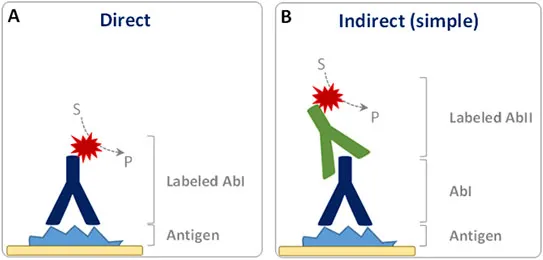
Immunohistochemistry US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Immunohistochemistry. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Immunohistochemistry US Medical PG Question 1: An investigator studying the molecular characteristics of various malignant cell lines collects tissue samples from several families with a known mutation in the TP53 tumor suppressor gene. Immunohistochemical testing performed on one of the cell samples stains positive for desmin. This sample was most likely obtained from which of the following neoplasms?
- A. Squamous cell carcinoma
- B. Rhabdomyosarcoma (Correct Answer)
- C. Prostate cancer
- D. Endometrial carcinoma
- E. Melanoma
Immunohistochemistry Explanation: ***Rhabdomyosarcoma***
- **Desmin** is an intermediate filament present in **muscle cells**, and its positive staining is a definitive marker for tumors of muscle origin
- A **rhabdomyosarcoma** is a malignant tumor of **skeletal muscle** differentiation, thus explaining the positive desmin staining.
*Squamous cell carcinoma*
- **Squamous cell carcinomas** are epithelial tumors that typically stain positive for **cytokeratin**, not desmin, as they originate from epithelial cells.
- They are characterized by features such as **intercellular bridges** and **keratinization**.
*Prostate cancer*
- **Prostate cancer** is an adenocarcinoma, meaning it's derived from glandular epithelial cells, and would stain positive for markers like **PSA (prostate-specific antigen)**, not desmin.
- This tumor type is characterized by glandular differentiation.
*Endometrial carcinoma*
- **Endometrial carcinomas** are adenocarcinomas of the uterine lining, derived from glandular epithelial cells, and would express **cytokeratins**, not desmin.
- Histologically, they show glandular structures and atypical endometrial cells.
*Melanoma*
- **Melanomas** are malignant tumors of melanocytes and would stain positive for markers such as **S-100**, **HMB-45**, and **Mart-1**, not desmin.
- These tumors originate from neural crest cells and are not muscle-derived.
Immunohistochemistry US Medical PG Question 2: A patient is infected with a pathogen and produces many antibodies to many antigens associated with that pathogen via Th cell-activated B cells. This takes place in the germinal center of the lymphoid tissues. If the same patient is later re-infected with the same pathogen, the immune system will respond with a much stronger response, producing antibodies with greater specificity for that pathogen in a shorter amount of time. What is the term for this process that allows the B cells to produce antibodies specific to that antigen?
- A. Affinity maturation (Correct Answer)
- B. Avidity
- C. Immunoglobulin class switching
- D. T cell negative selection
- E. T cell positive selection
Immunohistochemistry Explanation: ***Affinity maturation***
- **Affinity maturation** is the process by which B cells produce antibodies with progressively higher affinity for an antigen over the course of an immune response, allowing for a more specific and potent response upon re-exposure.
- This process occurs primarily in the **germinal centers** of lymphoid organs, driven by somatic hypermutation of antibody genes and subsequent selection of B cells exhibiting increased binding affinity.
*Avidity*
- **Avidity** refers to the overall strength of binding between a multivalent antibody and a multivalent antigen, taking into account the combined strength of multiple binding sites.
- While high avidity is a characteristic of effective antibody responses, it describes the strength of binding rather than the *process* of improving specificity and affinity over time.
*Immunoglobulin class switching*
- **Immunoglobulin class switching** (or isotype switching) is the process by which B cells change the class of antibody they produce (e.g., from IgM to IgG, IgA, or IgE), while retaining the same antigen specificity.
- This process diversifies the effector functions of antibodies but does not directly describe the *improvement in antigen binding affinity* or specificity.
*T cell negative selection*
- **T cell negative selection** is a critical process in the thymus where T cells that react too strongly to self-antigens are eliminated or inactivated to prevent autoimmunity.
- This process is fundamental for establishing central tolerance in T cells and is separate from the B cell-mediated improvement in antibody specificity described.
*T cell positive selection*
- **T cell positive selection** also occurs in the thymus, ensuring that only T cells capable of recognizing self-MHC molecules survive and mature.
- This process is essential for T cell function (MHC restriction) but is distinct from the described mechanism of B cell antibody refinement.
Immunohistochemistry US Medical PG Question 3: A 65-year-old man with a 40-pack-year smoking history presents with hemoptysis and a persistent cough. Chest CT shows a 3.5 cm centrally located mass in the right main bronchus. Positron emission tomography confirms a malignant nodule. Bronchoscopy with transbronchial biopsy is performed and a specimen sample of the nodule is sent for frozen section analysis. The tissue sample is most likely to show which of the following tumor types?
- A. Carcinoid tumor
- B. Metastasis of colorectal cancer
- C. Small cell lung carcinoma
- D. Large cell carcinoma
- E. Squamous cell carcinoma (Correct Answer)
Immunohistochemistry Explanation: ***Squamous cell carcinoma***
- This is the most likely diagnosis given the **central location** in the main bronchus, **heavy smoking history**, and presentation with **hemoptysis**.
- **Squamous cell carcinoma** accounts for 25-30% of lung cancers and characteristically arises in **central/proximal airways**, making it readily accessible by **bronchoscopy**.
- Histologically, it shows **keratin pearls** and **intercellular bridges** on biopsy.
- The **central endobronchial location** and ability to obtain tissue via transbronchial biopsy strongly favor squamous cell over peripheral tumors.
*Carcinoid tumor*
- **Carcinoid tumors** are **neuroendocrine tumors** that can present as central endobronchial masses and cause hemoptysis.
- However, they are typically **slow-growing** with more indolent presentation, and PET scans show **variable uptake** (often less intense than aggressive carcinomas).
- They represent only **1-2% of lung tumors** and occur more commonly in **younger, non-smoking patients**.
*Metastasis of colorectal cancer*
- While lung is a common site for **colorectal metastases**, these typically present as **multiple peripheral nodules** rather than a solitary central endobronchial mass.
- The clinical presentation strongly suggests **primary lung cancer** rather than metastatic disease.
- Without history of colorectal cancer, this is unlikely.
*Small cell lung carcinoma*
- **Small cell lung carcinoma** (SCLC) represents 15% of lung cancers and typically presents as a **large central mass** with early mediastinal involvement.
- However, SCLC is usually **too extensive at presentation** for transbronchial biopsy alone and often requires mediastinoscopy or CT-guided biopsy.
- Histology shows **small cells with scant cytoplasm**, **salt-and-pepper chromatin**, and **oat-cell morphology**.
- While possible, the single accessible endobronchial mass is more characteristic of squamous cell.
*Large cell carcinoma*
- **Large cell carcinoma** is a **diagnosis of exclusion** made when tumors lack features of adenocarcinoma, squamous cell, or small cell differentiation.
- It typically presents as **large peripheral masses** rather than central endobronchial lesions.
- It represents only **10% of lung cancers** and is less common than squamous cell carcinoma in this clinical scenario.
Immunohistochemistry US Medical PG Question 4: During an experiment, the immunophenotypes of different cells in a sample are determined. The cells are labeled with fluorescent antibodies specific to surface proteins, and a laser is then focused on the samples. The intensity of fluorescence created by the laser beam is then plotted on a scatter plot. The result shows most of the cells in the sample to be positive for CD8 surface protein. Which of the following cell types is most likely represented in this sample?
- A. Mature cytotoxic T lymphocytes (Correct Answer)
- B. Activated regulatory T lymphocytes
- C. Inactive B lymphocytes
- D. Dendritic cells
- E. Mature helper T lymphocytes
Immunohistochemistry Explanation: ***Mature cytotoxic T lymphocytes***
- **CD8** is a characteristic surface marker for **cytotoxic T lymphocytes**, indicating their immune function in directly killing infected or cancerous cells.
- The "mature" designation implies they have fully developed and are ready to exert their effector functions.
*Activated regulatory T lymphocytes*
- **Regulatory T lymphocytes** are typically identified by the expression of **CD4** and **CD25**, along with the intracellular transcription factor **FOXP3**, not CD8.
- Their primary role is immune suppression, not direct cytotoxicity.
*Inactive B lymphocytes*
- **B lymphocytes** are characterized by the expression of **CD19**, **CD20**, and surface immunoglobulins, which are distinct from the CD8 marker.
- Their main function is antibody production.
*Dendritic cells*
- **Dendritic cells** are primarily **antigen-presenting cells** and are identified by markers such as **CD11c** and **MHC class II molecules**, not CD8.
- While some rare subsets of dendritic cells can express CD8α, it is not their predominant or defining marker.
*Mature helper T lymphocytes*
- **Helper T lymphocytes** are defined by the expression of **CD4** and play a crucial role in coordinating the immune response.
- They do not express CD8, which is characteristic of cytotoxic T cells.
Immunohistochemistry US Medical PG Question 5: A 43-year-old woman presents to your clinic for the evaluation of an abnormal skin lesion on her forearm. The patient is worried because her mother passed away from melanoma. You believe that the lesion warrants biopsy for further evaluation for possible melanoma. Your patient is concerned about her risk for malignant disease. What is the most important prognostic factor of melanoma?
- A. Depth of invasion of atypical cells (Correct Answer)
- B. S-100 tumor marker present
- C. Evolution of lesion over time
- D. Age at presentation
- E. Level of irregularity of the borders
Immunohistochemistry Explanation: ***Depth of invasion of atypical cells***
- The **Breslow depth**, which measures the vertical thickness of the melanoma from the granular layer of the epidermis to the deepest part of the tumor, is the **single most important prognostic factor** for localized melanoma.
- A greater depth of invasion correlates directly with a higher risk of **metastasis** and a poorer prognosis due to increased likelihood of reaching dermal lymphatics or blood vessels.
*S-100 tumor marker present*
- While **S-100 protein** is a marker expressed in melanoma cells and can be used to detect metastatic disease (e.g., in lymph nodes), its mere presence does not serve as the primary prognostic indicator for the primary lesion itself.
- S-100 reflects the presence of melanoma cells but does not provide information about the **depth or biological aggressiveness** of the initial tumor.
*Evolution of lesion over time*
- The **evolution or change** in a lesion (e.g., in size, shape, color, new symptoms) is a crucial diagnostic criterion for identifying suspicious lesions for biopsy.
- While important for diagnosis, it is not a direct prognostic factor once melanoma is confirmed; the **pathological features** after biopsy, particularly depth, determine prognosis.
*Age at presentation*
- **Age** can influence treatment decisions and overall health status, but it is not the most important independent prognostic factor for melanoma.
- Prognosis is primarily driven by tumor-specific characteristics rather than the patient's age.
*Level of irregularity of the borders*
- **Border irregularity** is one of the ABCDE criteria (Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variation, Diameter >6mm, Evolving) used to identify suspicious pigmented lesions.
- It is a diagnostic indicator that warrants further investigation but does not independently determine **prognosis** as definitively as the Breslow depth after biopsy.
Immunohistochemistry US Medical PG Question 6: An investigator is processing a blood sample from a human subject. A reagent is added to the sample and the solution is heated to break the hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs. This solution is then cooled to allow artificial DNA primers in the solution to attach to the separated strands of the sample DNA molecules. An enzyme derived from the thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus is added and the solution is reheated. These steps are repeated multiple times until the aim of the test is achieved. The investigator most likely used which of the following laboratory procedures on the test sample?
- A. Northern blot
- B. Western blot
- C. Polymerase chain reaction (Correct Answer)
- D. Immunohistochemistry
- E. Fluorescence in-situ hybridization
Immunohistochemistry Explanation: ***Polymerase chain reaction***
- The process described, including **denaturation** by heating, **annealing** of primers upon cooling, and **extension** by a heat-stable DNA polymerase (like from *Thermus aquaticus*), are the hallmark steps of **Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)**.
- PCR is used to **amplify specific DNA sequences** exponentially, making it possible to detect and analyze even minute amounts of genetic material.
*Northern blot*
- **Northern blot** is a laboratory technique used to detect specific **RNA molecules** among a mixture of RNA. It involves electrophoresis, transfer to a membrane, and hybridization with a probe.
- It does not involve repetitive heating, cooling, or the use of DNA primers and heat-stable polymerases for amplification.
*Western blot*
- **Western blot** is a widely used analytical technique in molecular biology and immunogenetics to detect specific **proteins** in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract.
- This method separates proteins by size using gel electrophoresis, transfers them to a membrane, and then detects the target protein using specific antibodies. It does not involve DNA denaturation or amplification.
*Immunohistochemistry*
- **Immunohistochemistry (IHC)** is a histological technique that uses the principle of specific antibody-antigen binding to **detect specific antigens (proteins) in cells or tissues**.
- It involves staining tissues with antibodies labeled with a chromogenic reporter or fluorophore to visualize the location and distribution of target proteins within preserved tissue sections.
*Fluorescence in-situ hybridization*
- **Fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH)** is a cytogenetic technique used to detect and **localize specific DNA or RNA sequences within cells or tissues** using fluorescent probes that bind to parts of the chromosome.
- While it involves hybridization, it is primarily for visualizing genetic material within its cellular context, not for amplifying DNA like PCR.
Immunohistochemistry US Medical PG Question 7: A group of scientists is studying the mechanism by which the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine confers immunity. They observe that during inoculation of test subjects, certain viral proteins are taken up by the organism's antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and presented on major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules. Which of the following is the correct term for the process that the scientists are observing in this inoculation?
- A. Priming of CD4+ T cells
- B. Ubiquitination
- C. Endogenous antigen presentation
- D. Cross-presentation (Correct Answer)
- E. Adhesion
Immunohistochemistry Explanation: ***Cross-presentation***
- **Cross-presentation** occurs when an **antigen-presenting cell (APC)**, typically a dendritic cell, takes up **exogenous antigens** (like viral proteins from a vaccine) and presents them on **MHC class I molecules** to activate **CD8+ T cells**.
- This process is crucial for generating a strong **cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) response** against viruses and tumors when the pathogen does not directly infect the APC.
*Priming of CD4+ T cells*
- **Priming of CD4+ T cells** involves the presentation of antigens on **MHC class II molecules**, which are typically loaded with **exogenous antigens** that have been internalized by the APC.
- The scenario describes antigen presentation on **MHC class I**, which points towards activation of CD8+ T cells, not CD4+ T cells directly.
*Ubiquitination*
- **Ubiquitination** is a process where the protein **ubiquitin** is attached to another protein, often marking it for degradation by the **proteasome**.
- While ubiquitination is involved in preparing **endogenous antigens** for MHC class I presentation, it is a *step within* the broader antigen processing pathway, not the overall process of an APC presenting exogenous antigen on MHC class I.
*Endogenous antigen presentation*
- **Endogenous antigen presentation** refers to the presentation of **peptides derived from proteins synthesized within the cell** (e.g., viral proteins in an infected cell) on **MHC class I molecules**.
- In this scenario, the viral proteins are *inoculated* into the organism, meaning they are initially **exogenous** to the APC before uptake, making cross-presentation the more accurate description.
*Adhesion*
- **Adhesion** refers to the process by which cells attach to other cells or to the extracellular matrix, often mediated by **adhesion molecules**.
- While cell-cell interactions are important in immune responses, "adhesion" does not describe the specific mechanism of an APC taking up an antigen and presenting it on MHC class I.
Immunohistochemistry US Medical PG Question 8: A 72-year-old man goes to his primary care provider for a checkup after some blood work showed lymphocytosis 3 months ago. He says he has been feeling a bit more tired lately but doesn’t complain of any other symptoms. Past medical history is significant for hypertension and hyperlipidemia. He takes lisinopril, hydrochlorothiazide, and atorvastatin. Additionally, his right hip was replaced three years ago due to osteoarthritis. Family history is noncontributory. He drinks socially and does not smoke. Today, he has a heart rate of 95/min, respiratory rate of 17/min, blood pressure of 135/85 mm Hg, and temperature of 36.8°C (98.2°F). On physical exam, he looks well. His heartbeat has a regular rate and rhythm and lungs that are clear to auscultation bilaterally. Additionally, he has mild lymphadenopathy of his cervical lymph nodes. A complete blood count with differential shows the following:
Leukocyte count 5,000/mm3
Red blood cell count 3.1 million/mm3
Hemoglobin 11.0 g/dL
MCV 95 um3
MCH 29 pg/cell
Platelet count 150,000/mm3
Neutrophils 40%
Lymphocytes 40%
Monocytes 5%
A specimen is sent for flow cytometry that shows a population that is CD 5, 19, 20, 23 positive. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (Correct Answer)
- B. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura
- C. Aplastic anemia
- D. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- E. Tuberculosis
Immunohistochemistry Explanation: ***Chronic lymphocytic leukemia***
- The patient presents with mild **lymphadenopathy**, a **history of lymphocytosis**, and a **flow cytometry** showing cells positive for **CD5, CD19, CD20, and CD23**, which is pathognomonic for **CLL**.
- While the total leukocyte count is within normal limits due to the absolute neutrophil decrease, the persistent lymphocytosis and characteristic immunophenotype are highly indicative of CLL.
*Immune thrombocytopenic purpura*
- This condition is characterized by **isolated thrombocytopenia** caused by autoantibody-mediated platelet destruction, which is not supported by the patient's normal platelet count (150,000/mm3).
- While it can cause fatigue, it doesn't explain the lymphocytosis or the specific **CD marker profile**.
*Aplastic anemia*
- Aplastic anemia involves **pancytopenia** (decreased red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets) due to bone marrow failure, which is not consistent with the patient's normal-range leukocyte and platelet counts.
- The patient's presentation with lymphocytosis and lymphadenopathy further makes this diagnosis unlikely.
*Acute lymphoblastic leukemia*
- **ALL** typically presents with symptoms related to **bone marrow failure** (anemia, thrombocytopenia, infections) and often very **high blast counts** in the peripheral blood and bone marrow.
- While it involves lymphocytes, the specific **CD5/19/20/23 co-expression** is characteristic of CLL, and ALL usually involves more aggressive symptoms and a different immunophenotype.
*Tuberculosis*
- **Tuberculosis** is an infectious disease that can cause **lymphadenopathy** and systemic symptoms like fatigue, but it is typically associated with a **caseating granulomatous inflammation** and is diagnosed via cultures or PCR rather than flow cytometry.
- It would not explain the specific **B-cell lymphocytosis** with the described immunophenotype.
Immunohistochemistry US Medical PG Question 9: A 5-year-old male is brought to his pediatrician after recurrent, prolonged upper respiratory infections over a period of several months. Physical exam reveals petechiae on the patient's legs and arms. Laboratory studies show hemoglobin: 10 g/dL, platelet count: 35,000/mm^3, leukocyte count: 6,600/mm^3. A bone marrow aspiration shows an abundance of lymphoblasts indicative of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Positive immunostaining for which of the following would support a diagnosis of precursor B-cell leukemia?
- A. CD2, CD8
- B. TdT, HER-2
- C. CD4, CD5
- D. CD19, CD10 (Correct Answer)
- E. CD30, CD15
Immunohistochemistry Explanation: ***CD19, CD10***
- **CD19** is a pan B-cell marker, expressed on almost all B-lymphocytes from early pre-B-cells through mature B-cells. Its presence, along with **CD10**, is highly characteristic of **precursor B-cell ALL (B-ALL)**.
- **CD10**, also known as common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CALLA), is typically expressed on **early B-cell progenitors** and is a reliable marker for differentiating B-ALL from other leukemias.
*CD2, CD8*
- **CD2** and **CD8** are markers primarily associated with **T-lymphocytes**. While CD2 is a pan T-cell marker, CD8 identifies cytotoxic T cells.
- Their positivity would suggest a **T-cell ALL (T-ALL)**, not the precursor B-cell type indicated by the clinical scenario.
*TdT, HER-2*
- **Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)** is an enzyme found in immature lymphocytes (both B and T cells) and is positive in most ALL cases, but it is not specific for B-cell lineage.
- **HER-2** is an oncogene and a growth factor receptor overexpressed in certain solid tumors (especially breast cancer) but is not a marker used for leukemia classification.
*CD4, CD5*
- **CD4** is a marker for helper T cells, while **CD5** is expressed on a subset of T cells and some B-cell malignancies (e.g., chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma).
- These markers are primarily associated with **T-cell lineages** and would not support a diagnosis of precursor B-cell leukemia in this context.
*CD30, CD15*
- **CD30** and **CD15** are classical markers for **Hodgkin lymphoma** (specifically the classical type).
- Their presence would point towards a lymphoproliferative disorder different from acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Immunohistochemistry US Medical PG Question 10: An 11-month-old boy presents with a scaly erythematous rash on his back for the past 2 days. No significant past medical history. Family history is significant for the fact that the patient’s parents are first-degree cousins. In addition, his older sibling had similar symptoms and was diagnosed with a rare unknown skin disorder. On physical examination, whitish granulomatous plaques are present in the oral mucosa, which exhibit a tendency to ulcerate, as well as a scaly erythematous rash on his back. A complete blood count reveals that the patient is anemic. A plain radiograph of the skull shows lytic bone lesions. Which of the following immunohistochemical markers, if positive, would confirm the diagnosis in this patient?
- A. CD30
- B. CD1a (Correct Answer)
- C. CD15
- D. CD21
- E. CD40L
Immunohistochemistry Explanation: ***CD1a***
- The constellation of **scaly erythematous rash**, **oral granulomatous plaques**, **lytic bone lesions**, and **anemia** in an infant, especially with a history of **consanguinity** and an affected sibling, strongly suggests **Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH)**.
- **CD1a** is a classic and definitive **immunohistochemical marker** for Langerhans cells, which are the neoplastic cells in LCH.
*CD30*
- **CD30** is typically associated with **anaplastic large cell lymphoma** and **Hodgkin lymphoma**, and is not a marker for Langerhans cell histiocytosis.
- While some skin lesions can be present in these lymphomas, the overall clinical picture, particularly the lytic bone lesions and oral plaques, is inconsistent with CD30-positive lymphomas.
*CD15*
- **CD15** is primarily a marker for **neutrophils** and is also expressed in **Reed-Sternberg cells** of Hodgkin lymphoma.
- It does not characterize Langerhans cells and would not confirm the diagnosis of Langerhans cell histiocytosis.
*CD21*
- **CD21** is a marker for **B-lymphocytes**, follicular dendritic cells, and some epithelial cells, involved in complement receptor function.
- It is not expressed on Langerhans cells and is not relevant to the diagnosis of Langerhans cell histiocytosis.
*CD40L (CD154)*
- **CD40L (CD154)** is a **T-cell surface protein** crucial for T-cell help to B cells and macrophage activation. Its deficiency causes **X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome**.
- It is not a marker used for the direct diagnosis of Langerhans cell histiocytosis.
More Immunohistochemistry US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.