GI

On this page
🔥 The Gastrointestinal Battlefield: Your Clinical Command Center
You'll master the gastrointestinal system as a dynamic battlefield where inflammation, infection, obstruction, and ischemia create distinct clinical patterns demanding rapid recognition and precise intervention. This lesson builds your diagnostic framework from pathophysiology through pattern recognition to evidence-based treatment algorithms, teaching you to discriminate between life-threatening emergencies and manageable conditions while understanding how GI disease reverberates across every organ system. You'll develop the clinical instinct to connect a patient's story with underlying mechanisms, construct systematic differentials, and execute treatment decisions with confidence.
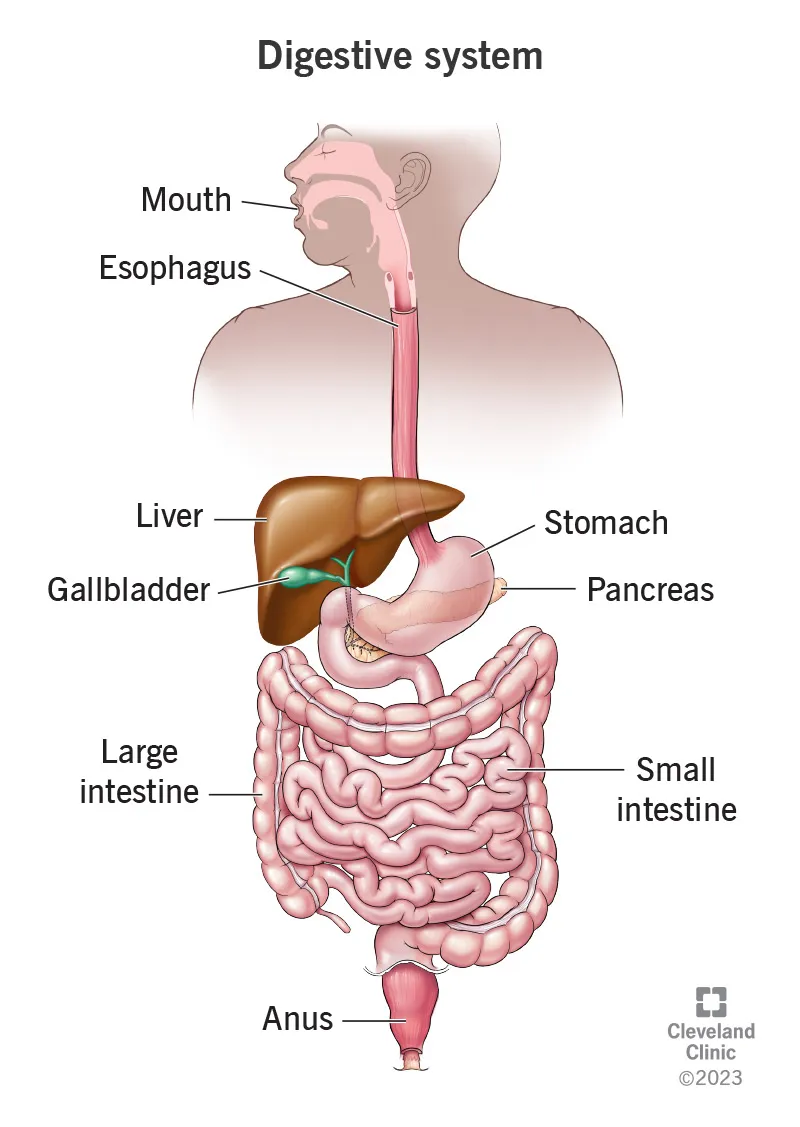
The GI system processes 2-3 liters of fluid daily while maintaining precise pH gradients from 1.5 (stomach) to 8.5 (pancreatic juice). This remarkable engineering feat becomes your diagnostic roadmap when pathology disrupts normal function.
📌 Remember: STOMACH - Secretion (2L/day), Transit (3-4 hours), Osmolality (300 mOsm), Motility (3 waves/min), Acidity (pH 1.5-3.5), Capacity (1.5L max), Hormones (gastrin, ghrelin)
The Anatomical Arsenal: Regional Specialization
-
Upper GI Territory (mouth to ligament of Treitz)
- Esophagus: 25cm muscular conduit with 2 sphincters
- Stomach: 4 anatomical regions with 3 histological zones
- Fundus: gas storage and accommodation
- Body: acid production (1-3L/day)
- Antrum: grinding and gastrin release
- Duodenum: C-shaped, 25cm, 3 parts with ampulla of Vater
-
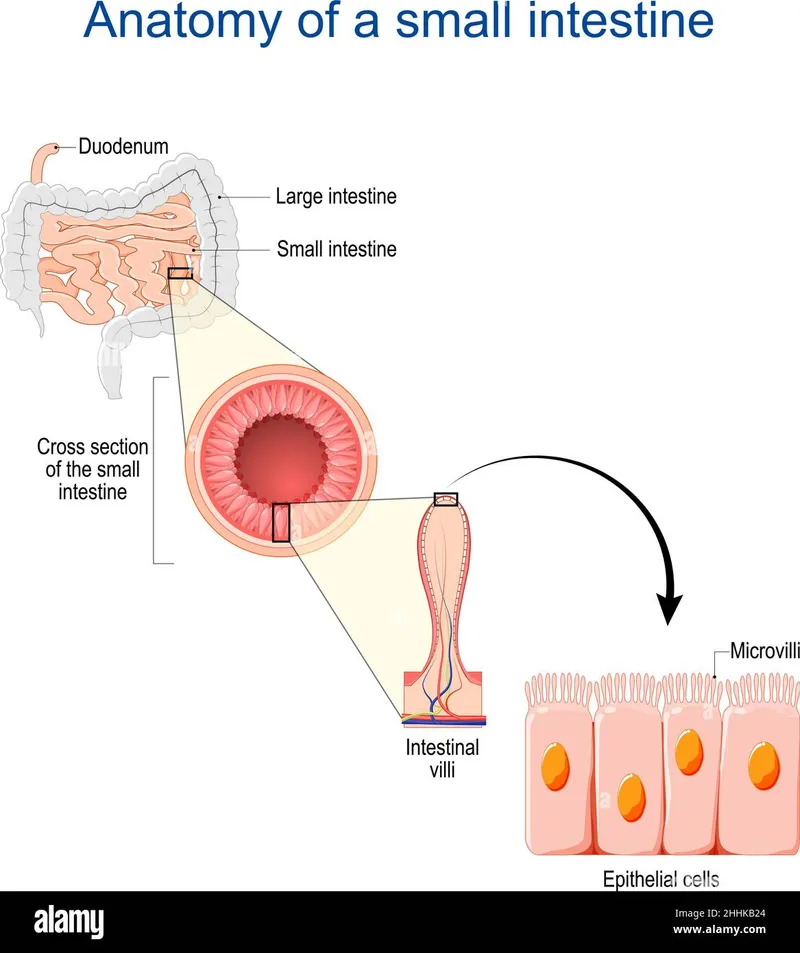
Small Bowel Network (6-7 meters of absorption mastery)
- Jejunum: 2.5m, thick walls, large plicae
- Ileum: 3.5m, thin walls, Peyer's patches
- Surface area: 200m² through villi and microvilli
- 600 villi/cm² creating 30-fold surface amplification
-
Colonic Command Center (1.5m of water reclamation)
- Cecum: 6cm diameter, appendix attachment
- Ascending/transverse/descending: distinct blood supply territories
- Sigmoid: S-shaped, 40cm, highest pressure zone
| Region | Length | Primary Function | Daily Volume | Transit Time | Key Pathology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Esophagus | 25cm | Transport | 1.5L saliva | 8-10 sec | GERD, cancer |
| Stomach | 15cm | Storage/digestion | 2-3L secretion | 3-4 hours | PUD, gastritis |
| Small bowel | 6-7m | Absorption | 8-10L total | 3-5 hours | Obstruction, IBD |
| Colon | 1.5m | Water absorption | 1-2L input | 12-48 hours | Cancer, diverticulitis |
| Rectum | 15cm | Storage/evacuation | 200ml capacity | Variable | Bleeding, masses |
💡 Master This: The ligament of Treitz divides upper from lower GI bleeding. Upper GI sources present with melena (>50ml blood), while lower GI sources cause hematochezia. Coffee-ground emesis indicates gastric acid exposure to blood, confirming upper GI source.
Connect this anatomical foundation through vascular territories to understand ischemic patterns and bleeding presentations that define emergency GI medicine.
🔥 The Gastrointestinal Battlefield: Your Clinical Command Center
⚡ The Inflammatory Cascade: Pathophysiology Command Center
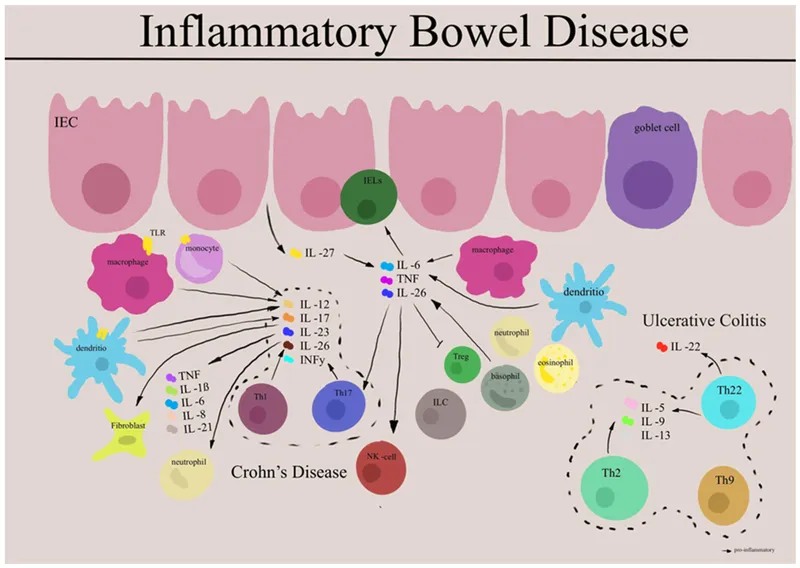
The Inflammatory Hierarchy: From Protection to Destruction
📌 Remember: CYTOKINES - Crohn's (TNF-α, IL-12), Yield (transmural damage), Th1 (dominant response), Obstruction (strictures), Known (skip lesions), Infliximab (anti-TNF therapy), Necrotizing (granulomas), Entire (GI tract), Smoking (worsens)
-
Acute Inflammatory Response (0-6 hours)
- Neutrophil recruitment: peak at 4-6 hours
- Prostaglandin E2: vasodilation and increased permeability
- Complement activation: C3a/C5a chemotaxis
- Normal C3: 90-180 mg/dL
- Inflammatory state: ↑200-300 mg/dL
-
Chronic Inflammatory Transition (days to weeks)
- Macrophage polarization: M1 (pro-inflammatory) vs M2 (healing)
- T-cell differentiation: Th1/Th17 vs Th2/Treg balance
- Tissue remodeling: collagen deposition and fibrosis
- Normal collagen turnover: 300 days
- Inflammatory state: accelerated to 30-60 days
Pathogen-Specific Inflammatory Patterns
| Pathogen | Inflammatory Pattern | Key Cytokines | Clinical Timeline | Diagnostic Markers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H. pylori | Th1/Th17 dominant | TNF-α, IL-1β | Years to decades | CagA+, VacA+ |
| C. difficile | Neutrophilic surge | IL-8, TNF-α | 24-72 hours | Toxin A/B |
| Salmonella | Th1 response | IFN-γ, IL-12 | 6-72 hours | Stool culture |
| Shigella | Epithelial invasion | IL-1β, IL-18 | 1-3 days | Fecal leukocytes |
| Campylobacter | Mixed Th1/Th2 | TNF-α, IL-10 | 2-5 days | Stool PCR |
⭐ Clinical Pearl: CagA-positive H. pylori strains increase gastric cancer risk by 3-fold compared to CagA-negative strains. IL-1β polymorphisms further increase risk by 2-3 fold, explaining why only 1-3% of infected patients develop malignancy.
- Barrier Function Disruption
- Tight junction proteins: claudin-1, occludin, ZO-1
- Normal intestinal permeability: lactulose/mannitol ratio <0.03
- IBD patients: ratio >0.09 indicating leaky gut
- Crohn's disease: transmural barrier loss
- Ulcerative colitis: superficial epithelial damage
💡 Master This: TNF-α drives transmural inflammation in Crohn's disease, explaining why anti-TNF therapy (infliximab, adalimumab) achieves mucosal healing in 60-70% of patients. IL-23/IL-17 axis represents the next therapeutic target with ustekinumab showing 65% clinical response rates.
Connect this inflammatory mastery through immune dysregulation patterns to understand autoimmune manifestations and therapeutic targeting strategies that define modern GI medicine.
⚡ The Inflammatory Cascade: Pathophysiology Command Center
🎯 Pattern Recognition Mastery: The Clinical Detective Framework
The Pain Pattern Matrix: Location Tells the Story
📌 Remember: APPENDIX - Anesthesia (right lower quadrant), Pain (periumbilical → RLQ), Position (flexed hip), Elevation (WBC >10,000), Nausea (early symptom), Defense (McBurney's point), Inflammation (CRP >3mg/dL), X-ray (CT sensitivity 95%)
-
Visceral Pain Territories (poorly localized, deep, cramping)
- Foregut (esophagus to ampulla): epigastric and substernal
- Midgut (small bowel to mid-transverse colon): periumbilical
- Hindgut (distal colon to rectum): suprapubic and left lower quadrant
- Visceral afferents: sympathetic pathways via splanchnic nerves
- Pain threshold: distension >30mmHg in small bowel
-
Somatic Pain Precision (sharp, localized, position-dependent)
- Parietal peritoneum: precise anatomical correlation
- Rebound tenderness: sudden release more painful than pressure
- Guarding: voluntary vs involuntary muscle contraction
- Voluntary guarding: anxiety or mild irritation
- Involuntary guarding: peritoneal inflammation requiring surgery
The Temporal Diagnostic Framework
| Onset Pattern | Duration | Classic Examples | Key Discriminators | Urgency Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sudden (<1 hour) | Minutes | Perforation, torsion | Severe pain (8-10/10) | Immediate |
| Rapid (1-6 hours) | Hours | Appendicitis, cholecystitis | Progressive worsening | Urgent |
| Gradual (6-24 hours) | Days | Bowel obstruction, IBD | Cramping pattern | Semi-urgent |
| Chronic (>weeks) | Weeks-months | Malignancy, chronic pancreatitis | Weight loss, night pain | Elective |
| Intermittent | Recurrent | Biliary colic, IBS | Trigger relationship | Outpatient |
| %%{init: {'flowchart': {'htmlLabels': true}}}%% | ||||
| flowchart TD |
Start["🩺 Abdominal Pain
• Clinical triage• Initial assessment"]
Onset{"📋 Onset Pattern
• Timing of pain• Pattern of onset"}
SuddenNode["⚠️ Perforation
• Acute rupture• Surgical emergency"]
SuddenDX["🔬 CT Contrast
• Check for free air• Confirm rupture"]
HoursNode["🩺 Inflammation
• Evolves over hrs• Localized pain"]
HoursDX["🔬 Labs + Imaging
• WBC and CRP• Focused US or CT"]
DaysNode["🩺 Obstruction
• Gradual onset• Infection risk"]
DaysDX["🔬 Plain Films + CT
• Bowel gas pattern• Transition zone"]
ChronicNode["🩺 Malignancy
• Chronic disease• Slow progression"]
ChronicDX["🔬 Endoscopy
• Direct visual• Tissue biopsy"]
Start --> Onset Onset -->|Sudden| SuddenNode SuddenNode --> SuddenDX
Onset -->|Hours| HoursNode HoursNode --> HoursDX
Onset -->|Days| DaysNode DaysNode --> DaysDX
Onset -->|Chronic| ChronicNode ChronicNode --> ChronicDX
style Start fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8 style Onset fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style SuddenNode fill:#FDF4F3, stroke:#FCE6E4, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#B91C1C style SuddenDX fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style HoursNode fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8 style HoursDX fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style DaysNode fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8 style DaysDX fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style ChronicNode fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8 style ChronicDX fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C
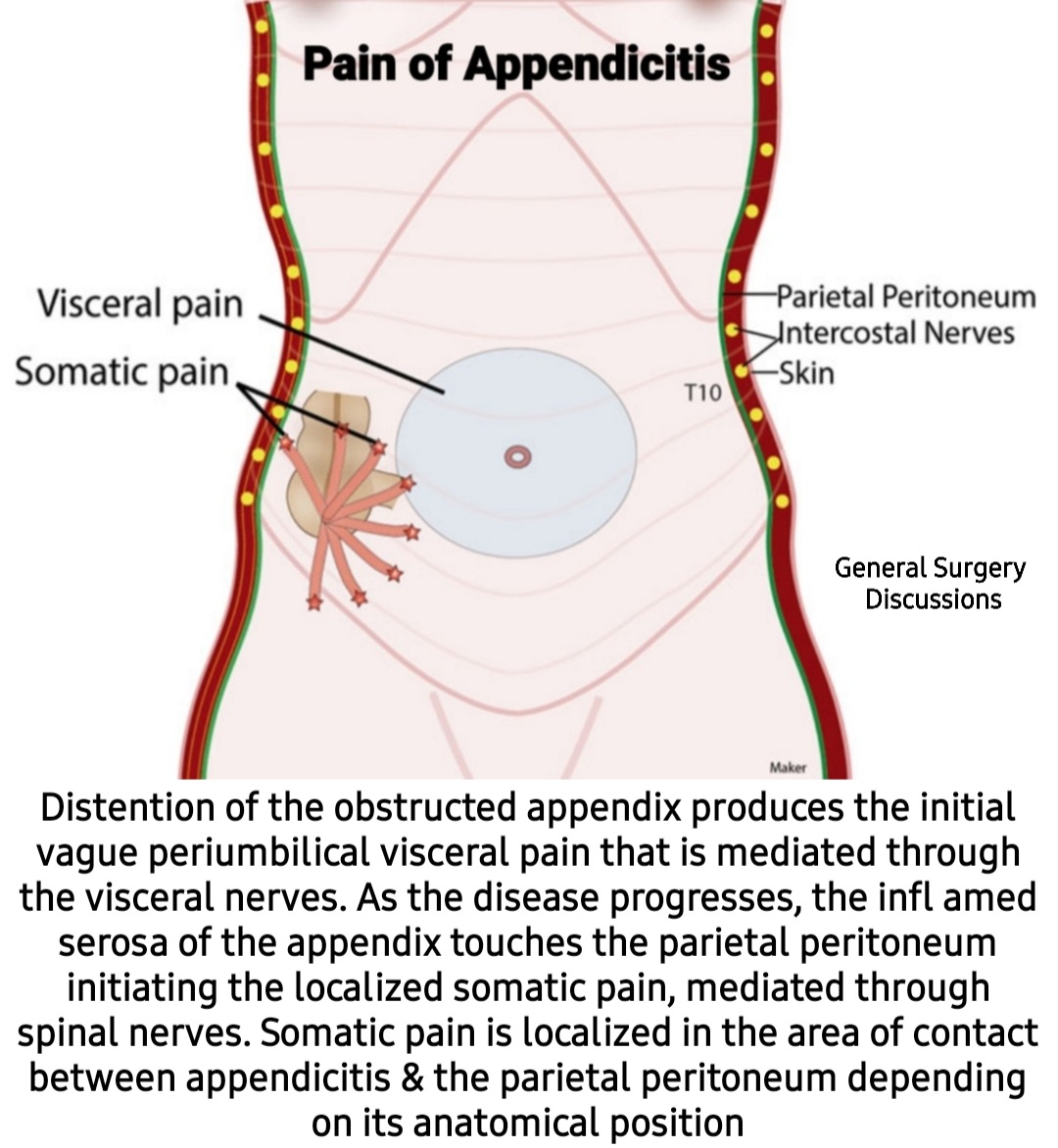
> ⭐ **Clinical Pearl**: **Appendicitis** follows **predictable pain migration** in **75%** of cases: **periumbilical** (visceral) → **right lower quadrant** (somatic). **Atypical presentations** occur in **25%**, especially **pregnant women** (pain shifts **upward**) and **elderly** (minimal pain despite **perforation**).
* **The Obstruction Recognition Pattern**
- **Small bowel obstruction**: **cramping every 4-5 minutes**
- **Large bowel obstruction**: **cramping every 6-8 minutes**
- **Closed-loop obstruction**: **constant severe pain** with **rapid deterioration**
+ **Normal bowel sounds**: **5-35/minute**
+ **Hyperactive sounds**: **>35/minute** in **early obstruction**
+ **Absent sounds**: **late obstruction** or **ileus**
* **The Bleeding Pattern Matrix**
- **Upper GI bleeding**: **hematemesis** or **melena**
+ **Melena**: requires **>50-100ml** blood loss
+ **Hematemesis**: **active bleeding** or **recent** (<6 hours)
- **Lower GI bleeding**: **hematochezia** (bright red blood)
+ **Massive upper GI**: can present as **hematochezia**
+ **Diverticular bleeding**: **painless**, **large volume**
+ **Ischemic colitis**: **cramping** with **bloody diarrhea**
> 💡 **Master This**: **Rovsing's sign** (RLQ pain with LLQ palpation) has **68%** sensitivity for appendicitis, while **psoas sign** (pain with hip extension) suggests **retrocecal appendix**. **Alvarado score ≥7** has **92%** sensitivity, but **CT remains gold standard** with **95%** sensitivity and **99%** specificity.
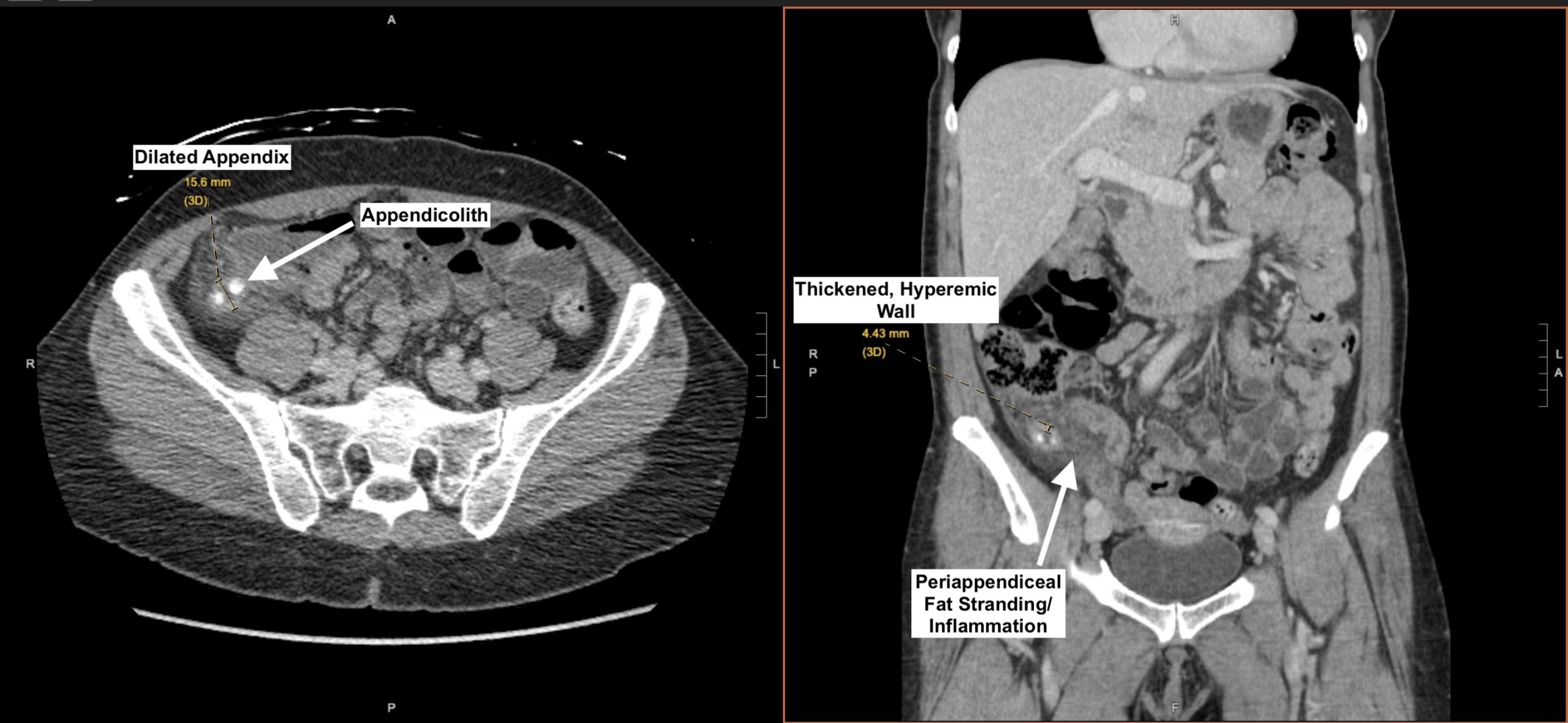
Connect these pattern recognition skills through **differential diagnosis frameworks** to understand **systematic exclusion strategies** that prevent **diagnostic anchoring** and **cognitive bias** in complex presentations.
🎯 Pattern Recognition Mastery: The Clinical Detective Framework
🔬 Systematic Discrimination: The Differential Diagnosis Matrix
The Emergency vs Non-Emergency Matrix
📌 Remember: SURGICAL - Sudden onset, Unstable vitals, Rigidity, Guarding (involuntary), Increasing pain, Constant pain, Age >65, Leukocytosis >15,000
-
Immediate Surgical Emergencies (minutes to hours)
- Perforated viscus: free air on imaging, rigid abdomen
- Mesenteric ischemia: pain out of proportion to exam
- Ruptured AAA: hypotension, pulsatile mass, back pain
- Volvulus: coffee bean sign, closed loop obstruction
- Mortality without surgery: >90% within 24 hours
- Diagnostic delay >6 hours: mortality increases 3-fold
-
Urgent Conditions (hours to days)
- Appendicitis: progressive RLQ pain, fever, leukocytosis
- Cholecystitis: RUQ pain, Murphy's sign, wall thickening >4mm
- Pancreatitis: epigastric pain, lipase >3x normal
- Bowel obstruction: cramping, distension, air-fluid levels
The Inflammatory Marker Discrimination Grid
| Condition | WBC Count | CRP (mg/dL) | Procalcitonin | ESR (mm/hr) | Lactate (mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appendicitis | 10-18,000 | 3-15 | 0.5-2.0 | 20-40 | <2.0 |
| Perforated appendix | >15,000 | >20 | >2.0 | >50 | >4.0 |
| Cholecystitis | 12-16,000 | 5-20 | 0.5-1.5 | 30-60 | <2.0 |
| Pancreatitis | 10-20,000 | 10-30 | 1.0-5.0 | 40-80 | 2-6 |
| Mesenteric ischemia | >20,000 | >25 | >5.0 | >80 | >6.0 |
| %%{init: {'flowchart': {'htmlLabels': true}}}%% | |||||
| flowchart TD |
Start["<b>🩺 Acute Abdomen</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Severe pain onset</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Clinical emergency</span>"]
Stable{"<b>📋 Hemodynamics?</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Check BP and HR</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Assess perfusion</span>"}
Emergency["<b>⚠️ Emergency Surgery</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Rapid fluid resus</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• STAT laparotomy</span>"]
Peritoneal{"<b>📋 Peritoneal Signs?</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Rebound or Guard</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Check rigidity</span>"}
Consult["<b>💊 CT + Surgery</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Contrast imaging</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Surgical consult</span>"]
Markers{"<b>🔬 Inflamm. Markers</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• CRP and WBC count</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Procalcitonin test</span>"}
Infection["<b>🩺 Infect. Process</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Inflam. condition</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• ⬆️ WBC likely</span>"]
Imaging["<b>🔬 Targeted Imaging</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• RUQ US or CT Scan</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Confirm source</span>"]
Functional["<b>🩺 Chronic Cond.</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Non-acute cause</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Functional issue</span>"]
Symptom["<b>💊 Symptom Mgmt</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Outpatient care</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Pain control</span>"]
Start --> Stable
Stable -->|No| Emergency
Stable -->|Yes| Peritoneal
Peritoneal -->|Yes| Consult
Peritoneal -->|No| Markers
Markers -->|Elevated| Infection
Markers -->|Normal| Functional
Infection --> Imaging
Functional --> Symptom
style Start fill:#F7F5FD,stroke:#F0EDFA,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#6B21A8
style Stable fill:#FEF8EC,stroke:#FBECCA,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#854D0E
style Emergency fill:#FDF4F3,stroke:#FCE6E4,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#B91C1C
style Peritoneal fill:#FEF8EC,stroke:#FBECCA,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#854D0E
style Consult fill:#F1FCF5,stroke:#BEF4D8,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#166534
style Markers fill:#FFF7ED,stroke:#FFEED5,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#C2410C
style Infection fill:#F7F5FD,stroke:#F0EDFA,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#6B21A8
style Imaging fill:#FFF7ED,stroke:#FFEED5,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#C2410C
style Functional fill:#F7F5FD,stroke:#F0EDFA,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#6B21A8
style Symptom fill:#F1FCF5,stroke:#BEF4D8,stroke-width:1.5px,rx:12,ry:12,color:#166534
> ⭐ **Clinical Pearl**: **Lactate >4.0 mmol/L** in abdominal pain suggests **mesenteric ischemia** or **perforated viscus** with **85%** sensitivity. **Normal lactate** doesn't exclude **early ischemia**, but **rising lactate** over **2-4 hours** predicts **bowel necrosis** requiring **immediate surgery**.
### Age-Stratified Differential Patterns
* **Pediatric Patterns** (<18 years)
- **Most common**: **appendicitis** (**7/1000** annual incidence)
- **Intussusception**: **peak 6-24 months**, **currant jelly stools**
- **Meckel's diverticulitis**: **rule of 2s** - **2%** population, **2 feet** from ileocecal valve
+ **Appendicitis in children**: **perforation rate 30-40%** (vs **15-20%** adults)
+ **Diagnostic accuracy**: **lower in <5 years** due to **communication barriers**
* **Adult Patterns** (18-65 years)
- **Gender differences**: **cholecystitis** (**F>M**, **4:1**), **appendicitis** (**M>F**, **1.3:1**)
- **Reproductive age females**: **ovarian pathology**, **ectopic pregnancy**
- **IBD onset**: **bimodal peaks** at **20-30** and **50-60 years**
* **Elderly Patterns** (>65 years)
- **Diverticulitis**: **prevalence >60%** in Western populations
- **Mesenteric ischemia**: **mortality >60%** if **diagnosis delayed**
- **Malignancy**: **colorectal cancer** **incidence 50x higher** than **<50 years**
+ **Atypical presentations**: **minimal pain** despite **severe pathology**
+ **Delayed diagnosis**: **common** due to **blunted inflammatory response**
> 💡 **Master This**: **Right lower quadrant pain** in **reproductive-age females** requires **pregnancy test** and **pelvic exam**. **Ovarian torsion** presents with **sudden onset**, **nausea**, and **adnexal mass**. **Ectopic pregnancy** shows **β-hCG** levels that **fail to double** every **48 hours** (normal doubling time).
* **The Imaging Decision Matrix**
- **CT with IV contrast**: **first-line** for **suspected appendicitis** (>30 years)
- **Ultrasound**: **first-line** for **cholecystitis**, **pregnancy-related pain**
- **MRI**: **pregnant patients**, **young patients** (radiation concern)
- **Plain films**: **bowel obstruction screening**, **perforation** (upright CXR)
+ **CT sensitivity**: **appendicitis 95%**, **cholecystitis 90%**, **pancreatitis 85%**
+ **Ultrasound sensitivity**: **cholecystitis 95%**, **appendicitis 75%** (operator-dependent)
Connect this systematic discrimination through **evidence-based treatment algorithms** to understand **therapeutic decision-making** that optimizes **patient outcomes** while **minimizing complications** and **healthcare costs**.
🔬 Systematic Discrimination: The Differential Diagnosis Matrix
⚖️ Treatment Algorithm Mastery: Evidence-Based Decision Trees
The Antibiotic Stewardship Matrix
📌 Remember: ANTIBIOTICS - Appropriate spectrum, Narrow when possible, Timing critical, IV to PO switch, Biomarkers guide duration, Infection source control, Organ function monitoring, Toxicity awareness, Immune status consideration, Culture-directed therapy, Stewardship principles
- Empiric Antibiotic Selection by Syndrome
- Uncomplicated appendicitis: cefoxitin 2g q6h or ertapenem 1g daily
- Complicated appendicitis: piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5g q6h + metronidazole
- C. difficile colitis: vancomycin 125mg PO q6h (first-line)
- Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: ceftriaxone 2g daily
- Duration: uncomplicated 5-7 days, complicated 7-14 days
- De-escalation: culture results at 48-72 hours
| Condition | First-Line Antibiotic | Duration | Success Rate | Alternative |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uncomplicated appendicitis | Cefoxitin 2g q6h | 5-7 days | 95% | Ertapenem 1g daily |
| Complicated appendicitis | Pip-tazo 4.5g q6h | 7-14 days | 85% | Meropenem 1g q8h |
| Diverticulitis (mild) | Cipro + metronidazole | 7-10 days | 90% | Amox-clav 875mg BID |
| C. diff (severe) | Vancomycin 125mg q6h | 10-14 days | 80% | Fidaxomicin 200mg BID |
| SBP | Ceftriaxone 2g daily | 5 days | 85% | Cefotaxime 2g q8h |
The Surgical Decision Framework
-
Appendicitis Management Algorithm
- Uncomplicated appendicitis: laparoscopic appendectomy within 24 hours
- Complicated appendicitis: antibiotics first vs immediate surgery
- Appendiceal mass: conservative management → interval appendectomy at 6-8 weeks
- Laparoscopic success rate: >95% for uncomplicated cases
- Conversion to open: 5-15% (higher with perforation)
- Negative appendectomy rate: <5% with CT guidance
-
IBD Treatment Escalation Ladder
- Step 1: 5-ASA compounds (mesalamine 2.4-4.8g daily)
- Step 2: corticosteroids (prednisone 40-60mg daily)
- Step 3: immunomodulators (azathioprine 2-2.5mg/kg)
- Step 4: biologics (anti-TNF, anti-integrin, anti-IL23)
- Mucosal healing rates: anti-TNF 60-70%, vedolizumab 40-50%
- Surgery-free survival: biologics improve by 30-40% at 5 years
💡 Master This: Anti-TNF therapy (infliximab, adalimumab) achieves clinical remission in 60-70% of moderate-to-severe IBD patients. Combination therapy with immunomodulators reduces immunogenicity and improves durability. Therapeutic drug monitoring optimizes dosing and predicts response.
The Emergency Surgery Criteria
-
Absolute Surgical Indications (no delay acceptable)
- Free perforation: pneumoperitoneum on imaging
- Hemodynamic instability: SBP <90 despite fluid resuscitation
- Peritonitis: diffuse abdominal rigidity
- Complete bowel obstruction: closed-loop or strangulation
- Time to surgery: <6 hours for optimal outcomes
- Delay >12 hours: mortality increases 2-3 fold
-
Relative Surgical Indications (timing flexible)
- Recurrent diverticulitis: >2 episodes in <50 years
- Complicated appendicitis: abscess >5cm or phlegmon
- IBD complications: stricture, fistula, dysplasia
- GI bleeding: >6 units PRBC or rebleeding
Connect this treatment mastery through multi-system integration to understand complex patient management where comorbidities, drug interactions, and physiological reserves influence therapeutic decision-making and outcome prediction.
⚖️ Treatment Algorithm Mastery: Evidence-Based Decision Trees
🔗 Multi-System Integration: The Physiological Network
The Hepato-GI Integration Matrix
📌 Remember: LIVER-GI - Lactate clearance, Insulin resistance, Vitamin synthesis, Enzyme production, RBC destruction, Glucose homeostasis, Immune function
-
Portal Circulation Dynamics
- Portal pressure: normal 5-10 mmHg, hypertension >12 mmHg
- Hepatic blood flow: 1500 mL/min (25% of cardiac output)
- Dual blood supply: hepatic artery 25%, portal vein 75%
- Portal hypertension consequences: varices, ascites, splenomegaly
- HVPG >12 mmHg: variceal bleeding risk increases 10-fold
- Child-Pugh Class C: surgical mortality >50%
-
Drug Metabolism Integration
- First-pass metabolism: oral bioavailability reduced in liver disease
- Cytochrome P450: CYP3A4 metabolizes 50% of medications
- Protein binding: albumin <2.5 g/dL increases free drug levels
- Warfarin sensitivity: INR prolongation in synthetic dysfunction
- Benzodiazepine accumulation: hepatic encephalopathy risk
- Opioid metabolism: morphine preferred over meperidine
| System | Normal Function | GI Disease Impact | Clinical Consequence | Monitoring Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatic | Synthesis, detox | Cirrhosis, fatty liver | Coagulopathy, encephalopathy | INR, bilirubin |
| Renal | Filtration, balance | Hepatorenal syndrome | Fluid retention, electrolyte shifts | Creatinine, BUN |
| Cardiac | Perfusion, preload | High-output failure | Decreased surgical tolerance | Echo, BNP |
| Pulmonary | Gas exchange | Hepatopulmonary syndrome | Hypoxemia, shunting | ABG, A-a gradient |
| Hematologic | Coagulation | Hypersplenism | Bleeding, thrombocytopenia | CBC, PT/PTT |
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Hepatorenal syndrome develops in 40% of cirrhotic patients with ascites. Type 1 HRS (rapid onset) has 80% mortality without liver transplantation. Terlipressin + albumin improves renal function in 60% of patients.
The Cardio-GI Risk Stratification
- Perioperative Cardiac Risk Assessment
- Revised Cardiac Risk Index: 6 predictors of major cardiac events
- High-risk surgery: emergency, aortic, prolonged procedures
- Functional capacity: <4 METs increases perioperative risk
- RCRI ≥3: cardiac event rate >5%
- Emergency surgery: risk increases 2-3 fold
- Age >70: baseline risk doubles
- Fluid Management in Multi-Organ Dysfunction
- Goal-directed therapy: stroke volume optimization
- Restrictive vs liberal: restrictive reduces complications
- Colloid vs crystalloid: balanced crystalloids preferred
- Fluid overload: increases anastomotic leak risk by 2-fold
- Optimal CVP: 8-12 mmHg (higher in mechanical ventilation)
- Lactate clearance: >20% in 6 hours predicts good outcomes
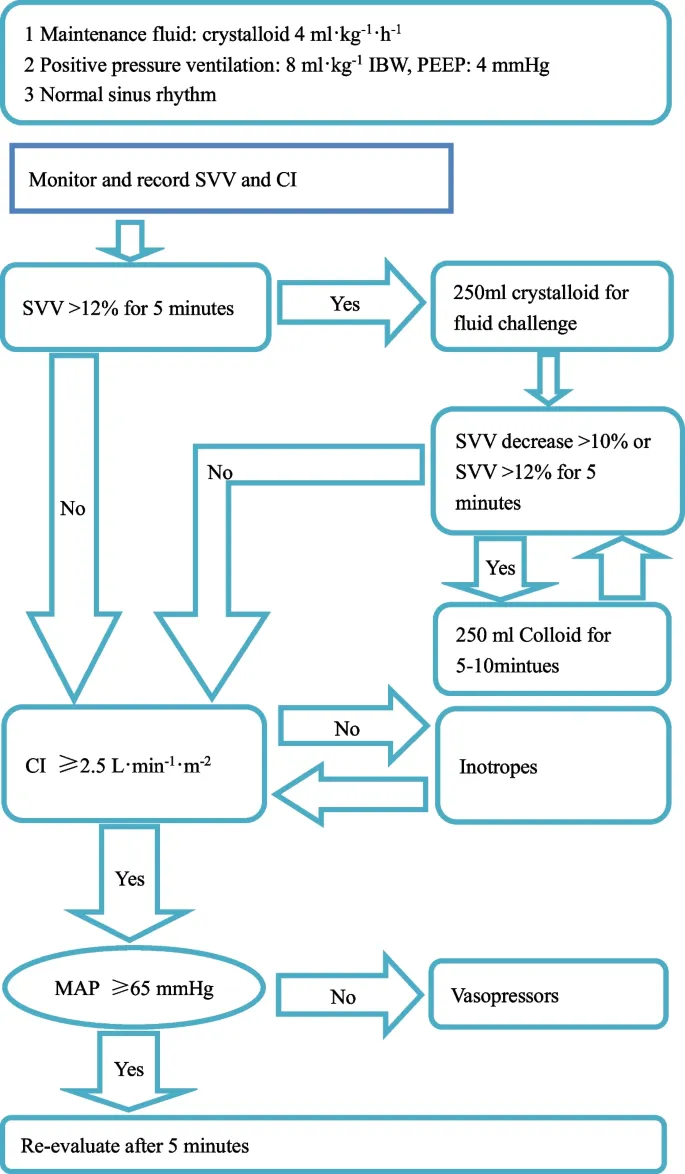
💡 Master This: Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) protocols reduce length of stay by 2-3 days and complications by 30-50%. Key elements include preoperative carbohydrate loading, multimodal analgesia, early feeding, and goal-directed fluid therapy.
The Immune-GI Interaction Network
-
Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (GALT)
- 70% of immune system resides in GI tract
- Peyer's patches: 200-300 in small intestine
- IgA production: 3-5 grams daily (most abundant antibody)
- Microbiome diversity: >1000 species in healthy gut
- Dysbiosis: antibiotic-associated changes persist months
- Probiotics: limited evidence for routine use
-
Stress Response Integration
- Sympathetic activation: splanchnic vasoconstriction
- HPA axis: cortisol affects gut permeability
- Inflammatory mediators: systemic vs local responses
- Stress ulcers: pH <4 for >18 hours increases bleeding risk
- PPI prophylaxis: reduces bleeding but increases pneumonia risk
- H2 blockers: alternative with lower infection risk
Connect this multi-system mastery through rapid clinical reference tools to understand point-of-care decision-making that integrates complex pathophysiology into practical patient management strategies.
🔗 Multi-System Integration: The Physiological Network
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Your Rapid-Fire Reference
The Essential Numbers Arsenal
📌 Remember: GI-CRITICAL - GI bleeding (>100mL/hr), Inflammation (CRP >10), Creatinine (>2.0 renal), Respiration (RR >24), Infection (WBC >15K), Temperature (>38.5°C), Ischemia (lactate >4), Cardiac (HR >120), Acidity (pH <7.3), Liver (INR >1.5)
- Hemodynamic Thresholds
- Class I shock: <15% blood loss, HR <100, normal BP
- Class II shock: 15-30% loss, HR 100-120, narrow pulse pressure
- Class III shock: 30-40% loss, HR 120-140, hypotension
- Class IV shock: >40% loss, HR >140, severe hypotension
- Massive transfusion: >10 units PRBC in 24 hours
- 1:1:1 ratio: PRBC:FFP:platelets for massive bleeding
| Clinical Scenario | Critical Threshold | Immediate Action | Success Metric | Time Frame |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper GI bleed | HR >100 or SBP <100 | 2 large-bore IVs + type & cross | Hemostasis 85% | <30 minutes |
| Appendicitis | WBC >15,000 + fever | CT + surgical consult | Negative appendectomy <5% | <4 hours |
| Bowel obstruction | Lactate >4 + distension | NGT + IV fluids + surgery | Mortality <10% | <6 hours |
| C. diff colitis | WBC >15K + creatinine ↑ | Vancomycin 125mg q6h | Clinical response 80% | 48-72 hours |
| Mesenteric ischemia | Pain >> exam + lactate >6 | CTA + immediate surgery | Survival 60% | <2 hours |
| %%{init: {'flowchart': {'htmlLabels': true}}}%% | ||||
| flowchart TD |
Start["🚨 GI Emergency
• Initial triage• Acute presentation"]
Hemo["📋 Hemodynamics
• Assess stability• BP and HR check"]
Resusc["⚠️ Resuscitation
• ICU / Stat care• Stabilize patient"]
Access["💊 IV Access
• 2 Large bore IVs• Blood products"]
Endo["🩺 Endoscopy/OR
• Surgery consult• Rapid control"]
Pain["📋 Pain Severity
• Numerical scale• Physical exam"]
Imaging["🔬 Imaging/Surg
• CT or X-ray scan• Surgery consult"]
Defin["🩺 Definitive Rx
• Targeted therapy• Fix pathology"]
Labs["🔬 Labs / Obs
• CBC and Chem-7• Monitor status"]
Disch["✅ Disposition
• Discharge home• Hospital admit"]
Start --> Hemo Hemo -->|Unstable| Resusc Hemo -->|Stable| Pain
Resusc --> Access Access --> Endo
Pain -->|Severe| Imaging Imaging --> Defin
Pain -->|Moderate| Labs Labs --> Disch
style Start fill:#FDF4F3, stroke:#FCE6E4, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#B91C1C style Hemo fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style Resusc fill:#FDF4F3, stroke:#FCE6E4, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#B91C1C style Access fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style Endo fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8 style Pain fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style Imaging fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style Defin fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8 style Labs fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style Disch fill:#F6F5F5, stroke:#E7E6E6, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#525252
> ⭐ **Clinical Pearl**: **Rockall score >8** predicts **40%** mortality in **upper GI bleeding**. **Glasgow-Blatchford score ≥12** identifies patients requiring **urgent intervention**. **Pre-endoscopy PPI** reduces **stigmata of bleeding** but **doesn't improve mortality**.
### The Rapid Diagnosis Matrix
* **The 5-Minute Assessment Protocol**
- **Vital signs**: **HR**, **BP**, **temp**, **O2 sat**
- **Pain assessment**: **location**, **quality**, **radiation**, **timing**
- **Physical exam**: **inspection**, **auscultation**, **palpation**, **percussion**
- **Key questions**: **onset**, **progression**, **associated symptoms**, **medications**
+ **Red flags**: **hemodynamic instability**, **peritoneal signs**, **age >65**
+ **Yellow flags**: **immunosuppression**, **anticoagulation**, **prior surgery**
* **Point-of-Care Ultrasound Applications**
- **FAST exam**: **free fluid** detection in **trauma**
- **Gallbladder**: **wall thickening >4mm**, **pericholecystic fluid**
- **Appendix**: **non-compressible**, **>6mm diameter**
- **Aorta**: **diameter >3cm** suggests **aneurysm**
+ **POCUS sensitivity**: **appendicitis 90%**, **cholecystitis 95%**
+ **Learning curve**: **50-100 scans** for **competency**
> 💡 **Master This**: **Lactate >4 mmol/L** with **abdominal pain** has **85%** sensitivity for **mesenteric ischemia**. **D-dimer >500** supports **diagnosis** but **lacks specificity**. **CTA** remains **gold standard** with **96%** sensitivity for **acute mesenteric ischemia**.
### The Treatment Quick-Reference
* **Emergency Drug Dosing**
- **Octreotide**: **50 mcg bolus** → **50 mcg/hr** for **variceal bleeding**
- **Pantoprazole**: **80mg bolus** → **8mg/hr** for **upper GI bleeding**
- **Vasopressin**: **0.2-0.4 units/min** for **lower GI bleeding**
- **Terlipressin**: **1-2mg q4-6h** for **hepatorenal syndrome**
+ **Octreotide duration**: **3-5 days** maximum
+ **PPI high-dose**: **reduces rebleeding** by **30%**
* **Surgical Timing Decisions**
- **Immediate** (<1 hour): **free perforation**, **exsanguination**
- **Urgent** (<6 hours): **appendicitis**, **cholecystitis**, **obstruction**
- **Semi-urgent** (<24 hours): **diverticulitis**, **IBD complications**
- **Elective** (days-weeks): **malignancy**, **chronic conditions**
This clinical arsenal transforms **theoretical knowledge** into **practical expertise**, enabling **rapid assessment**, **accurate diagnosis**, and **optimal treatment** of **complex GI emergencies** across **all clinical settings**.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Your Rapid-Fire Reference
Practice Questions: GI
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 3-year-old recent immigrant is diagnosed with primary tuberculosis. Her body produces T cells that do not have IL-12 receptors on their surface, and she is noted to have impaired development of Th1 T-helper cells. Which of the following cytokines would benefit this patient?













