Stages of labor

On this page
🎭 The Labor Symphony: Understanding Birth's Four-Act Drama
Labor unfolds as a precisely orchestrated physiological process where uterine contractions, cervical change, and fetal descent converge in predictable yet variable patterns. You'll master how to distinguish normal progression through latent, active, and transition phases from pathological deviations, interpret contraction mechanics that drive delivery, and apply evidence-based algorithms that optimize outcomes while recognizing when intervention becomes necessary. This framework transforms labor from an unpredictable event into a readable clinical narrative where pattern recognition saves lives.
📌 Remember: P-P-P Framework - Passenger (fetal size/position), Passage (pelvic dimensions), Powers (uterine contractions) - all three must align for successful vaginal delivery
The labor process follows predictable patterns with measurable milestones. Stage 1 accounts for 85-90% of total labor time, while Stage 2 typically lasts 30 minutes-3 hours in nulliparous women. Stage 3 normally completes within 30 minutes, and Stage 4 encompasses the critical first 2 hours postpartum.
| Stage | Nulliparous Duration | Multiparous Duration | Key Cervical Changes | Primary Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First | 12-20 hours | 6-8 hours | 0→10 cm dilation | Contraction pattern, FHR |
| Second | 30 min-3 hours | 5-30 minutes | Complete dilation | Descent, rotation |
| Third | 5-30 minutes | 5-30 minutes | Post-delivery | Placental separation |
| Fourth | 2 hours | 2 hours | Uterine contraction | Hemorrhage prevention |
Labor progression follows measurable parameters that guide clinical decision-making. Cervical dilation advances at minimum 1.2 cm/hour in nulliparous women and 1.5 cm/hour in multiparous women during active phase. Fetal descent occurs simultaneously, measured by station relative to ischial spines.
- Latent Phase Characteristics
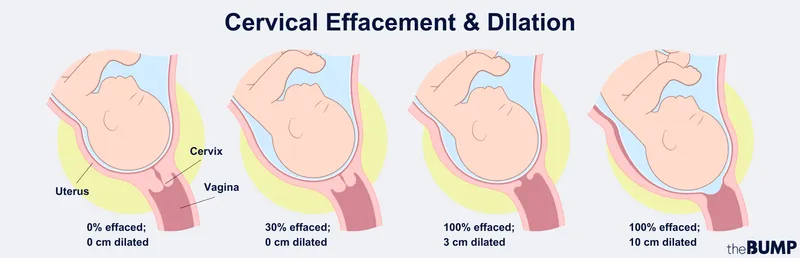
- Cervical effacement: 0-80% thinning
- Dilation rate: 0.5 cm/hour average
- Contraction frequency: Every 5-20 minutes
- Duration: 30-45 seconds
- Intensity: 25-40 mmHg
- Active Phase Dynamics
- Acceleration: 6-8 cm rapid dilation
- Maximum slope: 8-10 cm fastest progress
- Deceleration: 10 cm to full dilation
- Contraction frequency: Every 2-3 minutes
- Duration: 60-90 seconds
- Intensity: 50-80 mmHg
💡 Master This: 2-1-1 Rule for active labor recognition-contractions every 2 minutes, lasting 1 minute, for 1 hour consistently indicates established labor requiring hospital evaluation
Understanding normal labor progression enables early recognition of dystocia patterns. Protracted labor occurs when dilation rate falls below 1.2 cm/hour in nulliparous or 1.5 cm/hour in multiparous women. Arrest disorders develop when no cervical change occurs over 4 hours with adequate contractions or 6 hours with inadequate contractions.
📌 Remember: BISHOP Score predicts successful induction-Score ≥8 indicates 90% likelihood of vaginal delivery within 24 hours
Connect these foundational labor concepts through the next section to understand how uterine contractions generate the mechanical forces driving cervical change and fetal descent.
🎭 The Labor Symphony: Understanding Birth's Four-Act Drama
⚡ The Uterine Engine: Decoding Contraction Mechanics
The triple descending gradient ensures optimal contraction efficiency-fundal contractions are strongest and longest, mid-uterine contractions are moderate, and lower uterine segment contractions are weakest. This gradient prevents cervical spasm and facilitates coordinated fetal expulsion.
📌 Remember: FIGO Classification - Frequency (every 2-5 minutes), Intensity (40-80 mmHg), Duration (45-90 seconds) define adequate uterine activity for labor progression
Contraction assessment utilizes both external tocodynamometry and intrauterine pressure catheters (IUPC). External monitoring measures contraction frequency and duration but cannot quantify intensity. IUPC placement provides precise pressure measurements, with Montevideo Units (MVUs) calculating contraction adequacy.
| Assessment Method | Frequency Accuracy | Duration Accuracy | Intensity Measurement | Clinical Utility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| External Toco | Excellent | Good | Relative only | Routine monitoring |
| IUPC | Excellent | Excellent | Absolute mmHg | Dystocia evaluation |
| Palpation | Good | Fair | Subjective | Bedside assessment |
| Maternal Report | Variable | Poor | Subjective | Supplementary data |
Contraction patterns evolve throughout labor stages, with distinct characteristics defining normal progression versus pathological variants. Coupling occurs when contractions pair together, while tripling indicates uterine irritability. Tetanic contractions lasting >90 seconds or polysystole with <60 seconds between contractions require immediate intervention.
- Normal Contraction Patterns
- Latent phase: Every 5-20 minutes, 30-45 seconds
- Active phase: Every 2-3 minutes, 60-90 seconds
- Transition: Every 1-2 minutes, 90+ seconds
- Intensity progression: 25→50→80 mmHg
- Resting tone: 8-12 mmHg baseline
- Pathological Patterns
- Hyperstimulation: >5 contractions/10 minutes
- Tetanic: Duration >90 seconds
- Coupling: Two contractions without relaxation
- Polysystole: <60 seconds between contractions
- Hypertonus: Baseline >20 mmHg
💡 Master This: Tachysystole (>5 contractions/10 minutes) with Category II/III FHR changes requires immediate tocolysis with terbutaline 0.25 mg SQ or nitroglycerin 50-100 mcg IV
Pharmacological augmentation modifies contraction patterns when spontaneous uterine activity proves inadequate. Oxytocin increases both contraction frequency and intensity, starting at 1-2 mU/min and increasing by 1-2 mU/min every 15-40 minutes. Maximum doses typically remain below 20 mU/min to prevent hyperstimulation.
📌 Remember: ACOG Guidelines - Arrest of dilation requires 4 hours of adequate contractions (≥200 MVUs) or 6 hours of inadequate contractions before cesarean consideration
Connect contraction mechanics through the next section to understand how these powerful uterine forces translate into recognizable clinical patterns and assessment frameworks for labor management.
⚡ The Uterine Engine: Decoding Contraction Mechanics
🎯 Pattern Recognition Mastery: Clinical Labor Assessment
Cervical examination remains the gold standard for labor progress assessment, evaluating 5 key parameters: dilation (0-10 cm), effacement (0-100%), station (-3 to +3), consistency (firm to soft), and position (posterior to anterior). Digital examination frequency should be every 4 hours in normal labor to minimize infection risk.
📌 Remember: PEACE Assessment - Position, Effacement, Anterior/posterior, Consistency, Engagement (station) - systematic cervical evaluation prevents missed findings
| Clinical Parameter | Normal Range | Concerning Findings | Intervention Threshold | Assessment Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dilation Rate | 1.2-1.5 cm/hr | <1.0 cm/hr | No change 4 hrs | Every 4 hours |
| Fetal Station | -3 to +3 | No descent 2 hrs | Arrest of descent | With each exam |
| Contraction Frequency | 2-5 per 10 min | >5 per 10 min | Tachysystole | Continuous |
| FHR Baseline | 110-160 bpm | <110 or >160 | Category II/III | Continuous |
- FHR Pattern Recognition Framework
- Baseline Assessment
- Normal: 110-160 bpm stable
- Tachycardia: >160 bpm sustained
- Bradycardia: <110 bpm sustained
- Variability Interpretation
- Moderate: 6-25 bpm fluctuations (reassuring)
- Minimal: ≤5 bpm fluctuations (concerning)
- Absent: Undetectable fluctuations (ominous)
- Marked: >25 bpm fluctuations (investigate)
- Baseline Assessment
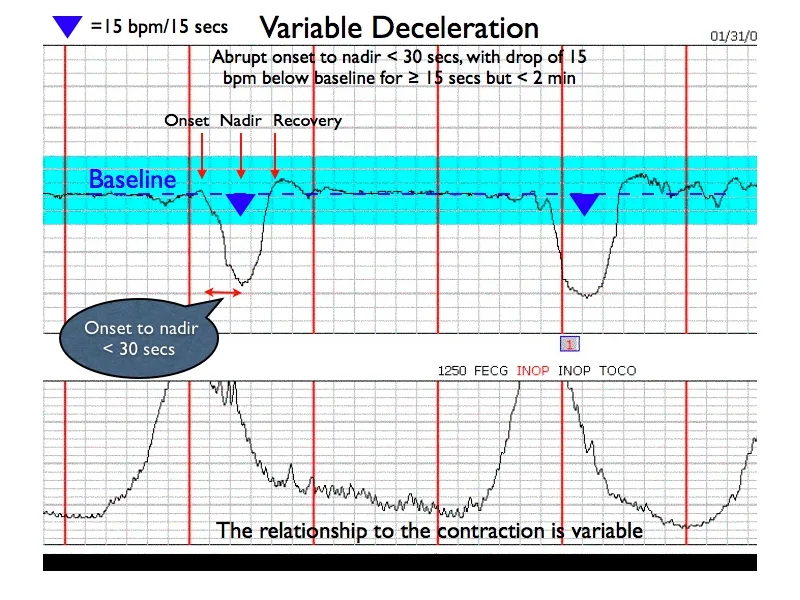
⭐ Clinical Pearl: VEAL CHOP mnemonic - Variable→Cord compression, Early→Head compression, Acceleration→OK, Late→Placental insufficiency
Labor dystocia recognition requires systematic evaluation of the three Ps: Power (uterine contractions), Passenger (fetal size/position), and Passage (pelvic adequacy). Protracted disorders show slow but continuous progress, while arrest disorders demonstrate complete cessation of progress despite adequate time and contractions.
- Dystocia Pattern Recognition
- Protracted Active Phase
- Nulliparous: <1.2 cm/hr dilation
- Multiparous: <1.5 cm/hr dilation
- Management: Augmentation consideration
- Arrest of Dilation
- ≥4 hours no cervical change with adequate contractions
- ≥6 hours no cervical change with inadequate contractions
- Management: Cesarean delivery consideration
- Arrest of Descent
- ≥3 hours no fetal descent (nulliparous)
- ≥2 hours no fetal descent (multiparous)
- Management: Operative delivery consideration
- Protracted Active Phase
💡 Master This: Zhang Curve replaced Friedman's-active labor begins at 6 cm, not 4 cm, and normal dilation rates vary significantly between 4-6 cm (slower) and 6-10 cm (faster)
Clinical decision algorithms integrate multiple assessment parameters to guide management. Intrauterine resuscitation for Category II/III FHR patterns includes maternal repositioning, IV fluid bolus, oxygen administration, and tocolysis if hyperstimulation present.
📌 Remember: ACOG Safe Prevention - 39+ weeks for elective delivery, 6 cm for active labor diagnosis, 4-6 hours for arrest diagnosis prevents unnecessary interventions
Connect pattern recognition skills through the next section to understand how systematic comparison frameworks differentiate normal labor variants from pathological conditions requiring intervention.
🎯 Pattern Recognition Mastery: Clinical Labor Assessment
🔬 Differential Diagnosis Framework: Normal vs. Pathological Labor
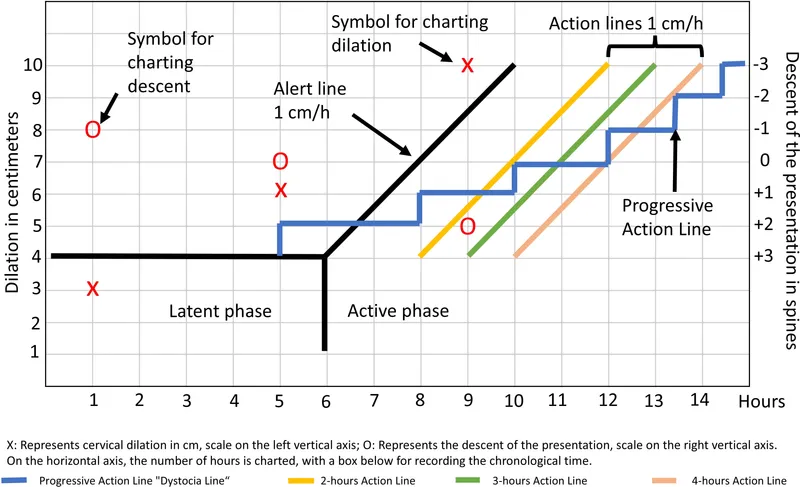
Temporal discrimination forms the foundation of labor assessment. Latent phase prolongation exceeds 20 hours (nulliparous) or 14 hours (multiparous), while active phase arrest requires 4+ hours without cervical change despite adequate contractions. Second stage prolongation exceeds 3 hours (nulliparous) or 2 hours (multiparous) with epidural anesthesia.
| Labor Parameter | Normal Nulliparous | Normal Multiparous | Pathological Threshold | Intervention Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latent Phase | <20 hours | <14 hours | Exceeds normal | Rest/augmentation |
| Active Phase Rate | ≥1.2 cm/hr | ≥1.5 cm/hr | <1.0 cm/hr | Evaluate 3 Ps |
| Second Stage | <3 hrs (epidural) | <2 hrs (epidural) | Exceeds limits | Operative delivery |
| Descent Rate | ≥1 cm/hr | ≥2 cm/hr | No progress 2 hrs | Assess position |
Contraction pattern analysis differentiates adequate from inadequate uterine activity. Normal contractions achieve ≥200 Montevideo Units, occur every 2-5 minutes, and last 45-90 seconds. Pathological patterns include hyperstimulation (>5 contractions/10 minutes), coupling, or inadequate intensity (<200 MVUs).
- Contraction Pattern Discrimination
- Adequate Uterine Activity
- Frequency: Every 2-5 minutes
- Duration: 45-90 seconds
- Intensity: ≥200 MVUs or ≥50 mmHg
- Resting tone: <20 mmHg
- Inadequate Patterns
- Infrequent: >5 minutes apart
- Brief: <45 seconds duration
- Weak: <200 MVUs or <40 mmHg
- Poor relaxation: >20 mmHg baseline
- Pathological Hyperstimulation
- Tachysystole: >5 contractions/10 minutes
- Tetanic: >90 seconds duration
- Coupling: No relaxation between
- Hypertonus: >25 mmHg baseline
- Adequate Uterine Activity
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Caldwell-Moloy Classification - Gynecoid pelvis (50% women) favors normal delivery, Android pelvis (20% women) increases dystocia risk by 300%
Fetal assessment parameters distinguish normal adaptive responses from pathological compromise. Category I FHR tracings indicate fetal well-being, Category II requires increased surveillance and possible intervention, while Category III mandates immediate delivery within 30 minutes.
- FHR Pattern Discrimination Framework
- Category I (Normal)
- Baseline: 110-160 bpm
- Variability: Moderate (6-25 bpm)
- Decelerations: None or early only
- Accelerations: Present with fetal movement
- Category II (Indeterminate)
- Baseline: Tachycardia or bradycardia
- Variability: Minimal or marked
- Decelerations: Variable without concerning features
- Accelerations: Absent >80 minutes
- Category III (Abnormal)
- Variability: Absent with any of:
- Decelerations: Recurrent late or variable
- Pattern: Sinusoidal appearance
- Bradycardia: <110 bpm sustained
- Category I (Normal)
💡 Master This: ABCD Approach to abnormal FHR - Assess category, Begin intrauterine resuscitation, Correct underlying cause, Deliver if no improvement
Maternal complication recognition requires systematic evaluation of vital signs, symptoms, and laboratory parameters. Chorioamnionitis presents with maternal fever >38°C, maternal tachycardia >100 bpm, fetal tachycardia >160 bpm, and uterine tenderness. Preeclampsia manifests as hypertension ≥140/90 mmHg with proteinuria or end-organ dysfunction.
📌 Remember: TORCH infections during labor - Toxoplasmosis, Other (syphilis, varicella), Rubella, CMV, Herpes require specific delivery precautions and neonatal prophylaxis
Connect differential diagnosis frameworks through the next section to understand evidence-based treatment algorithms that optimize maternal-fetal outcomes while minimizing unnecessary interventions.
🔬 Differential Diagnosis Framework: Normal vs. Pathological Labor
⚖️ Evidence-Based Management Algorithms: Optimizing Labor Outcomes
First stage management follows structured protocols based on cervical dilation and contraction adequacy. Latent phase management emphasizes therapeutic rest with morphine 10-15 mg IM or ambulation and hydration. Active phase requires continuous monitoring with intervention thresholds at 4-6 hours without progress.
Oxytocin augmentation protocols follow standardized dosing regimens to achieve adequate uterine activity while preventing hyperstimulation. Low-dose protocols start at 1-2 mU/min with 1-2 mU/min increases every 15-40 minutes. High-dose protocols use 4-6 mU/min starting doses with 4-6 mU/min increases every 15-20 minutes.
| Protocol Type | Starting Dose | Increment | Interval | Maximum Dose | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Dose | 1-2 mU/min | 1-2 mU/min | 30-40 min | 20 mU/min | 85-90% |
| High-Dose | 4-6 mU/min | 4-6 mU/min | 15-20 min | 40 mU/min | 90-95% |
| Physiologic | 1-2 mU/min | 1-2 mU/min | 15-30 min | 20 mU/min | 85-90% |
📌 Remember: ACOG Oxytocin Guidelines - Target 200-250 MVUs or 3-5 contractions per 10 minutes lasting 45-80 seconds for adequate augmentation
Second stage management balances maternal pushing efforts with fetal well-being monitoring. Delayed pushing in nulliparous women with epidural anesthesia allows passive fetal descent for 1-2 hours before active pushing, reducing operative delivery rates by 20-30%.
- Second Stage Protocol Framework
- Immediate Pushing (no epidural)
- Begin with complete dilation
- Open-glottis pushing preferred
- Position changes every 30 minutes
- Perineal support during crowning
- Delayed Pushing (epidural present)
- Passive descent 1-2 hours maximum
- Begin pushing with urge or station +1
- Directed pushing 10 seconds × 3 per contraction
- Vacuum/forceps if arrest >3 hours (nullip) or >2 hours (multip)
- Immediate Pushing (no epidural)
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Hands-on vs. hands-poised perineal protection shows no difference in third-degree tear rates (6.1% vs. 6.8%), but hands-on reduces episiotomy rates by 13%
Intrapartum fetal monitoring protocols guide intervention timing based on FHR category classification. Category II tracings trigger intrauterine resuscitation including maternal repositioning, IV fluid bolus 500-1000 mL, oxygen 8-10 L/min, and tocolysis if hyperstimulation present.
- Intrauterine Resuscitation Protocol
- Immediate Interventions
- Maternal positioning: Left lateral or knee-chest
- IV fluid bolus: 500-1000 mL lactated Ringer's
- Oxygen therapy: 8-10 L/min non-rebreather mask
- Discontinue oxytocin if hyperstimulation
- Tocolytic Therapy (if hyperstimulation)
- Terbutaline: 0.25 mg SQ (first-line)
- Nitroglycerin: 50-100 mcg IV (alternative)
- Magnesium sulfate: 2-4 g IV (preeclampsia)
- Delivery Preparation
- Category III: Delivery within 30 minutes
- Persistent Category II: Consider operative delivery
- Scalp stimulation: Test for acceleration response
- Immediate Interventions
💡 Master This: ACOG Practice Bulletin - Cesarean delivery for non-reassuring FHR should occur within 30 minutes of decision, but immediate delivery (<30 minutes) required only for uterine rupture, cord prolapse, or placental abruption
Third stage management employs active management protocols that reduce postpartum hemorrhage by 60% compared to expectant management. Active management includes oxytocin 10 units IM/IV, controlled cord traction, and uterine massage after placental delivery.
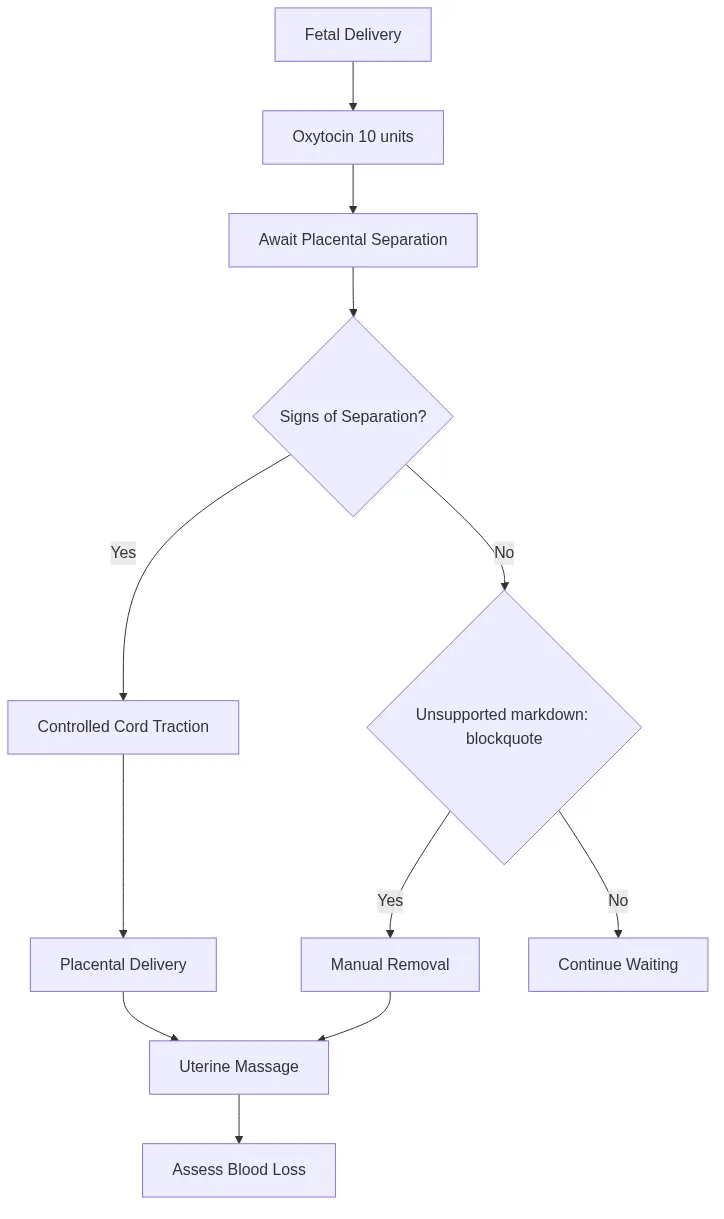
📌 Remember: WHO Active Management - Oxytocin within 1 minute of delivery, controlled cord traction with counter-pressure, uterine massage after placental delivery reduces PPH risk by 60%
Connect evidence-based management protocols through the next section to understand how multiple physiological systems integrate during labor to create the complex orchestration of successful delivery.
⚖️ Evidence-Based Management Algorithms: Optimizing Labor Outcomes
🔗 Multi-System Integration: The Labor Orchestration Network
Neuroendocrine integration drives labor initiation through fetal hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activation. Fetal cortisol increases 300% at term, stimulating placental CRH production that triggers prostaglandin synthesis. This positive feedback loop creates the hormonal cascade culminating in labor onset.
- Hormonal Cascade Architecture
- Fetal Maturation Signals
- Cortisol: Increases 300% weeks 36-40
- ACTH: Stimulates fetal adrenal function
- Surfactant proteins: Signal lung maturity
- Placental Hormone Production
- CRH: Increases exponentially near term
- Prostaglandin E2: Cervical ripening mediator
- Prostaglandin F2α: Uterine contraction stimulator
- Maternal Hormone Responses
- Oxytocin receptors: 200% increase at term
- Gap junctions: 500% increase (connexin-43)
- Prostaglandin receptors: Upregulated 10-fold
- Fetal Maturation Signals
📌 Remember: FETAL-PLACENTAL-MATERNAL axis - Fetal cortisol → Placental CRH → Maternal prostaglandins → labor initiation cascade
Cardiovascular adaptations accommodate increased metabolic demands during labor. Cardiac output increases 15-20% during contractions, blood pressure rises 10-20 mmHg, and uterine blood flow decreases 60% during peak contractions. Maternal positioning significantly impacts venous return and fetal oxygenation.
| Physiological Parameter | Baseline Pregnancy | During Contractions | Between Contractions | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiac Output | 6-7 L/min | 8-9 L/min | 6-7 L/min | Increased workload |
| Blood Pressure | 110/70 mmHg | 130/85 mmHg | 115/75 mmHg | Monitor hypertension |
| Uterine Blood Flow | 750 mL/min | 300 mL/min | 750 mL/min | Fetal hypoxia risk |
| Oxygen Consumption | 250 mL/min | 300 mL/min | 250 mL/min | Respiratory demands |
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Coached breathing during contractions prevents hyperventilation-induced alkalosis (pH >7.45) that reduces uteroplacental blood flow by 25% and increases fetal acidosis risk
Immune system modulation prevents maternal rejection of semi-allogeneic fetus while maintaining infection resistance. Th2 cytokine dominance shifts toward Th1 responses during labor, neutrophil counts increase 200%, and inflammatory mediators rise 500% to facilitate cervical remodeling and membrane rupture.
- Immunological Labor Adaptations
- Cytokine Profile Changes
- IL-1β: Increases 300% (cervical ripening)
- TNF-α: Increases 200% (membrane weakening)
- IL-6: Increases 500% (inflammatory response)
- IL-8: Increases 400% (neutrophil recruitment)
- Cellular Immune Responses
- Neutrophils: 200% increase in circulation
- Macrophages: Infiltrate cervix and membranes
- T-regulatory cells: Decrease 50% at labor onset
- Complement System Activation
- C3a/C5a: Increase 150% (anaphylatoxins)
- Membrane attack complex: Facilitates membrane rupture
- Cytokine Profile Changes
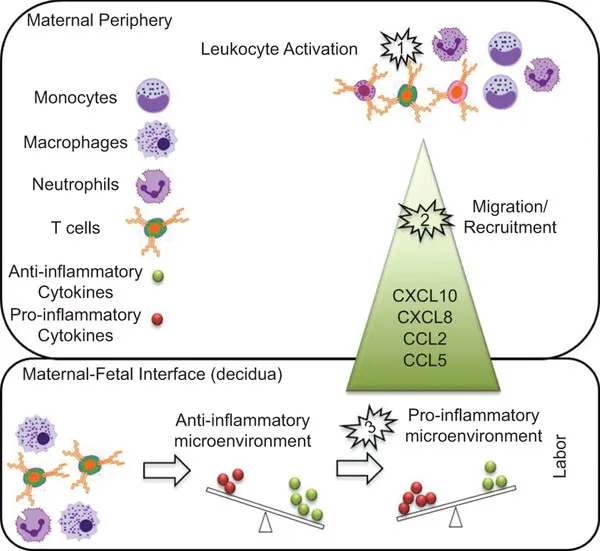
💡 Master This: Sterile inflammatory response of labor mimics infection - maternal fever, leukocytosis (15,000-20,000/μL), and elevated CRP occur normally, requiring clinical correlation to distinguish from chorioamnionitis
Renal system adaptations maintain fluid-electrolyte balance during increased metabolic demands. Glomerular filtration rate increases 50%, sodium retention rises 200%, and antidiuretic hormone levels fluctuate with oxytocin release. Bladder function becomes impaired due to mechanical compression and epidural effects.
📌 Remember: LABOR SYSTEMS integration - Lung ventilation, Adrenal hormones, Blood flow, Oxytocin receptors, Renal function coordinate through positive feedback loops to achieve delivery
Connect multi-system integration concepts through the final section to understand how this complex physiological orchestration translates into practical clinical mastery tools for optimal labor management.
🔗 Multi-System Integration: The Labor Orchestration Network
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Rapid Labor Assessment Tools
Rapid Assessment Framework integrates multiple data streams into actionable clinical decisions within 60-90 seconds. The LABOR mnemonic provides systematic evaluation: Location (station), Attitude (position), Bearing down (maternal effort), Openings (cervical dilation), Rate (contraction frequency).
📌 Remember: LABOR Assessment - Location of presenting part, Attitude/position, Bearing down efforts, Openings (cervical), Rate of contractions - complete evaluation in <2 minutes
| Assessment Component | Normal Findings | Concerning Findings | Critical Actions | Time to Decision |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cervical Dilation | 1.2+ cm/hr progress | <1 cm/hr or arrest | Augmentation/C-section | 4-6 hours |
| Fetal Station | Descent with pushing | No descent 2+ hours | Operative delivery | 2-3 hours |
| FHR Category | Category I | Category II/III | Intrauterine resuscitation | <30 minutes |
| Contraction Pattern | 200+ MVUs | <200 MVUs or >5/10min | Augment/tocolysis | 15-30 minutes |
- Critical Labor Thresholds
- Cervical Progress: 1.2 cm/hr (nullip), 1.5 cm/hr (multip)
- Arrest Diagnosis: 4 hours adequate contractions, 6 hours inadequate
- Second Stage Limits: 3 hours (nullip + epidural), 2 hours (multip + epidural)
- FHR Baselines: 110-160 bpm normal, <110 or >160 abnormal
- Contraction Adequacy: 200+ MVUs or 3-5 per 10 minutes
- Blood Loss Thresholds: 500 mL vaginal, 1000 mL cesarean
- Delivery Timing: 30 minutes for Category III FHR
- Bishop Score: ≥8 predicts successful induction
Intervention Decision Tree streamlines management algorithms into binary decision points that eliminate analysis paralysis. Each decision node requires <30 seconds evaluation with clear action pathways.
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Rule of 30s - 30 minutes maximum for Category III FHR response, 30 seconds for emergency cesarean decision, 30 minutes for complete delivery in true emergencies
Pattern Recognition Drills develop automatic responses to common scenarios. Scenario-based training with standardized patients improves decision speed by 60% and reduces errors by 35% compared to traditional didactic learning.
- High-Yield Pattern Recognition
- Arrest Patterns
- Protracted: Slow but continuous progress
- Secondary arrest: Progress stops after normal advancement
- Failure to descend: Cervical dilation without fetal descent
- FHR Emergency Patterns
- Prolonged bradycardia: <110 bpm >10 minutes
- Recurrent late decelerations: With minimal variability
- Severe variables: <70 bpm >60 seconds
- Obstetric Emergencies
- Cord prolapse: Immediate cesarean <30 minutes
- Uterine rupture: Fetal bradycardia + maternal pain
- Shoulder dystocia: Turtle sign + failed delivery
- Arrest Patterns
Communication Protocols ensure team coordination during critical situations. SBAR format (Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation) provides structured communication that reduces medical errors by 50% and improves response times by 40%.
💡 Master This: TEAMSTEPPS approach - Team structure, Exchange information, Assert concerns, Mutual support creates safety culture that reduces adverse events by 45% in labor units
Quality Metrics Dashboard tracks performance indicators that correlate with optimal outcomes. Primary cesarean rates <25%, VBAC success >70%, and Category III FHR response <30 minutes represent benchmark targets for high-performing units.
| Quality Metric | Target Range | Current Performance | Improvement Actions | Monitoring Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary C-Section Rate | <25% | Monitor monthly | Standardize protocols | Monthly |
| VBAC Success Rate | >70% | Track attempts | Counseling programs | Quarterly |
| Category III Response | <30 minutes | Document times | Team training | Real-time |
| PPH Rate | <5% | Blood loss tracking | Active management | Monthly |
Competency Validation Framework ensures skill maintenance through simulation training, case reviews, and peer assessment. Annual competency requirements include 10 emergency scenarios, 20 normal deliveries, and 5 operative procedures to maintain clinical privileges.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Rapid Labor Assessment Tools
Practice Questions: Stages of labor
Test your understanding with these related questions
Two days after vaginal delivery of a healthy newborn at term, a 32-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 2, is unable to breastfeed. Her labor was complicated by antepartum hemorrhage and she received two units of packed red blood cells. Her pulse is 99/min and blood pressure is 90/55 mm Hg. Further evaluation of this patient is most likely to show which of the following sets of serum findings? $$$ ACTH %%% Aldosterone %%% Cortisol $$$













