Physiology of parturition US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Physiology of parturition. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Physiology of parturition US Medical PG Question 1: A 22-year-old woman comes to the physician to discuss the prescription of an oral contraceptive. She has no history of major medical illness and takes no medications. She does not smoke cigarettes. She is sexually active with her boyfriend and has been using condoms for contraception. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. She is prescribed combined levonorgestrel and ethinylestradiol tablets. Which of the following is the most important mechanism of action of this drug in the prevention of pregnancy?
- A. Inhibition of rise in luteinizing hormone (Correct Answer)
- B. Suppression of ovarian folliculogenesis
- C. Thickening of cervical mucus
- D. Prevention of endometrial proliferation
- E. Increase of sex-hormone binding globulin
Physiology of parturition Explanation: ***Inhibition of rise in luteinizing hormone***
- Combined oral contraceptives (COCs) primarily prevent pregnancy by **suppressing the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis**, which inhibits the mid-cycle **Luteinizing Hormone (LH) surge** necessary for ovulation.
- Without the LH surge, the mature follicle does not rupture, and the **ovum is not released**.
*Suppression of ovarian folliculogenesis*
- While COCs do **suppress follicular development**, this is a consequence of the feedback inhibition on FSH secretion, and not the primary contraceptive mechanism.
- The direct **prevention of ovulation** via LH surge inhibition is the most crucial step.
*Thickening of cervical mucus*
- Progestin components of COCs cause the **cervical mucus to become thick and impermeable** to sperm, acting as a secondary contraceptive mechanism.
- However, this is not the most important or primary mechanism, as ovulation can still be theoretically prevented even without this effect.
*Prevention of endometrial proliferation*
- The progestin in COCs causes the endometrium to become **thin and atrophic**, making it less receptive to implantation.
- This is an **ancillary contraceptive effect** but not the primary way pregnancy is prevented, as preventing ovulation is more fundamental.
*Increase of sex-hormone binding globulin*
- Estrogen in COCs can **increase levels of sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG)**, affecting the bioavailability of endogenous androgens.
- This effect is largely responsible for reducing symptoms of androgen excess (e.g., acne) but plays **no direct role in contraception**.
Physiology of parturition US Medical PG Question 2: A 26-year-old gravida 4 para 1 presents to the emergency department with sudden severe abdominal pain and mild vaginal bleeding. Her last menstrual period was 12 weeks ago. She describes her pain as similar to uterine contractions. She has a history of 2 spontaneous abortions in the first trimester. She is not complaining of dizziness or dyspnea. On physical examination, the temperature is 36.9°C (98.4°F), the blood pressure is 120/85 mm Hg, the pulse is 95/min, and the respiratory rate is 17/min. The pelvic examination reveals mild active bleeding and an open cervical os. There are no clots. Transvaginal ultrasound reveals a fetus with no cardiac activity. She is counseled about the findings and the options are discussed. She requests to attempt medical management with mifepristone before progressing to surgical intervention. Which of the following describes the main mechanism of action for mifepristone?
- A. Interferes with cell growth in rapidly dividing cells
- B. Increase myometrial sensitivity to contractions and induce decidual breakdown (Correct Answer)
- C. Induce teratogenesis in the fetus
- D. Induce cervical dilation
- E. Interferes with placental blood supply to the fetus
Physiology of parturition Explanation: ***Increase myometrial sensitivity to contractions and induced decidual breakdown***
- **Mifepristone** acts primarily as a **progesterone receptor antagonist**, blocking progesterone's effects.
- This blockade leads to **decidual breakdown**, increased uterine contractility, and increased sensitivity of the myometrium to prostaglandins, facilitating expulsion of uterine contents.
*Interferes with cell growth in rapidly dividing cells*
- This mechanism describes **chemotherapeutic agents** like methotrexate, which targets rapidly dividing cells.
- **Mifepristone** does not interfere with cell growth in this manner; its action is receptor-mediated.
*Induce teratogenesis in the fetus*
- While mifepristone can affect fetal development by terminating a pregnancy, its primary mechanism of action is **not directly teratogenesis** (the induction of birth defects).
- Its purpose is to induce abortion or miscarriage, not to cause malformations in a continuing pregnancy.
*Induce cervical dilation*
- While cervical dilation occurs as a consequence of the abortion process facilitated by mifepristone, it is not the **primary mechanism of action** of the drug itself.
- Cervical dilation is often secondary to uterine contractions and the release of prostaglandins, which are downstream effects of mifepristone.
*Interferes with placental blood supply to the fetus*
- **Mifepristone's** main action is not directly on the placental blood supply; rather, it affects the **uterine lining and myometrial activity**.
- The disruption of pregnancy by mifepristone leads to secondary effects on the placenta and fetal viability, but it doesn't primarily block blood flow.
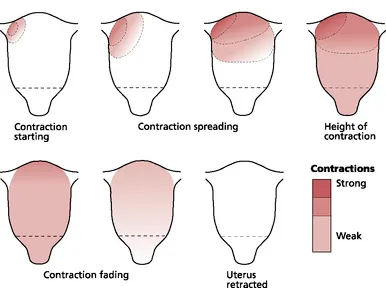
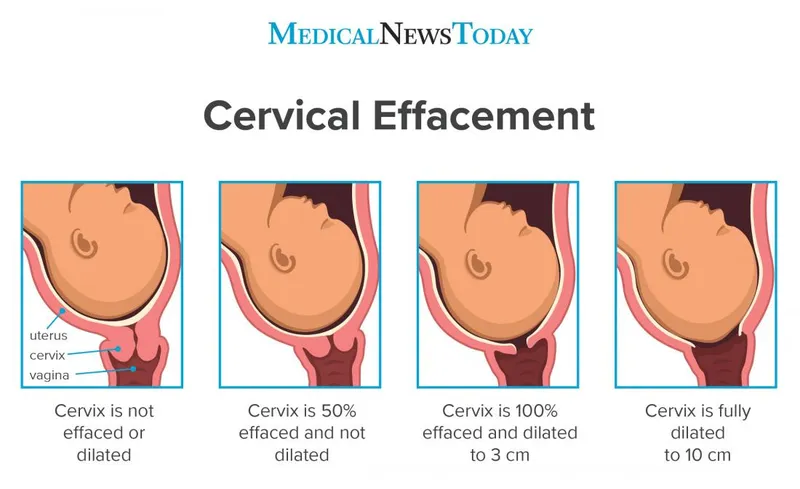
Physiology of parturition US Medical PG Question 3: A 24-year-old woman, gravida 1, at 35 weeks gestation is admitted to the hospital with regular contractions and pelvic pressure for the last 5 hours. Her pregnancy has been uncomplicated and she has attended many prenatal appointments and followed the physician's advice about screening for diseases, laboratory testing, diet, and exercise. She has had no history of fluid leakage or bleeding. At the hospital, her temperature is 37.2°C (99.0°F), blood pressure is 108/60 mm Hg, pulse is 88/min, and respirations are 16/min. Cervical examination shows 60% effacement and 5 cm dilation with intact membranes. Cardiotocography shows a contraction amplitude of 220 MVU in 10 minutes. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy at this time?
- A. Magnesium sulfate
- B. No pharmacotherapy at this time (Correct Answer)
- C. Dexamethasone
- D. Oxytocin
- E. Terbutaline
Physiology of parturition Explanation: ***No pharmacotherapy at this time***
- The patient is at **35 weeks gestation** and in **active labor** (5 cm dilated, 60% effacement, regular contractions with adequate Montevideo units). At this gestational age, labor is typically allowed to progress without intervention unless there are complications.
- Pharmacotherapy to stop labor (tocolysis) or induce fetal lung maturity (corticosteroids) is generally not indicated at or beyond 34 weeks gestation in uncomplicated cases.
*Magnesium sulfate*
- This is primarily used for **fetal neuroprotection** in anticipated preterm birth before 32 weeks gestation, or as a **tocolytic** to inhibit contractions, neither of which is indicated here.
- The patient is 35 weeks, beyond the typical window for neuroprotection, and stopping labor is not appropriate given her advanced dilation and gestational age.
*Dexamethasone*
- **Corticosteroids** like dexamethasone are administered to accelerate **fetal lung maturity** in cases of anticipated preterm birth, typically between 24 and 34 weeks gestation.
- At 35 weeks, the benefits of corticosteroids for lung maturity are minimal and generally not recommended.
*Oxytocin*
- **Oxytocin** is used to **induce or augment labor** if contractions are inadequate or to prevent **postpartum hemorrhage**.
- This patient is already in active, effective labor with adequate contractions (220 MVU in 10 minutes), so oxytocin for augmentation is not needed.
*Terbutaline*
- **Terbutaline** is a **beta-agonist tocolytic** used to relax the uterus and stop preterm labor.
- Given the patient's gestational age of 35 weeks and the progression of her labor (5 cm dilated), stopping contractions is not the appropriate management.
Physiology of parturition US Medical PG Question 4: A 23-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of a 5-day history of nausea and vomiting. There is no associated fever, abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, or dysuria. She is sexually active and uses condoms inconsistently. Her last menstrual period was 10 weeks ago. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 90/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg. There is no rebound tenderness or guarding. A urine pregnancy test is positive. Ultrasonography shows an intrauterine pregnancy consistent in size with an 8-week gestation. The hormone that was measured in this patient's urine to detect the pregnancy is also directly responsible for which of the following processes?
- A. Hypertrophy of the uterine myometrium
- B. Fetal angiogenesis
- C. Maintenance of the corpus luteum (Correct Answer)
- D. Inhibition of ovulation
- E. Stimulation of uterine contractions at term
Physiology of parturition Explanation: ***Maintenance of the corpus luteum***
- The hormone measured in the urine pregnancy test is **human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)**. hCG's primary role early in pregnancy is to **maintain the corpus luteum**, which in turn produces progesterone to support the uterine lining.
- The **corpus luteum** is essential for progesterone production until the placenta is sufficiently developed to take over this function, typically around 8-10 weeks gestation.
*Hypertrophy of the uterine myometrium*
- **Estrogen** and **progesterone** are primarily responsible for the hypertrophy and hyperplasia of the uterine myometrium during pregnancy.
- While hCG indirectly supports this by maintaining the corpus luteum (which produces estrogen and progesterone), it does not directly cause myometrial hypertrophy itself.
*Fetal angiogenesis*
- **Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)** and **fibroblast growth factor (FGF)** are key factors directly involved in fetal angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels in the fetus).
- While proper placental function, supported by hCG, is critical for fetal growth, hCG itself is not the direct mediator of fetal angiogenesis.
*Inhibition of ovulation*
- High levels of **estrogen** and **progesterone** (produced by the corpus luteum, maintained by hCG) provide **negative feedback** to the hypothalamus and pituitary, thus inhibiting the release of GnRH, FSH, and LH, which prevents further ovulation.
- hCG itself does not directly inhibit ovulation; rather, it sets in motion the hormonal cascade that leads to its inhibition.
*Stimulation of uterine contractions at term*
- **Oxytocin** is the primary hormone responsible for stimulating uterine contractions, particularly at term, often in conjunction with prostaglandins.
- hCG levels peak early in pregnancy and then decline, and it plays no direct role in stimulating labor contractions.
Physiology of parturition US Medical PG Question 5: Thirty minutes after vaginal delivery of a 2780-g (6-lb 2-oz) newborn at term, a 25-year-old woman, gravida 1, para 1, has heavy vaginal bleeding. Her pregnancy was complicated by pre-eclampsia. Her pulse is 111/min and blood pressure is 95/65 mm Hg. Physical examination shows a fundal height 2 inches below the xiphoid process of the sternum. A drug with which of the following mechanisms of action is most appropriate for this patient?
- A. Activation of phospholipase C (Correct Answer)
- B. Depolarization of the motor end plate
- C. Increased synthesis of cyclic AMP
- D. Inhibition of norepinephrine reuptake
- E. Binding to prostaglandin I2 receptors
Physiology of parturition Explanation: ***Activation of phospholipase C***
- This patient presents with **postpartum hemorrhage (PPH)**, characterized by heavy vaginal bleeding, tachycardia, hypotension, and a poorly contracted uterus (normal fundal height is at the umbilicus immediately after delivery; 2 inches below the xiphoid is high indicating uterine atony).
- The most appropriate first-line treatment for uterine atony is **oxytocin**, which acts by binding to G protein-coupled receptors, leading to the **activation of phospholipase C** and an increase in intracellular calcium, causing uterine muscle contraction.
*Depolarization of the motor end plate*
- This mechanism describes the action of **neuromuscular blocking agents** or agonists at the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, which are not used for treating postpartum hemorrhage.
- The motor end plate is involved in skeletal muscle contraction, not smooth muscle contraction of the uterus.
*Increased synthesis of cyclic AMP*
- **Increased cyclic AMP** generally leads to smooth muscle relaxation (e.g., beta-2 agonists like terbutaline), which would worsen uterine atony and postpartum hemorrhage.
- Tocolytic agents that would cause uterine relaxation would be contraindicated in this scenario.
*Inhibition of norepinephrine reuptake*
- This mechanism describes the action of certain **antidepressants** (e.g., tricyclic antidepressants, SNRIs) or **stimulants**, which primarily affect the central nervous system and are not used to manage postpartum hemorrhage.
- This action does not directly cause uterine contraction.
*Binding to prostaglandin I2 receptors*
- **Prostaglandin I2 (PGI2)**, also known as prostacyclin, is a potent vasodilator and inhibitor of platelet aggregation. Binding to its receptors would lead to smooth muscle relaxation and would increase bleeding, directly worsening postpartum hemorrhage.
- Uterotonic agents like carboprost (PGF2α analog) act on different prostaglandin receptors to induce uterine contraction.
Physiology of parturition US Medical PG Question 6: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
Physiology of parturition Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
Physiology of parturition US Medical PG Question 7: A 28-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 14 weeks' gestation, comes to the physician with a 3-day history of abnormal vaginal discharge. She has not had fever, chills, or abdominal pain. One week ago, her 2-year-old daughter had a urinary tract infection that quickly resolved after antibiotic therapy. The patient reports that she is sexually active with one male partner and they do not use condoms. Vital signs are within normal limits. Pelvic examination shows an inflamed and friable cervix. There is mucopurulent, foul-smelling discharge from the cervical os. There is no uterine or cervical motion tenderness. Vaginal pH measurement shows a pH of 3.5. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial step in management?
- A. Wet mount preparation
- B. Nucleic acid amplification test (Correct Answer)
- C. Amine test
- D. Urine analysis and culture
- E. Potassium hydroxide preparation
Physiology of parturition Explanation: ***Nucleic acid amplification test***
- The patient's symptoms of **inflamed, friable cervix** and **mucopurulent discharge**, along with a normal vaginal pH (3.5), are highly suggestive of **cervicitis**, commonly caused by *Chlamydia trachomatis* or *Neisseria gonorrhoeae*.
- **NAATs** are the most sensitive and specific tests for detecting these organisms, which is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment, especially in pregnancy, to prevent adverse outcomes.
*Wet mount preparation*
- A **wet mount** would be useful for identifying *Trichomonas vaginalis* or *Candida* species and diagnosing **bacterial vaginosis**, but the patient's normal vaginal pH makes these diagnoses less likely.
- While it can help rule out other common causes of vaginal discharge, it is **not sensitive enough** to reliably detect *Chlamydia* or *Gonorrhea*.
*Amine test*
- The **amine test** (or whiff test) is used to detect the release of amines in the presence of **bacterial vaginosis**, typically indicated by a **vaginal pH >4.5**.
- The patient's vaginal pH of 3.5 makes **bacterial vaginosis highly unlikely**, so an amine test would not be beneficial in this scenario.
*Urine analysis and culture*
- While the patient's daughter recently had a **urinary tract infection (UTI)**, the patient's symptoms are localized to the cervix (cervicitis) with **no fever, chills, or abdominal pain** indicative of a UTI.
- A urine analysis and culture would be appropriate if bladder symptoms were present, but it **will not diagnose cervicitis** or the specific sexually transmitted infections causing it.
*Potassium hydroxide preparation*
- A **KOH preparation** is primarily used to identify **fungal elements (hyphae and spores)**, indicating a *Candida* infection, which typically presents with thick, white, "cottage cheese" discharge and itching.
- This test is **not useful for diagnosing cervicitis** or bacterial causes of vaginal discharge, and the patient's symptoms are not consistent with candidiasis.
Physiology of parturition US Medical PG Question 8: A 31-year-old G6P6 woman with a history of fibroids gives birth to twins via vaginal delivery. Her pregnancy was uneventful, and she reported having good prenatal care. Both placentas are delivered immediately after the birth. The patient continues to bleed significantly over the next 20 minutes. Her temperature is 97.0°F (36.1°C), blood pressure is 124/84 mmHg, pulse is 95/min, respirations are 16/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Continued vaginal bleeding is noted. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial step in management?
- A. Oxytocin
- B. Blood product transfusion
- C. Uterine artery embolization
- D. Hysterectomy
- E. Bimanual massage (Correct Answer)
Physiology of parturition Explanation: ***Bimanual massage***
- The patient is experiencing **postpartum hemorrhage (PPH)**, indicated by significant bleeding post-delivery. **Uterine atony** is the most common cause of PPH, and bimanual massage helps stimulate uterine contractions to reduce bleeding.
- This is a **first-line, non-pharmacological intervention** that can be rapidly initiated to manage uterine atony.
*Oxytocin*
- While **oxytocin** is a uterotonic agent used to treat PPH, the initial step is typically **bimanual massage** to physically stimulate the uterus while preparing for medication administration.
- Oxytocin infusion would be administered concurrent with or immediately following bimanual massage, but manual compression is often initiated first.
*Blood product transfusion*
- Blood product transfusion is indicated for significant blood loss and hemodynamic instability, but it is a **supportive measure** rather than an initial intervention to stop the bleeding.
- The patient's current **blood pressure (124/84 mmHg)** and **pulse (95/min)** do not immediately suggest severe hypovolemic shock requiring immediate transfusion as the *first* step before attempting to control the source of bleeding.
*Uterine artery embolization*
- **Uterine artery embolization** is a highly invasive procedure typically reserved for cases where conservative measures, including uterotonic agents and bimanual compression, have failed to control PPH.
- It is not an appropriate initial step, as it requires specialized equipment and personnel and would delay immediate management of active bleeding.
*Hysterectomy*
- **Hysterectomy** is a last-resort intervention for intractable PPH that cannot be controlled by all other methods, including uterotonics, uterine massage, and other surgical or interventional radiology techniques.
- It is a highly invasive procedure with significant morbidity and is not considered an initial management step.
Physiology of parturition US Medical PG Question 9: A 32-year-old primigravida at 35 weeks gestation seeks evaluation at the emergency department for swelling and redness of the left calf, which started 2 hours ago. She reports that the pain has worsened since the onset. The patient denies a history of insect bites or trauma. She has never experienced something like this in the past. Her pregnancy has been uneventful so far. She does not use alcohol, tobacco, or any illicit drugs. She does not take any medications other than prenatal vitamins. Her temperature is 36.8℃ (98.2℉), the blood pressure is 105/60 mm Hg, the pulse is 110/min, and the respirations are 15/min. The left calf is edematous with the presence of erythema. The skin feels warm and pain is elicited with passive dorsiflexion of the foot. The femoral, popliteal, and pedal pulses are palpable bilaterally. An abdominal examination reveals a fundal height consistent with the gestational age. The lungs are clear to auscultation bilaterally. The patient is admitted to the hospital and appropriate treatment is initiated. Which of the following hormones is most likely implicated in the development of this patient’s condition?
- A. Human placental lactogen
- B. Human chorionic gonadotropin
- C. Progesterone (Correct Answer)
- D. Prolactin
- E. Estriol
Physiology of parturition Explanation: ***Progesterone***
- This patient presents with symptoms highly suggestive of **deep vein thrombosis (DVT)**, including unilateral leg swelling, warmth, erythema, and pain with dorsiflexion (**Homans' sign**). Pregnancy is a significant risk factor for DVT due to a **hypercoagulable state**.
- **Progesterone** is a key hormone in pregnancy that contributes to venous stasis by causing **venodilation** and decreasing vascular tone, making pregnant women more susceptible to DVT. It also contributes to the overall hypercoagulable state.
*Human placental lactogen*
- **Human placental lactogen (hPL)** is primarily involved in **insulin resistance** and glucose regulation in the mother to ensure nutrient supply to the fetus.
- It does not directly contribute to the thrombotic risk or venous changes seen in DVT.
*Human chorionic gonadotropin*
- **Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)** maintains the **corpus luteum** in early pregnancy and is associated with morning sickness.
- While essential for pregnancy, it does not directly influence coagulation or venous status to predispose to DVT.
*Prolactin*
- **Prolactin** is crucial for **mammary gland development** and **lactation**.
- It does not have a direct role in the physiological changes that increase DVT risk during pregnancy.
*Estriol*
- **Estriol** is a major estrogen in pregnancy, and like other estrogens, it contributes to the **hypercoagulable state** by increasing clotting factors and decreasing natural anticoagulants.
- However, progesterone's role in **venodilation and venous stasis** is more directly implicated in the acute development of DVT symptoms in the lower extremities during late pregnancy than the broad procoagulant effects of estrogen.
Physiology of parturition US Medical PG Question 10: A 33-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 26 weeks' gestation comes to the emergency department because of frequent contractions. The contractions are 40 seconds each, occurring every 2 minutes, and increasing in intensity. Her first child was delivered by lower segment transverse cesarean section because of a nonreassuring fetal heart rate. Her current medications include folic acid and a multivitamin. Her temperature is 36.9°C (98.4°F), heart rate is 88/min, and blood pressure is 126/76 mm Hg. Contractions are felt on the abdomen. There is clear fluid in the vulva and the introitus. The cervix is dilated to 5 cm, 70% effaced, and station of the head is -2. A fetal ultrasound shows polyhydramnios, a median cleft lip, and fused thalami. The corpus callosum, 3rd ventricle, and lateral ventricles are absent. The spine shows no abnormalities and there is a four chamber heart. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Initiate misoprostol therapy
- B. Allow vaginal delivery (Correct Answer)
- C. Perform dilation and evacuation
- D. Initiate nifedipine therapy
- E. Perform cesarean delivery
Physiology of parturition Explanation: ***Allow vaginal delivery***
- The presence of severe fetal anomalies, including **holoprosencephaly** (median cleft lip, fused thalami, absent corpus callosum, 3rd and lateral ventricles), indicates that the fetus is **incompatible with life**.
- Given the prognosis, the most appropriate and safest approach for the mother is to **allow vaginal delivery**, as there is no benefit to delaying delivery or attempting a surgical intervention that might pose more risks to the mother.
*Initiate misoprostol therapy*
- **Misoprostol** is a prostaglandin analog used to induce labor or abortion, particularly in cases of uterine atony or to ripen the cervix.
- While it aids in cervical ripening and uterine contractions, the cervix is already 5 cm dilated and 70% effaced, indicating a **rapidly progressing labor** not requiring additional induction.
*Perform dilation and evacuation*
- **Dilation and evacuation (D&E)** is typically performed in the second trimester for fetal demise or termination of pregnancy, usually before 24 weeks' gestation.
- At 26 weeks' gestation with advanced labor and significant cervical dilation, D&E is a **high-risk procedure** for the mother and less appropriate than vaginal delivery.
*Initiate nifedipine therapy*
- **Nifedipine is a tocolytic** used to suppress preterm labor by relaxing the uterine muscles.
- Given the **lethal fetal anomalies** and the advanced stage of labor (5 cm dilated, 70% effaced, intense contractions), stopping labor would only prolong a non-viable pregnancy and increase maternal risk.
*Perform cesarean delivery*
- **Cesarean delivery** would expose the mother to surgical risks (e.g., infection, hemorrhage, future pregnancy complications) without any benefit to the fetus, who has anomalies **incompatible with survival**.
- A previous cesarean section does not preclude a vaginal delivery in this context, especially when **fetal viability is not a concern**.
More Physiology of parturition US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.