Second trimester serum screening US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Second trimester serum screening. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
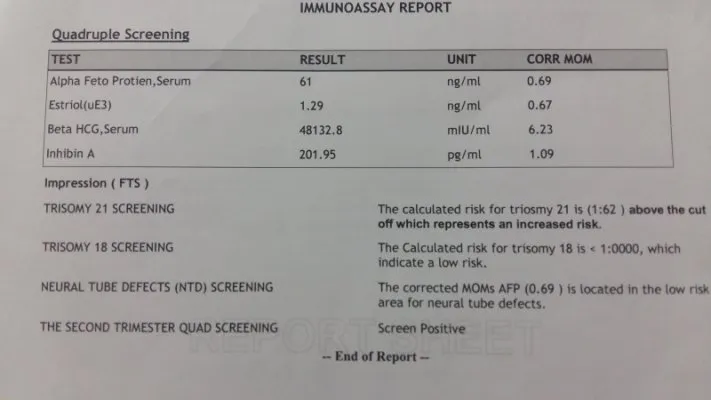
Second trimester serum screening US Medical PG Question 1: A 40-year-old woman in her 18th week of pregnancy based on the last menstrual period (LMP) presents to her obstetrician for an antenatal check-up.
The antenatal testing is normal, except the quadruple screen results which are given below:
Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (MS-AFP) low
Unconjugated estriol low
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) high
Inhibin-A high
Which of the following conditions is the most likely the cause of the abnormal quadruple screen?
- A. Fetal alcohol syndrome
- B. Spina bifida
- C. Gastroschisis
- D. Trisomy 21 (Correct Answer)
- E. Omphalocele
Second trimester serum screening Explanation: ***Trisomy 21***
- The classic quadruple screen pattern for **Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome)** includes **low MS-AFP**, **low unconjugated estriol**, **high hCG**, and **high inhibin-A**.
- This pattern reflects specific placental and fetal biochemical changes associated with the chromosomal abnormality.
*Fetal alcohol syndrome*
- **Fetal alcohol syndrome** is caused by maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy and is not detectable by a quadruple screen.
- It is characterized by specific facial features, growth restriction, and central nervous system abnormalities.
*Spina bifida*
- **Spina bifida**, an **open neural tube defect**, would typically present with a **high MS-AFP** due to leakage of fetal AFP from the open defect into the amniotic fluid and then into maternal circulation.
- This contradicts the **low MS-AFP** finding in the current case.
*Gastroschisis*
- **Gastroschisis**, an abdominal wall defect where intestines are outside the body, also results in a significantly **elevated MS-AFP** due to direct exposure of fetal blood vessels to the amniotic fluid.
- This condition is not associated with the pattern of unconjugated estriol, hCG, and inhibin-A seen in this quadruple screen.
*Omphalocele*
- **Omphalocele**, another abdominal wall defect where abdominal contents are covered by a membrane, usually presents with a **high MS-AFP**, though often less elevated than in gastroschisis or spina bifida.
- It is not associated with the specific pattern of low estriol, high hCG, and high inhibin-A seen in Trisomy 21.
Second trimester serum screening US Medical PG Question 2: A 36-year-old G3P2002 presents to her obstetrician’s office for her first prenatal visit at ten weeks and two days gestation. She notes that she has felt nauseous the last several mornings and has been especially tired for a few weeks. Otherwise, she feels well. The patient has had two uncomplicated spontaneous vaginal deliveries at full term with her last child born six years ago. She is concerned about the risk of Down syndrome in this fetus, as her sister gave birth to an affected child at age 43. The patient has a history of generalized anxiety disorder, atopic dermatitis, and she is currently on escitalopram. At this visit, this patient’s temperature is 98.6°F (37.0°C), pulse is 70/min, blood pressure is 121/67 mmHg, and respirations are 13/min. The patient appears anxious, but overall comfortable, and cardiopulmonary and abdominal exams are unremarkable. Pelvic exam reveals normal female external genitalia, a closed and slightly soft cervix, a ten-week-sized uterus, and no adnexal masses. Which of the following is the best next step for definitively determining whether this patient’s fetus has Down syndrome?
- A. Anatomy ultrasound
- B. Genetic testing of patient’s sister
- C. Chorionic villus sampling (Correct Answer)
- D. Nuchal translucency test
- E. Amniocentesis
Second trimester serum screening Explanation: ***Chorionic villus sampling***
- **Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)** is a diagnostic procedure performed between 10 and 13 weeks of gestation that involves taking a sample of placental tissue for genetic analysis. It provides a definitive diagnosis for chromosomal abnormalities like **Down syndrome** earlier in pregnancy than amniocentesis.
- Given the patient's anxiety and desire for definitive diagnosis due to family history, CVS is the most appropriate next step for an early and conclusive result.
*Anatomy ultrasound*
- An **anatomy ultrasound** (typically performed at 18-20 weeks) is a screening, not diagnostic, tool for fetal anomalies. While it can detect **structural abnormalities** associated with Down syndrome, it cannot definitively diagnose the condition.
- It would be too late to provide the early definitive diagnosis the patient is seeking regarding **Down syndrome**.
*Genetic testing of patient’s sister*
- The sister's genetic testing would confirm her child's diagnosis or carrier status for **chromosomal translocations**, but it does not provide information about the current patient's fetus.
- A definitive diagnosis for the current pregnancy must come from **fetal genetic material**.
*Nuchal translucency test*
- The **nuchal translucency test** is a **screening test** performed between 11 and 14 weeks that measures the fluid at the back of the fetal neck and is used in conjunction with biochemical markers (first-trimester screening) to assess the risk of Down syndrome. It is not diagnostic.
- An abnormal result would indicate an increased risk but would still require a **diagnostic test** like CVS or amniocentesis for confirmation.
*Amniocentesis*
- **Amniocentesis** is a diagnostic procedure that samples amniotic fluid for genetic analysis, typically performed between 15 and 20 weeks of gestation.
- While it provides a definitive diagnosis for **chromosomal abnormalities**, it is usually performed later in pregnancy than CVS. The patient is at 10 weeks and two days, making CVS a timelier option for early diagnosis.
Second trimester serum screening US Medical PG Question 3: A 35-year-old woman gravida 2, para 1, comes to the physician for her first prenatal visit. Pregnancy and delivery of her first child were uncomplicated. She is not sure about the date of her last menstrual period. Pelvic examination shows a uterus consistent in size with a 10-week gestation. An ultrasound examination confirms the gestational age and shows one fetus with no indication of multiple gestations. During counseling on pregnancy risks and possible screening and diagnostic tests, the patient states she would like to undergo screening for Down syndrome. She would prefer immediate and secure screening with a low risk to herself and the fetus. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management at this time?
- A. Nuchal translucency, pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A, human chorionic gonadotropin
- B. Maternal serum α-fetoprotein, human chorionic gonadotropin, unconjugated estriol, and inhibin A
- C. Chorionic villus sampling
- D. Amniocentesis
- E. Cell-free fetal DNA testing (Correct Answer)
Second trimester serum screening Explanation: ***Cell-free fetal DNA testing***
- This is the most appropriate choice given the patient's desire for **immediate and secure screening with low risk** because it is a **non-invasive prenatal screening (NIPS)** method offering high sensitivity and specificity for Down syndrome, particularly in higher-risk pregnancies.
- It involves a simple maternal blood draw and can be performed as early as **10 weeks of gestation**, perfectly aligning with the patient's current gestational age and desire for early screening.
*Nuchal translucency, pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A, human chorionic gonadotropin*
- This combination represents the **first-trimester combined screen**, which is typically performed between 11 and 14 weeks of gestation. While suitable for early screening, **cell-free DNA testing offers higher detection rates and lower false-positive rates** for Down syndrome.
- The patient specifically asked for the most **secure and least risky** screening, and NIPS outperforms the combined screen in terms of diagnostic accuracy for aneuploidies.
*Maternal serum α-fetoprotein, human chorionic gonadotropin, unconjugated estriol, and inhibin A*
- This refers to the **quad screen**, which is typically performed in the **second trimester (15-20 weeks)**, making it too late for the patient's desire for immediate screening at 10 weeks gestational age.
- While a widely used screening tool, the quad screen has a **lower detection rate** for Down syndrome compared to cell-free DNA testing.
*Chorionic villus sampling*
- **Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)** is a **diagnostic, invasive procedure** that carries a small risk of miscarriage (approximately 1 in 455 or 0.22%) and is not a screening test.
- Although it can be performed earlier (typically between 10 and 13 weeks), the patient specifically requested a **low-risk screening** option, which CVS is not.
*Amniocentesis*
- **Amniocentesis** is also an **invasive diagnostic procedure** with a risk of miscarriage (approximately 1 in 900 or 0.11%) and is typically performed in the **second trimester (15-20 weeks)**.
- This option is unsuitable because the patient is at 10 weeks gestation and desires **immediate and low-risk screening**, not a diagnostic procedure with procedural risks a few weeks later.
Second trimester serum screening US Medical PG Question 4: A 28-year-old G2P1 female is concerned that she may give birth to another child with Down syndrome. She states that she may not be able to take care of another child with this disorder. Which of the following tests can confirm the diagnosis of Down syndrome in utero?
- A. Ultrasound
- B. Triple marker test
- C. Integrated test
- D. Quadruple marker test
- E. Amniocentesis (Correct Answer)
Second trimester serum screening Explanation: ***Amniocentesis***
- **Amniocentesis** is a **diagnostic procedure** that involves collecting amniotic fluid to obtain fetal cells for **karyotyping**, which can definitively confirm the presence of an extra chromosome 21, the cause of Down syndrome.
- This test is typically performed between **15 and 20 weeks of gestation** and carries a small risk of complication but offers conclusive results.
*Ultrasound*
- **Ultrasound** is a **screening tool** that can detect anatomical features suggestive of Down syndrome, such as **nuchal translucency** or heart defects, but it cannot definitively diagnose the condition.
- It identifies **markers** that increase the suspicion of Down syndrome, prompting further diagnostic testing, but does not provide genetic confirmation.
*Triple marker test*
- The **triple marker test** is a **screening test** that measures levels of **alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)**, **unconjugated estriol (uE3)**, and **human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)** in maternal blood.
- While it can estimate the risk of Down syndrome, it is not a diagnostic test and only provides a **risk assessment**, not a definitive diagnosis.
*Integrated test*
- The **integrated test** combines results from first-trimester screening (nuchal translucency and PAPP-A) and second-trimester screening (quadruple marker test) to provide a **single risk assessment**.
- Like other screening tests, it calculates a **risk probability** for Down syndrome but does not offer a definitive diagnosis.
*Quadruple marker test*
- The **quadruple marker test** measures AFP, uE3, hCG, and **inhibin A** in maternal blood during the second trimester.
- It is a **screening test** used to assess the risk of Down syndrome and open neural tube defects, but it is not a diagnostic tool.
Second trimester serum screening US Medical PG Question 5: A 25-year-old G1P0000 presents to her obstetrician’s office for her first prenatal visit. She had a positive pregnancy test 6 weeks ago, and her last period was about two months ago, though at baseline her periods are irregular. Aside from some slight nausea in the mornings, she feels well. Which of the following measurements would provide the most accurate dating of this patient’s pregnancy?
- A. Crown-rump length (Correct Answer)
- B. Femur length
- C. Abdominal circumference
- D. Biparietal diameter
- E. Serum beta-hCG
Second trimester serum screening Explanation: ***Crown-rump length***
- This measurement, typically obtained via **transvaginal ultrasound** in the first trimester (up to 13 weeks 6 days), provides the **most accurate gestational age dating**.
- It's highly precise because fetal growth is very consistent during this early period, minimizing variability.
*Femur length*
- This is a biometric measurement typically used for dating in the **second and third trimesters**.
- Its accuracy for dating is lower than CRL in the first trimester and becomes more variable in later pregnancy due to individual fetal growth differences.
*Abdominal circumference*
- This measurement is primarily used in the **late second and third trimetes**r to assess fetal growth and weight, rather than for accurate dating.
- It is highly susceptible to variations based on fetal nutrition and health, making it a poor choice for initial dating.
*Biparietal diameter*
- This is a reliable measurement for dating from the **late first trimester through the second trimester**, but it is less accurate than CRL in the very early first trimester.
- After the first trimester, its accuracy declines compared to earlier measurements as individual variations in head size become more prominent.
*Serum beta-hCG*
- While a **positive beta-hCG test** confirms pregnancy and quantitative levels can suggest gestational age ranges, it's not a precise dating tool.
- Levels vary widely among individuals and with different types of pregnancies (e.g., multiples), making it unsuitable for accurate dating.
Second trimester serum screening US Medical PG Question 6: A 30-year-old primigravida schedules an appointment with her obstetrician for a regular check-up. She says that everything is fine, although she reports that her baby has stopped moving as much as previously. She is 22 weeks gestation. She denies any pain or vaginal bleeding. The obstetrician performs an ultrasound and also orders routine blood and urine tests. On ultrasound, there is no fetal cardiac activity or movement. The patient is asked to wait for 1 hour, after which the scan is to be repeated. The second scan shows the same findings. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Missed abortion
- B. Ectopic pregnancy
- C. Complete abortion
- D. Fetal demise (Correct Answer)
- E. Incomplete abortion
Second trimester serum screening Explanation: ***Fetal demise***
- The absence of fetal cardiac activity and movement on repeated ultrasound scans at 22 weeks' gestation, after previously reporting fetal movement, is consistent with **fetal demise**.
- **Fetal demise** refers to the death of a fetus in utero at or after 20 weeks of gestation, or when the fetus weighs 350 grams or more.
*Missed abortion*
- **Missed abortion** (or missed miscarriage) is typically defined as a non-viable intrauterine pregnancy with a retained fetus or embryo without cardiac activity before 20 weeks of gestation.
- The patient is 22 weeks gestation, which places the condition beyond the general definition of a missed abortion.
*Ectopic pregnancy*
- In an **ectopic pregnancy**, the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tube, and would not have reached 22 weeks with reported fetal movement.
- An ectopic pregnancy would present with earlier symptoms like **abdominal pain** and **vaginal bleeding**, and an ultrasound would show an empty uterus or evidence of extrauterine pregnancy.
*Complete abortion*
- A **complete abortion** involves the complete expulsion of all products of conception from the uterus.
- This would be characterized by **heavy vaginal bleeding** and the passage of tissue, which the patient denies.
*Incomplete abortion*
- An **incomplete abortion** occurs when some, but not all, products of conception have been expelled from the uterus.
- Similar to complete abortion, an incomplete abortion would typically involve **vaginal bleeding** and retained tissue, accompanied by **cramping**, which are absent in this case.
Second trimester serum screening US Medical PG Question 7: A 38-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 24 weeks' gestation comes to the physician for a routine prenatal evaluation. She has no history of major medical illness and takes no medications. Fetal ultrasonography shows a cardiac defect resulting from abnormal development of the endocardial cushions. This defect is most likely to result in which of the following?
- A. Transposition of the great vessels
- B. Atrioventricular septal defect (Correct Answer)
- C. Dextrocardia
- D. Patent foramen ovale
- E. Sinus venosus defect
Second trimester serum screening Explanation: ***Atrioventricular septal defect***
- **Endocardial cushion defects** are a hallmark of atrioventricular septal defects, leading to a common atrioventricular valve and an interatrial and/or interventricular communication.
- This defect commonly presents in individuals with **Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)**, though it can occur in isolation.
*Transposition of the great vessels*
- This defect results from abnormal **spiraling of the conotruncal septum**, not from endocardial cushion malformation.
- It leads to the **aorta arising from the right ventricle** and the **pulmonary artery from the left ventricle**, a circulation incompatible with life without a shunt.
*Dextrocardia*
- **Dextrocardia** is a condition where the heart is located on the right side of the chest, usually due to abnormal embryonic folding, and is not directly caused by endocardial cushion defects.
- It can occur as an isolated finding or as part of a more complex syndrome like **Kartagener syndrome**.
*Patent foramen ovale*
- A **patent foramen ovale** is a common remnant of fetal circulation, occurring when the foramen ovale fails to close after birth.
- It is a defect of the **atrial septum secondary to incomplete fusion between the septum primum and septum secundum**, not an endocardial cushion defect.
*Sinus venosus defect*
- A **sinus venosus defect** is a type of atrial septal defect occurring near the entrance of the superior or inferior vena cava.
- It is caused by **abnormal development of the sinus venosus** and is not directly related to endocardial cushion malformation.
Second trimester serum screening US Medical PG Question 8: A 28-year-old primigravid woman comes to the emergency department because of a 12-hour history of lower abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. She also had nausea and fatigue for the past 3 weeks. Her last menstrual period was 8 weeks ago. Prior to that, her menses occurred regularly at 30-day intervals and lasted for 4 days. There is no history of medical illness, and she takes no medications. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 95/min, and blood pressure is 100/70 mm Hg. Pelvic examination is painful and shows a uterus consistent in size with a 13-week gestation. A urine pregnancy test is positive. β-HCG level is 106,000 mIU/mL (N < 5 mIU/mL). Transvaginal ultrasonography shows unclear, amorphous fetal parts and a large placenta with multiple cystic spaces. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
- A. Placenta implantation into myometrium
- B. Trophoblastic proliferation with chorionic villi distention (Correct Answer)
- C. Embryonic death with cervical dilation
- D. Malpositioned placenta overlying the cervix
- E. Malignant transformation of trophoblastic tissue
Second trimester serum screening Explanation: ***Trophoblastic proliferation with chorionic villi distention***
- This description fits a **hydatidiform mole** (molar pregnancy), characterized by abnormal **trophoblastic proliferation** and **swollen, cystic chorionic villi**.
- The ultrasound findings of unclear, amorphous fetal parts and a large placenta with multiple cystic spaces ("snowstorm appearance") are classic for a **partial hydatidiform mole**, consistent with the highly elevated **β-hCG level**.
*Placenta implantation into myometrium*
- This describes **placenta accreta**, where the placenta abnormally adheres to or invades the **myometrium**.
- It is typically diagnosed in the third trimester due to bleeding and is not associated with early, high β-hCG levels or the ultrasound features seen here.
*Embryonic death with cervical dilation*
- This suggests an **incomplete or inevitable abortion**. While it can cause pain and bleeding, the specific ultrasound findings of a **large placenta with multiple cystic spaces** and very high β-hCG are not typical.
- In embryonic death, β-hCG levels would typically fall or plateau, not be excessively high.
*Malpositioned placenta overlying the cervix*
- This refers to **placenta previa**, where the placenta covers the internal cervical os. It primarily causes **painless vaginal bleeding** in the second or third trimester.
- The ultrasound findings and the extremely elevated β-hCG in the first trimester are inconsistent with placenta previa.
*Malignant transformation of trophoblastic tissue*
- While a hydatidiform mole can progress to **gestational trophoblastic neoplasia** (GTN), including choriocarcinoma, this option describes a subsequent complication rather than the initial presentation of the mole itself.
- GTN would typically be diagnosed after evacuation of a mole, or if β-hCG levels persist or rise post-evacuation. The initial diagnosis here is the mole.
Second trimester serum screening US Medical PG Question 9: A 27-year-old woman presented with a malodorous discharge in the vagina which started a week earlier. On examination, Whiff's test is positive and the gram stain shows the presence of clue cells. This infection is commonly treated with which of the following?
- A. Metronidazole (Correct Answer)
- B. Azithromycin
- C. Nystatin pessary
- D. Tetracycline
Second trimester serum screening Explanation: ***Metronidazole***
- This patient's symptoms (malodorous vaginal discharge, positive **Whiff test**, and presence of **clue cells** on Gram stain) are classic findings for **bacterial vaginosis (BV)**.
- **Metronidazole** is the first-line and most effective antibiotic for treating bacterial vaginosis, as it targets the anaerobic bacteria overgrowing in the vagina.
*Azithromycin*
- **Azithromycin** is primarily used to treat infections like **chlamydia**, gonorrhea, or some respiratory tract infections.
- It is **not effective** against the anaerobic bacteria responsible for bacterial vaginosis.
*Nystatin pessary*
- **Nystatin** is an **antifungal medication** specifically used to treat **vulvovaginal candidiasis (yeast infection)**.
- The patient's presentation (malodorous discharge, positive Whiff test, clue cells) does not align with a yeast infection, making nystatin ineffective.
*Tetracycline*
- **Tetracycline** is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, but it is **not the preferred treatment** for bacterial vaginosis.
- Its use is often associated with a higher risk of side effects and is typically reserved for other bacterial infections like **chlamydia**, acne, or Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
Second trimester serum screening US Medical PG Question 10: A female presents with postcoital bleeding. Which of the following is the most appropriate investigation?
- A. Pap smear, HCV DNA, electrophoresis
- B. Liquid-based cytology, cervical biopsy
- C. Cervical biopsy, HBV DNA
- D. Pap smear, HPV DNA testing (Correct Answer)
Second trimester serum screening Explanation: **Pap smear, HPV DNA testing**
- **Postcoital bleeding** is a classic symptom of **cervical cancer**, which can be identified by a **Pap smear** to detect abnormal cervical cells.
- **HPV DNA testing** is essential as persistent infection with high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) genotypes is the primary cause of cervical cancer.
*Pap smear, HCV DNA, electrophoresis*
- While a **Pap smear** is appropriate for cervical cytology, **HCV DNA testing** is for Hepatitis C virus infection and is not routinely indicated for postcoital bleeding.
- **Electrophoresis** is used to analyze proteins (e.g., hemoglobinopathies) and has no direct role in evaluating postcoital bleeding or cervical pathology.
*Liquid-based cytology, cervical biopsy*
- **Liquid-based cytology** is a method of preparing a Pap smear, but it's not a standalone investigation.
- A **cervical biopsy** is a more invasive procedure done *after* initial screening (like Pap smear with HPV testing) suggests abnormalities, not as a primary first-line investigation for postcoital bleeding unless there are visible lesions.
*Cervical biopsy, HBV DNA*
- A **cervical biopsy** is typically performed following an abnormal **Pap smear** or colposcopy findings, not as the initial diagnostic step for postcoital bleeding.
- **HBV DNA testing** is for Hepatitis B virus infection and is irrelevant to the workup of postcoital bleeding.
More Second trimester serum screening US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.