Benign epithelial tumors US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Benign epithelial tumors. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Benign epithelial tumors US Medical PG Question 1: A 23-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 5-month history of a pruritic rash on the bilateral upper extremities. She has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. A skin biopsy of the rash shows intraepidermal accumulation of edematous fluid and widening of intercellular spaces between keratinocytes. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Dermatitis herpetiformis
- B. Eczematous dermatitis (Correct Answer)
- C. Acanthosis nigricans
- D. Lichen planus
- E. Psoriasis vulgaris
Benign epithelial tumors Explanation: ***Eczematous dermatitis***
- The biopsy findings of **intraepidermal edema** and **widening of intercellular spaces between keratinocytes (spongiosis)** are classic histopathologic features of eczematous dermatitis.
- The clinical presentation of a **pruritic rash** on the upper extremities further supports this diagnosis, as eczema is characterized by itching and inflammation.
*Dermatitis herpetiformis*
- This condition is characterized by **subepidermal vesicles** and **neutrophilic infiltrates** in the dermal papillae, with IgA deposition, which differs from the findings described.
- It is strongly associated with **celiac disease** and presents with intensely pruritic, grouped papules and vesicles, predominantly on extensor surfaces.
*Acanthosis nigricans*
- Histologically, acanthosis nigricans shows **papillomatosis** and **hyperkeratosis**, with epidermal thickening, rather than intraepidermal edema or spongiosis.
- Clinically, it presents as **hyperpigmented, velvety plaques** in intertriginous areas, not a generalized pruritic rash.
*Lichen planus*
- Biopsy of lichen planus would reveal a **band-like lymphocytic infiltrate** at the dermoepidermal junction, **sawtooth rete ridges**, and **Civatte bodies**.
- Clinically, it often presents with **pruritic, polygonal, purple, planar papules and plaques** (the 6 Ps), which is not consistent with the described rash.
*Psoriasis vulgaris*
- Histopathologically, psoriasis is characterized by **acanthosis**, **parakeratosis**, **Munro microabscesses**, and **dilated blood vessels** in the dermal papillae.
- Clinically, it manifests as **erythematous plaques with silvery scales**, typically on extensor surfaces, distinguishing it from a generalized pruritic rash with spongiosis.
Benign epithelial tumors US Medical PG Question 2: A 70-year-old man comes to the physician because of a painless skin lesion on his neck for the past 5 months. The lesion has gradually become darker in color and is often pruritic. He has a similar lesion on the back. He is a retired landscaper. He has smoked half a pack of cigarettes daily for 45 years. Physical examination shows a 0.9-cm hyperpigmented papule on the neck with a greasy, wax-like, and stuck-on appearance. Histopathologic examination is most likely to show which of the following?
- A. Nests of melanocytes at the base of rete ridges and the dermis
- B. Fibroblast proliferation with small, benign dermal growth
- C. S100-positive epithelioid cells with fine granules in the cytoplasm
- D. Koilocytes in the granular cell layer of the epidermis
- E. Immature keratinocytes with small keratin-filled cysts (Correct Answer)
Benign epithelial tumors Explanation: ***Immature keratinocytes with small keratin-filled cysts***
- The clinical presentation of a **hyperpigmented papule** with a **greasy, wax-like, and stuck-on appearance** is highly characteristic of a **seborrheic keratosis**.
- Histopathologically, seborrheic keratoses are characterized by a proliferation of **immature keratinocytes** and often contain **horn cysts** (small keratin-filled cysts) and pseudo-horn cysts.
*Nests of melanocytes at the base of rete ridges and the dermis*
- This description is characteristic of a **melanocytic nevus** (mole) or potentially a melanoma, especially if there are nests of atypical melanocytes in the dermis.
- While seborrheic keratoses can be hyperpigmented, their clinical appearance is distinct from melanocytic lesions, lacking features like irregular borders or rapid changes.
*Fibroblast proliferation with small, benign dermal growth*
- This histological finding is more consistent with a **dermatofibroma** (fibrous histiocytoma), which presents as a firm, often pigmented nodule that may dimple inward when compressed.
- Dermatofibromas do not typically have the **greasy, stuck-on appearance** seen in seborrheic keratoses.
*S100-positive epithelioid cells with fine granules in the cytoplasm*
- **S100 positivity** is a marker for neural crest-derived cells, including melanocytes and Schwann cells. Epithelioid cells with fine granules could be seen in conditions like **granular cell tumor**, which stains positive for S100 protein.
- A granular cell tumor usually presents as a solitary, firm nodule and does not typically have the classic "greasy, stuck-on" appearance of a seborrheic keratosis.
*Koilocytes in the granular cell layer of the epidermis*
- **Koilocytes** are characteristic of **human papillomavirus (HPV) infection**, leading to conditions like common warts (verruca vulgaris) or genital warts (condyloma acuminatum).
- Warts typically have a rough, verrucous surface and do not present with the greasy, wax-like texture of a seborrheic keratosis.
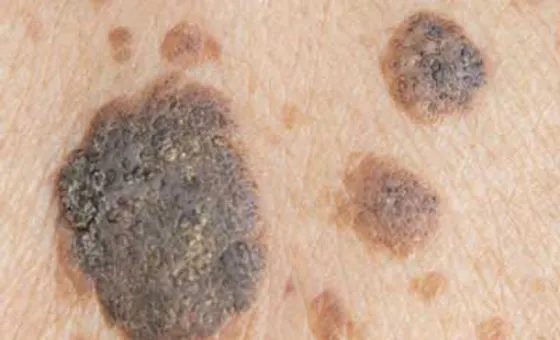
Benign epithelial tumors US Medical PG Question 3: A 65-year-old woman presents to a dermatology clinic complaining about a couple of well-demarcated, dark, round skin lesions on her face. She claims she has had these lesions for 3 or 4 years. The lesions are painless, not pruritic, and have never bled. However, she is moderately distressed about the potential malignancy of these lesions after she heard that a close friend was just diagnosed with a melanoma. The medical history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals a few well-demarcated, round, verrucous lesions, with a stuck-on appearance, distributed on the patient's back and face (see image). Under a dermatoscope, the lesions showed multiple comedo-like openings, milia cysts, and a cerebriform pattern. What is the best next step of management?
- A. Shave excision
- B. Topical fluorouracil
- C. Cryotherapy
- D. Excisional biopsy
- E. Reassure the patient and provide general recommendations (Correct Answer)
Benign epithelial tumors Explanation: ***Reassure the patient and provide general recommendations***
- The description of the lesions (well-demarcated, dark, round, verrucous, stuck-on appearance, comodo-openings, milia cysts, cerebriform pattern) is classic for **seborrheic keratoses**, which are benign.
- Given the benign nature and the patient's distress about potential malignancy, reassurance is the primary and most appropriate step. Removal is only indicated for cosmetic reasons, irritation, or diagnostic uncertainty.
*Shave excision*
- While a shave excision can remove seborrheic keratoses for cosmetic reasons or if symptomatic, it is an invasive procedure and not the **best first step** when the diagnosis is clear and the patient's main concern is malignancy.
- The lesions are clinically and dermatoscopically consistent with benign seborrheic keratoses, making a diagnostic excision unnecessary at this point.
*Topical fluorouracil*
- **Topical fluorouracil** is used to treat actinic keratoses and superficial basal cell carcinomas, not seborrheic keratoses.
- Applying this medication for seborrheic keratoses would be ineffective and potentially cause unnecessary side effects.
*Cryotherapy*
- **Cryotherapy** can be used to remove seborrheic keratoses, but similar to shave excision, it's a treatment for removal rather than an initial management step when the primary need is reassurance regarding a benign condition.
- It would be considered if the patient later desired removal for cosmetic reasons or irritation after being appropriately reassured.
*Excisional biopsy*
- An **excisional biopsy** is typically performed to completely remove a suspicious lesion with adequate margins or to provide a definitive diagnosis, particularly for suspected malignancies like melanoma.
- Given the classic presentation of benign seborrheic keratoses, an excisional biopsy is **overly aggressive** and unnecessary as the initial step.
Benign epithelial tumors US Medical PG Question 4: A 66-year-old man presents to his family physician complaining of a sandpaper-like sensation when he touches the lesion on his forehead. His medical history is relevant for hypertension and hypercholesterolemia, for which he is taking losartan and atorvastatin. He used to work as a gardener, but he retired 3 years ago. His vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination of his forehead reveals male-pattern baldness and thin, adherent, yellow-colored skin lesions that feel rough to the touch (see image). His family physician refers to him to a dermatologist for further management and treatment. Which of the following conditions would the patient most likely develop if this skin condition is left untreated?
- A. Squamous cell carcinoma (Correct Answer)
- B. Mycosis fungoides
- C. Seborrheic keratosis
- D. Actinic cheilitis
- E. Basal cell carcinoma
Benign epithelial tumors Explanation: ***Squamous cell carcinoma***
- The description of a **rough, sandpaper-like, yellow-colored lesion** on a sun-exposed area like the forehead, in a patient with a history of outdoor work (gardener), is highly characteristic of **actinic keratosis**.
- **Actinic keratosis** is a premalignant lesion that can progress to **invasive squamous cell carcinoma** if left untreated.
*Mycosis fungoides*
- This is a form of **cutaneous T-cell lymphoma** and typically presents as patches, plaques, or tumors that are often pruritic.
- It does not present as a rough, sandpaper-like lesion and is not directly associated with sun exposure in the same way as actinic keratosis.
*Seborrheic keratosis*
- Seborrheic keratoses are **benign epidermal tumors** that appear as "stuck-on" lesions, often waxy or greasy, and can be various shades of brown or black.
- While they can be rough, they are typically not described as "sandpaper-like" and do not carry the risk of malignant transformation like actinic keratosis.
*Actinic cheilitis*
- **Actinic cheilitis** is a variant of actinic keratosis that specifically affects the **lips**, primarily the lower lip, due to chronic sun exposure.
- While also premalignant and able to progress to squamous cell carcinoma, the lesion described in the question is on the **forehead**, not the lips.
*Basal cell carcinoma*
- **Basal cell carcinoma (BCC)** is another common skin cancer linked to sun exposure, but it typically presents as a **pearly nodule**, often with rolled borders and telangiectasias, or as a superficial red patch.
- While BCC can develop in sun-exposed areas, actinic keratosis is a direct precursor to squamous cell carcinoma, not basal cell carcinoma.
Benign epithelial tumors US Medical PG Question 5: A 43-year-old woman comes to the physician for an annual health maintenance examination. On questioning, she has had fatigue and headaches for the last month. A few weeks ago, she had to have her wedding ring resized because it had become too small for her finger. She has mild persistent asthma and anxiety disorder. She drinks 2–3 glasses of red wine per night and has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 16 years. She works a desk job in accounting and has recently been working long hours due to an upcoming company merger. Her father has a history of a pituitary adenoma. Current medications include alprazolam, a fluticasone inhaler, and an albuterol inhaler. She is 160 cm (5 ft 3 in) tall and weighs 81.6 kg (180 lb); her BMI is 32 kg/m2. Her temperature is 37.2°C (99°F), pulse is 92/min, and blood pressure is 132/80 mm Hg. Examination shows no abnormalities. Fasting laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 13 g/dL
Serum
Na+ 135 mEq/L
K+
4.6 mEq/L
Cl- 105 mEq/L
HCO3- 22 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen 17 mg/dL
Glucose 160 mg/dL
Creatinine 0.9 mg/dL
Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of this patient's hyperglycemia?
- A. Decreased insulin production
- B. Adverse effect of medication
- C. Stress
- D. Insulin resistance (Correct Answer)
- E. Hypersecretion of ACTH
Benign epithelial tumors Explanation: ***Insulin resistance***
- The patient's **obesity (BMI 32 kg/m2)**, **sedentary lifestyle**, and **fasting hyperglycemia** (glucose 160 mg/dL) indicate **insulin resistance**, which is the underlying mechanism of hyperglycemia in **type 2 diabetes**.
- The **ring resizing due to finger enlargement**, **fatigue**, **headaches**, and **family history of pituitary adenoma** raise suspicion for **acromegaly** (growth hormone excess), which also causes hyperglycemia through **insulin resistance** - growth hormone antagonizes insulin action at peripheral tissues.
- Regardless of whether this represents type 2 diabetes or acromegaly, **insulin resistance is the direct mechanism** causing the hyperglycemia in this patient.
*Decreased insulin production*
- Decreased insulin production is characteristic of **type 1 diabetes** or late-stage type 2 diabetes with beta-cell exhaustion.
- The patient's **obesity** and typical metabolic risk factors suggest **insulin resistance** rather than decreased production as the primary mechanism.
- No clinical features suggest autoimmune destruction or significant pancreatic damage.
*Adverse effect of medication*
- The patient's medications (**alprazolam**, **fluticasone inhaler**, **albuterol**) are unlikely to cause significant fasting hyperglycemia.
- While high-dose systemic **corticosteroids** can cause hyperglycemia, **inhaled fluticasone** at typical asthma doses has minimal systemic absorption and is not a common cause of sustained hyperglycemia.
- **Alprazolam** and **albuterol** do not typically cause hyperglycemia.
*Stress*
- **Acute stress** can transiently elevate blood glucose through counter-regulatory hormones (cortisol, catecholamines).
- However, the **fasting glucose of 160 mg/dL** suggests a chronic metabolic derangement rather than acute stress response alone.
- Work-related stress may be a contributing factor but is not the primary underlying mechanism.
*Hypersecretion of ACTH*
- **ACTH hypersecretion** (Cushing's disease) causes excess cortisol production, leading to hyperglycemia, weight gain, and fatigue.
- This patient lacks classic features of Cushing's syndrome: **central obesity with thin extremities**, **moon facies**, **buffalo hump**, **purple striae**, **skin thinning**, or **easy bruising**.
- While the patient is obese, the distribution appears generalized rather than the characteristic centripetal pattern of Cushing's syndrome.
Benign epithelial tumors US Medical PG Question 6: A 27-year-old G2P0A2 woman comes to the office complaining of light vaginal spotting. She received a suction curettage 2 weeks ago for an empty gestational sac. Pathology reports showed hyperplastic and hydropic trophoblastic villi, but no fetal tissue. The patient denies fever, abdominal pain, dysuria, dyspareunia, or abnormal vaginal discharge. She has no chronic medical conditions. Her periods are normally regular and last 3-4 days. One year ago, she had an ectopic pregnancy that was treated with methotrexate. She has a history of chlamydia and gonorrhea that was treated 5 years ago with azithromycin and ceftriaxone. Her temperature is 98°F (36.7°C), blood pressure is 125/71 mmHg, and pulse is 82/min. On examination, hair is present on the upper lip, chin, and forearms. A pelvic examination reveals a non-tender, 6-week-sized uterus and bilateral adnexal masses. There is scant dark blood in the vaginal vault on speculum exam. A quantitative beta-hCG is 101,005 mIU/mL. Two weeks ago, her beta-hCG was 63,200 mIU/mL. A pelvic ultrasound shows bilaterally enlarged ovaries with multiple thin-walled cysts between 2-3 cm in size. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the patient’s adnexal masses?
- A. Endometrioma
- B. Ectopic pregnancy
- C. Corpus luteal cysts
- D. Theca lutein cysts (Correct Answer)
- E. Dermoid cysts
Benign epithelial tumors Explanation: ***Theca lutein cysts***
- The patient's **elevated and rising beta-hCG** levels, along with the history of a **hydatidiform mole** (implied by hyperplastic/hydropic trophoblastic villi without fetal tissue), are characteristic of theca lutein cysts.
- These cysts develop due to **excessive stimulation of the ovaries by high levels of hCG**, leading to bilateral, multicystic enlargement.
*Endometrioma*
- While endometriomas can present as adnexal masses, they are typically associated with **pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea, or dyspareunia**, which this patient denies.
- Their formation is not directly linked to **hCG levels or gestational trophoblastic disease**.
*Ectopic pregnancy*
- This patient's prior ectopic pregnancy is a risk factor, but her current presentation with **bilateral adnexal masses** and a **6-week sized uterus** (after a curettage for a molar pregnancy) makes an hCG-driven ovarian response more likely.
- An ectopic pregnancy typically presents with **falling or suboptimally rising hCG** and a visible ectopic gestation, which is not described.
*Corpus luteal cysts*
- Corpus luteal cysts are common during early pregnancy and are typically **unilateral**, resolving spontaneously as hCG levels decline.
- This patient's **bilateral, multicystic ovaries** and persistently **high/rising hCG after a molar pregnancy** differentiate from corpus luteum formation.
*Dermoid cysts*
- Dermoid cysts (mature cystic teratomas) are **benign ovarian tumors** that can be bilateral, but their growth is not influenced by **hCG levels**.
- They typically have a **heterogeneous appearance on ultrasound** containing various tissue types, which differs from the thin-walled, fluid-filled cysts seen here.
Benign epithelial tumors US Medical PG Question 7: A 48-year-old man is brought to the emergency department with a stab wound to his chest. The wound is treated in the emergency room. Three months later he develops a firm 4 x 3 cm nodular mass with intact epithelium over the site of the chest wound. On local examination, the scar is firm, non-tender, and there is no erythema. The mass is excised and microscopic examination reveals fibroblasts with plentiful collagen. Which of the following processes is most likely related to the series of events mentioned above?
- A. Development of a fibrosarcoma
- B. Foreign body response from suturing
- C. Staphylococcal wound infection
- D. Poor wound healing from diabetes mellitus
- E. Keloid scar formation (Correct Answer)
Benign epithelial tumors Explanation: ***Keloid scar formation***
- A **keloid** is a raised, firm, nodular scar that extends beyond the original wound boundaries and is characterized by excessive collagen deposition from **fibroblasts**.
- The delayed presentation (3 months), firm nature, absence of inflammation (no erythema, non-tender), and microscopic findings of fibroblasts with plentiful collagen are classic features of a keloid.
*Development of a fibrosarcoma*
- A fibrosarcoma is a **malignant tumor** of fibroblasts, which would typically present with more aggressive growth, often pain, and possibly ulceration, none of which are described.
- While composed of fibroblasts, fibrosarcomas exhibit **cellular atypia**, mitotic activity, and invasion, which are not mentioned in the microscopic description.
*Foreign body response from suturing*
- A foreign body response usually involves a **granulomatous inflammation** around foreign material, such as suture remnants.
- The microscopic description of "fibroblasts with plentiful collagen" without mention of inflammatory cells or foreign bodies makes this less likely.
*Staphylococcal wound infection*
- A **bacterial infection** would typically present with signs of acute inflammation such as erythema, warmth, pain, and possibly pus, shortly after the wound.
- The mass is described as non-tender with no erythema, and the 3-month delay makes an active infection less probable.
*Poor wound healing from diabetes mellitus*
- Poor wound healing in diabetes often manifests as **delayed closure**, chronic ulcers, and increased susceptibility to infection, rather than an overgrowth of fibrous tissue in the form of a nodular mass.
- While diabetes can affect wound healing, the specific description of a firm, nodular mass with excessive collagen points away from typical diabetic wound complications.
Benign epithelial tumors US Medical PG Question 8: A 41-year-old male who takes NSAIDs regularly for his chronic back pain develops severe abdominal pain worse with eating. Upper endoscopy is performed and the medical student asks the supervising physician how the histological differentiation between a gastric ulcer and erosion is made. Which of the following layers of the gastric mucosa MUST be breached for a lesion to be considered an ulcer?
- A. Epithelium, lamina propria
- B. Epithelium
- C. Epithelium, lamina propria, muscularis mucosa (Correct Answer)
- D. Epithelium, lamina propria, muscularis mucosa, submucosa, and adventitia
- E. Epithelium, lamina propria, muscularis mucosa, and submucosa
Benign epithelial tumors Explanation: ***Epithelium, lamina propria, muscularis mucosa***
- A **gastric ulcer** by definition involves a breach of the **entire mucosal thickness**, meaning the lesion extends through the muscularis mucosa.
- This deep penetration distinguishes an ulcer from an erosion, which is a more superficial lesion confined to the epithelium and lamina propria.
*Epithelium, lamina propria*
- This describes an **erosion**, a superficial lesion of the gastric mucosa that does not penetrate the **muscularis mucosa**.
- While erosions can cause symptoms, they are generally less severe and have a lower risk of complications like perforation compared to ulcers.
*Epithelium*
- A lesion confined solely to the **epithelium** would be considered a very superficial mucosal injury, often referred to as an **erosion** or sometimes a **superficial abrasion**.
- This degree of injury does not meet the criteria for either an erosion or an ulcer in a histological context.
*Epithelium, lamina propria, muscularis mucosa, submucosa, and adventitia*
- Penetration through the **submucosa** means the ulcer has become a **deep ulcer** or potentially a **perforating ulcer**, if it breaches the entire wall to the adventitia (serosa in the GI tract).
- While an ulcer *can* extend to these layers, only reaching the muscularis mucosa is the *minimum* requirement to be classified as an ulcer.
*Epithelium, lamina propria, muscularis mucosa, and submucosa*
- An ulcer that extends into the **submucosa** is indeed a true ulcer and a more severe one, but the defining histological feature separating an erosion from an ulcer is the breach of the **muscularis mucosa**.
- Therefore, reaching the submucosa is beyond the *minimum* requirement for an ulcer classification.
Benign epithelial tumors US Medical PG Question 9: A 50-year-old woman with rheumatoid arthritis on methotrexate develops rapidly progressive painful ulcers on her legs with violaceous undermined borders. Biopsy shows neutrophilic dermal infiltrate with areas of necrosis, but no vasculitis or infection. Wound cultures are negative. Despite debridement, the ulcers worsen. C-ANCA and P-ANCA are negative. Evaluate the diagnosis and determine the management that addresses both the cutaneous condition and systemic disease.
- A. Discontinue all immunosuppression to allow wound healing
- B. Increase methotrexate dose and add wound care
- C. Discontinue methotrexate, start cyclosporine and prednisone
- D. Start broad-spectrum antibiotics and surgical debridement
- E. Continue methotrexate, add TNF-alpha inhibitor and systemic corticosteroids (Correct Answer)
Benign epithelial tumors Explanation: ***Continue methotrexate, add TNF-alpha inhibitor and systemic corticosteroids***
- This patient presents with **Pyoderma Gangrenosum (PG)**, a neutrophilic dermatosis characterized by **violaceous undermined borders** and **pathergy**, where surgical debridement cause lesion expansion.
- **TNF-alpha inhibitors** (e.g., adalimumab, infliximab) are first-line for recalcitrant PG and simultaneously provide excellent control for the underlying **Rheumatoid Arthritis**.
*Discontinue all immunosuppression to allow wound healing*
- Since PG is an **autoimmune inflammatory condition**, withdrawing immunosuppression would result in rapid progression of the ulcers rather than healing.
- Wound healing in PG requires **suppressing the inflammatory response** rather than the typical wound care approach for infected ulcers.
*Increase methotrexate dose and add wound care*
- While **methotrexate** treats RA, it is often insufficient as a monotherapy for the acute, rapidly progressive phase of **Pyoderma Gangrenosum**.
- Standard wound care alone is ineffective because the primary driver is **neutrophilic infilatration**, which requires targeted biologic or corticosteroid therapy.
*Discontinue methotrexate, start cyclosporine and prednisone*
- While **cyclosporine** and **prednisone** are used for PG, discontinuing methotrexate may lead to a flare of the patient’s **Rheumatoid Arthritis**.
- Maintaining a coordinated regimen that addresses both the skin and the joints, such as adding a **TNF-alpha inhibitor**, is preferred over switching all medications.
*Start broad-spectrum antibiotics and surgical debridement*
- **Surgical debridement** is contraindicated in PG due to **pathergy**, a phenomenon where trauma to the skin induces new or worsening lesions.
- **Antibiotics** are unnecessary as the biopsy and cultures confirmed a **sterile neutrophilic infiltrate** rather than an infectious process.
Benign epithelial tumors US Medical PG Question 10: A 25-year-old woman presents with painful oral ulcers and a pustular rash at venipuncture sites. She has genital ulcers and a history of recurrent uveitis. Skin biopsy from a pustule shows neutrophilic infiltrate in the dermis without vasculitis or infection. HLA-B51 testing is positive. She is planning pregnancy. Evaluate the management strategy considering disease control and pregnancy planning.
- A. Start methotrexate for disease control
- B. Start colchicine monotherapy and proceed with pregnancy
- C. Start high-dose corticosteroids and azathioprine, delay pregnancy
- D. Start infliximab, use contraception, then transition to low-risk therapy before conception (Correct Answer)
- E. Avoid all immunosuppression and manage symptoms only
Benign epithelial tumors Explanation: ***Start infliximab, use contraception, then transition to low-risk therapy before conception***
- This patient has **Beh'et's disease** with **recurrent uveitis**, which is **sight-threatening** and requires aggressive biological therapy like **infliximab** or **TNF-inhibitors** for rapid remission.
- Achievng **remission** before pregnancy is vital; while TNF-inhibitors are often continued, transitioning to pregnancy-compatible agents like **azathioprine** or **colchicine** ensures long-term safety.
*Start methotrexate for disease control*
- **Methotrexate** is strictly **teratogenic** and must be avoided in patients planning pregnancy or discontinued months before conception.
- While it can treat some aspects of systemic inflammation, it is not the first-line gold standard for **acute ocular Beh'et's** compared to biologics.
*Start colchicine monotherapy and proceed with pregnancy*
- **Colchicine** is excellent for **mucocutaneous** symptoms (oral and genital ulcers) but is insufficient as monotherapy to prevent blindness from **recurrent uveitis**.
- Relying on monotherapy in a patient with active ocular disease risks **permanent vision loss** during the pregnancy period.
*Start high-dose corticosteroids and azathioprine, delay pregnancy*
- While **azathioprine** is used for maintenance, **high-dose corticosteroids** carry significant side effects and are usually a bridge, not a comprehensive plan for ocular stabilization.
- This strategy lacks the rapid, potent **TNF-alpha inhibition** needed to quickly arrest the neutrophilic inflammation seen in severe Beh'et's flare-ups.
*Avoid all immunosuppression and manage symptoms only*
- **Beh'et's disease** is a multi-system inflammatory disorder; leaving **uveitis** and systemic vasculitis untreated leads to irreversible organ damage and **blindness**.
- Symptomatic management alone ignores the **neutrophilic infiltrate** and underlying autoimmune process, which could also lead to pregnancy complications due to active maternal disease.
More Benign epithelial tumors US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.