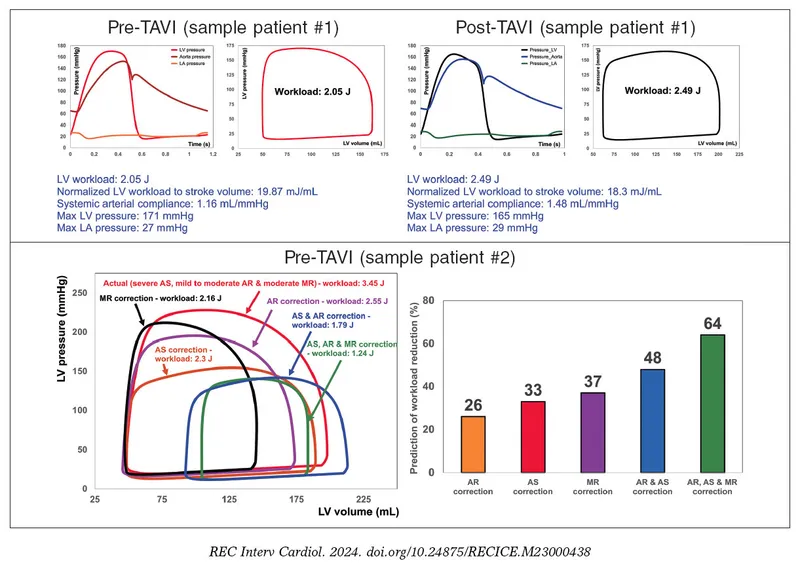
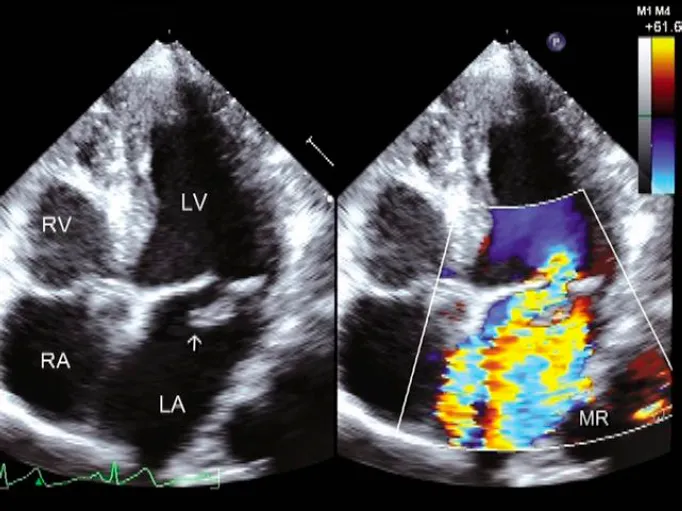
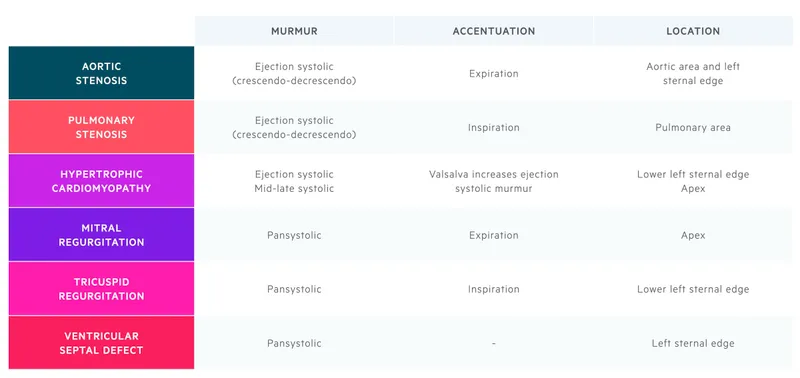
Valvular heart disease US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Valvular heart disease. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Valvular heart disease US Medical PG Question 1: A 58-year-old female presents to her primary care physician with complaints of chest pain and palpitations. A thorough past medical history reveals a diagnosis of rheumatic fever during childhood. Echocardiography is conducted and shows enlargement of the left atrium and narrowing of the mitral valve opening. Which of the following should the physician expect to hear on cardiac auscultation?
- A. Continuous, machine-like murmur
- B. Holosystolic murmur that radiates to the axilla
- C. Opening snap following S2 (Correct Answer)
- D. High-pitched, blowing decrescendo murmur in early diastole
- E. Mid-systolic click
Valvular heart disease Explanation: ***Opening snap following S2***
- The patient's history of **rheumatic fever** and echocardiographic findings of **left atrial enlargement** and **mitral valve narrowing** (mitral stenosis) are classic for this condition.
- An **opening snap** is a high-pitched, sharp sound that occurs shortly after **S2** (the second heart sound) and is pathognomonic for **mitral stenosis**, caused by the sudden tensing of the stenotic mitral valve leaflets as they open during diastole.
- The **S2-OS interval** indicates severity: a shorter interval suggests more severe stenosis.
*Continuous, machine-like murmur*
- This type of murmur is characteristic of a **patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)**, which is a congenital heart defect.
- The patient's symptoms and echocardiographic findings are not consistent with PDA.
*Holosystolic murmur that radiates to the axilla*
- This murmur describes **mitral regurgitation**, which is a leaky mitral valve. While rheumatic fever can cause mitral regurgitation, the echocardiogram shows **narrowing** of the mitral valve, not leakage.
- The radiation to the axilla is classical for the regurgitant jet flowing into the left atrium during systole.
*High-pitched, blowing decrescendo murmur in early diastole*
- This murmur is typical for **aortic regurgitation**, indicating a leaky aortic valve.
- The patient's presentation and echocardiogram findings specifically point to **mitral valve involvement** rather than aortic valve issues.
*Mid-systolic click*
- A **mid-systolic click** is characteristic of **mitral valve prolapse**, often followed by a late systolic murmur.
- The echocardiogram findings of **mitral valve narrowing** are not consistent with mitral valve prolapse.
Valvular heart disease US Medical PG Question 2: A 31-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 5-day history of fever, chills, and dyspnea. His temperature is 38.9°C (102°F) and pulse is 90/min. Cardiac examination shows a murmur. In addition to other measures, cardiac catheterization is performed. A graph showing the results of the catheterization is shown. This patient most likely has which of the following valvular heart defects?
- A. Mitral regurgitation
- B. Aortic regurgitation (Correct Answer)
- C. Mitral stenosis
- D. Pulmonary regurgitation
- E. Aortic stenosis
Valvular heart disease Explanation: ***Aortic regurgitation***
- Aortic regurgitation is characterized by a high-pitched **diastolic decrescendo murmur**, best heard at the left sternal border.
- The catheterization graph shows a **rapid decline in aortic pressure during diastole**, signifying blood flowing back into the left ventricle, which is characteristic of aortic regurgitation.
*Mitral regurgitation*
- Mitral regurgitation would cause a **pansystolic murmur** and a large **V wave in the pulmonary capillary wedge pressure tracing**, neither of which is implied by the provided information.
- Its primary hemodynamic feature is blood flowing back into the **left atrium during systole**, not diastolic aortic pressure changes.
*Mitral stenosis*
- Mitral stenosis typically presents with a **diastolic rumble** and an **opening snap**, which are different from the findings described.
- Hemodynamically, it would show an **elevated left atrial pressure** and a pressure gradient across the mitral valve during diastole.
*Pulmonary regurgitation*
- Pulmonary regurgitation involves the flow of blood from the pulmonary artery back into the **right ventricle during diastole**.
- This condition would lead to characteristic changes in **right ventricular and pulmonary artery pressures**, not the left-sided heart pressures shown in the graph.
*Aortic stenosis*
- Aortic stenosis causes a **systolic crescendo-decrescendo murmur**, often with radiation to the carotids.
- Hemodynamically, it would show a **significant pressure gradient across the aortic valve during systole** and a delayed carotid upstroke.
Valvular heart disease US Medical PG Question 3: A 2-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her mother for a well-child examination. Cardiac auscultation is shown. When she clenches her fist forcefully for a sustained time, the intensity of the murmur increases. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's auscultation findings?
- A. Failure of the ductus arteriosus to close
- B. Defect in the atrial septum
- C. Fusion of the right and left coronary leaflets
- D. Prolapse of the mitral valve
- E. Defect in the ventricular septum (Correct Answer)
Valvular heart disease Explanation: ***Defect in the ventricular septum***
- A **ventricular septal defect (VSD)** causes a holosystolic, harsh murmur, often loudest at the **left lower sternal border**.
- **Clenching the fist forcefully increases systemic vascular resistance (afterload)**, which enhances the left-to-right shunting through a VSD, thereby **increasing the intensity** of the murmur.
*Failure of the ductus arteriosus to close*
- A **patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)** typically presents with a **continuous "machinery-like" murmur**, not one that increases with clenching a fist.
- The murmur of a PDA is usually best heard in the **pulmonary area** (left upper sternal border).
*Defect in the atrial septum*
- An **atrial septal defect (ASD)** usually causes a **systolic ejection murmur** over the pulmonic area due to increased flow across the pulmonary valve, and a **fixed split S2**.
- Its intensity is generally **not significantly altered by acute changes in systemic vascular resistance** like clenching a fist.
*Fusion of the right and left coronary leaflets*
- This description is characteristic of a **bicuspid aortic valve** leading to **aortic stenosis**.
- Aortic stenosis typically causes a **systolic ejection murmur** that **decreases** in intensity with maneuvers that increase afterload (like clenching a fist) due to reduced stroke volume.
*Prolapse of the mitral valve*
- **Mitral valve prolapse (MVP)** is characterized by a **mid-systolic click** followed by a **late-systolic murmur**.
- **Increasing afterload** (clenching a fist) would typically **delay the click and shorten the murmur**, or make it softer, as it *reduces* the degree of prolapse.
Valvular heart disease US Medical PG Question 4: A 72-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for a general checkup. The patient works as a farmer and has no concerns about his health. He has a past medical history of hypertension and obesity. His current medications include lisinopril and metoprolol. His temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 177/108 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, respirations are 17/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Physical exam is notable for a murmur after S2 over the left sternal border. The patient demonstrates a stable gait and 5/5 strength in his upper and lower extremities. Which of the following is another possible finding in this patient?
- A. Murmur that radiates to the carotids
- B. Wedge pressure lower than expected
- C. Femoral artery murmur (Correct Answer)
- D. Rumbling heard at the cardiac apex
- E. Audible click heard at the cardiac apex
Valvular heart disease Explanation: ***Femoral artery murmur***
- A murmur heard after S2 over the left sternal border in an elderly patient suggests **aortic regurgitation (AR)**.
- In AR, a **femoral artery murmur (Duroziez's sign)** can be heard, characterized by a systolic murmur over the femoral artery with proximal compression and a diastolic murmur with distal compression.
*Murmur that radiates to the carotids*
- A murmur radiating to the carotids is characteristic of **aortic stenosis**, which typically presents as a systolic murmur, not a diastolic one as heard in this patient.
- Aortic stenosis is also associated with a **crescendo-decrescendo murmur**, in contrast to the diastolic murmur described.
*Wedge pressure lower than expected*
- This patient likely has **aortic regurgitation**, which increases **left ventricular end-diastolic pressure** and, consequently, **pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP)**.
- A lower than expected wedge pressure would be inconsistent with the volume overload often seen in significant AR.
*Rumbling heard at the cardiac apex*
- A rumbling murmur at the cardiac apex is characteristic of **mitral stenosis**, which is typically preceded by an opening snap.
- The patient's murmur is heard after S2 (diastolic) at the left sternal border, not the apex, making mitral stenosis less likely.
*Audible click heard at the cardiac apex*
- An audible click at the cardiac apex is typically associated with **mitral valve prolapse**, often followed by a mid-systolic murmur.
- This finding is not consistent with the diastolic murmur heard after S2 at the left sternal border.
Valvular heart disease US Medical PG Question 5: A 61-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of fatigue and progressively worsening shortness of breath that is worse when lying down. Recently, he started using two pillows to avoid waking up short of breath at night. Examination shows a heart murmur. A graph with the results of cardiac catheterization is shown. Given this patient's valvular condition, which of the following murmurs is most likely to be heard on cardiac auscultation?
- A. High-frequency, diastolic murmur heard best at the 2nd left intercostal space
- B. Harsh, late systolic murmur that radiates to the carotids
- C. Blowing, early diastolic murmur heard best at the Erb point
- D. High-pitched, holosystolic murmur that radiates to the axilla (Correct Answer)
- E. Rumbling, delayed diastolic murmur heard best at the cardiac apex
Valvular heart disease Explanation: ***High-pitched, holosystolic murmur that radiates to the axilla***
- The patient's symptoms of **fatigue**, **dyspnea on exertion** and **orthopnea**, combined with a heart murmur, are highly suggestive of **heart failure** caused by **mitral regurgitation**.
- A **high-pitched**, **holosystolic murmur** heard best at the **apex** and **radiating to the axilla** is the classic description of mitral regurgitation.
*High-frequency, diastolic murmur heard best at the 2nd left intercostal space*
- This describes the murmur of **pulmonary regurgitation**, which is typically heard best at the **left upper sternal border**.
- The patient's symptoms are more consistent with left-sided heart failure due to a different valvular issue.
*Harsh, late systolic murmur that radiates to the carotids*
- This is the characteristic murmur of **aortic stenosis**, which is heard best at the **right upper sternal border**.
- While aortic stenosis can cause similar symptoms, the description of the murmur and the specific context of heart failure symptoms here point away from it.
*Blowing, early diastolic murmur heard best at the Erb point*
- This describes the **diastolic murmur of aortic regurgitation**, often heard best at the **Erb's point** (3rd intercostal space, left sternal border).
- While aortic regurgitation can cause heart failure, its murmur is diastolic, not holosystolic, and the maximal intensity and radiation differ from the classic mitral regurgitation.
*Rumbling, delayed diastolic murmur heard best at the cardiac apex*
- This is the characteristic murmur of **mitral stenosis**, which is typically preceded by an **opening snap**.
- Mitral stenosis would lead to different hemodynamic changes and often presents with symptoms related to pulmonary congestion, but the murmur timing and quality are distinct from a holosystolic murmur of regurgitation.
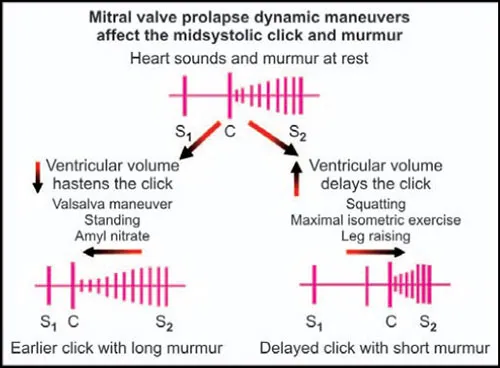
Valvular heart disease US Medical PG Question 6: A 47-year-old man presents for a routine physical examination as part of an insurance medical assessment. He has no complaints and has no family history of cardiac disease or sudden cardiac death. His blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, temperature is 36.7°C (98.1°F), and pulse is 75/min and is regular. On physical examination, he appears slim and his cardiac apex beat is of normal character and non-displaced. On auscultation, he has a midsystolic click followed by a late-systolic high-pitched murmur over the cardiac apex. On standing, the click and murmur occur earlier in systole, and the murmur is of increased intensity. While squatting, the click and murmur occur later in systole, and the murmur is softer in intensity. Echocardiography of this patient will most likely show which of the following findings?
- A. Left atrial mass arising from the region of the septal fossa ovalis
- B. Doming of the mitral valve leaflets in diastole
- C. Prolapse of a mitral valve leaflet of ≥2 mm above the level of the annulus in systole (Correct Answer)
- D. Retrograde blood flow into the right atrium
- E. High pressure gradient across the aortic valve
Valvular heart disease Explanation: ***Prolapse of a mitral valve leaflet of ≥2 mm above the level of the annulus in systole***
- The clinical presentation with a **midsystolic click** followed by a **late-systolic high-pitched murmur over the cardiac apex** is characteristic of **mitral valve prolapse (MVP)**.
- The changes in the click and murmur timing and intensity with **standing (earlier, louder)** and **squatting (later, softer)** are classic findings, reflecting changes in left ventricular volume that affect the onset of valve prolapse.
*Left atrial mass arising from the region of the septal fossa ovalis*
- This description is highly suggestive of a **myxoma**, typically found in the left atrium, which can cause symptoms of **obstructive heart failure** or **embolism**.
- A myxoma would not typically present with the characteristic **midsystolic click** and **late-systolic murmur** that changes with position.
*Doming of the mitral valve leaflets in diastole*
- **Doming of the mitral valve leaflets in diastole** is characteristic of **mitral stenosis**, where the valve fails to open properly.
- Mitral stenosis would present with a **diastolic murmur**, not a midsystolic click and late-systolic murmur.
*Retrograde blood flow into the right atrium*
- **Retrograde blood flow into the right atrium** indicates **tricuspid regurgitation**, which would typically manifest as a **holosystolic murmur** best heard at the lower left sternal border, often with prominent jugular venous pulsations.
- This finding is inconsistent with the patient's auscultatory findings at the cardiac apex.
*High pressure gradient across the aortic valve*
- A **high pressure gradient across the aortic valve** signifies **aortic stenosis**, which is characterized by a **systolic ejection murmur** best heard at the right upper sternal border with radiation to the carotids.
- This condition would not produce a midsystolic click or a late-systolic murmur at the apex.
Valvular heart disease US Medical PG Question 7: A 32-year-old male presents for a new patient visit. He states that he is in good health but has had decreasing exercise tolerance and increased levels of shortness of breath over the past 5 years. He believed that it was due to aging; he has not seen a doctor in 10 years. On auscultation, you note an early diastolic decrescendo blowing murmur that radiates along the left sternal border. In the United States, what is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
- A. Connective tissue disease
- B. Congenital bicuspid aortic valve (Correct Answer)
- C. Syphilis
- D. Rheumatic heart disease
- E. Myxomatous degeneration
Valvular heart disease Explanation: ***Congenital bicuspid aortic valve***
- The patient's age (32 years old), progressive symptoms of **aortic regurgitation** (decreasing exercise tolerance, shortness of breath, early diastolic decrescendo murmur), and location of the murmur are highly suggestive of a **bicuspid aortic valve**.
- This is the **most common congenital heart defect**, affecting 1-2% of the population, and is the leading cause of **aortic stenosis** and **aortic insufficiency** in younger adults in developed countries.
*Connective tissue disease*
- While connective tissue diseases such as **Marfan syndrome** or **Ehlers-Danlos syndrome** can cause aortic root dilation and regurgitation, they are less common than a bicuspid aortic valve as a primary cause of isolated aortic regurgitation in this age group.
- These conditions typically present with other systemic features (e.g., arachnodactyly, skin hyperextensibility) that are not mentioned in the patient's history.
*Syphilis*
- **Syphilitic aortitis** can cause aortic root dilation and aortic regurgitation, typically as a late-stage manifestation of **tertiary syphilis**.
- While possible, it is less common in developed countries today due to effective antibiotic treatment, and the patient's asymptomatic progression over 5 years might suggest a congenital rather than an infectious cause in this context.
*Rheumatic heart disease*
- **Rheumatic fever** is a common cause of valvular heart disease globally, but its incidence has significantly declined in developed countries due to improved hygiene and antibiotic use for **streptococcal infections**.
- While it can affect the aortic valve, it more commonly affects the **mitral valve** and usually presents with symptoms earlier in life or with a history of recurrent fevers.
*Myxomatous degeneration*
- **Myxomatous degeneration** primarily affects the **mitral valve**, leading to **mitral valve prolapse** and regurgitation.
- While it can sometimes affect the aortic valve, it is a less common cause of isolated aortic regurgitation and often presents with different clinical features or imaging findings.
Valvular heart disease US Medical PG Question 8: A 28-year-old primigravida presents to the office with complaints of heartburn while lying flat on the bed at night and mild constipation that started a couple of weeks ago. She is 10 weeks pregnant, as determined by her last menstrual period. Her first menstruation was at 13 years of age and she has always had regular 28-day cycles. Her past medical history is insignificant. She does not smoke cigarettes or drink alcohol and does not take any medications. Her father died of colon cancer at 70 years of age, while her mother has diabetes and hypertension. Her vital signs include: temperature 36.9℃ (98.4℉), blood pressure 98/52 mm Hg, pulse 113/minute, oxygen saturation 99%, and respiratory rate 12 /minute. The physical examination was unremarkable, except for a diastolic murmur heard over the apex. Which of the following is considered abnormal in this woman?
- A. Decreased vascular resistance
- B. Diastolic murmur (Correct Answer)
- C. Tachycardia
- D. Increased cardiac output
- E. Low blood pressure
Valvular heart disease Explanation: ***Diastolic murmur***
- Diastolic murmurs in pregnancy are **never normal** and always require further investigation to rule out significant **cardiac pathology**, such as valvular stenosis or regurgitation.
- While physiological changes in pregnancy can lead to systolic murmurs, **diastolic murmurs** are considered pathological.
*Decreased vascular resistance*
- **Peripheral vasodilation** due to hormonal changes (**progesterone**) is a normal physiological adaptation in early pregnancy, leading to decreased systemic vascular resistance.
- This decrease helps accommodate the **increased blood volume** and cardiac output, contributing to a slight drop in blood pressure.
*Tachycardia*
- An **increased heart rate** is a normal physiological response in pregnancy, typically seen as early as the first trimester.
- This compensatory mechanism helps maintain **cardiac output** in the face of decreased systemic vascular resistance and increased blood volume.
*Increased cardiac output*
- **Cardiac output increases** significantly during pregnancy, primarily due to increases in both heart rate and stroke volume, to meet the metabolic demands of the mother and fetus.
- This increase begins in the **first trimester** and peaks in the second trimester, remaining elevated until delivery.
*Low blood pressure*
- A **mild decrease in blood pressure**, particularly the diastolic pressure, is common in early pregnancy due to generalized vasodilation.
- The given blood pressure (98/52 mm Hg) is within the expected physiological range for a healthy pregnant woman in her first trimester.
Valvular heart disease US Medical PG Question 9: A patient with a history of Tetralogy of Fallot is being evaluated for long-term complications. This patient is at greatest risk of damage to which of the following cardiovascular structures?
- A. Cardiac septum
- B. Coronary artery
- C. Temporal artery
- D. Pulmonary valve (Correct Answer)
- E. Cardiac conduction system
Valvular heart disease Explanation: ***Pulmonary valve***
- Patients with **Tetralogy of Fallot** often have severe **pulmonary stenosis**, which can lead to significant long-term damage and insufficiency of the pulmonary valve, frequently requiring replacement.
- The elevated right ventricular pressure from **outflow obstruction** and the **ventricular septal defect** alter flow dynamics, putting continuous strain on the pulmonary valve and the right ventricular outflow tract.
*Cardiac septum*
- While a **ventricular septal defect (VSD)** is a key feature of Tetralogy of Fallot, it is a structural anomaly present from birth and usually does not *suffer additional damage* over time in the same way a valve does, although its size can impact shunt dynamics.
- Damage to the septum itself (beyond the initial defect) is not the primary long-term risk for this cardiovascular structure in Tetralogy of Fallot.
*Coronary artery*
- Anomalies of the **coronary arteries** can occur in Tetralogy of Fallot but are not consistently present and are not the primary structure at greatest risk of *damage* as a direct consequence of the typical hemodynamics of the condition.
- Coronary artery disease is generally a later-life atherosclerotic process and not directly linked to the congenital defect itself.
*Temporal artery*
- The **temporal artery** is an extracardiac artery and is not a cardiovascular structure at risk of damage in Tetralogy of Fallot.
- Conditions like giant cell arteritis affect the temporal artery, which is unrelated to this congenital heart defect.
*Cardiac conduction system*
- While there is a risk of **arrhythmias** in patients with Tetralogy of Fallot, particularly with surgical repairs, the direct *damage* to the cardiac conduction system itself from the pathophysiology is not the greatest risk compared to the structural deterioration of the pulmonary valve.
- Scarring from corrective surgery can predispose to conduction abnormalities, but the primary pathology and greatest unaddressed risk is often related to the right ventricular outflow tract and pulmonary valve.
Valvular heart disease US Medical PG Question 10: A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department complaining of palpitations, dry cough, and shortness of breath for 1 week. She immigrated to the United States from Korea at the age of 20. She says that her heart is racing and she has never felt these symptoms before. Her cough is dry and is associated with shortness of breath that occurs with minimal exertion. Her past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. She has no allergies and is not currently taking any medications. She is a nonsmoker and an occasional drinker. She denies illicit drug use. Her blood pressure is 100/65 mm Hg, pulse is 76/min, respiratory rate is 23/min, and temperature is 36.8°C (98.2°F). Her physical examination is significant for bibasilar lung crackles and a non-radiating, low-pitched, mid-diastolic rumbling murmur best heard at the apical region. In addition, she has jugular vein distention and bilateral pitting edema in her lower extremities. Which of the following best describes the infectious agent that led to this patient’s condition?
- A. A bacterium that induces partial lysis of red cells with hydrogen peroxide
- B. A bacterium that requires an anaerobic environment to grow properly
- C. A bacterium that does not lyse red cells
- D. A bacterium that induces heme degradation of the red cells of a blood agar plate
- E. A bacterium that induces complete lysis of the red cells of a blood agar plate with an oxygen-sensitive cytotoxin (Correct Answer)
Valvular heart disease Explanation: ***A bacterium that induces complete lysis of the red cells of a blood agar plate with an oxygen-sensitive cytotoxin***
- This describes **Group A Streptococcus (GAS)**, specifically *Streptococcus pyogenes*, which causes **rheumatic fever** leading to **mitral stenosis**. Mitral stenosis is characterized by a **mid-diastolic rumbling murmur** at the apex, left atrial enlargement causing **palpitations**, and **pulmonary congestion** leading to dyspnea, cough, and bibasilar crackles.
- The delayed onset of symptoms (immigrated at 20, symptoms at 43) is typical for **rheumatic heart disease**, where repeated GAS infections in childhood/adolescence lead to valve damage that manifests years later. GAS produces **streptolysin O**, an **oxygen-labile cytotoxin** responsible for **beta-hemolysis** (complete lysis) on blood agar.
*A bacterium that induces partial lysis of red cells with hydrogen peroxide*
- This describes **alpha-hemolytic** bacteria like *Streptococcus pneumoniae* or *Viridans streptococci*, which cause **partial hemolysis** (greenish discoloration) on blood agar due to **hydrogen peroxide** production.
- While *Viridans streptococci* can cause **infective endocarditis**, the clinical picture of **rheumatic mitral stenosis** is more consistent with a history of recurrent streptococcal pharyngitis (GAS).
*A bacterium that requires an anaerobic environment to grow properly*
- This description typically refers to **anaerobic bacteria**, such as *Clostridium* or *Bacteroides* species.
- These bacteria are generally not associated with the primary cause of acute rheumatic fever or the subsequent development of chronic valvular heart disease like mitral stenosis.
*A bacterium that does not lyse red cells*
- This describes **gamma-hemolytic** (non-hemolytic) bacteria, such as *Enterococcus faecalis* or some *Staphylococcus* species.
- These organisms do not cause the characteristic hemolysis seen with the streptococci responsible for rheumatic fever.
*A bacterium that induces heme degradation of the red cells of a blood agar plate*
- This description is **too vague** and does not specifically identify the organism. While heme degradation occurs with various types of hemolysis, the key distinguishing feature of **Group A Streptococcus** is **complete lysis (beta-hemolysis)** combined with production of the **oxygen-sensitive toxin streptolysin O**.
- This option lacks the specificity needed to identify GAS as the causative agent of rheumatic fever. Both alpha- and beta-hemolytic organisms can degrade heme, but only beta-hemolytic GAS causes rheumatic heart disease.
More Valvular heart disease US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.