Diabetes screening in pregnancy US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Diabetes screening in pregnancy. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Diabetes screening in pregnancy US Medical PG Question 1: A 32-year-old G1P0 woman at 27 weeks estimated gestational age presents for her first prenatal care appointment. She recently immigrated to the United States and didn’t receive any prenatal care in her country. Her blood pressure is 130/70 mm Hg, pulse is 85/min, and respirations are 16/min. Her BMI is 38.3 kg/m2. Physical examination is unremarkable except for normal pregnancy changes. Fetal ultrasound is performed and reveals fetal macrosomia. Which one of the following diagnostic tests is most likely to reveal the cause of this fetal abnormality?
- A. Leptin
- B. C-peptide
- C. Oral glucose tolerance test (Correct Answer)
- D. Glycated hemoglobin
- E. Serum insulin
Diabetes screening in pregnancy Explanation: ***Oral glucose tolerance test***
- The patient has several risk factors for **gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM)**, including **obesity (BMI 38.3)**, **late presentation to prenatal care**, and **fetal macrosomia**.
- An **oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)** is the gold standard for diagnosing GDM, which is the most likely cause of fetal macrosomia in this context.
*Leptin*
- **Leptin** is a hormone involved in appetite and energy balance, and while it can be elevated in obesity, it is **not a primary diagnostic test for GDM** or fetal macrosomia.
- While leptin resistance is implicated in obesity and insulin resistance, directly measuring leptin levels is **not used for diagnosing diabetes** in pregnancy.
*C-peptide*
- **C-peptide** levels reflect endogenous insulin production, but measuring it directly is **not the initial diagnostic test for GDM**.
- While it can be used to assess residual beta-cell function in known diabetes, it's not the primary diagnostic tool for a new presentation with macrosomia.
*Glycated hemoglobin*
- **Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c)** measures average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months and is used to diagnose **pre-existing diabetes** or monitor long-term glucose control.
- It is **not the preferred diagnostic test for GDM** due to its lower sensitivity during pregnancy and limitations in reflecting rapidly changing glucose levels.
*Serum insulin*
- Direct measurement of **serum insulin** is not used as a primary diagnostic test for GDM because insulin levels fluctuate significantly and **do not directly reflect glucose intolerance** as well as an OGTT.
- While insulin resistance is central to GDM, direct insulin levels are not part of the standard diagnostic criteria for GDM.
Diabetes screening in pregnancy US Medical PG Question 2: A 31-year-old G1P0000 presents to her obstetrician for her first prenatal visit after having a positive home pregnancy test one week ago. She states that her last menstrual period was 8 weeks ago. The patient has a past medical history of type I diabetes mellitus since childhood and is on insulin. Her hemoglobin A1c two weeks ago was 13.7%. At that time, she was also found to have microalbuminuria on routine urinalysis, and her primary care provider prescribed lisinopril but the patient has not yet started taking it. The patient’s brother is autistic, but family history is otherwise unremarkable. At this visit, her temperature is 98.6°F (37.0°C), blood pressure is 124/81 mmHg, pulse is 75/min, and respirations are 14/min. Exam is unremarkable. This fetus is at increased risk for which of the following?
- A. Post-term delivery
- B. Oligohydramnios
- C. Neural tube defect (Correct Answer)
- D. Aneuploidy
- E. Neonatal hyperglycemia
Diabetes screening in pregnancy Explanation: ***Neural tube defect***
- The patient's **poorly controlled type 1 diabetes mellitus** is evidenced by her **HbA1c of 13.7%**. Uncontrolled maternal hyperglycemia during organogenesis significantly increases the risk for fetal malformations, including neural tube defects due to impaired folate metabolism.
- This risk is highest when hyperglycemia occurs during the first 8 weeks of gestation, a period crucial for neural tube closure, which aligns with this patient's presentation at 8 weeks' gestation.
*Post-term delivery*
- **Uncontrolled maternal diabetes** is typically associated with **macrosomia and polyhydramnios**, which can lead to complications such as **shoulder dystocia, premature rupture of membranes (PROM)**, and often precipitates **earlier induction of labor** rather than post-term delivery.
- While exact delivery timing can vary, the direct causal link between uncontrolled diabetes and post-term delivery is not primary; rather, such pregnancies are often managed with earlier interventions.
*Oligohydramnios*
- Poorly controlled maternal diabetes, particularly type 1, is generally associated with **polyhydramnios** due to fetal polyuria caused by hyperglycemia, not oligohydramnios.
- **Oligohydramnios** can be associated with severe **placental insufficiency**, prolonged rupture of membranes, or fetal renal agenesis, none of which are directly indicated by uncontrolled maternal diabetes alone.
*Aneuploidy*
- The primary risk factor for **aneuploidy** (e.g., Down syndrome) is **advanced maternal age**, which is not present in this 31-year-old patient.
- **Maternal diabetes** itself is not a direct risk factor for aneuploidy; genetic factors related to nondisjunction are the main cause.
*Neonatal hyperglycemia*
- Maternal hyperglycemia leads to fetal hyperglycemia, causing **fetal hyperinsulinemia**. After birth, the neonate's elevated insulin levels, in the absence of maternal glucose supply, result in **neonatal hypoglycemia**, not hyperglycemia.
- **Neonatal hyperglycemia** is rare and usually associated with specific genetic defects or administration of excessive glucose postnatally, not maternal diabetes.
Diabetes screening in pregnancy US Medical PG Question 3: A 31-year-old G1P0 woman at 26 weeks gestation presents to the clinic for evaluation of an abnormal glucose tolerance test. She denies any symptoms, but states that she was given 50 g of oral glucose 1 week earlier and demonstrated a subsequent venous plasma glucose level of 156 mg/dL 1 hour later. The vital signs are: blood pressure, 112/78 mm Hg; pulse, 81/min; and respiratory rate, 16/min. Physical examination is within normal limits. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Administer an oral, 3-hour 100 g glucose dose (Correct Answer)
- B. Advise the patient to follow an American Diabetic Association diet plan
- C. Repeat the 50 g oral glucose challenge
- D. Begin insulin treatment
- E. Order a fetal ultrasound examination
Diabetes screening in pregnancy Explanation: ***Administer an oral, 3-hour 100 g glucose dose***
- This patient failed the initial **50 g, 1-hour glucose challenge test** (screen) because her plasma glucose was 156 mg/dL, which is above the typical threshold of 130-140 mg/dL.
- The next appropriate step for a failed screening test is to perform a **diagnostic 3-hour, 100 g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)** to confirm or rule out gestational diabetes.
*Advise the patient to follow an American Diabetic Association diet plan*
- While lifestyle modifications are important for managing gestational diabetes, this step is premature as the diagnosis has not yet been confirmed by the **diagnostic 3-hour OGTT**.
- Diet modification is part of the treatment for confirmed gestational diabetes, not the next diagnostic step.
*Repeat the 50 g oral glucose challenge*
- Repeating the screening test is not appropriate after a positive result; a diagnostic test is required to confirm the condition.
- The **50 g challenge** is a screening test with a high sensitivity but lower specificity, thus requiring a follow-up diagnostic test.
*Begin insulin treatment*
- **Insulin treatment** is reserved for patients officially diagnosed with gestational diabetes whose blood glucose levels cannot be controlled with diet and exercise alone.
- Prescribing insulin without a confirmed diagnosis is inappropriate and potentially harmful.
*Order a fetal ultrasound examination*
- A fetal ultrasound is used to monitor for complications of gestational diabetes like **macrosomia**, but it is not the next step in diagnosing the condition.
- While important for fetal surveillance in confirmed cases, it does not aid in the initial diagnosis of gestational diabetes itself.
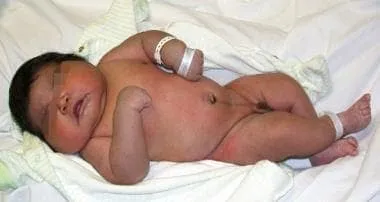
Diabetes screening in pregnancy US Medical PG Question 4: A newborn whose mother had uncontrolled diabetes mellitus during pregnancy is likely to have which of the following findings?
- A. Amyloid deposits in pancreatic islets
- B. Atrophy of pancreatic islets cells
- C. Hyperglycemia
- D. Ketoacidosis
- E. Hypoglycemia (Correct Answer)
Diabetes screening in pregnancy Explanation: ***Hypoglycemia***
- Uncontrolled maternal diabetes leads to **fetal hyperglycemia**, causing the fetal pancreas to produce **excessive insulin** (fetal hyperinsulinism) to compensate.
- After birth, the maternal glucose supply is cut off, but the newborn's pancreas continues to overproduce insulin, leading to **rapid drops in blood glucose** and severe hypoglycemia.
*Amyloid deposits in pancreatic islets*
- **Amyloid deposits** in pancreatic islets are characteristic of **Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus** in adults, typically not seen in newborns or as a direct consequence of maternal diabetes.
- This condition involves the accumulation of **islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP)**, which is different from the physiological responses seen in infants of diabetic mothers.
*Atrophy of pancreatic islets cells*
- **Atrophy of pancreatic islet cells** is seen in late-stage **Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus** due to autoimmune destruction, not in infants of diabetic mothers, who typically have hypertrophied islets.
- In newborns of diabetic mothers, the pancreatic beta cells are usually **hypertrophic and hyperplastic** due to chronic glucose stimulation.
*Hyperglycemia*
- While the fetus experiences **hyperglycemia** in utero due to maternal diabetes, the newborn after birth typically develops **hypoglycemia** once the continuous maternal glucose supply is removed.
- The newborn's elevated insulin levels, in response to chronic fetal hyperglycemia, quickly deplete available glucose post-delivery, leading to low blood sugar.
*Ketoacidosis*
- **Ketoacidosis** occurs when the body produces high levels of **ketones** due to severe insulin deficiency and high glucose, which is primarily seen in **Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus** or severe stress states.
- Newborns of diabetic mothers are more prone to hypoglycemia due to **hyperinsulinism**, which inhibits ketogenesis, rather than ketoacidosis.
Diabetes screening in pregnancy US Medical PG Question 5: A 21-year-old primigravida presents to her physician for a prenatal visit. She has a positive pregnancy test 1 week ago. The estimated gestational age is 16 weeks. She has no complaints. She has a history of type 1 diabetes mellitus and takes insulin for glucose control. The urine dipstick test shows 3+ glucose and negative for protein. The blood tests ordered at the last visit 1 week ago are as follows:
Fasting glucose 110 mg/dL
HbA1c 8.3%
Which of the following tests should be highly recommended for this patient?
- A. Chorionic villus sampling
- B. Triple test (Correct Answer)
- C. Serum creatinine
- D. C-peptide assessment
- E. Oral glucose tolerance test
Diabetes screening in pregnancy Explanation: ***Triple test***
- This 21-year-old patient with **pre-existing diabetes** and an **HbA1c of 8.3%** has a significantly increased risk of fetal neural tube defects and other chromosomal abnormalities. The triple test, performed between **15 and 20 weeks**, can screen for these risks by measuring **alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)**, **human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)**, and **unconjugated estriol (uE3)**.
- Given the patient's **poor glycemic control** (HbA1c 8.3% indicates consistently high blood glucose levels), the triple test offers a non-invasive screening method to assess these elevated risks.
*Chorionic villus sampling*
- While CVS can detect chromosomal abnormalities and some genetic disorders, it is an **invasive procedure** associated with a risk of miscarriage and is typically performed earlier in pregnancy (10-13 weeks).
- It is usually reserved for cases with **higher risk factors** identified through non-invasive screening or a history of genetic disorders, which are not explicitly stated as the primary concern here compared to the hyperglycemia-related defects.
*Serum creatinine*
- **Serum creatinine** is used to assess kidney function and is essential in diabetic patients to monitor for nephropathy, but it is **not a screening test for fetal abnormalities**.
- While important for the mother's health management, it does not directly address the immediate concern of fetal risk due to uncontrolled diabetes during pregnancy.
*C-peptide assessment*
- **C-peptide** is a marker of endogenous insulin production and is useful in classifying diabetes type or assessing residual beta-cell function; however, this patient is a known **type 1 diabetic** taking insulin.
- While it has diagnostic utility for the mother's condition, it does not provide information about fetal well-being or the risk of congenital anomalies.
*Oral glucose tolerance test*
- An **oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)** is used to diagnose **gestational diabetes mellitus** (GDM) in women without pre-existing diabetes, or to confirm it in those with borderline values.
- This patient already has a confirmed diagnosis of **type 1 diabetes**; therefore, an OGTT is not indicated for her as she is already being treated for diabetes.
Diabetes screening in pregnancy US Medical PG Question 6: A 21-year-old female presents to her primary care doctor for prenatal counseling before attempting to become pregnant for the first time. She is an avid runner, and the physician notes her BMI of 17.5. The patient complains of chronic fatigue, which she attributes to her busy lifestyle. The physician orders a complete blood count that reveals a Hgb 10.2 g/dL (normal 12.1 to 15.1 g/dL) with an MCV 102 µm^3 (normal 78 to 98 µm^3). A serum measurement of a catabolic derivative of methionine returns elevated. Which of the following complications is the patient at most risk for if she becomes pregnant?
- A. Placenta abruptio (Correct Answer)
- B. Placenta previa
- C. Placenta accreta
- D. Neural tube defects
- E. Gestational diabetes
Diabetes screening in pregnancy Explanation: **Placenta abruptio**
* The patient presents with several risk factors for **placental abruption**, including **low BMI**, **anemia** (Hgb 10.2), and **elevated homocysteine** (indicated by elevated catabolic derivative of methionine, implying **folate or B12 deficiency**, which leads to high homocysteine).
* **Anemia** and **folate deficiency** are associated with an increased risk of placental abruption.
*Placenta previa*
* **Placenta previa** is characterized by the placenta covering the cervical os, typically associated with risk factors like **previous C-section**, **multiparity**, and **advanced maternal age**.
* The patient's profile (first pregnancy, young) does not align with the typical risk factors for placenta previa.
*Placenta accreta*
* **Placenta accreta** involves abnormal placental adherence to the uterine wall, most commonly linked to **prior uterine surgery** (especially C-sections) and **placenta previa**.
* The patient has no history of uterine surgery, making placenta accreta an unlikely primary risk.
*Neural tube defects*
* **Neural tube defects** are associated with **folate deficiency**, which is likely present given the **macrocytic anemia** (MCV 102) and elevated homocysteine.
* However, the question asks for the complication the patient is *most* at risk for due to her overall profile including her low BMI and anemia, and while NTDs are a risk, the combination of factors points more strongly to placental abruption.
*Gestational diabetes*
* **Gestational diabetes** is linked to risk factors like **obesity**, **family history of diabetes**, and **advanced maternal age**.
* The patient's **low BMI** (17.5) and young age make gestational diabetes an unlikely significant risk.
Diabetes screening in pregnancy US Medical PG Question 7: A 65-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for a pre-operative evaluation. He is scheduled for cataract surgery in 3 weeks. His past medical history is notable for diabetes, hypertension, and severe osteoarthritis of the right knee. His medications include metformin, hydrochlorothiazide, lisinopril, and aspirin. His surgeon ordered blood work 1 month ago, which showed a hemoglobin of 14.2 g/dL, INR of 1.2, and a hemoglobin A1c of 6.9%. His vital signs at the time of the visit show BP: 130/70 mmHg, Pulse: 80, RR: 12, and T: 37.2 C. He has no current complaints and is eager for his surgery. Which of the following is the most appropriate course of action for this patient at this time?
- A. Tell the patient he will have to delay his surgery for at least 1 year
- B. Medically clear the patient for surgery (Correct Answer)
- C. Repeat the patient's CBC and coagulation studies
- D. Schedule the patient for a stress test and ask him to delay surgery for at least 6 months
- E. Perform an EKG
Diabetes screening in pregnancy Explanation: **Medically clear the patient for surgery**
- The patient's **blood pressure is well-controlled** (130/70 mmHg), and his **hemoglobin A1c of 6.9%** indicates good glycemic control, both of which are favorable for elective surgery.
- He is currently on **aspirin**, which, for cataract surgery (a low-risk bleeding procedure), can generally be continued, and his **INR of 1.2 is within a safe range** for surgery.
*Tell the patient he will have to delay his surgery for at least 1 year*
- There are **no indications for such a prolonged delay** based on the provided clinical information.
- His chronic conditions (diabetes, hypertension) are **adequately managed**, and his lab values are acceptable.
*Repeat the patient's CBC and coagulation studies*
- The **existing blood work from 1 month ago is recent enough** for a pre-operative evaluation for cataract surgery, especially with no new symptoms.
- Repeating these tests without a clinical indication would be **unnecessary and inefficient**.
*Schedule the patient for a stress test and ask him to delay surgery for at least 6 months*
- The patient has **no active cardiac symptoms** (e.g., chest pain, shortness of breath), and his well-controlled hypertension does not automatically warrant a stress test for low-risk surgery.
- A stress test and a **6-month delay are not indicated** for a low-risk procedure like cataract surgery in an asymptomatic patient.
*Perform an EKG*
- While an EKG might be considered in some pre-operative evaluations for patients with cardiac risk factors, there are **no specific symptoms or significant new risk factors** presented that necessitate an EKG for this low-risk cataract surgery.
- Given his stable condition and controlled hypertension, an EKG is **not a mandatory part of medical clearance** for this procedure.
Diabetes screening in pregnancy US Medical PG Question 8: A 45-year-old woman presents with a history of cervical erosion and spotting for the past 2 months. What is the next best step?
- A. LBC + HPV (Correct Answer)
- B. Pap smear + HSV
- C. Pap smear + HBV
- D. LBC + HSV
Diabetes screening in pregnancy Explanation: ***LBC + HPV***
- Cervical erosion and spotting are concerning for **cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN)** or **cervical cancer**, making **Liquid-Based Cytology (LBC)** the appropriate screening method.
- **Human Papillomavirus (HPV) testing** is crucial as persistent high-risk HPV infection is the primary cause of cervical cancer and helps in risk stratification and management.
*Pap smear + HSV*
- A **routine Pap smear** (conventional cytology) is less sensitive than LBC for detecting abnormal cervical cells and is generally being phased out by LBC.
- **Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)** causes genital herpes and is not directly associated with cervical cancer, thus testing for it in this context is not the most appropriate immediate next step.
*Pap smear + HBV*
- As mentioned, a **routine Pap smear** is not the preferred method for cervical cancer screening compared to LBC.
- **Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)** causes liver disease and is entirely unrelated to cervical pathology; therefore, testing for it would be irrelevant to the patient's symptoms.
*LBC + HSV*
- While **LBC** is the correct advanced cytology method, adding **HSV testing** is not indicated as HSV does not cause cervical cancer or intraepithelial lesions that present with cervical erosion and spotting.
- Focus should be on identifying potential malignancy or pre-malignant changes with HPV co-testing, not sexually transmitted infections unrelated to cancer risk.
Diabetes screening in pregnancy US Medical PG Question 9: A 36-year-old primigravida presents to her obstetrician for antenatal care. She is at 24 weeks of gestation and does not have any current complaint except for occasional leg cramps. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. Family history is irrelevant. Her temperature is 36.9°C (98.42°F), blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, and pulse of 95/minute. Her body mass index is 21 kg/m² (46 pounds/m²). Physical examination reveals a palpable uterus above the umbilicus with no other abnormalities. Which of the following screening tests is suitable for this patient?
- A. Fasting and random glucose testing for gestational diabetes mellitus
- B. HbA1C for gestational diabetes mellitus
- C. Oral glucose tolerance test for gestational diabetes mellitus (Correct Answer)
- D. Complete blood count for iron deficiency anemia
- E. Wet mount microscopy of vaginal secretions for bacterial vaginosis
Diabetes screening in pregnancy Explanation: ***Oral glucose tolerance test for gestational diabetes mellitus***
- The **oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)**, typically performed between **24 and 28 weeks of gestation**, is the gold standard for screening and diagnosing **gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM)**. This patient is at 24 weeks, making it the appropriate time for this screening.
- GDM, if undiagnosed and untreated, can lead to significant maternal and fetal complications, including **macrosomia**, **preeclampsia**, **neonatal hypoglycemia**, and **shoulder dystocia**.
*Fasting and random glucose testing for gestational diabetes mellitus*
- While **fasting** or **random glucose** values can indicate hyperglycemia, they are **not sensitive or specific enough** on their own to reliably screen for or diagnose GDM.
- A single elevated reading might prompt further testing, but it's not the primary or most suitable screening method.
*HbA1C for gestational diabetes mellitus*
- **HbA1c** reflects **average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months** and is primarily used for diagnosing and monitoring **pre-existing diabetes** or assessing glycemic control in non-pregnant individuals.
- Due to the **physiological changes in red blood cell turnover during pregnancy** and the acute onset nature of GDM, HbA1c is **not recommended** as a first-line screening tool for GDM.
*Complete blood count for iron deficiency anemia*
- While **complete blood count (CBC)** is a routine prenatal screening test to check for **anemia**, it is typically done earlier in pregnancy and again in the third trimester. There are no specific symptoms in this patient that strongly suggest immediate concern for anemia beyond routine.
- The question specifically asks for the "most suitable" screening test at this gestational age, and the **GDM screening** takes precedence given the timing.
*Wet mount microscopy of vaginal secretions for bacterial vaginosis*
- There are **no symptoms of vaginal infection** (e.g., unusual discharge, itching, odor) mentioned in the patient's presentation that would warrant immediate screening for **bacterial vaginosis (BV)** at this visit.
- While BV can be associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes, routine asymptomatic screening by wet mount is **not universally recommended** at 24 weeks gestation without other indications.
Diabetes screening in pregnancy US Medical PG Question 10: A 27-year-old Hispanic G2P1 presents for a routine antepartum visit at 26 weeks gestation. She has no complaints. The vital signs are normal, the physical examination is within normal limits, and the gynecologic examination corresponds to 25 weeks gestation. The oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) with a 75-g glucose load is significant for a glucose level of 177 mg/dL at 1 hour and 167 mg/dL at 2 hour. The fasting blood glucose level is 138 mg/dL (7.7 mmol/L), and the HbA1c is 7%. Which of the following represents the proper initial management?
- A. Sitagliptin
- B. Dietary and lifestyle modification
- C. Metformin
- D. Glyburide
- E. Insulin (Correct Answer)
Diabetes screening in pregnancy Explanation: **Insulin**
- The patient's **fasting glucose of 138 mg/dL** and **HbA1c of 7%** indicate pre-existing **Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus**, not just gestational diabetes. Both values exceed the diagnostic thresholds for overt diabetes in pregnancy.
- **Insulin** is the preferred initial pharmacologic treatment for **overt diabetes in pregnancy** because it does not cross the placenta, ensuring fetal safety, and is highly effective in controlling maternal glucose levels.
*Sitagliptin*
- **Sitagliptin** is a **DPP-4 inhibitor** and is not recommended during pregnancy due to limited safety data and the availability of safer alternatives.
- Oral hypoglycemic agents are generally avoided as first-line therapy for established diabetes in pregnancy due to potential for placental transfer and adverse fetal effects.
*Dietary and lifestyle modification*
- While crucial, **dietary and lifestyle modification** alone are insufficient for managing overt diabetes with such high fasting glucose and HbA1c levels.
- These measures are usually the first step for **gestational diabetes**, but a patient with overt diabetes requires immediate pharmacologic intervention to prevent complications.
*Metformin*
- **Metformin** can be used in pregnancy but is primarily considered for **gestational diabetes** or as an alternative to insulin if the patient has milder hyperglycemia, or if insulin is poorly tolerated.
- Given the patient's significantly elevated fasting glucose and HbA1c, **insulin** is a more effective and immediate treatment to achieve glycemic control and reduce risks.
*Glyburide*
- **Glyburide** is an **oral sulfonylurea** that can cross the placenta, leading to potential fetal hyperinsulinemia and neonatal hypoglycemia.
- Its use in pregnancy is generally discouraged due to these risks, making **insulin** a safer and more appropriate choice.
More Diabetes screening in pregnancy US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.