Vasculitis US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Vasculitis. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Vasculitis US Medical PG Question 1: A 72-year-old man presents to his primary care provider complaining of fatigue, mild headache, and discomfort with chewing for roughly 1 week. Before this, he felt well overall, but now he is quite bothered by these symptoms. His medical history is notable for hypertension and hyperlipidemia, both controlled. On examination, he is uncomfortable but nontoxic-appearing. There is mild tenderness to palpation over his right temporal artery, but otherwise the exam is not revealing. Prompt recognition and treatment can prevent which of the following feared complications:
- A. Renal failure
- B. Cognitive impairment
- C. Blindness (Correct Answer)
- D. Pulmonary fibrosis
- E. Pericarditis
Vasculitis Explanation: ***Blindness***
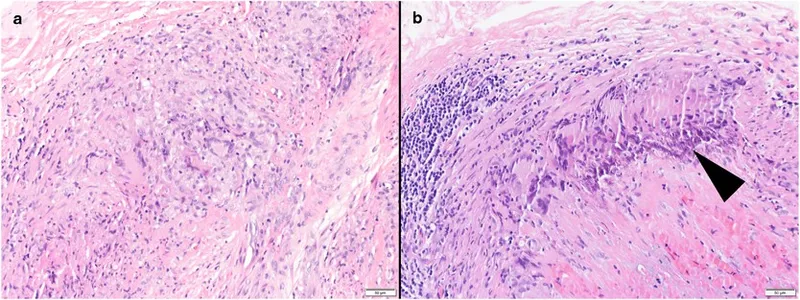
- **Giant cell arteritis (GCA)**, suggested by the patient's symptoms (fatigue, headache, jaw claudication, tender temporal artery), can lead to irreversible **vision loss** if not treated promptly with high-dose steroids.
- The most feared complication is **ischemic optic neuropathy** due to inflammation of the ophthalmic artery or its branches, supplying the optic nerve.
*Renal failure*
- While some vasculitides can affect the kidneys, **renal failure** is not a characteristic or feared complication directly associated with untreated giant cell arteritis.
- Other systemic vasculitides like **ANCA-associated vasculitis** are more commonly linked to kidney involvement.
*Cognitive impairment*
- Although GCA can cause headache and general malaise, it does not typically lead to **progressive cognitive impairment** as a direct or feared complication.
- **Stroke** can occur but is less common than visual loss, and a stroke would be a cause of acute cognitive deficits.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- **Pulmonary fibrosis** is not a known complication of giant cell arteritis.
- It is more commonly associated with conditions like **systemic sclerosis**, certain autoimmune diseases, or environmental exposures.
*Pericarditis*
- **Pericarditis** (inflammation of the sac surrounding the heart) is not a typical or feared complication of giant cell arteritis.
- While GCA can affect large vessels, it does not commonly target the pericardium.
Vasculitis US Medical PG Question 2: A 58-year-old woman presents to the physician with a throbbing headache. She says she had it for the last year and it’s usually located in the right temporal area. There is localized tenderness over the scalp. During the last 2 weeks, she experienced 3 episodes of transient loss of vision on the right side, without ocular pain. On physical examination, her vital signs are normal. Palpation reveals that the pulsations of the superficial temporal artery on the right side are reduced in amplitude. Laboratory studies show:
Blood hemoglobin 10.7 g/dL (6.64 mmol/L)
Leukocyte count 8,000/mm3 (8.0 x 109/L)
Platelet count 470,000/mm3 (470 x 109/L)
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate 60 mm/h (60 mm/h)
Which of the following conditions is most likely to co-exist with the presenting complaint in this woman?
- A. Amyloidosis
- B. Sjogren’s syndrome
- C. Fibromyalgia
- D. Polymyalgia rheumatica (Correct Answer)
- E. Dermatomyositis
Vasculitis Explanation: ***Polymyalgia rheumatica***
- This patient's symptoms are highly suggestive of **giant cell arteritis** (temporal arteritis) due to the throbbing headache, temporal tenderness, reduced temporal artery pulsation, **amaurosis fugax**, and elevated ESR.
- **Polymyalgia rheumatica** is closely associated with giant cell arteritis, often co-existing in up to 50% of patients. Both conditions are characterized by systemic inflammation.
*Amyloidosis*
- **Amyloidosis** is a disorder caused by the deposition of abnormal proteins in various tissues, leading to organ dysfunction.
- It does not typically present with the acute inflammatory symptoms or vascular complications seen in this patient, and there is no direct link to giant cell arteritis.
*Sjogren’s syndrome*
- **Sjogren's syndrome** is an autoimmune disease primarily affecting the **exocrine glands**, leading to dry eyes and dry mouth.
- While it can cause systemic symptoms, it does not typically manifest with temporal arteritis or its specific visual and cranial symptoms.
*Fibromyalgia*
- **Fibromyalgia** is a chronic condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and sleep disturbances, often without clear inflammation markers.
- It is not associated with giant cell arteritis or the inflammatory markers (high ESR) and vascular occlusion symptoms (amaurosis fugax) seen in this patient.
*Dermatomyositis*
- **Dermatomyositis** is an inflammatory myopathy characterized by muscle weakness and distinctive skin rashes.
- While it is an inflammatory condition, it does not typically present with the specific headache, temporal artery abnormalities, or visual symptoms that are hallmarks of giant cell arteritis.
Vasculitis US Medical PG Question 3: A 4-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his parents after 10 days of fever, varying from 38.0–40.0°C (100.4–104.0°F). On physical examination, the child is ill-looking with an extensive rash over his trunk with patchy desquamation. His hands are swollen, and he also shows signs of a bilateral conjunctivitis. The laboratory test results are as follows:
Hemoglobin 12.9 g/dL
Hematocrit 37.7%
Mean corpuscular volume 82.2 μm3
Leukocyte count 10,500/mm3
Neutrophils 65%
Lymphocytes 30%
Monocytes 5%
Platelet count 290,000/mm3
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) 35 mm/h
What is the next best step in the management of this patient’s condition?
- A. High-dose aspirin (Correct Answer)
- B. Influenza vaccine
- C. Echocardiography
- D. Low-dose aspirin
- E. Corticosteroids
Vasculitis Explanation: ***High-dose aspirin***
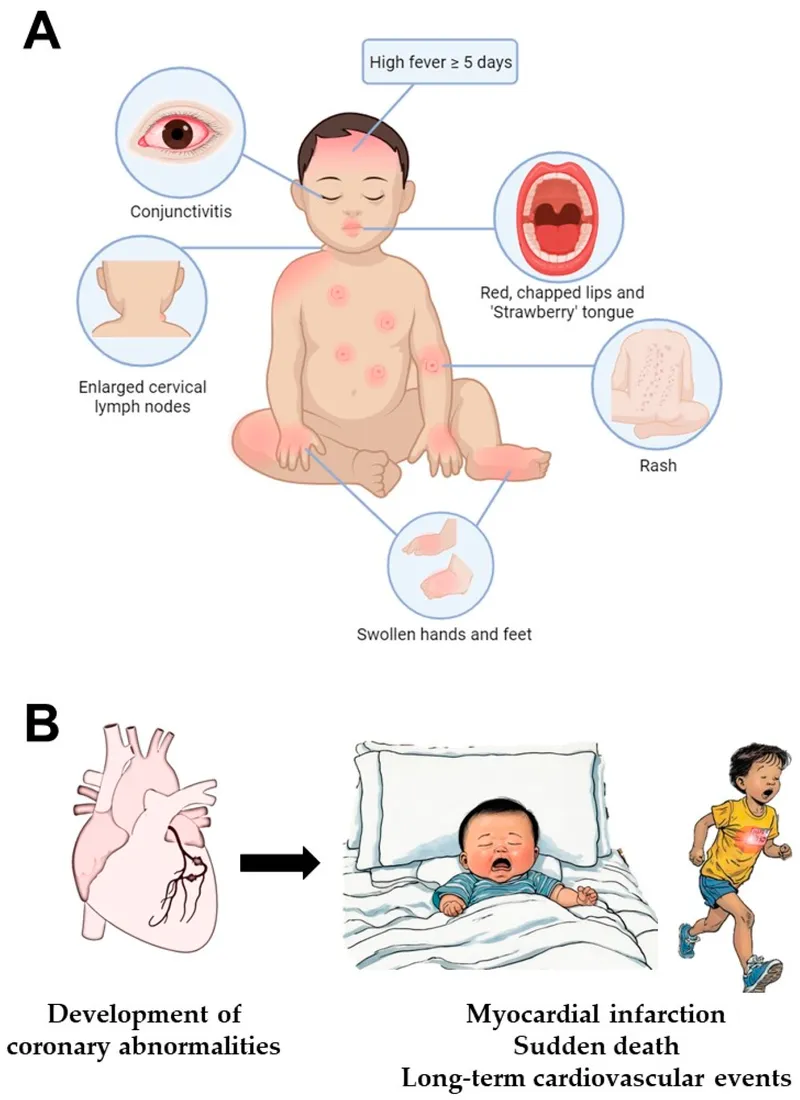
- This patient presents with classic **Kawasaki disease**: prolonged fever (10 days), bilateral conjunctivitis, rash with desquamation, and extremity changes (swollen hands).
- Standard treatment for Kawasaki disease includes **IVIG (2 g/kg) plus high-dose aspirin (80-100 mg/kg/day)**. While both should be given together, **high-dose aspirin** is the best *therapeutic* option among those listed.
- High-dose aspirin provides anti-inflammatory effects during the acute phase and helps reduce fever and systemic inflammation.
- Treatment should be initiated promptly (ideally within 10 days of fever onset) to reduce the risk of **coronary artery aneurysms**.
*Influenza vaccine*
- The influenza vaccine is not a treatment for acute illness and has no role in managing Kawasaki disease.
- Vaccination would not address the ongoing systemic inflammation or prevent cardiac complications.
*Echocardiography*
- **Echocardiography should be performed** in all cases of Kawasaki disease to assess for coronary artery abnormalities, both at diagnosis and during follow-up.
- However, it is a **diagnostic/monitoring tool**, not a therapeutic intervention. Medical treatment to reduce inflammation takes priority over imaging.
- The question asks for the "next best step in management," which implies therapeutic action rather than diagnostic testing.
*Low-dose aspirin*
- Low-dose aspirin (3-5 mg/kg/day) is used during the **convalescent phase** for its antiplatelet effects, typically after fever resolution.
- It is transitioned to after the acute inflammatory phase is controlled with high-dose aspirin.
- Not appropriate for initial acute management where anti-inflammatory dosing is needed.
*Corticosteroids*
- Corticosteroids are reserved for **IVIG-refractory cases** or patients with severe coronary artery involvement.
- They are not part of initial first-line therapy and should not be used before IVIG administration.
- Their use is indicated only when standard therapy fails.
Vasculitis US Medical PG Question 4: A 53-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a 1-month history of cough productive of small amounts of blood-tinged sputum. During this time, he has also developed fatigue, myalgia, and shortness of breath on exertion. He has had a 4-lb (2-kg) weight loss over the past 2 months. He has no personal history of serious illness. His mother has systemic lupus erythematosus. His temperature is 37.2°C (99.0 °F), pulse is 98/min, respirations are 22/min, and blood pressure is 152/98 mm Hg. Diffuse rhonchi are heard on auscultation of the chest bilaterally. There are multiple palpable, erythematous, nonblanching lesions on the lower extremities bilaterally. Laboratory studies show:
Leukocyte count 12,300 cells/mm3
Platelet count 400,000 cells/mm3
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate 83 mm/hr
Serum
Creatinine 2.1 mg/dL
Antinuclear antibody 1:40
Urine
Protein 3+
Blood 2+
RBC casts numerous
A biopsy specimen of the skin shows inflammation of the arterioles and capillaries without granuloma formation. Further evaluation of this patient is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Hepatitis B surface antigen
- B. Increased serum cryoglobulins
- C. Myeloperoxidase antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (Correct Answer)
- D. Anti-glomerular basement membrane antibodies
- E. Anti-double stranded DNA antibodies
Vasculitis Explanation: ***Myeloperoxidase antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody***
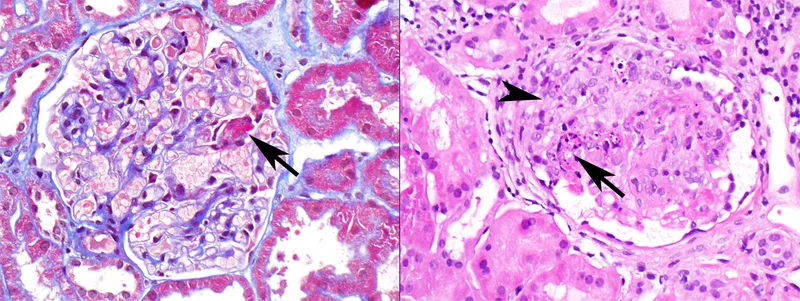
- The patient presents with **pulmonary-renal syndrome** and vasculitic skin lesions.
- The skin biopsy shows **inflammation of arterioles and capillaries without granuloma formation**, pointing towards a small vessel vasculitis such as **microscopic polyangiitis**, which is commonly associated with **MPO-ANCA (p-ANCA)** positivity.
*Hepatitis B surface antigen*
- **Polyarteritis nodosa** is a medium-sized vessel vasculitis often associated with **hepatitis B virus infection**.
- However, the skin biopsy showing **small vessel vasculitis** (arterioles and capillaries) makes polyarteritis nodosa less likely.
*Increased serum cryoglobulins*
- **Cryoglobulinemic vasculitis** is associated with **hepatitis C virus infection** and often presents with palpable purpura, arthralgias, and renal involvement.
- While the patient has palpable purpura and renal involvement, the absence of **hepatitis C risk factors** and the specific biopsy findings make this less probable than microscopic polyangiitis.
*Anti-glomerular basement membrane antibodies*
- **Goodpasture syndrome** is characterized by rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis and pulmonary hemorrhage due to **anti-GBM antibodies**.
- While the patient has both pulmonary and renal involvement, a skin vasculitis is not typical for Goodpasture syndrome, and the biopsy would show **linear IgG deposition** along the GBM, not inflammation of arterioles and capillaries.
*Anti-double stranded DNA antibodies*
- **Anti-dsDNA antibodies** are highly specific for **systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)**, which can cause vasculitis and renal disease.
- While the patient's mother has SLE, his clinical presentation, particularly the lung involvement and the specific type of skin vasculitis, is more classic for an **ANCA-associated vasculitis** than for SLE.
Vasculitis US Medical PG Question 5: A 50-year-old man comes to the physician for the evaluation of recurrent episodes of chest pain, difficulty breathing, and rapid heart beating over the past two months. During this period, he has had a 4-kg (8.8-lb) weight loss, malaise, pain in both knees, and diffuse muscle pain. Five years ago, he was diagnosed with chronic hepatitis B infection and was started on tenofovir. His temperature is 38°C (100.4°F), pulse is 110/min, and blood pressure is 150/90 mm Hg. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities except for tachycardia. There are several ulcerations around the ankle and calves bilaterally. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 11 g/dL
Leukocyte count 14,000/mm3
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate 80 mm/h
Serum
Perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies negative
Hepatitis B surface antigen positive
Urine
Protein +2
RBC 6-7/hpf
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
- B. Giant cell arteritis
- C. Thromboangiitis obliterans
- D. Polyarteritis nodosa (Correct Answer)
- E. Takayasu arteritis
Vasculitis Explanation: ***Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN)***
- This patient presents with **fever**, **weight loss**, **myalgia**, and **arthralgia** along with **skin ulcerations** and **renal involvement** (proteinuria, hematuria), signs of systemic inflammation, and **medium-sized vessel vasculitis**. The history of **chronic Hepatitis B infection** is strongly associated with PAN.
- The elevated **ESR** and **leukocytosis** indicate ongoing inflammation, and the chest pain/rapid heart beating could be signs of cardiac involvement, which is common in PAN. The negative p-ANCA also helps rule out other vasculitides.
*Granulomatosis with polyangiitis*
- This condition is typically associated with **upper and lower respiratory tract involvement**, **glomerulonephritis**, and **c-ANCA positivity** (anti-PR3 antibodies).
- The patient's symptoms do not primarily involve sinusitis, pulmonary nodules, or other upper/lower airway disease, and p-ANCA is negative, rather than c-ANCA positive.
*Giant cell arteritis*
- This is a vasculitis affecting primarily **large-sized arteries**, especially the carotid artery branches, and typically occurs in patients **older than 50 years** (though this patient is 50, other symptoms rule it out).
- Key symptoms include **new-onset headache**, **jaw claudication**, **scalp tenderness**, and potential vision loss, none of which are reported here.
*Thromboangiitis obliterans*
- This condition is strongly linked to **heavy tobacco use** and results in **segmental thrombosis and inflammation of small and medium-sized arteries and veins** in the extremities.
- It primarily causes **ischemia of the digits** (fingers and toes), leading to pain, ulcerations, and gangrene, which is not fully consistent with the patient's widespread systemic symptoms and organ involvement.
*Takayasu arteritis*
- This is a **large-vessel vasculitis** primarily affecting the **aorta and its major branches**, typically seen in **younger women**.
- Symptoms often include **claudication**, **absent or diminished pulses**, and **discrepancies in blood pressure between limbs**, which are not described in this patient.
Vasculitis US Medical PG Question 6: A 71-year-old woman comes to the physician because of sudden loss of vision in her right eye for 15 minutes that morning, which subsided spontaneously. Over the past 4 months, she has had fatigue, a 4-kg (8.8-lb) weight loss, and has woken up on several occasions at night covered in sweat. She has had frequent headaches and pain in her jaw while chewing for the past 2 months. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. Her temperature is 37.5°C (99.5°F), pulse is 88/min, and blood pressure is 118/78 mm Hg. Examination shows a visual acuity of 20/25 in the left eye and 20/30 in the right eye. The pupils are equal and reactive. There is no swelling of the optic discs. Her hemoglobin concentration is 10.5 g/dL, platelet count is 420,000/mm3, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate is 69 mm/h. The patient's condition puts her at the greatest risk of developing which of the following complications?
- A. Pulmonary artery hypertension
- B. Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis
- C. Thoracic aortic aneurysm (Correct Answer)
- D. Internal carotid artery stenosis
- E. Myocardial infarction
Vasculitis Explanation: ***Thoracic aortic aneurysm***
- This patient presents with symptoms highly suggestive of **giant cell arteritis (GCA)**, including sudden, transient vision loss (amaurosis fugax), jaw claudication, headaches, fatigue, weight loss, night sweats, and an elevated ESR. GCA is a **large-vessel vasculitis** that can affect the aorta.
- **Aortic aneurysm and dissection** are serious long-term complications of GCA, affecting up to 15-30% of patients, with the thoracic aorta being particularly vulnerable.
*Pulmonary artery hypertension*
- While systemic inflammatory conditions can sometimes be associated with secondary pulmonary hypertension, it is **not a direct or common complication** of giant cell arteritis.
- Pulmonary artery hypertension is more typically associated with conditions like **scleroderma**, chronic thromboembolic disease, or left heart failure.
*Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis*
- This condition is characterized by a rapid decline in renal function and is typically seen in **ANCA-associated vasculitides** (e.g., granulomatosis with polyangiitis, microscopic polyangiitis) or anti-GBM disease.
- While GCA is a vasculitis, it primarily affects **large and medium-sized arteries** and does not typically cause rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis.
*Internal carotid artery stenosis*
- While GCA can affect the **carotid arteries**, leading to symptoms like amaurosis fugax due to involvement of the ophthalmic artery (a branch of the internal carotid), it primarily causes **vasculitic inflammation** rather than typical atherosclerotic stenosis which is its own distinct complication.
- The risk of an aneurysm in a large vessel like the aorta is a more distinct and severe systemic complication in this context than focal stenosis of the internal carotid due to the vasculitic process itself.
*Myocardial infarction*
- GCA can increase the risk of cardiovascular events due to sustained inflammation and potential accelerated atherosclerosis, but **myocardial infarction** is not the *greatest risk* or a direct, typical complication of the vasculitic process itself in the way an aortic aneurysm is.
- The primary target of inflammation in GCA is the arterial wall, which directly predisposes to conditions like aneurysm and dissection, especially in the aorta.
Vasculitis US Medical PG Question 7: A 4-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his mother with a rash on his trunk, malaise, and fever with spikes up to 38.5°C (101.3°F) for the past 2 weeks. The patient's mother says she tried giving him Tylenol with little improvement. Past medical history includes a spontaneous vaginal delivery at full term. The patient's vaccines are up-to-date and he has met all developmental milestones. On physical examination, his lips are cracking, and he has painful cervical lymphadenopathy. The rash is morbilliform and involves his trunk, palms, and the soles of his feet. There is fine desquamation of the skin of the perianal region. Which of the following anatomical structures is most important to screen for possible complications in this patient?
- A. Mitral valve
- B. Kidneys
- C. Gallbladder
- D. Coronary artery (Correct Answer)
- E. Pylorus
Vasculitis Explanation: ***Coronary artery***
- The constellation of symptoms, including prolonged fever, rash on trunk, palms, and soles, cracked lips, cervical lymphadenopathy, and perianal desquamation, is highly indicative of **Kawasaki disease**.
- **Coronary artery aneurysms** are the most serious complication of Kawasaki disease, occurring in 15-25% of untreated children, necessitating close monitoring and screening.
*Mitral valve*
- While other forms of vasculitis or rheumatic fever can affect heart valves, **mitral valve** involvement is not a primary or characteristic complication of Kawasaki disease.
- The main cardiac concern in Kawasaki disease is direct arterial inflammation, not valvular dysfunction.
*Kidneys*
- **Renal involvement**, such as acute kidney injury, is not a typical or prominent feature of Kawasaki disease.
- Kawasaki disease primarily targets medium-sized muscular arteries throughout the body, with a predilection for the coronary arteries.
*Gallbladder*
- **Hydrops of the gallbladder** can occur in Kawasaki disease, leading to acute cholecystitis-like symptoms, but it is generally a self-limiting complication.
- While it's a potential finding, it is not as life-threatening or essential to screen for as coronary artery complications.
*Pylorus*
- There is no direct association between Kawasaki disease and primary involvement or complications of the **pylorus**.
- Gastrointestinal symptoms can occur, but these are typically non-specific and do not involve anatomical changes to the pylorus.
Vasculitis US Medical PG Question 8: A 54-year-old man comes to the physician because of a cough with blood-tinged sputum for 1 week. He also reports fever and a 5-kg (11 lb) weight loss during the past 2 months. Over the past year, he has had 4 episodes of sinusitis. Physical examination shows palpable nonblanching skin lesions over the hands and feet. Examination of the nasal cavity shows ulceration of the nasopharyngeal mucosa and a depressed nasal bridge. Oral examination shows a painful erythematous gingival enlargement that bleeds easily on contact. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the patient's symptoms?
- A. Metalloprotease enzyme deficiency
- B. Malignant myeloid cell proliferation
- C. Arteriovenous malformation
- D. Immune complex deposition
- E. Neutrophil-mediated damage (Correct Answer)
Vasculitis Explanation: ***Neutrophil-mediated damage***
- The constellation of **sinusitis**, **pulmonary symptoms** (cough with blood-tinged sputum), **renal involvement** (indicated by systemic symptoms and often associated with microhematuria in this condition), and **skin lesions (palpable purpura)**, along with **nasal ulceration**, a **depressed nasal bridge**, and **gingival enlargement**, is highly characteristic of **Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (GPA)**.
- GPA is an **ANCA-associated vasculitis** characterized by **necrotizing granulomatous inflammation** and **vasculitis** of small to medium-sized vessels, primarily driven by **neutrophil activation** and subsequent tissue damage.
*Metalloprotease enzyme deficiency*
- This description commonly refers to conditions like **alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency**, which primarily causes **emphysema** and liver disease, not the widespread vasculitic manifestations seen here.
- It does not explain the diverse multi-organ involvement including skin, ENT, and likely renal symptoms.
*Malignant myeloid cell proliferation*
- This would suggest conditions like **leukemia** or **myelodysplastic syndromes**, which present with altered blood counts, fatigue, infections, and bleeding, but typically not this specific pattern of vasculitis and granulomatous inflammation.
- While constitutional symptoms like weight loss can occur, the localized findings like depressed nasal bridge and gingival enlargement are not characteristic.
*Arteriovenous malformation*
- An **arteriovenous malformation (AVM)** is an abnormal connection between arteries and veins; depending on its location, it can cause bleeding (e.g., hemoptysis if pulmonary) or neurological symptoms if cerebral.
- However, AVMs do not explain the systemic inflammatory symptoms, skin lesions, sinusitis, depressed nasal bridge, or gingival changes.
*Immune complex deposition*
- **Immune complex vasculitis** (e.g., IgA vasculitis, cryoglobulinemic vasculitis) often presents with palpable purpura and can affect kidneys and GI tract.
- However, the prominent **granulomatous inflammation** causing **nasal ulceration** and **depressed nasal bridge**, and the specific type of **pulmonary-renal syndrome** seen in GPA, are more indicative of **ANCA-mediated neutrophil damage** rather than immune complex deposition.
Vasculitis US Medical PG Question 9: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
Vasculitis Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
Vasculitis US Medical PG Question 10: A 32-year-old woman who recently emigrated to the USA from Japan comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of night sweats, malaise, and joint pain. During this time, she has also had a 6-kg (13-lb) weight loss. Physical examination shows weak brachial and radial pulses. There are tender subcutaneous nodules on both legs. Carotid bruits are heard on auscultation bilaterally. Laboratory studies show an erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 96 mm/h. A CT scan of the chest shows thickening and narrowing of the aortic arch. Microscopic examination of the aortic arch is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Fibrinoid necrosis of the intima and media
- B. Calcification of the media
- C. Granulomatous inflammation of the media (Correct Answer)
- D. Subendothelial hyaline deposition
- E. Subendothelial immune complex deposition
Vasculitis Explanation: ***Granulomatous inflammation of the media***
- The clinical presentation, including **night sweats, malaise, weight loss, weak brachial and radial pulses** (pulseless disease), and **thickening and narrowing of the aortic arch**, is highly suggestive of **Takayasu arteritis**.
- **Takayasu arteritis** is a **large-vessel vasculitis** characterized pathologically by **granulomatous inflammation** primarily affecting the **tunica media** of the aorta and its major branches.
*Fibrinoid necrosis of the intima and media*
- **Fibrinoid necrosis** is typically seen in **small-to-medium vessel vasculitides** (e.g., polyarteritis nodosa) or in severe **hypertensive vasculopathy**.
- It involves the deposition of **fibrin-like material** in the vessel wall, which is not the primary histological feature of Takayasu arteritis.
*Calcification of the media*
- **Medial calcification** (Mönckeberg arteriosclerosis) primarily affects **muscular arteries** and is typically seen in older individuals, often incidentally.
- It does not cause significant luminal narrowing, inflammation, or the systemic symptoms described in this patient.
*Subendothelial hyaline deposition*
- **Hyaline deposition** in the subendothelium is characteristic of **hyaline arteriolosclerosis**, commonly seen in **benign hypertension** or **diabetes mellitus**, affecting small arteries and arterioles.
- This finding is not consistent with the specific large-vessel inflammatory process seen in Takayasu arteritis.
*Subendothelial immune complex deposition*
- **Immune complex deposition** in the subendothelium is typical of **Type III hypersensitivity reactions**, such as those seen in **lupus nephritis** or **Type II cryoglobulinemia**, often affecting glomeruli or small vessels.
- While Takayasu arteritis is immune-mediated, its hallmark is **granulomatous inflammation**, not primary immune complex deposition in the vessel wall.
More Vasculitis US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.