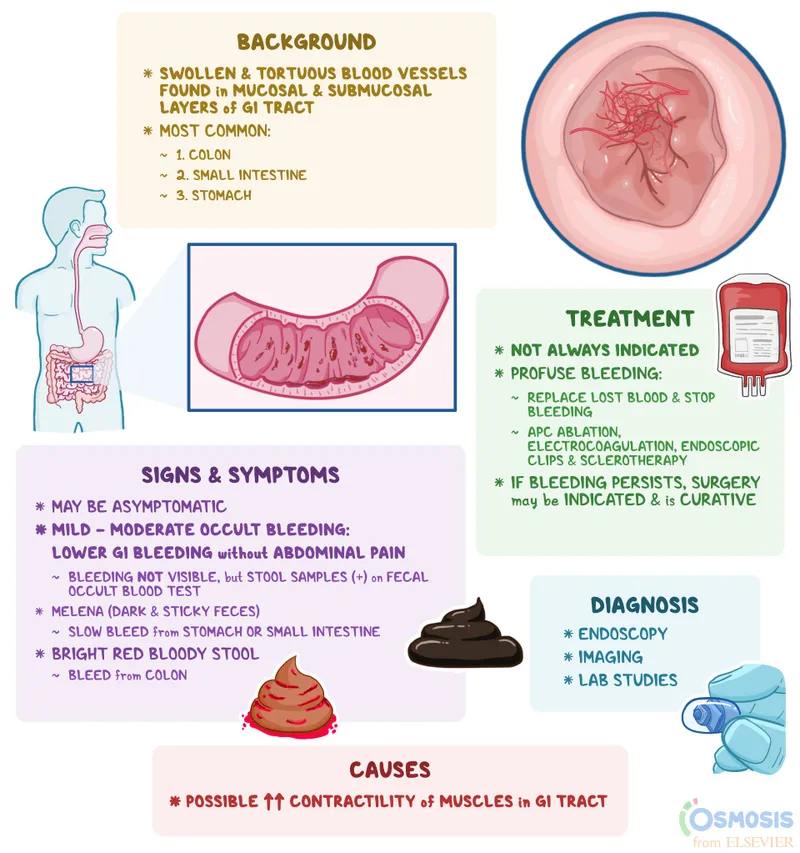
Vascular disorders of bowel US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Vascular disorders of bowel. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Vascular disorders of bowel US Medical PG Question 1: A 75-year-old male is hospitalized for bloody diarrhea and abdominal pain after meals. Endoscopic work-up and CT scan lead the attending physician to diagnose ischemic colitis at the splenic flexure. Which of the following would most likely predispose this patient to ischemic colitis:
- A. Juxtaglomerular cell tumor
- B. Hyperreninemic hyperaldosteronism secondary to type II diabetes mellitus
- C. Obstruction of the abdominal aorta following surgery (Correct Answer)
- D. Essential hypertension
- E. Increased splanchnic blood flow following a large meal
Vascular disorders of bowel Explanation: ***Obstruction of the abdominal aorta following surgery***
- A surgical procedure, especially one involving manipulation or clamping of the abdominal aorta, can lead to **reduced blood flow** to the intestinal arteries, making the **splenic flexure** particularly vulnerable to **ischemic colitis** due to its watershed area blood supply between the SMA and IMA territories.
- Reduced arterial flow to the colon results in **ischemia**, which causes inflammation, damage, and can present with bloody diarrhea and abdominal pain.
- Aortic surgery is a recognized risk factor for acute ischemic colitis due to interruption of mesenteric blood flow.
*Juxtaglomerular cell tumor*
- This tumor causes **renin-dependent hypertension**, leading to increased blood pressure, but does not directly cause **colonic ischemia**.
- Its primary effect is on the **renal blood vessels** and **fluid-electrolyte balance**, not intestinal circulation.
*Hyperreninemic hyperaldosteronism secondary to type II diabetes mellitus*
- This condition involves **high renin** and **aldosterone levels**, predisposing to hypertension and electrolyte imbalances, and is often a complication of **diabetes**, but it does not directly cause **ischemia of the colon**.
- While diabetes can cause microvascular complications, this specific presentation of **hyperaldosteronism** is not a direct cause of **ischemic colitis**.
*Essential hypertension*
- While **chronic hypertension** is a risk factor for generalized **atherosclerosis**, it is not as direct and acute a cause of **ischemic colitis** as a specific arterial obstruction.
- The effects of **essential hypertension** on the colon are often less acute and more diffuse than the localized ischemia experienced in this case.
*Increased splanchnic blood flow following a large meal*
- Postprandial **increased splanchnic blood flow** is a normal physiological response that facilitates digestion and nutrient absorption, and would not itself cause **ischemic colitis**.
- The postprandial pain in ischemic colitis occurs because the **diseased vasculature cannot meet increased metabolic demands** during digestion (supply-demand mismatch), not because the increased flow itself is harmful.
- In fact, reduced splanchnic blood flow due to underlying vascular disease, coupled with increased demand after meals, is the actual mechanism for **ischemic colitis** symptoms.
Vascular disorders of bowel US Medical PG Question 2: A 30-year-old man comes to the physician because of an episode of bloody vomiting this morning and a 1-week history of burning upper abdominal pain. Two weeks ago, he sustained a head injury and was in a coma for 3 days. An endoscopy shows multiple, shallow hemorrhagic lesions predominantly in the gastric fundus and greater curvature. Biopsies show patchy loss of epithelium and an acute inflammatory infiltrate in the lamina propria that does not extend beyond the muscularis mucosa. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Type B gastritis
- B. Cushing ulcer (Correct Answer)
- C. Erosive gastritis
- D. Dieulafoy lesion
- E. Penetrating ulcer
Vascular disorders of bowel Explanation: ***Cushing ulcer***
- A **Cushing ulcer** is a type of **stress ulcer** specifically associated with **intracranial injury**, which causes increased vagal stimulation leading to hypersecretion of gastric acid.
- The patient's history of a **head injury** followed by **bloody vomiting** and **upper abdominal pain**, along with endoscopic findings of shallow, hemorrhagic lesions, is highly consistent with a Cushing ulcer.
*Type B gastritis*
- **Type B gastritis** is primarily caused by **Helicobacter pylori infection**, often leading to chronic inflammation and sometimes ulcers, not acute stress-related lesions after a head injury.
- While it can cause epigastric pain and bleeding, the strong association with a recent head injury makes Cushing ulcer a more specific diagnosis.
*Erosive gastritis*
- **Erosive gastritis** is a broad term encompassing various causes of gastric mucosal erosions, including NSAIDs, alcohol, and stress.
- While Cushing ulcer represents a specific form of stress-related erosive gastritis, **Cushing ulcer is the most specific and accurate diagnosis** given the distinct history of intracranial injury and coma.
- The temporal relationship between head trauma and gastric symptoms is pathognomonic for Cushing ulcer.
*Dieulafoy lesion*
- A **Dieulafoy lesion** is characterized by an abnormally large submucosal artery that erodes the overlying mucosa, leading to sudden, massive gastrointestinal bleeding.
- This condition is typically isolated, not presenting with multiple, shallow hemorrhagic lesions across the gastric fundus and greater curvature, and is not directly linked to head injury.
*Penetrating ulcer*
- A **penetrating ulcer** is a complication of a chronic peptic ulcer where the ulcer extends beyond the muscularis propria into adjacent organs.
- The biopsy findings of inflammation not extending beyond the **muscularis mucosa** indicate superficial damage (erosions), not a deep penetrating ulcer.
Vascular disorders of bowel US Medical PG Question 3: A 57-year-old man presents with 2 days of severe, generalized, abdominal pain that is worse after meals. He is also nauseated and reports occasional diarrhea mixed with blood. Apart from essential hypertension, his medical history is unremarkable. His vital signs include a temperature of 36.9°C (98.4°F), blood pressure of 145/92 mm Hg, and an irregularly irregular pulse of 105/min. Physical examination is only notable for mild periumbilical tenderness. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Diverticular disease
- B. Acute pancreatitis
- C. Gastroenteritis
- D. Crohn's disease
- E. Acute mesenteric ischemia (Correct Answer)
Vascular disorders of bowel Explanation: ***Acute mesenteric ischemia***
- The patient's presentation with **severe, generalized abdominal pain worse after meals**, along with **bloody diarrhea** and **irregularly irregular pulse** (suggesting **atrial fibrillation**), is highly indicative of acute mesenteric ischemia.
- Atrial fibrillation can lead to **emboli** that occlude mesenteric arteries, causing rapid onset of **ischemic bowel injury** with disproportionate pain and often minimal findings on physical exam.
*Diverticular disease*
- While diverticulitis can cause abdominal pain, it is typically localized to the **left lower quadrant** and often associated with fever and leukocytosis, which are absent here.
- **Diverticular bleeding** usually presents as painless rectal bleeding, not severe, diffuse abdominal pain with ischemic features.
*Acute pancreatitis*
- Characterized by severe **epigastric pain radiating to the back**, often associated with nausea and vomiting, but not typically with bloody diarrhea.
- Elevated **lipase** and **amylase** levels are diagnostic markers, and an irregularly irregular pulse is not a direct symptom.
*Gastroenteritis*
- Often causes diffuse abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, but the pain is rarely as severe or disproportionate to physical findings as described.
- **Bloody diarrhea** can occur, but the rapid onset of severe pain, particularly in the context of possible **embolic source** (atrial fibrillation), makes ischemia more likely.
*Crohn's disease*
- A chronic inflammatory bowel disease presenting with **abdominal pain**, **diarrhea** (often bloody), and weight loss, developing over weeks to months.
- The acute, severe onset of symptoms in this patient does not fit the typical chronic presentation of Crohn's disease.
Vascular disorders of bowel US Medical PG Question 4: A 52-year-old woman complains of intermittent diffuse abdominal pain that becomes worse after eating meals and several episodes of diarrhea, the last of which was bloody. These symptoms have been present for the previous 6 months but have worsened recently. She has had significant weight loss since the onset of symptoms. Her past medical history includes systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), which has been difficult to manage medically. Vital signs include a blood pressure of 100/70 mm Hg, temperature of 37.1°C (98.8 °F), and pulse of 95/min. On physical examination, the patient appears to be in severe pain, and there is mild diffuse abdominal tenderness. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Ischemic bowel disease (Correct Answer)
- B. Small bowel obstruction
- C. Acute pancreatitis
- D. Gastroenteritis
- E. Ulcerative colitis
Vascular disorders of bowel Explanation: ***Ischemic bowel disease***
- The patient's history of **diffuse abdominal pain worsening after meals** (postprandial pain or "abdominal angina"), **bloody diarrhea**, and **significant weight loss** is highly suggestive of **chronic mesenteric ischemia**.
- Her history of **systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)**, which can cause **vasculitis** and **hypercoagulability**, increases the risk of mesenteric artery thrombosis or emboli, leading to bowel ischemia.
*Small bowel obstruction*
- This typically presents with **colicky abdominal pain**, **vomiting**, and **abdominal distension**, often with obstipation.
- While it can cause pain, it does not typically lead to **bloody diarrhea** or chronic postprandial worsening of symptoms.
*Acute pancreatitis*
- Characterized by **severe epigastric pain** radiating to the back, often associated with nausea and vomiting, and elevated lipase/amylase.
- It does not typically present with **bloody diarrhea** or a chronic history of symptoms worsening after eating.
*Gastroenteritis*
- Usually presents with **acute onset** of nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever, often resolving within a few days to a week.
- The **chronic nature** (6 months) of symptoms, significant weight loss, and the specific pattern of postprandial pain make gastroenteritis unlikely.
*Ulcerative colitis*
- While it causes **bloody diarrhea** and abdominal pain, it typically involves the colon and rectum, and pain is less commonly described as diffuse and worsening specifically after meals due to ischemia.
- The primary symptoms are usually **tenesmus**, frequent bowel movements, and rectal bleeding, and it does not typically present with the specific "abdominal angina" associated with mesenteric ischemia.
Vascular disorders of bowel US Medical PG Question 5: Three days after admission to the hospital with a clinical diagnosis of ischemic colitis, a 65-year-old man has recovered from his initial symptoms of bloody diarrhea and abdominal pain with tenderness. He feels well at this point and wishes to go home. He has a 15-year history of diabetes mellitus. Currently, he receives nothing by mouth, and he is on IV fluids, antibiotics, and insulin. His temperature is 36.7°C (98.1°F), pulse is 68/min, respiratory rate is 13/min, and blood pressure is 115/70 mm Hg. Physical examination of the abdomen shows no abnormalities. His most recent laboratory studies are all within normal limits, including glucose. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Laparoscopy
- B. Discharge home with follow-up in one month
- C. Laparotomy
- D. Total parenteral nutrition
- E. Colonoscopy (Correct Answer)
Vascular disorders of bowel Explanation: ***Colonoscopy***
- A colonoscopy is crucial for **evaluating the extent of ischemic damage**, identifying strictures, and ruling out other pathologies like inflammatory bowel disease or malignancy.
- While the patient is clinically stable, direct visualization of the colonic mucosa a few days after the acute event is necessary to **assess healing** and guide future management.
*Laparoscopy*
- **Laparoscopy is an invasive surgical procedure** primarily used for diagnosis and intervention in acute abdominal conditions, which are not present here.
- Given the patient's stable condition and resolution of symptoms, a less invasive diagnostic tool like colonoscopy is more appropriate at this stage.
*Discharge home with follow-up in one month*
- Discharging the patient without further investigation is **premature** as the full extent of the ischemic injury and potential long-term complications are unknown.
- There is a risk of **stricture formation** or recurrent ischemia, necessitating a comprehensive assessment before discharge.
*Laparotomy*
- **Laparotomy is a major open surgical procedure** reserved for cases with severe ischemia, perforation, or peritonitis, none of which are indicated by the patient's current status.
- The patient's stable vital signs and resolution of initial symptoms make this overly aggressive and unnecessary.
*Total parenteral nutrition*
- **Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) is used when the gastrointestinal tract cannot be used** for an extended period, such as in severe short bowel syndrome or prolonged postoperative ileus.
- The patient is currently on IV fluids and is NPO, but there's no indication of long-term inability to use his gut, and the nutritional support does not address the need for structural assessment of the colon.
Vascular disorders of bowel US Medical PG Question 6: A 65-year-old man presents to the emergency department with vague, constant abdominal pain, and worsening shortness of breath for the past several hours. He has baseline shortness of breath and requires 2–3 pillows to sleep at night. He often wakes up because of shortness of breath. Past medical history includes congestive heart failure, diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. He regularly takes lisinopril, metoprolol, atorvastatin, and metformin. His temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F), respiratory rate 25/min, pulse 67/min, and blood pressure 98/82 mm Hg. On physical examination, he has bilateral crackles over both lung bases and a diffusely tender abdomen. His subjective complaint of abdominal pain is more severe than the observed tenderness on examination. Which of the following vessels is involved in the disease affecting this patient?
- A. Left anterior descending
- B. Celiac artery and superior mesenteric artery (Correct Answer)
- C. Left colic artery
- D. Right coronary artery
- E. Meandering mesenteric artery
Vascular disorders of bowel Explanation: **Celiac artery and superior mesenteric artery**
- The patient's presentation with **vague, constant abdominal pain** out of proportion to physical exam findings (**abdominal pain more severe than tenderness**) in the setting of **congestive heart failure** and **hypotension** is highly suggestive of **non-occlusive mesenteric ischemia (NOMI)**.
- NOMI results from **splanchnic vasoconstriction** leading to hypoperfusion of the bowel, primarily affecting the territories supplied by the **celiac artery** and **superior mesenteric artery**, which supply the foregut and midgut, respectively.
*Left anterior descending*
- The left anterior descending (LAD) artery primarily supplies the **left ventricle** and interventricular septum.
- Occlusion of the LAD typically causes a **myocardial infarction** with chest pain, EKG changes, and elevated cardiac enzymes, which is not the primary presentation here, although a degree of cardiac compromise exacerbates the NOMI.
*Left colic artery*
- The left colic artery is a branch of the **inferior mesenteric artery** and supplies portions of the **descending colon**.
- While bowel ischemia can affect this region, NOMI, a more widespread condition, is unlikely to be isolated to the left colic artery distribution, and the patient's symptoms are more consistent with multi-vessel involvement.
*Right coronary artery*
- The right coronary artery (RCA) supplies the **right ventricle**, inferior wall of the left ventricle, and often the **SA and AV nodes**.
- RCA occlusion typically leads to **inferior wall myocardial infarction** and can cause bradyarrhythmias, but it would not directly cause the described abdominal pain and out-of-proportion findings.
*Meandering mesenteric artery*
- The meandering mesenteric artery is an anatomical variant, an **anastomotic connection** between the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries.
- While it can be a source of collateral flow, it is not a primary vessel targeted in the pathogenesis of NOMI, which affects the main mesenteric arteries due to global hypoperfusion.
Vascular disorders of bowel US Medical PG Question 7: An unconscious middle-aged man is brought to the emergency department. He is actively bleeding from the rectum. He has no past medical history. At the hospital, his pulse is 110/min, the blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, the respirations are 26/min, and the oxygen saturation is 96% at room air. His extremities are cold. Resuscitation is started with IV fluids and cross-matched blood arranged. His vitals are stabilized after resuscitation and blood transfusion. His hemoglobin is 7.6 g/dL, hematocrit is 30%, BUN is 33 mg/dL, and PT/aPTT is within normal limits. A nasogastric tube is inserted, which drains bile without blood. Rectal examination and proctoscopy reveal massive active bleeding, without any obvious hemorrhoids or fissure. The physician estimates the rate of bleeding at 2-3 mL/min. What is the most appropriate next step in diagnosis?
- A. Exploratory laparotomy with segmental bowel resection
- B. Radiolabeled RBC scan
- C. Colonoscopy
- D. Mesenteric angiography (Correct Answer)
- E. EGD
Vascular disorders of bowel Explanation: ***Mesenteric angiography***
- Mesenteric angiography is indicated for **active lower GI bleeding** when the bleeding rate is high (2-3 mL/min) and colonoscopy is challenging due to massive bleeding. It can localize the source of bleeding and allow for therapeutic embolization.
- The patient's presentation with **massive rectal bleeding**, signs of hypovolemia, and the exclusion of upper GI bleeding (bile without blood in NG tube) points to a lower GI source.
*Exploratory laparotomy with segmental bowel resection*
- This is an **invasive surgical procedure** typically reserved for cases where other less invasive diagnostic and therapeutic methods have failed, or in cases of uncontrolled life-threatening hemorrhage.
- Doing an exploratory laparotomy without clear localization of the bleeding site carries significant risks and may lead to unnecessary bowel resections.
*Radiolabeled RBC scan*
- A radiolabeled RBC scan is a highly sensitive diagnostic tool for **detecting intermittent or slow GI bleeding**, but it requires a very low rate of bleeding (as low as 0.1 mL/min).
- Given the patient's **active and massive bleeding** (2-3 mL/min), a more rapid and precise localization method like angiography is preferred.
*Colonoscopy*
- While colonoscopy is the primary diagnostic tool for lower GI bleeding, it is often **challenging to perform effectively in the presence of massive active bleeding**, as the view can be obscured by blood.
- The patient's hemodynamic instability has been corrected, but the high bleeding rate makes a diagnostic colonoscopy difficult.
*EGD*
- EGD (Esophagogastroduodenoscopy) is used to diagnose **upper GI bleeding**, which has been effectively ruled out by the nasogastric tube draining bile without blood.
- This procedure would not be helpful for localizing a lower GI bleeding source.
Vascular disorders of bowel US Medical PG Question 8: A 53-year-old man is brought to the emergency department for confusion. He was in his usual state of health until about 3 hours ago when he tried to use his sandwich to turn off the TV. He also complained to his wife that he had a severe headache. Past medical history is notable for hypertension, which has been difficult to control on multiple medications. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), the pulse is 70/min, and the blood pressure is 206/132 mm Hg. On physical exam he is alert and oriented only to himself, repeating over and over that his head hurts. The physical exam is otherwise unremarkable and his neurologic exam is nonfocal. The noncontrast CT scan of the patient's head is shown and reveals an acute intraparenchymal hemorrhage in the basal ganglia. Which of the following diagnostic tests would be most helpful in determining the underlying cause of this patient's hemorrhage?
- A. Lumbar puncture
- B. Electroencephalogram (EEG)
- C. MRI of the brain
- D. CT angiography of the neck
- E. CT angiography of the brain (Correct Answer)
Vascular disorders of bowel Explanation: ***CT angiography of the brain***
- Following identification of an **intracerebral hemorrhage** on noncontrast CT, **CT angiography (CTA) of the brain** is the most appropriate next diagnostic test to identify underlying vascular abnormalities such as **arteriovenous malformations (AVMs)**, **aneurysms**, **dural arteriovenous fistulas**, or **moyamoya disease**.
- While this patient has severe hypertension (a common cause of basal ganglia hemorrhage), CTA should still be performed to rule out secondary causes, particularly in patients under 70 years old or those with atypical features.
- CTA can be performed rapidly in the acute setting and has high sensitivity for detecting vascular lesions that may require specific treatment.
*MRI of the brain*
- MRI with specialized sequences (GRE, SWI, FLAIR) can provide detailed information about **chronic microhemorrhages**, **cerebral amyloid angiopathy**, **underlying tumors**, or **cavernomas**.
- However, MRI is typically performed **after CTA** in the workup of intracerebral hemorrhage, not as the immediate next step.
- MRI is less readily available in the acute setting and takes longer to perform than CTA.
*CT angiography of the neck*
- This test visualizes the **carotid and vertebral arteries** in the neck to detect **stenosis**, **dissection**, or **atherosclerotic disease**.
- It is not directly useful for identifying the cause of an **intraparenchymal hemorrhage** within the brain substance itself.
*Lumbar puncture*
- Lumbar puncture analyzes **cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)** and is primarily used for suspected **subarachnoid hemorrhage** (when CT is negative), **meningitis**, or **encephalitis**.
- It is **contraindicated** in patients with significant intraparenchymal hemorrhage due to risk of herniation from increased intracranial pressure.
*Electroencephalogram (EEG)*
- EEG measures **electrical activity in the brain** and is used to diagnose **seizure disorders** or evaluate altered mental status from metabolic or epileptic causes.
- While confusion can result from seizures, the primary pathology is the **intracerebral hemorrhage** identified on CT, which EEG cannot diagnose or characterize.
Vascular disorders of bowel US Medical PG Question 9: A 27-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician for evaluation of involuntary weight loss and recurrent abdominal pain. She noticed blood in her stool several times. The medical history is significant for the polycystic ovarian syndrome. The vital signs are as follows: temperature, 38.0°C (100.4°F); heart rate, 78/min; respiratory rate, 14/min; and blood pressure, 110/80 mm Hg. The family history is notable for paternal colon cancer. A colonoscopy is performed and is presented in the picture. What findings are expected?
- A. Crypt abscess (Correct Answer)
- B. Dermatitis herpetiformis
- C. Blunting of villi and crypt hyperplasia
- D. Non-caseating granulomas
- E. Aphthous stomatitis
Vascular disorders of bowel Explanation: ***Crypt abscess***
- The image provided shows **neutrophils infiltrating and filling the crypt lumina**, which are characteristic findings of crypt abscesses seen in **ulcerative colitis**.
- This pathology, combined with the patient's symptoms of **bloody diarrhea**, involuntary weight loss, and recurrent abdominal pain, points towards an inflammatory bowel disease, most consistent with ulcerative colitis.
*Dermatitis herpetiformis*
- This is a **skin manifestation of celiac disease**, presenting as intensely pruritic papules and vesicles, typically on extensor surfaces.
- It is not directly associated with inflammatory bowel disease, especially ulcerative colitis, and is not a histological finding in the colon.
*Blunting of villi and crypt hyperplasia*
- These are characteristic histological findings of **celiac disease** in the **small intestine**.
- The patient's symptoms and the histological image are from the colon, ruling out celiac disease as the primary diagnosis.
*Aphthous stomatitis*
- While **aphthous ulcers** are common extraintestinal manifestations in both Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, it is a clinical finding in the oral cavity, not a histological finding in the colon.
- The question asks for *other findings expected* in the context of the provided colonic histology.
*Non-caseating granulomas*
- **Non-caseating granulomas** are a hallmark histological feature of **Crohn's disease**, not ulcerative colitis.
- The image shown, with widespread crypt abscesses and diffuse inflammatory infiltrate, is more typical of ulcerative colitis rather than Crohn's disease.
Vascular disorders of bowel US Medical PG Question 10: A 24-year-old woman comes to the physician because of progressively worsening episodes of severe, crampy abdominal pain and nonbloody diarrhea for the past 3 years. Examination of the abdomen shows mild distension and generalized tenderness. There is a fistula draining stool in the perianal region. Immunohistochemistry shows dysfunction of the nucleotide oligomerization binding domain 2 (NOD2) protein. This dysfunction most likely causes overactivity of which of the following immunological proteins in this patient?
- A. Interferon-γ
- B. β-catenin
- C. IL-1β
- D. IL-10
- E. NF-κB (Correct Answer)
Vascular disorders of bowel Explanation: ***NF-κB***
- **NOD2** is a pattern recognition receptor that normally detects bacterial products and regulates inflammatory responses. In **Crohn's disease**, loss-of-function **NOD2 mutations** lead to impaired bacterial sensing and clearance.
- This defective NOD2 function results in **compensatory overactivation of NF-κB** through alternative inflammatory pathways (particularly TLR signaling), causing excessive **pro-inflammatory cytokine** production.
- This **NF-κB hyperactivation** is a key driver of chronic inflammation in **Crohn's disease**, contributing to symptoms like fistulas, strictures, and transmural inflammation.
*Interferon-γ*
- **Interferon-γ** is an important pro-inflammatory cytokine in Crohn's disease and is part of the Th1-mediated immune response.
- However, its production is downstream of **NF-κB** activation and other inflammatory cascades. **NOD2 dysfunction** does not directly cause **IFN-γ** overactivity through the primary molecular pathway.
*β-catenin*
- **β-catenin** is a key component of the **Wnt signaling pathway** involved in cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation.
- It is not directly affected by **NOD2 dysfunction**. Dysregulation of **β-catenin** is more commonly associated with colorectal adenomas and cancer, not the inflammatory mechanisms of Crohn's disease.
*IL-1β*
- **IL-1β** is a potent pro-inflammatory cytokine that is indeed elevated in **Crohn's disease**.
- However, **IL-1β** is produced **downstream** of **NF-κB** activation. The primary molecular consequence of **NOD2 dysfunction** is the overactivity of **NF-κB**, which then drives production of various cytokines including **IL-1β**.
*IL-10*
- **IL-10** is an **anti-inflammatory cytokine** essential for maintaining intestinal immune homeostasis and suppressing excessive inflammatory responses.
- In Crohn's disease, **IL-10** signaling is often **impaired or deficient** rather than overactive. The question asks about overactivity, making this the opposite of what occurs in the disease.
More Vascular disorders of bowel US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.
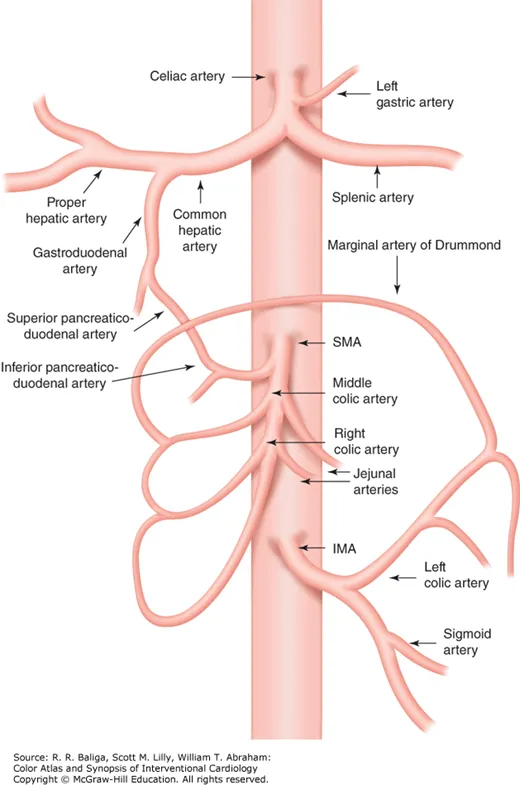 Caption: Anatomy of the celiac, superior mesenteric (SMA), and inferior mesenteric (IMA) arteries and their collateral circulation.
Caption: Anatomy of the celiac, superior mesenteric (SMA), and inferior mesenteric (IMA) arteries and their collateral circulation.