Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease US Medical PG Question 1: A 41-year-old female complains of frequent diarrhea and abdominal pain between meals. Endoscopy reveals a duodenal ulcer distal to the duodenal bulb. CT scan of the abdomen demonstrates a pancreatic mass, and subsequent tissue biopsy of the pancreas reveals a malignant islet cell tumor. Which of the following hormones is likely to be markedly elevated in this patient:
- A. Secretin
- B. Vasoactive intestinal peptide
- C. Cholecystokinin
- D. Gastrin (Correct Answer)
- E. Motilin
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease Explanation: ***Gastrin***
- A pancreatic mass (likely a **gastrinoma**) producing excess **gastrin** leads to Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, characterized by refractory **peptic ulcers** (especially distal to the duodenal bulb) and **diarrhea** due to increased gastric acid.
- The high gastrin levels stimulate parietal cells to secrete an excessive amount of **hydrochloric acid**, overwhelming the neutralizing capacity of the duodenum and causing ulcers.
*Secretin*
- Secretin is released from S cells in the duodenum in response to acid and fatty acids, stimulating **bicarbonate secretion** from the pancreas and bile ducts.
- While secretin can be used diagnostically to confirm gastrinoma (paradoxical increase in gastrin), it is not the primary hormone elevated in this syndrome causing the symptoms.
*Vasoactive intestinal peptide*
- Elevated vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) is characteristic of a **VIPoma**, which causes **profuse watery diarrhea** (pancreatic cholera), hypokalemia, and achlorhydria.
- This patient's symptoms include abdominal pain and duodenal ulcers which are not typical for a VIPoma.
*Cholecystokinin*
- **Cholecystokinin (CCK)** is primarily involved in stimulating gallbladder contraction and pancreatic enzyme secretion in response to fats and proteins.
- While it can be produced by some neuroendocrine tumors, it does not typically cause the constellation of symptoms (refractory duodenal ulcers, severe diarrhea) seen in this patient.
*Motilin*
- Motilin is responsible for initiating the **migrating motor complex** during the interdigestive phase, promoting gut motility.
- While altered motility can contribute to diarrhea, motilin is not typically associated with ulcer formation or pancreatic islet cell tumors causing gastric hypersecretion.
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease US Medical PG Question 2: A 45-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a 1-day history of black, tarry stools. He has also had upper abdominal pain that occurs immediately after eating and a 4.4-kg (9.7-lb) weight loss in the past 6 months. He has no history of major medical illness but drinks 3 beers daily. His only medication is acetaminophen. He is a financial consultant and travels often for work. Physical examination shows pallor and mild epigastric pain. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy shows a bleeding 15-mm ulcer in the antrum of the stomach. Which of the following is the strongest predisposing factor for this patient's condition?
- A. Alcohol consumption
- B. Age above 40 years
- C. Helicobacter pylori infection (Correct Answer)
- D. Acetaminophen use
- E. Work-related stress
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease Explanation: ***Helicobacter pylori infection***
- The patient presents with classic symptoms of a **peptic ulcer disease** including **melena**, **epigastric pain** immediately after eating, and **weight loss**. While not explicitly mentioned, **H. pylori infection** is the most common cause of gastric and duodenal ulcers, especially in the absence of NSAID use.
- The chronic nature of the symptoms and the location of the ulcer in the **antrum** further support H. pylori as the primary predisposing factor, as it leads to mucosal inflammation and damage.
*Alcohol consumption*
- While **chronic alcohol consumption** can irritate the gastric mucosa and contribute to gastritis, it is generally considered a minor risk factor for peptic ulcer disease compared to H. pylori or NSAID use.
- The patient's 3 beers daily is likely not sufficient to directly cause a bleeding gastric ulcer of this magnitude.
*Age above 40 years*
- **Age** itself is not a direct predisposing factor for peptic ulcers, although the incidence of ulcers tends to increase with age.
- This is more likely due to the cumulative exposure to risk factors like H. pylori and NSAIDs over time, rather than age being an independent cause for ulcer formation.
*Acetaminophen use*
- **Acetaminophen (paracetamol)** is generally considered safe for the gastric mucosa and does not cause ulcers in therapeutic doses, unlike NSAIDs.
- It works through a different mechanism of action and does not inhibit cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) in the gastric lining, which is responsible for ulcer formation with NSAIDs.
*Work-related stress*
- While **stress** can exacerbate symptoms of gastrointestinal conditions, it has not been scientifically proven to be a direct cause of peptic ulcer formation.
- The role of psychological stress in ulcer genesis is considered minimal compared to established factors like H. pylori and NSAIDs.
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease US Medical PG Question 3: A 56-year-old woman with a longstanding history of gastroesophageal reflux presents for follow-up evaluation of endoscopically confirmed gastric and duodenal ulcers. Her symptoms have been unresponsive to proton pump inhibitors and histamine receptor antagonists in the past. Results for H. pylori infection are still pending. Which of the following changes is expected in the patient's duodenum, given her peptic ulcer disease?
- A. Proliferation of secretin-releasing S cells
- B. Increased secretions from crypts of Lieberkühn
- C. Increased glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP) release from K cells
- D. Expansion of gastrointestinal lymphoid tissue
- E. Hyperplasia of submucosal bicarbonate-secreting glands (Correct Answer)
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease Explanation: ***Hyperplasia of submucosal bicarbonate-secreting glands***
- The duodenum attempts to protect itself from excessive acid due to gastric and duodenal ulcers by increasing **bicarbonate secretion**.
- **Bicarbonate-secreting glands (Brunner's glands)** in the duodenum undergo hyperplasia to neutralize the acidic chyme entering from the stomach, especially when peptic ulcers are present.
*Proliferation of secretin-releasing S cells*
- While secretin is released in response to acid in the duodenum and stimulates bicarbonate secretion, **S cell proliferation** itself is not a primary expected histological change in peptic ulcer disease.
- The main adaptation is the increased functional capacity of bicarbonate-secreting glands, rather than an increase in the number of secretin-producing cells.
*Increased secretions from crypts of Lieberkühn*
- The **crypts of Lieberkühn** are involved in fluid and electrolyte secretion, as well as cell turnover in the small intestine.
- While they contribute to the intestinal environment, their primary role is not to counteract the high acid load seen in peptic ulcer disease, and their secretions are not predominantly bicarbonate-rich.
*Increased glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP) release from K cells*
- **GIP** is released from K cells in response to glucose and fat in the duodenum, stimulating insulin secretion.
- Its release is primarily linked to nutrient absorption and glucose homeostasis, not a direct compensatory mechanism for acid-induced peptic ulcer disease.
*Expansion of gastrointestinal lymphoid tissue*
- **Gastrointestinal lymphoid tissue (GALT)**, such as Peyer's patches, is involved in immune surveillance in the intestine.
- While chronic inflammation can lead to lymphoid hyperplasia, it is not a direct or primary protective mechanism against acid per se in peptic ulcer disease; rather, it indicates an immune response, which might occur with H. pylori infection but isn't the duodenum's main anti-acid adaptation.
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease US Medical PG Question 4: A 42-year-old man comes to his primary care physician complaining of abdominal pain. He describes intermittent, burning, epigastric pain over the past 4 months. He reports that the pain worsens following meals. He had an upper gastrointestinal endoscopy done 2 months ago that showed a gastric ulcer without evidence of malignancy. The patient was prescribed pantoprazole with minimal improvement in symptoms. He denies nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or melena. The patient has no other medical problems. He had a total knee replacement 3 years ago following a motor vehicle accident for which he took naproxen for 2 months for pain management. He has smoked 1 pack per day since the age of 22 and drinks 1-2 beers several nights a week with dinner. He works as a truck driver, and his diet consists mostly of fast food. His family history is notable for hypertension in his paternal grandfather and coronary artery disease in his mother. On physical examination, the abdomen is soft, nondistended, and mildly tender in the mid-epigastric region. A stool test is positive for Helicobacter pylori antigen. In addition to antibiotic therapy, which of the following is the most likely to decrease the recurrence of the patient's symptoms?
- A. Celecoxib
- B. Low-fat diet
- C. Increase milk consumption
- D. Octreotide
- E. Smoking cessation (Correct Answer)
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease Explanation: ***Smoking cessation***
- **Smoking** is a significant risk factor for **peptic ulcer disease** and has been shown to impair ulcer healing and increase the risk of recurrence.
- Quitting smoking helps to reduce gastric acid secretion, improve mucosal blood flow, and enhance the efficacy of ulcer treatment.
*Celecoxib*
- **Celecoxib** is a **selective COX-2 inhibitor**, which, while less damaging to the gastric mucosa than non-selective NSAIDs like naproxen, can still contribute to ulcer formation or recurrence, especially in patients with a history of ulcers.
- The patient's previous use of naproxen for a short period is not the primary ongoing risk factor, and substituting it with another NSAID without strong indication would likely worsen rather than improve ulcer recurrence.
*Low-fat diet*
- While a healthy diet is beneficial for overall health, there is no direct evidence that a specific **low-fat diet** will significantly decrease the recurrence of peptic ulcers.
- Dietary modifications typically focus on avoiding specific trigger foods that worsen symptoms, but a general low-fat diet isn't a primary intervention for ulcer recurrence.
*Increase milk consumption*
- Historically, **milk** was thought to soothe ulcers, but studies have shown it can actually **stimulate acid secretion** and provide only transient relief, potentially worsening the condition in the long run.
- Therefore, increasing milk consumption would be counterproductive for preventing ulcer recurrence.
*Octreotide*
- **Octreotide** is a synthetic analog of **somatostatin** used primarily to treat conditions involving excessive hormone secretion, such as **variceal bleeding** or neuroendocrine tumors.
- It is not a standard treatment for typical peptic ulcer disease caused by *H. pylori* or other common factors, and would not address the underlying causes of recurrence in this patient.
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease US Medical PG Question 5: A 53-year-old patient presents to his primary care provider with a 1-week history of abdominal pain at night and between meals. He has attempted taking antacids, which help briefly, but then the pain returns. The patient has not noticed any changes to the color of his stool but states that he has been having some loose bowel movements. The patient reports that he has had duodenal ulcers in the past and is concerned that this is a recurrence. On exam, his temperature is 98.4°F (36.9°C), blood pressure is 130/84 mmHg, pulse is 64/min, and respirations are 12/min. The abdomen is soft, nontender, and nondistended in clinic today. A fecal occult blood test is positive for blood in the stool. During outpatient workup, H. pylori stool antigen is negative, endoscopy demonstrates duodenal ulcers, and gastrin levels are elevated after a secretin stimulation test. Which of the following should also be examined in this patient?
- A. Parathyroid hormone (Correct Answer)
- B. Plasma metanephrines
- C. Vasoactive intestinal peptide
- D. Calcitonin
- E. Thyroid stimulating hormone
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease Explanation: ***Parathyroid hormone***
- Elevated gastrin levels after a secretin stimulation test and recurrent duodenal ulcers are characteristic of **Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (ZES)**, which is often associated with **Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 1 (MEN1)**.
- MEN1 involves tumors of the **parathyroid glands**, **pituitary gland**, and **pancreatic islet cells**. Therefore, parathyroid hormone levels should be checked to screen for **primary hyperparathyroidism**, a common component of MEN1.
*Plasma metanephrines*
- **Plasma metanephrines** are used to screen for **pheochromocytoma**, a tumor of the adrenal medulla which is associated with **MEN2**.
- This patient's presentation is consistent with ZES, which is linked to MEN1, not MEN2.
*Vasoactive intestinal peptide*
- **Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP)** levels are elevated in **VIPomas**, which cause **watery diarrhea, hypokalemia, and achlorhydria (WDHA syndrome)**.
- While VIPomas are pancreatic tumors, the patient's symptoms (abdominal pain, duodenal ulcers, elevated gastrin) point towards ZES, not a VIPoma.
*Calcitonin*
- **Calcitonin** is a marker for **medullary thyroid carcinoma**, which is a component of **MEN2**.
- Given the classic presentation of ZES, screening for MEN1 components is appropriate, not MEN2.
*Thyroid stimulating hormone*
- **Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)** is used to assess thyroid function. While thyroid disorders can present with various symptoms, they are not directly linked to ZES or MEN1 in the same way parathyroid disease is.
- There is no specific indication from the patient's symptoms (abdominal pain, ulcers, elevated gastrin) that warrants TSH evaluation as the next step in this context.
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease US Medical PG Question 6: A 45-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of severe abdominal pain for the past 2 hours. He has a 2-year history of burning epigastric pain that gets worse with meals. His pulse is 120/min, respirations are 22/min, and blood pressure is 60/40 mm Hg. Despite appropriate lifesaving measures, he dies. At autopsy, examination shows erosion of the right gastric artery. Perforation of an ulcer in which of the following locations most likely caused this patient's findings?
- A. Anterior duodenum
- B. Posterior duodenum
- C. Lesser curvature of the stomach (Correct Answer)
- D. Greater curvature of the stomach
- E. Fundus of the stomach
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease Explanation: ***Lesser curvature of the stomach***
- Erosion of the **right gastric artery** by a gastric ulcer is characteristic of an ulcer located on the **lesser curvature of the stomach**.
- Ulcers in this location can erode into adjacent blood vessels, leading to **severe hemorrhage** as evidenced by the patient's **hypotension** and subsequent death.
*Anterior duodenum*
- Ulcers in the **anterior duodenum** typically present with **perforation into the peritoneal cavity**, leading to generalized peritonitis, not primarily hemorrhage from a major artery.
- While bleeding can occur, it's usually from smaller duodenal arteries and less commonly involves large arteries like the right gastric artery.
*Posterior duodenum*
- Ulcers in the **posterior duodenum** are known to erode into the **gastroduodenal artery**, leading to massive upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
- This is a distinct arterial involvement compared to the erosion of the right gastric artery.
*Greater curvature of the stomach*
- Ulcers on the **greater curvature of the stomach** are less common and often associated with malignancy.
- If they bleed, it would typically involve branches of the **gastroepiploic arteries**, not the right gastric artery.
*Fundus of the stomach*
- Ulcers in the **fundus** are rare.
- If a vessel were involved, it would typically be a short gastric artery, not the right gastric artery which courses along the lesser curvature.
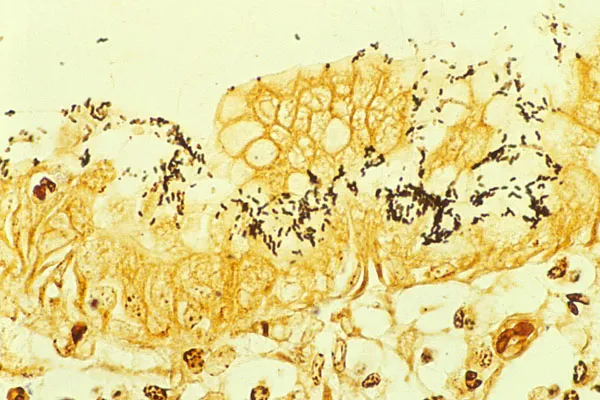
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease US Medical PG Question 7: A 51-year-old man seeks evaluation from his family physician with a complaint of heartburn, which has been gradually increasing over the last 10 years. The heartburn gets worse after eating spicy foods and improves with antacids. The past medical history is benign. He is a security guard and works long hours at night. He admits to smoking 1.5 packs of cigarettes every day. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy reveals several gastric ulcers and regions of inflammation. A biopsy is obtained, which revealed gram-negative bacteria colonized on the surface of the regenerative epithelium of the stomach, as shown in the micrograph below. Which of the following bacterial products is responsible for neutralizing the acidity of the stomach?
- A. Urease (Correct Answer)
- B. Hyaluronidase
- C. Streptokinase
- D. β-lactamase
- E. Prostaglandins
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease Explanation: ***Urease***
- The bacteria described is likely ***Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)***, which produces **urease**.
- **Urease** hydrolyzes urea into **ammonia** and carbon dioxide, with the **ammonia** neutralizing stomach acid locally, allowing the bacteria to survive and colonize the gastric mucosa.
*Hyaluronidase*
- **Hyaluronidase** is an enzyme that breaks down **hyaluronic acid**, part of the **extracellular matrix**, aiding in bacterial invasion.
- While it can be a virulence factor, it does not directly neutralize stomach acidity.
*Streptokinase*
- **Streptokinase** is an enzyme produced by *Streptococcus* species that converts **plasminogen to plasmin**, leading to the dissolution of blood clots.
- It is a virulence factor that helps in tissue invasion but has no role in neutralizing stomach acid.
*β-lactamase*
- **β-lactamase** is an enzyme that breaks down the **β-lactam ring** in antibiotics like penicillin, conferring antibiotic resistance.
- It does not have any function in neutralizing stomach acidity.
*Prostaglandins*
- **Prostaglandins** are signaling molecules produced by **host cells (not bacteria)** that play a role in **mucosal protection** and **inflammation** in the stomach.
- They are not bacterial products and therefore cannot be the answer to this question.
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease US Medical PG Question 8: A 74-year-old man presents to the emergency department with sudden onset of abdominal pain that is most felt around the umbilicus. The pain began 16 hours ago and has no association with meals. He has not been vomiting, but he has had several episodes of bloody loose bowel movements. He was hospitalized 1 week ago for an acute myocardial infarction. He has had diabetes mellitus for 35 years and hypertension for 20 years. He has smoked 15–20 cigarettes per day for the past 40 years. His temperature is 36.9°C (98.4°F), blood pressure is 95/65 mm Hg, and pulse is 95/min. On physical examination, the patient is in severe pain, there is a mild periumbilical tenderness, and a bruit is heard over the epigastric area. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Acute mesenteric ischemia (Correct Answer)
- B. Chronic mesenteric ischemia
- C. Colonic ischemia
- D. Irritable bowel syndrome
- E. Peptic ulcer disease
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease Explanation: ***Acute mesenteric ischemia***
- The sudden onset of severe, **periumbilical abdominal pain** out of proportion to physical exam findings in a patient with significant **atherosclerotic risk factors** (recent MI, diabetes, hypertension, smoking) is highly suggestive of acute mesenteric ischemia.
- **Bloody loose bowel movements** (due to mucosal sloughing) and the presence of an **epigastric bruit** further support the diagnosis of arterial occlusion to the bowel.
*Chronic mesenteric ischemia*
- This typically presents with **postprandial abdominal pain** (abdominal angina) and **weight loss** due to fear of eating.
- The patient's pain is sudden in onset, not associated with meals, and severe, which is characteristic of acute ischemia.
*Colonic ischemia*
- While it can cause bloody diarrhea, colonic ischemia typically presents with pain localized to the **left or right lower quadrants** and is often less severe than the pain described here.
- The patient's risk factors and abrupt, severe periumbilical pain point away from isolated colonic involvement.
*Irritable bowel syndrome*
- This is a **functional gastrointestinal disorder** characterized by chronic abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits (constipation, diarrhea, or both).
- It does not present with sudden, severe pain, bloody stools, or in the context of acute cardiovascular events and associated risk factors.
*Peptic ulcer disease*
- This typically causes **epigastric pain** that can be burning or gnawing, often relieved or exacerbated by food, and may cause melena or hematemesis.
- The patient's severe, diffuse periumbilical pain, bloody stools (not melena), and recent MI are not typical for peptic ulcer disease.
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease US Medical PG Question 9: A 27-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician for evaluation of involuntary weight loss and recurrent abdominal pain. She noticed blood in her stool several times. The medical history is significant for the polycystic ovarian syndrome. The vital signs are as follows: temperature, 38.0°C (100.4°F); heart rate, 78/min; respiratory rate, 14/min; and blood pressure, 110/80 mm Hg. The family history is notable for paternal colon cancer. A colonoscopy is performed and is presented in the picture. What findings are expected?
- A. Crypt abscess (Correct Answer)
- B. Dermatitis herpetiformis
- C. Blunting of villi and crypt hyperplasia
- D. Non-caseating granulomas
- E. Aphthous stomatitis
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease Explanation: ***Crypt abscess***
- The image provided shows **neutrophils infiltrating and filling the crypt lumina**, which are characteristic findings of crypt abscesses seen in **ulcerative colitis**.
- This pathology, combined with the patient's symptoms of **bloody diarrhea**, involuntary weight loss, and recurrent abdominal pain, points towards an inflammatory bowel disease, most consistent with ulcerative colitis.
*Dermatitis herpetiformis*
- This is a **skin manifestation of celiac disease**, presenting as intensely pruritic papules and vesicles, typically on extensor surfaces.
- It is not directly associated with inflammatory bowel disease, especially ulcerative colitis, and is not a histological finding in the colon.
*Blunting of villi and crypt hyperplasia*
- These are characteristic histological findings of **celiac disease** in the **small intestine**.
- The patient's symptoms and the histological image are from the colon, ruling out celiac disease as the primary diagnosis.
*Aphthous stomatitis*
- While **aphthous ulcers** are common extraintestinal manifestations in both Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, it is a clinical finding in the oral cavity, not a histological finding in the colon.
- The question asks for *other findings expected* in the context of the provided colonic histology.
*Non-caseating granulomas*
- **Non-caseating granulomas** are a hallmark histological feature of **Crohn's disease**, not ulcerative colitis.
- The image shown, with widespread crypt abscesses and diffuse inflammatory infiltrate, is more typical of ulcerative colitis rather than Crohn's disease.
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease US Medical PG Question 10: A 59-year-old woman comes to the clinic complaining of an intermittent, gnawing epigastric pain for the past 2 months. The pain is exacerbated with food and has been getting progressively worse. The patient denies any weight changes, nausea, vomiting, cough, or dyspepsia. Medical history is significant for chronic back pain for which she takes ibuprofen. Her father passed at the age of 55 due to pancreatic cancer. Labs were unremarkable except for a mild decrease in hemoglobin. What medication is most appropriate to be switched to from the current medication at this time?
- A. Naproxen
- B. Ranitidine
- C. Aspirin
- D. Acetaminophen
- E. Omeprazole (Correct Answer)
Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease Explanation: ***Omeprazole***
- The patient's symptoms of **gnawing epigastric pain** exacerbated by food, along with a history of chronic ibuprofen use and mild anemia, strongly suggest a **peptic ulcer**.
- **Omeprazole**, a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), is the most effective medication for healing ulcers and preventing their recurrence by reducing gastric acid production.
*Naproxen*
- **Naproxen** is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), similar to ibuprofen, and would likely worsen the patient's symptoms by further inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis necessary for gastric mucosal protection.
- Continuing an NSAID without gastroprotection would increase the risk of ulcer complications, such as bleeding.
*Ranitidine*
- **Ranitidine** is an H2-receptor antagonist, which reduces stomach acid, but it is generally less potent than PPIs like omeprazole for treating and healing ulcers, especially in cases of NSAID-induced gastropathy.
- Its efficacy for advanced or severe peptic ulcer disease is inferior to that of PPIs.
- Note: Ranitidine was withdrawn from the US market in 2020 due to NDMA contamination; alternative H2 blockers include famotidine.
*Aspirin*
- **Aspirin** is an NSAID with significant antiplatelet effects and is well-known to cause and exacerbate peptic ulcers and gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Switching to aspirin would be contraindicated in the presence of strong evidence suggesting active peptic ulcer disease.
*Acetaminophen*
- **Acetaminophen** (paracetamol) is an analgesic that does not have significant anti-inflammatory properties and is not associated with gastric irritation or ulcer formation.
- While it could be used for pain relief, it does not address the underlying issue of peptic ulcer disease or provide gastroprotection, making it an inadequate switch for effective management.
More Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.