First trimester screening US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for First trimester screening. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
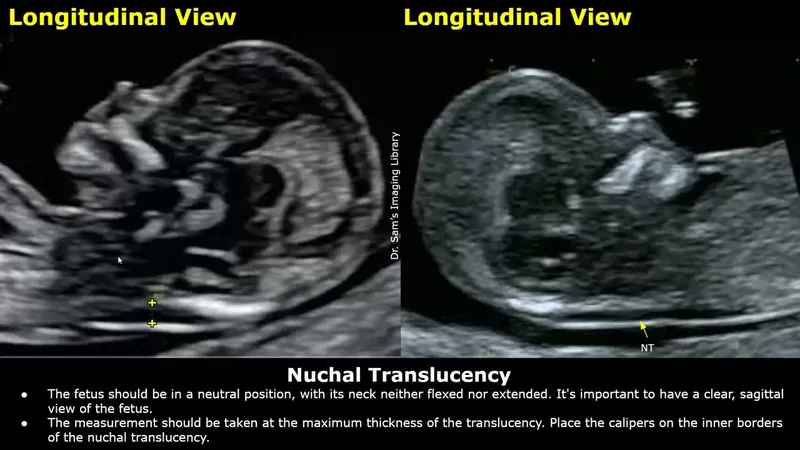
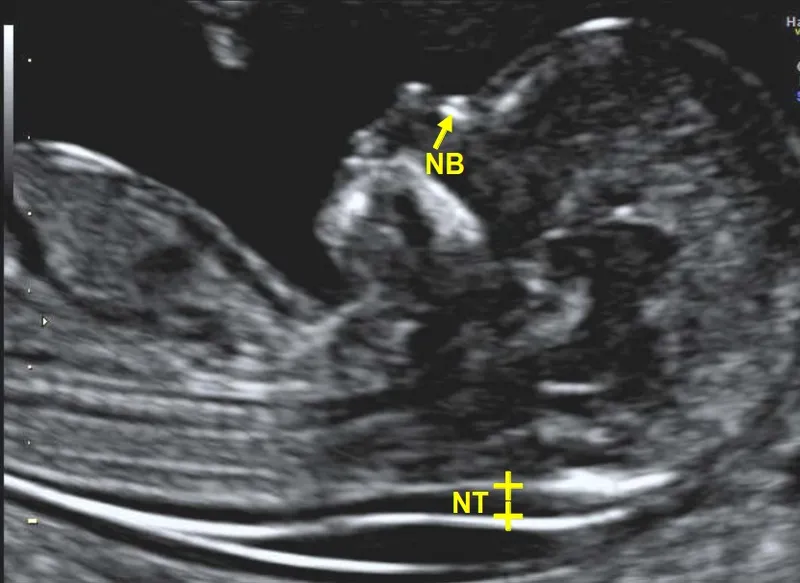
First trimester screening US Medical PG Question 1: A 32-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 14-weeks' gestation comes to the physician for a prenatal visit. Routine first trimester screening shows increased nuchal translucency, decreased β-hCG concentration, and decreased levels of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A. Amniocentesis shows trisomy of chromosome 13. This fetus is at increased risk for which of the following?
- A. Duodenal atresia
- B. Cutis aplasia (Correct Answer)
- C. Cystic hygroma
- D. Optic glioma
- E. Prominent occiput
First trimester screening Explanation: ***Cutis aplasia***
- **Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome)** is characterized by **cutis aplasia**, which is a congenital absence of skin, typically on the scalp.
- Other common features of Trisomy 13 include **midline defects**, microphthalmia, cleft lip/palate, polydactyly, and severe intellectual disability.
*Duodenal atresia*
- **Duodenal atresia** is strongly associated with **Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome)**, not Trisomy 13.
- It presents with a "double bubble" sign on imaging due to dilation of the stomach and proximal duodenum.
*Cystic hygroma*
- **Cystic hygromas**, which are lymphatic malformations, are a common finding in **Turner syndrome (XO)** and **Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome)**.
- While increased nuchal translucency is noted, a cystic hygroma itself is not a specific finding for Trisomy 13.
*Optic glioma*
- **Optic gliomas** are tumors of the optic nerve most frequently associated with **neurofibromatosis type 1**, an autosomal dominant disorder.
- They are not a characteristic finding of Trisomy 13.
*Prominent occiput*
- A **prominent occiput** is a classic feature of **Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome)**.
- This condition is also associated with rocker-bottom feet, micrognathia, and clenched hands with overlapping fingers.
First trimester screening US Medical PG Question 2: A 37-year-old primigravid woman comes to the physician at 13 weeks' gestation for a prenatal visit. She feels well. Her only medication is folic acid. Vital signs are within normal limits. Pelvic examination shows a uterus consistent in size with a 13-week gestation. Ultrasonography shows a nuchal translucency above the 99th percentile. Maternal serum pregnancy-associated plasma protein A is decreased and human chorionic gonadotropin concentrations are elevated to 2 times the median level. Which of the following is most likely to confirm the diagnosis?
- A. Chorionic villus sampling (Correct Answer)
- B. Cell-free DNA testing
- C. Triple screening test
- D. Amniocentesis
- E. Quadruple marker test
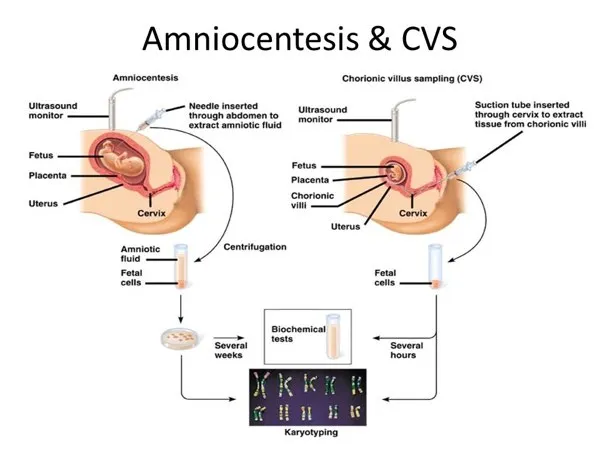
First trimester screening Explanation: ***Chorionic villus sampling***
- This procedure can be performed between **10 to 13 weeks of gestation** to obtain fetal cells for genetic analysis, which is within the patient's gestational age.
- It provides a definitive diagnosis of **chromosomal abnormalities** by directly sampling placental tissue, which shares the same genetic material as the fetus.
*Cell-free DNA testing*
- While it has high sensitivity and specificity for various **aneuploidies**, it is a **screening test**, not a diagnostic one.
- An abnormal result from cell-free DNA testing still requires **confirmatory diagnostic testing** such as CVS or amniocentesis.
*Triple screening test*
- This test is typically performed between **15 and 20 weeks of gestation**, which is too late to confirm the findings presented at 13 weeks gestation.
- It measures **AFP, hCG, and unconjugated estriol**, and an abnormal result would indicate a need for further diagnostic testing.
*Amniocentesis*
- This procedure is generally performed later in pregnancy, typically between **15 and 20 weeks gestation**, so it would require waiting several more weeks.
- While it provides definitive genetic results, **chorionic villus sampling is preferred at 13 weeks** due to earlier diagnostic potential.
*Quadruple marker test*
- This test is also performed between **15 and 20 weeks of gestation** and measures **AFP, hCG, unconjugated estriol, and inhibin A**.
- It is a **screening test**, similar to the triple screen, and does not provide a definitive diagnosis, requiring further confirmatory testing if abnormal.
First trimester screening US Medical PG Question 3: A 38-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, at 12 weeks' gestation comes to her obstetrician for a prenatal visit. Screening tests in the first trimester showed a decreased level of pregnancy-associated plasma protein and an increased level of β-hCG. A genetic disorder is suspected. Which of the following results from an additional diagnostic test is most likely to confirm the diagnosis?
- A. Decreased estriol in maternal serum
- B. Increased inhibin A in maternal serum
- C. Triploidy in amniotic fluid
- D. Increased nuchal translucency on ultrasound
- E. Trisomy 21 on chorionic villus sampling (Correct Answer)
First trimester screening Explanation: ***Trisomy 21 on chorionic villus sampling***
- The combination of **decreased PAPP-A** and **increased β-hCG** in the first trimester is highly suggestive of **Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome)**.
- **Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)** is a diagnostic test performed in the first trimester that can directly analyze fetal chromosomes to confirm the presence of Trisomy 21.
*Decreased estriol in maternal serum*
- This finding is typically seen in the **second-trimester quad screen** (along with α-fetoprotein, β-hCG, and inhibin A), not the first-trimester screening.
- While low estriol is associated with aneuploidies, it's not the most direct or earliest confirmatory diagnostic test in this specific scenario.
*Increased inhibin A in maternal serum*
- Similar to estriol, **increased inhibin A** is a marker used in the **second-trimester quad screen** and is associated with Trisomy 21.
- It is not a component of the standard first-trimester screening blood tests mentioned (PAPP-A and β-hCG).
*Triploidy in amniotic fluid*
- **Triploidy** is a rare and severe chromosomal abnormality (three sets of chromosomes) with a distinct pattern on first-trimester screening (often very low β-hCG and PAPP-A, along with severe growth restriction and structural anomalies).
- The observed screening results (decreased PAPP-A, increased β-hCG) are much more characteristic of Trisomy 21 than triploidy.
*Increased nuchal translucency on ultrasound*
- **Increased nuchal translucency (NT)** is a significant **screening marker** for aneuploidies, including Trisomy 21, and is part of the first-trimester combined screening.
- While a strong indicator, it is a screening result, not a definitive diagnostic confirmation like chromosomal analysis from CVS.
First trimester screening US Medical PG Question 4: A 28-year-old G2P1 female is concerned that she may give birth to another child with Down syndrome. She states that she may not be able to take care of another child with this disorder. Which of the following tests can confirm the diagnosis of Down syndrome in utero?
- A. Ultrasound
- B. Triple marker test
- C. Integrated test
- D. Quadruple marker test
- E. Amniocentesis (Correct Answer)
First trimester screening Explanation: ***Amniocentesis***
- **Amniocentesis** is a **diagnostic procedure** that involves collecting amniotic fluid to obtain fetal cells for **karyotyping**, which can definitively confirm the presence of an extra chromosome 21, the cause of Down syndrome.
- This test is typically performed between **15 and 20 weeks of gestation** and carries a small risk of complication but offers conclusive results.
*Ultrasound*
- **Ultrasound** is a **screening tool** that can detect anatomical features suggestive of Down syndrome, such as **nuchal translucency** or heart defects, but it cannot definitively diagnose the condition.
- It identifies **markers** that increase the suspicion of Down syndrome, prompting further diagnostic testing, but does not provide genetic confirmation.
*Triple marker test*
- The **triple marker test** is a **screening test** that measures levels of **alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)**, **unconjugated estriol (uE3)**, and **human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)** in maternal blood.
- While it can estimate the risk of Down syndrome, it is not a diagnostic test and only provides a **risk assessment**, not a definitive diagnosis.
*Integrated test*
- The **integrated test** combines results from first-trimester screening (nuchal translucency and PAPP-A) and second-trimester screening (quadruple marker test) to provide a **single risk assessment**.
- Like other screening tests, it calculates a **risk probability** for Down syndrome but does not offer a definitive diagnosis.
*Quadruple marker test*
- The **quadruple marker test** measures AFP, uE3, hCG, and **inhibin A** in maternal blood during the second trimester.
- It is a **screening test** used to assess the risk of Down syndrome and open neural tube defects, but it is not a diagnostic tool.
First trimester screening US Medical PG Question 5: A 25-year-old G1P0000 presents to her obstetrician’s office for her first prenatal visit. She had a positive pregnancy test 6 weeks ago, and her last period was about two months ago, though at baseline her periods are irregular. Aside from some slight nausea in the mornings, she feels well. Which of the following measurements would provide the most accurate dating of this patient’s pregnancy?
- A. Crown-rump length (Correct Answer)
- B. Femur length
- C. Abdominal circumference
- D. Biparietal diameter
- E. Serum beta-hCG
First trimester screening Explanation: ***Crown-rump length***
- This measurement, typically obtained via **transvaginal ultrasound** in the first trimester (up to 13 weeks 6 days), provides the **most accurate gestational age dating**.
- It's highly precise because fetal growth is very consistent during this early period, minimizing variability.
*Femur length*
- This is a biometric measurement typically used for dating in the **second and third trimesters**.
- Its accuracy for dating is lower than CRL in the first trimester and becomes more variable in later pregnancy due to individual fetal growth differences.
*Abdominal circumference*
- This measurement is primarily used in the **late second and third trimetes**r to assess fetal growth and weight, rather than for accurate dating.
- It is highly susceptible to variations based on fetal nutrition and health, making it a poor choice for initial dating.
*Biparietal diameter*
- This is a reliable measurement for dating from the **late first trimester through the second trimester**, but it is less accurate than CRL in the very early first trimester.
- After the first trimester, its accuracy declines compared to earlier measurements as individual variations in head size become more prominent.
*Serum beta-hCG*
- While a **positive beta-hCG test** confirms pregnancy and quantitative levels can suggest gestational age ranges, it's not a precise dating tool.
- Levels vary widely among individuals and with different types of pregnancies (e.g., multiples), making it unsuitable for accurate dating.
First trimester screening US Medical PG Question 6: A 19-year-old woman presents for a sports physical. She says she feels healthy and has no concerns. Past medical history is significant for depression and seasonal allergies. Current medications are fluoxetine and oral estrogen/progesterone contraceptive pills. Family history is significant for a sister with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). The patient denies current or past use of alcohol, recreational drugs, or smoking. She reports that she has been on oral birth control pills since age 14 and uses condoms inconsistently. No history of STDs. She is sexually active with her current boyfriend, who was treated for chlamydia 2 years ago. She received and completed the HPV vaccination series starting at age 11. Her vital signs include: temperature 36.8°C (98.2°F), pulse 97/min, respiratory rate 16/min, blood pressure 120/75 mm Hg. Physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following are the recommended guidelines for cervical cancer screening for this patient at this time?
- A. Cytology (pap smear) and HPV DNA co-testing every 3 years
- B. Cytology (pap smear) every 3 years
- C. Cytology (pap smear) annually
- D. Cytology (pap smear) and HPV DNA co-testing every 5 years
- E. No cervical cancer screening is indicated at this time (Correct Answer)
First trimester screening Explanation: ***No cervical cancer screening is indicated at this time***
- Current guidelines recommend initiating **cervical cancer screening** at age 21, regardless of sexual activity initiation.
- The patient is 19 years old, therefore, screening is not yet indicated per standard recommendations.
*Cytology (pap smear) and HPV DNA co-testing every 3 years*
- This option is incorrect because **co-testing** with cytology and HPV DNA is generally recommended for women aged 30-65 years, not for women under 21.
- While cytology every 3 years is a recommendation for women 21-29, co-testing is not the primary recommendation in this age group, and the patient is below the screening age.
*Cytology (pap smear) every 3 years*
- This screening interval is recommended for women aged 21-29 years, but the patient is currently 19 years old.
- Initiating screening earlier than 21 years is not recommended due to the high incidence of **transient HPV infections** and low risk of cervical cancer in younger individuals.
*Cytology (pap smear) annually*
- **Annual Pap smears** are no longer recommended for routine screening; guidelines have shifted to longer intervals due to the slow progression of cervical cancer and high rates of HPV clearance.
- Even if screening were indicated, annual cytology is not the current recommendation for any age group, especially not for a 19-year-old.
*Cytology (pap smear) and HPV DNA co-testing every 5 years*
- This screening strategy (**co-testing every 5 years**) is recommended for women aged 30-65 years.
- This patient is only 19 years old, making this recommendation inappropriate for her age.
First trimester screening US Medical PG Question 7: A 45-year-old woman presents with a history of cervical erosion and spotting for the past 2 months. What is the next best step?
- A. LBC + HPV (Correct Answer)
- B. Pap smear + HSV
- C. Pap smear + HBV
- D. LBC + HSV
First trimester screening Explanation: ***LBC + HPV***
- Cervical erosion and spotting are concerning for **cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN)** or **cervical cancer**, making **Liquid-Based Cytology (LBC)** the appropriate screening method.
- **Human Papillomavirus (HPV) testing** is crucial as persistent high-risk HPV infection is the primary cause of cervical cancer and helps in risk stratification and management.
*Pap smear + HSV*
- A **routine Pap smear** (conventional cytology) is less sensitive than LBC for detecting abnormal cervical cells and is generally being phased out by LBC.
- **Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)** causes genital herpes and is not directly associated with cervical cancer, thus testing for it in this context is not the most appropriate immediate next step.
*Pap smear + HBV*
- As mentioned, a **routine Pap smear** is not the preferred method for cervical cancer screening compared to LBC.
- **Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)** causes liver disease and is entirely unrelated to cervical pathology; therefore, testing for it would be irrelevant to the patient's symptoms.
*LBC + HSV*
- While **LBC** is the correct advanced cytology method, adding **HSV testing** is not indicated as HSV does not cause cervical cancer or intraepithelial lesions that present with cervical erosion and spotting.
- Focus should be on identifying potential malignancy or pre-malignant changes with HPV co-testing, not sexually transmitted infections unrelated to cancer risk.
First trimester screening US Medical PG Question 8: The following set of instruments are used for which procedure?
- A. Biopsy
- B. Dilatation and curettage
- C. Pap smear (Correct Answer)
- D. Hysteroscopy
First trimester screening Explanation: ***Pap smear***
- The image displays a complete set of instruments used for a **Pap smear**, including **glass slides** for sample collection, a **cervical brush**, a **spatula** (cytobrush and Ayre spatula), and a **speculum** to visualize the cervix.
- These tools are specifically designed for collecting cervical cells to screen for **cervical cancer** and **precancerous changes**.
*Biopsy*
- A biopsy typically involves specialized instruments like **punch biopsy tools**, **forceps**, or needles to extract tissue samples, which are not depicted here.
- While glass slides might be used for processing biopsy samples, the primary collection tools are absent.
*Dilatation and curettage*
- This procedure requires instruments such as **dilators** to open the cervix and **curetters** to scrape the uterine lining, which are not shown in the image.
- The instruments shown are for surface cell collection, not for uterine cavity procedures.
*Hysteroscopy*
- Hysteroscopy uses a **hysteroscope**—a thin, lighted tube with a camera—to visualize the inside of the uterus.
- The instruments in the image are for external examination and cervical cell collection, not for direct visualization of the uterine cavity.
First trimester screening US Medical PG Question 9: A mother presents to the family physician with her 16-year-old son. She explains, "There's something wrong with him doc. His grades are getting worse, he's cutting class, he's gaining weight, and his eyes are often bloodshot." Upon interviewing the patient apart from his mother, he seems withdrawn and angry at times when probed about his social history. The patient denies abuse and sexual history. What initial test should be sent to rule out the most likely culprit of this patient's behavior?
- A. Complete blood count
- B. Sexually transmitted infection (STI) testing
- C. Blood culture
- D. Urine toxicology screen (Correct Answer)
- E. Slit lamp examination
First trimester screening Explanation: ***Urine toxicology screen***
- The patient's presentation with **declining grades**, **cutting class**, **weight gain**, **bloodshot eyes**, and **irritability** are classic signs of **substance abuse** in an adolescent.
- A **urine toxicology screen** is the most appropriate initial test to detect common illicit substances, especially given the clear signs pointing towards drug use.
*Slit lamp examination*
- This test is used to examine the **anterior segment of the eye**, including the conjunctiva, cornea, iris, and lens.
- While the patient has **bloodshot eyes**, this specific test would be more relevant for ruling out ocular infections or injuries, not for diagnosing the underlying cause of systemic behavioral changes.
*Complete blood count*
- A **complete blood count (CBC)** measures different components of the blood, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- A CBC is a general health indicator and while it can detect infections or anemia, it is not specific or sensitive enough to identify the cause of the behavioral changes described.
*Sexually transmitted infection (STI) testing*
- Although the patient denies sexual history, all adolescents presenting with certain risk factors or symptoms may warrant STI testing in a broader health assessment.
- However, in this scenario, the primary cluster of symptoms (poor grades, cutting class, bloodshot eyes, irritability) points more directly to substance abuse than to an STI.
*Blood culture*
- A **blood culture** is used to detect the presence of bacteria or other microorganisms in the bloodstream, indicating a systemic infection (sepsis).
- The patient's symptoms are not indicative of an acute bacterial bloodstream infection, and a blood culture would not be the initial test for the presented behavioral changes.
First trimester screening US Medical PG Question 10: A 36-year-old G3P2002 presents to her obstetrician’s office for her first prenatal visit at ten weeks and two days gestation. She notes that she has felt nauseous the last several mornings and has been especially tired for a few weeks. Otherwise, she feels well. The patient has had two uncomplicated spontaneous vaginal deliveries at full term with her last child born six years ago. She is concerned about the risk of Down syndrome in this fetus, as her sister gave birth to an affected child at age 43. The patient has a history of generalized anxiety disorder, atopic dermatitis, and she is currently on escitalopram. At this visit, this patient’s temperature is 98.6°F (37.0°C), pulse is 70/min, blood pressure is 121/67 mmHg, and respirations are 13/min. The patient appears anxious, but overall comfortable, and cardiopulmonary and abdominal exams are unremarkable. Pelvic exam reveals normal female external genitalia, a closed and slightly soft cervix, a ten-week-sized uterus, and no adnexal masses. Which of the following is the best next step for definitively determining whether this patient’s fetus has Down syndrome?
- A. Anatomy ultrasound
- B. Genetic testing of patient’s sister
- C. Chorionic villus sampling (Correct Answer)
- D. Nuchal translucency test
- E. Amniocentesis
First trimester screening Explanation: ***Chorionic villus sampling***
- **Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)** is a diagnostic procedure performed between 10 and 13 weeks of gestation that involves taking a sample of placental tissue for genetic analysis. It provides a definitive diagnosis for chromosomal abnormalities like **Down syndrome** earlier in pregnancy than amniocentesis.
- Given the patient's anxiety and desire for definitive diagnosis due to family history, CVS is the most appropriate next step for an early and conclusive result.
*Anatomy ultrasound*
- An **anatomy ultrasound** (typically performed at 18-20 weeks) is a screening, not diagnostic, tool for fetal anomalies. While it can detect **structural abnormalities** associated with Down syndrome, it cannot definitively diagnose the condition.
- It would be too late to provide the early definitive diagnosis the patient is seeking regarding **Down syndrome**.
*Genetic testing of patient’s sister*
- The sister's genetic testing would confirm her child's diagnosis or carrier status for **chromosomal translocations**, but it does not provide information about the current patient's fetus.
- A definitive diagnosis for the current pregnancy must come from **fetal genetic material**.
*Nuchal translucency test*
- The **nuchal translucency test** is a **screening test** performed between 11 and 14 weeks that measures the fluid at the back of the fetal neck and is used in conjunction with biochemical markers (first-trimester screening) to assess the risk of Down syndrome. It is not diagnostic.
- An abnormal result would indicate an increased risk but would still require a **diagnostic test** like CVS or amniocentesis for confirmation.
*Amniocentesis*
- **Amniocentesis** is a diagnostic procedure that samples amniotic fluid for genetic analysis, typically performed between 15 and 20 weeks of gestation.
- While it provides a definitive diagnosis for **chromosomal abnormalities**, it is usually performed later in pregnancy than CVS. The patient is at 10 weeks and two days, making CVS a timelier option for early diagnosis.
More First trimester screening US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.