Fetal heart rate monitoring US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Fetal heart rate monitoring. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Fetal heart rate monitoring US Medical PG Question 1: A 31-year-old woman gives birth to a boy in the labor and delivery ward of the local hospital. The child is immediately assessed and found to be crying vigorously. He is pink in appearance with blue extremities that appear to be flexed. Inducing some discomfort shows that both his arms and legs move slightly but remain largely flexed throughout. His pulse is found to be 128 beats per minute. What is the most likely APGAR score for this newborn at this time?
- A. 8 (Correct Answer)
- B. 5
- C. 9
- D. 6
- E. 7
Fetal heart rate monitoring Explanation: ***8***
- The assessment breaks down as: **Appearance** (pink body with blue extremities/acrocyanosis) = 1 point; **Pulse** (128 bpm, >100) = 2 points; **Grimace** (crying vigorously in response to discomfort) = 2 points; **Activity** (slight movement but remains largely flexed) = 1 point; **Respiration** (crying vigorously) = 2 points. Total = **8**.
- An APGAR score of 8-10 is considered **normal** and indicates a healthy newborn with only minor deductions (in this case, acrocyanosis which is common and benign).
*7*
- A score of 7 would require one fewer point, such as only 1 point for **Respiration** (weak cry or slow breathing) instead of 2 points.
- The infant's **vigorous crying** clearly merits 2 points for respiration, not 1, making a score of 7 incorrect.
*9*
- A score of 9 would require either fully pink appearance (2 points for Appearance) or active movement against resistance (2 points for Activity).
- The infant's **acrocyanosis** (blue extremities) limits Appearance to 1 point, and **limited activity** (largely flexed with only slight movement) prevents a score of 9.
*5*
- A score of 5 suggests moderate distress with significantly lower scores across multiple categories.
- The infant's strong pulse (2 points), vigorous crying (2 points each for Grimace and Respiration), and reasonable activity contradict an APGAR score of 5.
*6*
- A score of 6 would imply lower scores in at least two categories compared to the given findings.
- The infant's excellent cardiovascular (pulse 128 bpm = 2 points) and respiratory status (vigorous cry = 2 points) make a score of 6 too low.
Fetal heart rate monitoring US Medical PG Question 2: A 30-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, comes for a prenatal visit at 33 weeks' gestation. She delivered her first child spontaneously at 38 weeks' gestation; pregnancy was complicated by oligohydramnios. She has no other history of serious illness. Her blood pressure is 100/70 mm Hg. On pelvic examination, uterine size is found to be smaller than expected for dates. The fetus is in a longitudinal lie, with vertex presentation. The fetal heart rate is 144/min. Ultrasonography shows an estimated fetal weight below the 10th percentile, and decreased amniotic fluid volume. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in this patient?
- A. Serial nonstress tests (Correct Answer)
- B. Emergent cesarean delivery
- C. Amnioinfusion
- D. Reassurance only
- E. Weekly fetal weight estimation
Fetal heart rate monitoring Explanation: ***Serial nonstress tests***
- This patient presents with **intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)** and **oligohydramnios**, placing her fetus at high risk for fetal compromise and stillbirth.
- **Serial nonstress tests (NSTs)** are essential for monitoring fetal well-being in such high-risk pregnancies, as they assess fetal heart rate accelerations in response to fetal movement, indicating a healthy central nervous system and adequate oxygenation.
*Emergent cesarean delivery*
- While the fetus has IUGR and oligohydramnios, there is no immediate evidence of **fetal distress** (e.g., severe decelerations or persistent bradycardia) that would warrant an **emergent** delivery at 33 weeks.
- Delivery at 33 weeks increases the risk of **neonatal complications** associated with prematurity, so conservative management with close monitoring is preferred if the fetus is not in acute distress.
*Amnioinfusion*
- **Amnioinfusion** involves introducing saline into the amniotic cavity and is primarily used to alleviate **umbilical cord compression** during labor by increasing amniotic fluid volume.
- It is **not indicated** for chronic oligohydramnios in the antepartum period as a primary treatment and does not address the underlying pathology of IUGR.
*Reassurance only*
- Given the findings of **IUGR** (estimated fetal weight below 10th percentile) and **oligohydramnios**, the situation is not benign and requires active management and monitoring.
- **Reassurance only** would be inappropriate and potentially harmful, as these conditions significantly increase the risk of adverse perinatal outcomes.
*Weekly fetal weight estimation*
- While **fetal weight estimation** is important for diagnosing and tracking IUGR, performing it **weekly** is unnecessarily frequent and not the primary method for ongoing surveillance of fetal well-being.
- **Biophysical profiles (BPPs)** or **nonstress tests (NSTs)** combined with amniotic fluid index measurements are more appropriate for regular surveillance of fetal compromise in IUGR.
Fetal heart rate monitoring US Medical PG Question 3: A 32-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 38 weeks' gestation comes to the emergency department because of vaginal bleeding for the past hour. The patient reports that she felt contractions prior to the onset of the bleeding, but the contractions stopped after the bleeding started. She also has severe abdominal pain. Her first child was delivered by lower segment transverse cesarean section because of a nonreassuring fetal heart rate. Her pulse is 110/min, respirations are 17/min, and blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg. Examination shows diffuse abdominal tenderness with no rebound or guarding; no contractions are felt. The fetal heart rate shows recurrent variable decelerations. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Uterine inertia
- B. Amniotic fluid embolism
- C. Uterine rupture (Correct Answer)
- D. Vasa previa
- E. Abruptio placentae
Fetal heart rate monitoring Explanation: ***Uterine rupture***
- The patient's history of a prior **cesarean section**, sudden onset of **vaginal bleeding** and **severe abdominal pain**, resolution of contractions, and signs of **hypovolemic shock** (tachycardia, hypotension) coupled with fetal distress (variable decelerations) are highly indicative of uterine rupture.
- Diffuse abdominal tenderness without rebound or guarding, and no palpable contractions, are also consistent with rupture.
*Uterine inertia*
- This condition is characterized by **weak or uncoordinated uterine contractions** leading to prolonged labor, but it does not typically present with acute vaginal bleeding, sudden severe abdominal pain, or hypovolemic shock.
- Fetal distress in uterine inertia would more likely be due to prolonged labor rather than acute compromise following a sudden event.
*Amniotic fluid embolism*
- This is a rare, life-threatening obstetric emergency characterized by sudden **cardiovascular collapse, respiratory distress**, and **coagulopathy**, often occurring during labor or immediately postpartum.
- While it can cause fetal distress, vaginal bleeding and severe abdominal pain are not primary presenting symptoms.
*Vasa previa*
- Characterized by **painless vaginal bleeding** when fetal vessels within the membranes cross the internal cervical os, making them vulnerable to rupture during cervical dilation or amniotomy.
- The bleeding is typically fetal blood, and fetal distress occurs rapidly, but the mother would not experience severe abdominal pain or signs of hypovolemic shock unless the bleeding is substantial and prolonged.
*Abruptio placentae*
- This involves the **premature separation of the placenta**, causing painful vaginal bleeding, uterine tenderness, and frequent, strong contractions.
- While it can cause hypovolemic shock and fetal distress, the description of contractions stopping after bleeding started, along with a previous C-section scar, points more specifically to uterine rupture rather than an abruption.
Fetal heart rate monitoring US Medical PG Question 4: A 22-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 41 weeks' gestation is admitted to the hospital in active labor. Pregnancy has been uncomplicated. At the beginning of the second stage of labor, the cervix is 100% effaced and 10 cm dilated; the vertex is at -1 station. The fetal heart rate is reactive with no decelerations. As she pushes, it is noted that the fetal heart rate decreases, as seen on cardiotocography (CTG). Which of the following is the most likely cause of this finding?
- A. Fetal myocardial depression
- B. Maternal hypotension
- C. Placental insufficiency
- D. Umbilical cord compression
- E. Fetal head compression (Correct Answer)
Fetal heart rate monitoring Explanation: ***Fetal head compression***
- During the second stage of labor, **fetal head compression** commonly occurs with uterine contractions and maternal pushing efforts.
- This compression leads to a reflex vagal response, causing a **decrease in fetal heart rate (early decelerations)**, which is typically benign and resolves after the contraction.
*Fetal myocardial depression*
- **Fetal myocardial depression** can cause a decrease in fetal heart rate, but it is typically associated with **prolonged hypoxia or acidosis** and would likely manifest as late or prolonged decelerations or bradycardia, not just during pushing.
- There are no indications in the scenario of fetal distress or metabolic compromise that would point to myocardial depression.
*Maternal hypotension*
- **Maternal hypotension** would lead to **decreased placental perfusion**, resulting in **late decelerations** due to uteroplacental insufficiency.
- The scenario describes a reactive fetal heart rate with decelerations specifically during pushing, not a pattern consistent with sustained maternal hypotension impacting placental blood flow.
*Placental insufficiency*
- **Placental insufficiency** typically manifests as **late decelerations**, which are gradual decreases in fetal heart rate that begin after the peak of the contraction and return to baseline after the contraction ends.
- The fetal heart rate in the scenario is described as reactive with no decelerations prior to pushing, making placental insufficiency less likely as the primary cause of an acute deceleration during pushing.
*Umbilical cord compression*
- **Umbilical cord compression** causes **variable decelerations**, which are abrupt, often dramatic drops in fetal heart rate.
- While cord compression can occur during labor, the described pattern of deceleration specifically with pushing and the absence of other signs of cord impingement makes head compression a more direct and common cause in this context.
Fetal heart rate monitoring US Medical PG Question 5: A 26-year-old G1P0 female who is 39 weeks pregnant presents to the emergency department in labor. She reports following her primary care physician’s recommendations throughout her pregnancy and has not had any complications. During delivery, the baby’s head turtled back into the vaginal canal and did not advance any further. The neonatal intensivist was called for shoulder dystocia and a baby girl was able to be delivered vaginally 6 minutes later. Upon initial assessment, the baby appeared pale throughout, had her arms and legs flexed without active motion, and had some flexion of extremities when stimulated. Her pulse is 120/min and had irregular respirations. What is this baby’s initial APGAR score?
- A. 5 (Correct Answer)
- B. 6
- C. 7
- D. 4
- E. 3
Fetal heart rate monitoring Explanation: ***5***
- The APGAR score is calculated based on five criteria: **Appearance**, **Pulse**, **Grimace**, **Activity**, and **Respiration**.
- This baby's score is calculated as follows: **Appearance** (pale all over) = 0, **Pulse** (120/min) = 2, **Grimace** (some flexion of extremities with stimulation) = 1, **Activity** (arms and legs flexed without active motion) = 1, and **Respiration** (irregular) = 1.
- Total score: 0 + 2 + 1 + 1 + 1 = **5 points**
- A score of 5 indicates **moderate neonatal compromise** requiring close monitoring and possible intervention.
*4*
- A score of 4 would indicate more severe compromise, such as absent respirations (0 points) rather than irregular respirations (1 point).
- This baby has irregular respirations present, which earns 1 point, not 0 points.
*6*
- A score of 6 would require improvement in at least one category, such as **acrocyanosis** (blue extremities but pink body = 1 point for appearance) instead of pallor throughout.
- This baby's complete pallor limits the score to 5.
*7*
- A score of 7 or higher is generally considered reassuring and indicates a **healthy transition** from intrauterine to extrauterine life.
- This baby's concerning signs, including **complete pallor**, **irregular respirations**, and **poor muscle tone**, are inconsistent with a score of 7.
*3*
- A score of 3 would indicate severe depression with findings such as **heart rate less than 100 bpm**, completely absent reflexes, or flaccid muscle tone.
- This baby has a reassuring pulse of 120/min (2 points), some reflex response (1 point), and some muscle tone (1 point), making the total score higher than 3.
Fetal heart rate monitoring US Medical PG Question 6: Five minutes after initiating a change of position and oxygen inhalation, the oxytocin infusion is discontinued. A repeat CTG that is done 10 minutes later shows recurrent variable decelerations and a total of 3 uterine contractions in 10 minutes. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Restart oxytocin infusion
- B. Emergent Cesarean section
- C. Administer terbutaline
- D. Monitor without intervention
- E. Amnioinfusion (Correct Answer)
Fetal heart rate monitoring Explanation: ***Amnioinfusion***
- **Recurrent variable decelerations** persisting after discontinuing oxytocin and changing maternal position often indicate **cord compression**, which can be relieved by amnioinfusion.
- Adding fluid to the amniotic cavity **cushions the umbilical cord**, reducing compression during uterine contractions.
*Restart oxytocin infusion*
- Reinitiating oxytocin would likely **worsen the recurrent variable decelerations** by increasing uterine contraction frequency and intensity, thereby exacerbating cord compression.
- The goal is to alleviate fetal distress, not to intensify uterine activity that is already causing issues.
*Emergent Cesarean section*
- While an emergent Cesarean section is indicated for **unresolved fetal distress**, it's usually considered after less invasive measures, such as amnioinfusion, have failed.
- There is still an opportunity for a simpler intervention to resolve the issue before resorting to surgery.
*Administer terbutaline*
- Terbutaline is a **tocolytic agent** used to reduce uterine contractions, which can be helpful in cases of tachysystole or hyperstimulation.
- In this scenario, the contraction frequency is low (3 in 10 minutes), so reducing contractions is not the primary aim; rather, the focus is on resolving the cord compression causing decelerations.
*Monitor without intervention*
- **Recurrent variable decelerations** are an concerning sign of **fetal distress** and require intervention to prevent potential harm to the fetus.
- Simply monitoring without intervention would be inappropriate and could lead to worsening fetal hypoxemia and acidosis.
Fetal heart rate monitoring US Medical PG Question 7: A 25-year-old G2P1001 at 32 weeks gestation presents to the hospital with painless vaginal bleeding. The patient states that she was taking care of laundry at home when she experienced a sudden sensation of her water breaking and saw that her groin was covered in blood. Her prenatal history is unremarkable according to the clinic records, but she has not seen an obstetrician for the past 14 weeks. Her previous delivery was by urgent cesarean section for placenta previa. Her temperature is 95°F (35°C), blood pressure is 125/75 mmHg, pulse is 79/min, respirations are 18/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Cervical exam shows gross blood in the vaginal os. The fetal head is not palpable. Fetal heart rate monitoring demonstrates decelerations and bradycardia. Labs are pending. IV fluids are started. What is the best next step in management?
- A. Cesarean section (Correct Answer)
- B. Betamethasone
- C. Red blood cell transfusion
- D. Vaginal delivery
- E. Lumbar epidural block
Fetal heart rate monitoring Explanation: ***Cesarean section***
- This patient presents with signs highly suggestive of **placenta previa with possible vasa previa or placental abruption**, with life-threatening complications for both mother and fetus. The presence of **painless vaginal bleeding**, a prior **cesarean section for placenta previa**, and **fetal heart rate decelerations/bradycardia** necessitate immediate delivery via cesarean section to prevent **fetal demise** and severe **maternal hemorrhage**.
- The rapid deterioration of the fetal status, indicated by **decelerations and bradycardia**, confirms the urgency. A **cesarean section** is the quickest and safest way to deliver the baby and address the underlying obstetric emergency.
*Betamethasone*
- **Betamethasone** is administered to promote **fetal lung maturity** in cases of preterm delivery. While this patient is preterm at 32 weeks, the critical nature of the fetal distress and bleeding requires immediate delivery, making the delay for betamethasone administration inappropriate.
- The benefits of steroids for lung maturity are outweighed by the **immediate risk of fetal demise** and severe maternal complications if delivery is delayed.
*Red blood cell transfusion*
- While the patient is actively bleeding and may eventually require a **blood transfusion**, starting IV fluids and proceeding with an **immediate cesarean section** are higher priorities to stabilize the mother and rescue the fetus.
- Transfusions are supportive measures once the source of hemorrhage is addressed and vital signs are stabilized during or after surgery.
*Vaginal delivery*
- Given the patient's history of **placenta previa**, current **painless vaginal bleeding**, and signs of **fetal distress**, a vaginal delivery is contraindicated due to the high risk of **exsanguinating hemorrhage** for the mother and severe fetal compromise.
- The prior **cesarean section for placenta previa** also increases the risk of recurrent previa and **placenta accreta spectrum**, further contraindicating vaginal delivery.
*Lumbar epidural block*
- A **lumbar epidural block** is used for pain management during labor, but in this emergent situation with active bleeding and fetal distress, immediate delivery is paramount.
- The time required to safely administer an **epidural**, along with the potential for **hypotension** in a hypovolemic patient, makes it an inappropriate next step.
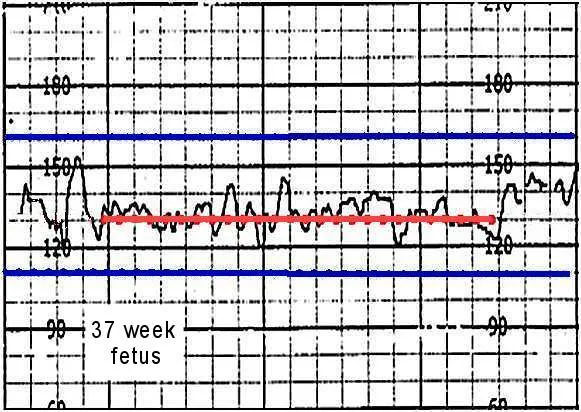
Fetal heart rate monitoring US Medical PG Question 8: A 30-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 38 weeks' gestation comes to the hospital for regular, painful contractions that have been increasing in frequency. Her pregnancy has been complicated by gestational diabetes treated with insulin. Pelvic examination shows the cervix is 50% effaced and 4 cm dilated; the vertex is at -1 station. Ultrasonography shows no abnormalities. A tocometer and Doppler fetal heart monitor are placed on the patient's abdomen. The fetal heart rate monitoring strip shows a baseline heart rate of 145/min with a variability of ≥ 15/min. Within a 20-minute recording, there are 7 uterine contractions, 4 accelerations, and 3 decelerations that have a nadir occurring within half a minute. The decelerations occur at differing intervals relative to the contractions. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
- A. Vibroacoustic stimulation
- B. Routine monitoring (Correct Answer)
- C. Administer tocolytics
- D. Emergent cesarean delivery
- E. Placement of fetal scalp electrode
Fetal heart rate monitoring Explanation: ***Routine monitoring***
- The presented FHR tracing exhibits a **normal baseline rate** (145/min), **moderate variability** (≥15/min), and the presence of **accelerations**, indicating a reassuring fetal status.
- The described decelerations are **variable decelerations** due to their sudden onset, nadir within 30 seconds, and variable relationship to contractions, which are generally benign unless prolonged, deep, or repetitive. Given the otherwise reassuring status, continued routine monitoring is appropriate.
*Vibroacoustic stimulation*
- This intervention is used to elicit **fetal accelerations** or movement during non-stress tests (NSTs) when the fetus is quiet or shows a non-reactive pattern.
- In this case, the fetus is already showing **accelerations** and moderate variability, so stimulation is not needed to assess fetal well-being.
*Administer tocolytics*
- **Tocolytics** are used to stop or slow down labor, typically in cases of preterm labor or uterine tachysystole causing fetal distress.
- This patient is at **38 weeks' gestation** and in active labor, and there are no signs of fetal distress warranting the cessation of contractions.
*Emergent cesarean delivery*
- **Emergent cesarean delivery** is indicated for acute fetal distress, such as prolonged decelerations, significant bradycardia, or absent variability in conjunction with other concerning FHR patterns.
- The FHR tracing described is largely reassuring with moderate variability and accelerations, and the variable decelerations are not indicative of immediate threat, making emergent delivery unnecessary.
*Placement of fetal scalp electrode*
- A **fetal scalp electrode** provides a more accurate and continuous measure of the FHR, often used when external monitoring is difficult or when there are concerns about the reliability of the tracing.
- While it can be useful in some situations, the current tracing is **interpretable as reassuring**, making invasive monitoring currently unnecessary.
Fetal heart rate monitoring US Medical PG Question 9: A 29-year-old woman, gravida 1, para 0, at 36 weeks' gestation is brought to the emergency department after an episode of dizziness and vomiting followed by loss of consciousness lasting 1 minute. She reports that her symptoms started after lying down on her back to rest, as she felt tired during yoga class. Her pregnancy has been uncomplicated. On arrival, she is diaphoretic and pale. Her pulse is 115/min and blood pressure is 90/58 mm Hg. On examination, the patient is lying in the supine position with a fundal height of 36 cm. There is a prolonged fetal heart rate deceleration to 80/min. Which of the following is the most appropriate action to reverse this patient's symptoms in the future?
- A. Performing the Muller maneuver
- B. Gentle compression with an abdominal binder
- C. Lying in the supine position and elevating legs
- D. Lying in the left lateral decubitus position (Correct Answer)
- E. Performing the Valsava maneuver
Fetal heart rate monitoring Explanation: ***Lying in the left lateral decubitus position***
- This position relieves **aortocaval compression** by moving the uterus off the **inferior vena cava (IVC)** and aorta.
- Alleviating IVC compression increases **venous return** to the heart, improving **cardiac output** and blood pressure, thereby resolving the patient's symptoms and improving **fetal oxygenation**.
*Performing the Muller maneuver*
- The **Muller maneuver** involves forced inspiration against a closed glottis, creating **negative intrathoracic pressure**.
- This maneuver is used to evaluate **upper airway compromise** and would not address the underlying issue of aortocaval compression.
*Gentle compression with an abdominal binder*
- An **abdominal binder** would apply external pressure to the abdomen, which could worsen rather than alleviate **aortocaval compression**.
- This would further reduce **venous return** and potentially exacerbate the patient's **hypotension** and fetal distress.
*Lying in the supine position and elevating legs*
- Lying in the **supine position** is the cause of the patient's symptoms due to **aortocaval syndrome**.
- While **elevating the legs** can temporarily increase venous return from the legs, it would not relieve the compression of the IVC by the gravid uterus.
*Performing the Valsava maneuver*
- The **Valsalva maneuver** involves forced exhalation against a closed glottis, which increases **intrathoracic pressure** and decreases **venous return**.
- This would further reduce **cardiac output** and worsen the symptoms of **hypotension** and **fetal compromise**.
Fetal heart rate monitoring US Medical PG Question 10: A 30-year-old primigravida schedules an appointment with her obstetrician for a regular check-up. She says that everything is fine, although she reports that her baby has stopped moving as much as previously. She is 22 weeks gestation. She denies any pain or vaginal bleeding. The obstetrician performs an ultrasound and also orders routine blood and urine tests. On ultrasound, there is no fetal cardiac activity or movement. The patient is asked to wait for 1 hour, after which the scan is to be repeated. The second scan shows the same findings. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Missed abortion
- B. Ectopic pregnancy
- C. Complete abortion
- D. Fetal demise (Correct Answer)
- E. Incomplete abortion
Fetal heart rate monitoring Explanation: ***Fetal demise***
- The absence of fetal cardiac activity and movement on repeated ultrasound scans at 22 weeks' gestation, after previously reporting fetal movement, is consistent with **fetal demise**.
- **Fetal demise** refers to the death of a fetus in utero at or after 20 weeks of gestation, or when the fetus weighs 350 grams or more.
*Missed abortion*
- **Missed abortion** (or missed miscarriage) is typically defined as a non-viable intrauterine pregnancy with a retained fetus or embryo without cardiac activity before 20 weeks of gestation.
- The patient is 22 weeks gestation, which places the condition beyond the general definition of a missed abortion.
*Ectopic pregnancy*
- In an **ectopic pregnancy**, the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tube, and would not have reached 22 weeks with reported fetal movement.
- An ectopic pregnancy would present with earlier symptoms like **abdominal pain** and **vaginal bleeding**, and an ultrasound would show an empty uterus or evidence of extrauterine pregnancy.
*Complete abortion*
- A **complete abortion** involves the complete expulsion of all products of conception from the uterus.
- This would be characterized by **heavy vaginal bleeding** and the passage of tissue, which the patient denies.
*Incomplete abortion*
- An **incomplete abortion** occurs when some, but not all, products of conception have been expelled from the uterus.
- Similar to complete abortion, an incomplete abortion would typically involve **vaginal bleeding** and retained tissue, accompanied by **cramping**, which are absent in this case.
More Fetal heart rate monitoring US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.