Environmental pathology US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Environmental pathology. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Environmental pathology US Medical PG Question 1: A 45-year-old male reports several years of asbestos exposure while working in the construction industry. He reports smoking 2 packs of cigarettes per day for over 20 years. Smoking and asbestos exposure increase the incidence of which of the following diseases?
- A. Emphysema
- B. Malignant pulmonary mesothelioma
- C. Multiple myeloma
- D. Bronchogenic carcinoma (Correct Answer)
- E. Chronic bronchitis
Environmental pathology Explanation: ***Bronchogenic carcinoma***
- **Smoking** is the leading cause of **bronchogenic carcinoma**, and **asbestos exposure** significantly *multiplies* its risk, rather than simply adding to it.
- This synergistic effect means that smokers exposed to asbestos have a **much higher incidence** of lung cancer compared to those with either exposure alone.
*Emphysema*
- Primarily linked to **smoking** and chronic exposure to irritants, but asbestos exposure does not significantly increase its incidence.
- While both smoking and asbestos can cause pulmonary issues, their primary mechanisms for emphysema are distinct.
*Malignant pulmonary mesothelioma*
- **Malignant mesothelioma** is strongly associated with **asbestos exposure**, but its incidence is *not significantly increased* by smoking.
- Smoking is a risk factor for lung cancer, but not a primary risk factor for mesothelioma itself.
*Multiple myeloma*
- This is a **hematologic malignancy** (cancer of plasma cells) and has no established link with either **smoking** or **asbestos exposure**.
- Its risk factors are largely genetic and related to other environmental factors, but not directly linked to respiratory toxins.
*Chronic bronchitis*
- **Chronic bronchitis** is primarily caused by **smoking** and exposure to environmental pollutants.
- While asbestos exposure can cause lung damage, it doesn't directly or significantly increase the incidence of chronic bronchitis.
Environmental pathology US Medical PG Question 2: A 44-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after sustaining high-voltage electrical burns over his left upper limb. On examination, the tip of his left middle finger is charred, and there are 2nd-degree burns involving the whole of the left upper limb. Radial and ulnar pulses are strong, and there are no signs of compartment syndrome. An exit wound is present over the sole of his right foot. His temperature is 37.7°C (99.8°F), the blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, the pulse is 105/min, and the respiratory rate is 26/min. His urine is reddish-brown, and urine output is 0.3 mL/kg/h. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 13.9 g/dL
Hematocrit 33%
Leukocyte count 11,111/mm3
Serum
Creatinine 4.6 mg/dL
Creatine phosphokinase 15,230 U/L
K+ 7.7 mEq/L
Na+ 143 mEq/L
What is the most likely mechanism for this patient's renal failure?
- A. Septicemia leading to acute pyelonephritis
- B. Rhabdomyolysis, myoglobinuria, and renal injury (Correct Answer)
- C. Direct visceral electrical injury to the kidneys
- D. Fluid and electrolyte loss and hypovolemia
- E. Volume overload because of excessive intravenous fluid resuscitation
Environmental pathology Explanation: ***Rhabdomyolysis, myoglobinuria, and renal injury***
- The high **creatine phosphokinase (CPK)** level of 15,230 U/L indicates significant **muscle damage** (**rhabdomyolysis**) from the high-voltage electrical burn.
- **Myoglobin** released from damaged muscle is **nephrotoxic** and precipitates in the renal tubules, leading to **acute kidney injury**, evidenced by **reddish-brown urine** and elevated **creatinine (4.6 mg/dL)**.
*Septicemia leading to acute pyelonephritis*
- While burns can lead to infection, there are no specific signs of **septicemia** or **pyelonephritis** (e.g., fever, flank pain) in the provided information.
- The patient's **hyperkalemia** and elevated **CPK** are not typical findings for pyelonephritis.
*Direct visceral electrical injury to the kidneys*
- **Direct electrical injury** to internal organs such as the kidneys is **rare** unless the electrical current traverses the abdomen.
- The entry and exit wounds (left upper limb and right foot) suggest a current path that is **less likely** to directly involve the kidneys.
*Fluid and electrolyte loss and hypovolemia*
- Although **burn injuries** can cause significant fluid loss, this patient's **blood pressure (110/70 mm Hg)** and **heart rate (105/min)** do not strongly suggest severe **hypovolemic shock**.
- The **hemoglobin (19.9 g/dL)** and **hematocrit (33%)** also do not directly point to severe acute fluid loss as the primary cause of renal failure in the context of other findings.
*Volume overload because of excessive intravenous fluid resuscitation*
- The patient's **low urine output (0.3 mL/kg/h)** suggests **renal failure**, not fluid overload.
- There is no mention of **fluid resuscitation** being administered, making this an unlikely cause of the current presentation.
Environmental pathology US Medical PG Question 3: A neonate suffering from neonatal respiratory distress syndrome is given supplemental oxygen. Which of the following is a possible consequence of oxygen therapy in this patient?
- A. Anosmia
- B. Atelectasis
- C. Atopy
- D. Blindness (Correct Answer)
- E. Cardiac anomalies
Environmental pathology Explanation: ***Blindness***
- High concentrations of supplemental oxygen in neonates, particularly premature infants, can lead to **retinopathy of prematurity (ROP)**.
- ROP involves abnormal growth of blood vessels in the retina, which can detach the retina and result in **permanent blindness**.
*Anosmia*
- **Anosmia** is the loss of the sense of smell, typically caused by nasal polyps, head trauma, or certain viral infections.
- It is **not a recognized complication** of oxygen therapy in neonates.
*Atelectasis*
- **Atelectasis** refers to the collapse of lung tissue, which can be caused by bronchial obstruction or hypoventilation.
- While underlying respiratory distress syndrome can predispose to atelectasis, oxygen therapy itself typically aims to improve ventilation and **does not directly cause atelectasis**.
*Atopy*
- **Atopy** is a genetic predisposition to developing allergic diseases such as asthma, eczema, and allergic rhinitis.
- It is **unrelated to oxygen therapy** and is determined by genetic factors and environmental exposures.
*Cardiac anomalies*
- **Cardiac anomalies** (congenital heart defects) are structural problems in the heart present at birth, resulting from abnormal fetal development.
- They are **not a consequence of oxygen therapy** given postpartum; oxygen therapy may be used to manage their symptoms.
Environmental pathology US Medical PG Question 4: A 65-year-old man presents to the emergency department for shortness of breath. He was at home working on his car when he suddenly felt very short of breath, which failed to improve with rest. He states he was working with various chemicals and inhalants while trying to replace a broken piece in the engine. The patient was brought in by paramedics and is currently on 100% O2 via nasal cannula. The patient has a 52 pack-year smoking history and drinks 2 to 3 alcoholic drinks every night. He has a past medical history of asthma but admits to not having seen a physician since high school. His temperature is 98.2°F (36.8°C), blood pressure is 157/108 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, respirations are 29/min, and oxygen saturation is 77%. Physical exam demonstrates tachycardia with a systolic murmur heard best along the right upper sternal border. Breath sounds are diminished over the right upper lobe. Bilateral lower extremity pitting edema is noted. Which of the following best describes the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Fe3+ hemoglobin in circulating red blood cells
- B. Severe bronchoconstriction
- C. Pulmonary edema secondary to decreased cardiac output
- D. Ischemia of the myocardium
- E. Rupture of an emphysematous bleb (Correct Answer)
Environmental pathology Explanation: ***Rupture of an emphysematous bleb***
- The patient's significant **smoking history** (52 pack-years), acute onset of shortness of breath while straining (working on car), diminished breath sounds over the right upper lobe, and very low oxygen saturation of 77% strongly suggest a **spontaneous pneumothorax** likely due to a ruptured emphysematous bleb.
- The history of asthma, while a confounder, does not explain the sudden, severe onset and unilateral diminished breath sounds in the context of extensive smoking.
*Fe3+ hemoglobin in circulating red blood cells*
- This describes **methemoglobinemia**, which can cause dyspnea and hypoxemia. However, it's typically associated with exposure to specific oxidizing agents (e.g., nitrates, certain local anesthetics), which are not explicitly mentioned as the chemicals the patient was using.
- While it causes **cyanosis** and low oxygen saturation, the unilateral diminished breath sounds and acute onset with strain point away from this being the primary diagnosis.
*Severe bronchoconstriction*
- While the patient has a history of asthma, the **sudden, severe onset of shortness of breath**, very low oxygen saturation, and unilateral diminished breath sounds are not typical for an acute asthma exacerbation alone.
- Asthma exacerbations usually involve **bilateral wheezing** and diffuse airway narrowing, not localized diminished breath sounds.
*Pulmonary edema secondary to decreased cardiac output*
- Pulmonary edema would typically present with **bilateral crackles** on examination and is commonly associated with left ventricular dysfunction or acute myocardial infarction, which is not clearly indicated.
- The unilateral diminished breath sounds are inconsistent with a diffuse process like pulmonary edema.
*Ischemia of the myocardium*
- While the patient's age, smoking history, and hypertension put him at risk for cardiac events, the sudden onset of dyspnea, **unilateral diminished breath sounds**, and severe hypoxemia are more indicative of a pulmonary mechanical issue than acute myocardial ischemia.
- Although angina can present as dyspnea, the physical exam findings of diminished breath sounds point to a primary lung pathology.
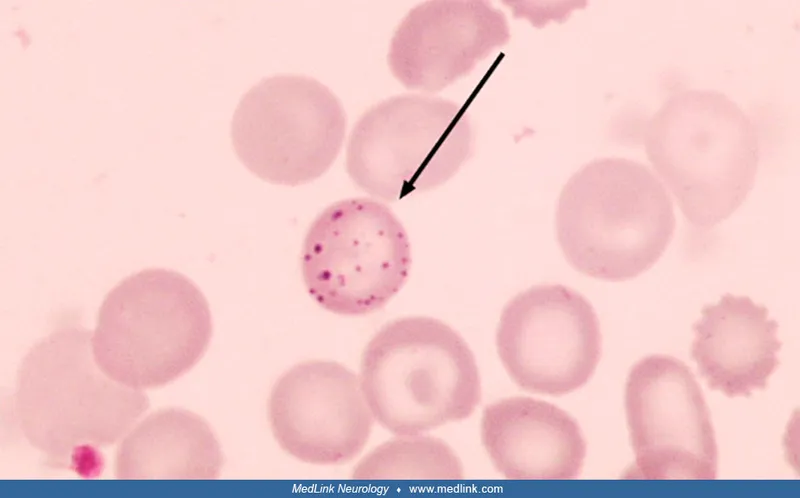
Environmental pathology US Medical PG Question 5: A 46-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 6-week history of fatigue and cramping abdominal pain. He works at a gun range. Examination shows pale conjunctivae and gingival hyperpigmentation. There is weakness when extending the left wrist against resistance. Further evaluation of this patient is most likely to show which of the following?
- A. Beta‑2 microglobulin in urine
- B. Septal thickening on chest x-ray
- C. Basophilic stippling of erythrocytes (Correct Answer)
- D. White bands across the nails
- E. Increased total iron binding capacity
Environmental pathology Explanation: ***Basophilic stippling of erythrocytes***
- This patient's symptoms (fatigue, anemic conjunctivae, abdominal pain, gingival hyperpigmentation, wrist drop) and occupational exposure (gun range) are classic signs of **lead poisoning**.
- **Basophilic stippling** is a characteristic finding on a peripheral blood smear in lead poisoning, resulting from the aggregation of ribosomal RNA due to impaired heme synthesis.
*Beta‑2 microglobulin in urine*
- **Beta-2 microglobulinuria** is typically associated with **renal tubular damage** or increased cell turnover (e.g., multiple myeloma), not directly with lead poisoning.
- While lead toxicity can affect the kidneys in the long term, this is not the most direct or common initial diagnostic finding for acute or subacute lead poisoning.
*Septal thickening on chest x-ray*
- **Septal thickening** on a chest x-ray suggests conditions like **pulmonary fibrosis**, **interstitial lung disease**, or cardiac conditions causing fluid overload.
- It is not a typical manifestation or diagnostic feature of lead poisoning.
*White bands across the nails*
- **White bands across the nails**, known as **Mees' lines**, are associated with **arsenic poisoning**, not lead poisoning.
- The clinical picture presented strongly points away from arsenic toxicity.
*Increased total iron binding capacity*
- **Increased total iron binding capacity (TIBC)** is characteristic of **iron deficiency anemia**, as the body attempts to make more transferrin to capture what little iron is available.
- In lead poisoning, TIBC is usually normal or decreased, as lead inhibits heme synthesis, leading to anemia but not necessarily iron deficiency.
Environmental pathology US Medical PG Question 6: A 33-year-old pilot is transported to the emergency department after she was involved in a cargo plane crash during a military training exercise in South Korea. She is conscious but confused. She has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. Physical examination shows numerous lacerations and ecchymoses over the face, trunk, and upper extremities. The lower extremities are cool to the touch. There is continued bleeding despite the application of firm pressure to the sites of injury. The first physiologic response to develop in this patient was most likely which of the following?
- A. Increased respiratory rate
- B. Increased capillary refill time
- C. Decreased systolic blood pressure
- D. Decreased urine output
- E. Increased heart rate (Correct Answer)
Environmental pathology Explanation: ***Increased heart rate***
- **Tachycardia** is often the first physiological response to **hypovolemia** (due to hemorrhage, such as that stemming from multiple lacerations). The heart attempts to compensate for reduced circulating blood volume by increasing its pumping rate.
- This sympathetic nervous system response aims to maintain **cardiac output** and tissue perfusion as **blood pressure** and **venous return** start to fall.
*Increased respiratory rate*
- An increased respiratory rate, or **tachypnea**, typically occurs later as the body attempts to compensate for decreased oxygen delivery and metabolic acidosis that can result from sustained hypoperfusion and shock.
- While significant, it usually follows the initial hemodynamic adjustments of the heart.
*Increased capillary refill time*
- **Increased capillary refill time** indicates impaired peripheral perfusion and is a sign of more significant **hypovolemic shock**, often occurring after initial compensatory mechanisms have been activated.
- This reflects **peripheral vasoconstriction**, a later compensatory mechanism, rather than the very first physiological response.
*Decreased systolic blood pressure*
- **Decreased systolic blood pressure** (hypotension) is a later sign of shock and indicates a failure of the body's compensatory mechanisms to maintain adequate blood volume and perfusion, often reflecting a loss of more than 30-40% of blood volume.
- The body initially tries to maintain blood pressure through increased heart rate and vasoconstriction before it drops.
*Decreased urine output*
- **Decreased urine output** (oliguria) is a renal compensatory mechanism in response to reduced renal perfusion and increased antidiuretic hormone (ADH) release, aiming to conserve fluid.
- This response takes time to manifest and is not typically the very first physiological change after acute blood loss.
Environmental pathology US Medical PG Question 7: A 7-month old boy, born to immigrant parents from Greece, presents to the hospital with pallor and abdominal distention. His parents note that they recently moved into an old apartment building and have been concerned about their son's exposure to chipped paint from the walls. On physical exam, the patient is found to have hepatosplenomegaly and frontal skull bossing. Hemoglobin electrophoresis reveals markedly increased HbF and HbA2 levels. What would be the most likely findings on a peripheral blood smear?
- A. Microcytosis and hypochromasia of erythrocytes (Correct Answer)
- B. Sickling of erythrocytes
- C. Basophilic stippling of erythrocytes
- D. Macrocytosis of erythrocytes with hypersegmented neutrophils
- E. Schistocytes and normocytic erythrocytes
Environmental pathology Explanation: ### ***Microcytosis and hypochromasia of erythrocytes***
- This patient presents with **β-thalassemia major**, as evidenced by **Greek ancestry** (Mediterranean population at high risk), **markedly elevated HbF and HbA2 levels** on hemoglobin electrophoresis, **frontal skull bossing** from bone marrow expansion, and **hepatosplenomegaly** from extramedullary hematopoiesis.
- The peripheral blood smear in β-thalassemia major characteristically shows **severe microcytic, hypochromic anemia** with target cells, nucleated RBCs, and marked anisocytosis and poikilocytosis.
- The inadequate β-globin chain production leads to ineffective erythropoiesis and severe hemolysis, resulting in the microcytic, hypochromic pattern.
### *Basophilic stippling of erythrocytes*
- While **basophilic stippling** can be seen in β-thalassemia, it is not the **most characteristic** finding and is more commonly associated with **lead poisoning**.
- The chipped paint exposure in this case is a distractor; **lead poisoning does NOT cause elevated HbF/HbA2, frontal bossing, or this degree of organomegaly** in a 7-month-old.
- The hemoglobin electrophoresis findings definitively point to thalassemia, not lead toxicity.
### *Sickling of erythrocytes*
- **Sickling** is pathognomonic for **sickle cell disease**, which presents with elevated HbS (not HbF and HbA2) on electrophoresis.
- While both are hemoglobinopathies affecting Mediterranean populations, the electrophoresis pattern and clinical features clearly indicate thalassemia, not sickle cell disease.
### *Schistocytes and normocytic erythrocytes*
- **Schistocytes** indicate **microangiopathic hemolytic anemia** (e.g., TTP, HUS, DIC), which involves mechanical RBC fragmentation in damaged microvasculature.
- The patient's chronic presentation, organomegaly, skeletal changes, and hemoglobin electrophoresis findings are inconsistent with microangiopathic hemolysis.
### *Macrocytosis of erythrocytes with hypersegmented neutrophils*
- **Macrocytic anemia with hypersegmented neutrophils** is characteristic of **megaloblastic anemia** from vitamin B12 or folate deficiency.
- β-thalassemia causes **microcytic** anemia due to deficient hemoglobin synthesis, not macrocytic anemia from impaired DNA synthesis.
Environmental pathology US Medical PG Question 8: A 55-year-old man presents to the emergency department with fatigue and a change in his memory. The patient and his wife state that over the past several weeks the patient has been more confused and irritable and has had trouble focusing. He has had generalized and non-specific pain in his muscles and joints and is constipated. His temperature is 99.3°F (37.4°C), blood pressure is 172/99 mmHg, pulse is 79/min, respirations are 14/min, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. Physical exam is unremarkable. Laboratory studies are ordered as seen below.
Hemoglobin: 9.0 g/dL
Hematocrit: 30%
Leukocyte count: 6,500/mm^3 with normal differential
Platelet count: 166,000/mm^3
MCV: 78 fL
Serum:
Na+: 141 mEq/L
Cl-: 103 mEq/L
K+: 4.6 mEq/L
HCO3-: 25 mEq/L
BUN: 20 mg/dL
Glucose: 99 mg/dL
Creatinine: 0.9 mg/dL
Ca2+: 10.2 mg/dL
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Iron deficiency
- B. Heavy metal exposure (Correct Answer)
- C. Systemic lupus erythematosus
- D. Guillain-Barre syndrome
- E. Vitamin B12 deficiency
Environmental pathology Explanation: ***Heavy metal exposure***
- The patient presents with **microcytic anemia** (Hemoglobin 9.0 g/dL, MCV 78 fL), **neuropsychiatric symptoms** (confusion, memory changes, irritability), **constipation**, **hypertension**, and **muscle/joint pain** - a constellation highly suggestive of **lead poisoning**.
- **Lead poisoning** classically causes **microcytic anemia** (due to inhibition of heme synthesis), **neurological symptoms** (encephalopathy, cognitive dysfunction), **GI symptoms** (constipation, abdominal pain/"lead colic"), and **hypertension**.
- The combination of **microcytic anemia with multisystem involvement** (CNS, GI, cardiovascular, musculoskeletal) points to **heavy metal toxicity** rather than simple iron deficiency.
- Confirmatory testing would include **blood lead levels** and **peripheral blood smear** (showing basophilic stippling).
*Iron deficiency*
- While **iron deficiency** causes **microcytic anemia**, it does NOT adequately explain the **neuropsychiatric symptoms** (confusion, irritability, memory changes), **hypertension**, or the **severe constipation**.
- Iron deficiency typically presents with **fatigue and weakness** but not the prominent **CNS dysfunction** seen in this patient.
- The **multisystem involvement** suggests a toxic or systemic process rather than simple nutritional deficiency.
*Systemic lupus erythematosus*
- While **SLE** can cause fatigue and joint pain, it typically presents with **malar rash, photosensitivity, serositis, and specific autoantibodies**.
- **SLE-associated anemia** is typically **normocytic** (anemia of chronic disease) or **hemolytic**, not microcytic.
- The lack of typical **autoimmune features** makes this diagnosis less likely.
*Guillain-Barre syndrome*
- **GBS** presents with **acute ascending paralysis** and **areflexia** following an infection.
- The patient's symptoms are **central** (confusion, memory issues), while **GBS affects the peripheral nervous system**.
- **GBS does not cause anemia** or the constellation of symptoms described.
*Vitamin B12 deficiency*
- **Vitamin B12 deficiency** causes **macrocytic anemia** (elevated MCV), not microcytic.
- The blood work shows **low MCV (78 fL)**, which rules out B12 deficiency.
- Neurological symptoms of B12 deficiency include **subacute combined degeneration** (posterior column dysfunction), **paresthesias**, and **gait disturbances**, distinct from the presentation here.
Environmental pathology US Medical PG Question 9: A 61-year-old man presents with gradually increasing shortness of breath. For the last 2 years, he has had a productive cough on most days. Past medical history is significant for hypertension and a recent admission to the hospital for pneumonia. He uses a triamcinolone inhaler and uses an albuterol inhaler as a rescue inhaler. He also takes lisinopril and a multivitamin daily. He has smoked a pack a day for the last 32 years and has no intention to quit now. Today, his blood pressure is 142/97 mm Hg, heart rate is 97/min, respiratory rate is 22/min, and temperature is 37.4°C (99.3°F). On physical exam, he has tachypnea and has some difficulty finishing his sentences. His heart has a regular rate and rhythm. Auscultation of his lungs reveals wheezing and rhonchi that improves after a deep cough. Fremitus is absent. Pulmonary function tests show FEV1/FVC of 55% with no change in FEV1 after albuterol treatment. Which of the following is the most likely pathology associated with this patient's disease?
- A. Airway hypersensitivity
- B. Chronic granulomatous inflammation with bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy
- C. Consolidation and red hepatization
- D. Inflamed bronchus with hypertrophy and hyperplasia of mucous glands (Correct Answer)
- E. Permanent bronchial dilation
Environmental pathology Explanation: ***Inflamed bronchus with hypertrophy and hyperplasia of mucous glands***
- The patient's history of a **productive cough for 2 years**, a **32-pack-year smoking history**, and **irreversible obstructive lung disease** (FEV1/FVC of 55% with no change after albuterol) are classic signs of **chronic bronchitis**.
- The defining pathological feature of chronic bronchitis involves **inflammation of the large airways**, leading to **mucous gland hypertrophy** and **hyperplasia**, resulting in excessive mucus production and airway obstruction.
*Airway hypersensitivity*
- **Airway hypersensitivity** is characteristic of **asthma**, where triggers cause sudden bronchoconstriction, which is typically **reversible** with bronchodilators.
- The patient's FEV1/FVC ratio **did not improve with albuterol**, indicating an irreversible obstruction not typical of hypersensitivity alone.
*Chronic granulomatous inflammation with bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy*
- This description is characteristic of **sarcoidosis**, a systemic inflammatory disease.
- While sarcoidosis can cause respiratory symptoms, it does not fit the typical presentation of **chronic productive cough** in a heavy smoker, and the classic PFT findings for sarcoidosis are **restrictive**, not obstructive.
*Consolidation and red hepatization*
- **Consolidation** and **red hepatization** are pathological features seen in the acute phase of **lobar pneumonia**, reflecting alveolar inflammation and exudation.
- The patient had a recent admission for pneumonia, but his current chronic symptoms and PFT results point to an underlying **obstructive lung disease (chronic bronchitis)**, not acute pneumonia.
*Permanent bronchial dilation*
- **Permanent bronchial dilation** is known as **bronchiectasis**, which results from chronic inflammation and infection leading to destruction of the bronchial walls.
- While chronic bronchitis can sometimes lead to bronchiectasis, the primary and most direct pathological finding for the symptoms described (chronic productive cough in a smoker with irreversible obstruction) is the **inflammation and mucous gland changes** within the bronchi.
Environmental pathology US Medical PG Question 10: A 53-year-old woman presents to the emergency room with severe chest pain radiating to the back. She was diagnosed with acute aortic dissection. A few hours into the resuscitation, she was having oliguria. Laboratory findings show a serum creatinine level of 5.3 mg/dL. Which of the following casts are most likely to be seen on urinalysis?
- A. RBC casts
- B. Fatty casts
- C. Muddy brown casts (Correct Answer)
- D. Waxy casts
- E. Hyaline casts
Environmental pathology Explanation: ***Muddy brown casts***
- **Acute tubular necrosis (ATN)**, likely caused by **renal hypoperfusion** in the context of an aortic dissection, is characterized by the presence of **muddy brown granular casts** in urinalysis. The significantly elevated **creatinine (5.3 mg/dL)** and **oliguria** support a diagnosis of acute kidney injury with ATN.
- These casts are pathognomonic for ATN and are formed from shed **epithelial cells** and debris accumulating in the renal tubules.
*RBC casts*
- **Red blood cell (RBC) casts** are indicative of **glomerulonephritis** or other causes of **glomerular injury**, which are not directly suggested by the presentation of aortic dissection and subsequent oliguria.
- While hematuria can occur in various renal conditions, the presence of **RBC casts** points to bleeding originating from the glomerulus, which is a different pathology than ATN.
*Fatty casts*
- **Fatty casts** are typically associated with **nephrotic syndrome**, a condition characterized by significant proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, and edema.
- There is no clinical information to suggest nephrotic syndrome in this patient, whose acute renal failure is likely due to hypoperfusion.
*Waxy casts*
- **Waxy casts** are generally indicative of **chronic kidney disease** and highly advanced, severe tubular damage, representing a later stage of kidney injury.
- While the patient has acute kidney injury, the timeline and acute nature of the insult make muddy brown casts more likely than waxy casts.
*Hyaline casts*
- **Hyaline casts** are composed primarily of Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein, a normal protein secreted by renal tubule cells.
- These casts can be seen in normal urine, especially after exercise or dehydration, and are not specific for any particular kidney pathology or acute kidney injury.
More Environmental pathology US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.