Patient education topics US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Patient education topics. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Patient education topics US Medical PG Question 1: You are counseling a pregnant woman who plans to breast-feed exclusively regarding her newborn's nutritional requirements. The child was born at home and the mother only plans for her newborn to receive vaccinations but no other routine medical care. Which vitamins should be given to the newborn?
- A. Vitamin B6
- B. Vitamin K and Vitamin D (Correct Answer)
- C. Vitamin K
- D. Folic acid
- E. Vitamin D
Patient education topics Explanation: ***Vitamin K and Vitamin D***
- All newborns should receive a prophylactic dose of **Vitamin K** to prevent **Vitamin K Deficiency Bleeding (VKDB)**, as placental transfer is poor and breast milk contains low levels.
- Breastfed infants, especially those exclusively breastfed, require **Vitamin D** supplementation (400 IU daily) to prevent **rickets**, as breast milk Vitamin D levels are often insufficient.
*Vitamin B6*
- While essential for development, **Vitamin B6** supplementation is not routinely recommended for all healthy newborns, especially those exclusively breastfed by a healthy mother.
- Deficiency in newborns is rare and typically associated with specific metabolic disorders or maternal malnutrition, which are not suggested here.
*Vitamin K*
- While **Vitamin K** is critically important for all newborns, it is only one of the essential vitamins needed for breastfed infants.
- Exclusive breastfeeding also necessitates **Vitamin D** supplementation, making this option incomplete.
*Folic acid*
- **Folic acid** (Vitamin B9) is crucial during pregnancy for preventing neural tube defects and is found in adequate amounts in breast milk for a healthy full-term infant.
- Routine supplementation of folic acid is not recommended for healthy newborns, as deficiency is rare.
*Vitamin D*
- While **Vitamin D** supplementation is essential for exclusively breastfed infants, this option is incomplete as it misses the critical need for **Vitamin K** prophylaxis at birth.
- Both vitamins are critical for newborn health in this scenario.
Patient education topics US Medical PG Question 2: A 27-year-old primigravid woman at 32 weeks' gestation comes to the physician for a prenatal visit. She has had swollen legs, mild shortness of breath, and generalized fatigue for the past 2 weeks. Medications include iron supplements and a multivitamin. Her temperature is 37.2°C (99°F), pulse is 93/min, respirations are 20/min, and blood pressure is 108/60 mm Hg. There is 2+ pitting edema of the lower extremities, but no erythema or tenderness. The lungs are clear to auscultation. Cardiac examination shows an S3 gallop. Pelvic examination shows a uterus consistent in size with a 32-week gestation. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management for this patient's symptoms?
- A. Ventilation-perfusion scan
- B. Urinalysis
- C. Echocardiography (Correct Answer)
- D. Lower extremity doppler
- E. Reassurance and monitoring
Patient education topics Explanation: ***Echocardiography***
- The patient presents with classic signs of **peripartum cardiomyopathy**, including **new-onset heart failure** symptoms (dyspnea, fatigue, edema) in the late stages of pregnancy (32 weeks) with an **S3 gallop**.
- **Echocardiography** is the definitive diagnostic tool to visualize cardiac function, assess ventricular size, and measure the **ejection fraction** to confirm cardiomyopathy.
*Ventilation-perfusion scan*
- This test is primarily used to diagnose **pulmonary embolism**, which typically presents with sudden onset dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, and sometimes hypoxemia, none of which are prominent here.
- While shortness of breath is present, the **S3 gallop** and widespread edema are more indicative of cardiac dysfunction than pulmonary embolism.
*Urinalysis*
- A urinalysis is used to screen for kidney issues or **preeclampsia** (proteinuria), which can present with edema and hypertension.
- However, this patient's blood pressure is normal, and her symptoms point more directly to cardiac rather than renal pathology.
*Lower extremity doppler*
- This is used to diagnose **deep vein thrombosis (DVT)**, which would typically cause unilateral leg swelling, warmth, and tenderness.
- The patient has **bilateral pitting edema** with no erythema or tenderness, making DVT less likely as the primary cause of her symptoms.
*Reassurance and monitoring*
- Given the patient's significant and worsening symptoms (**dyspnea, S3 gallop, widespread edema**), simply reassuring her and monitoring would be inappropriate and could lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment of a serious cardiac condition.
- These symptoms are beyond the normal physiological changes of pregnancy and warrant urgent investigation.
Patient education topics US Medical PG Question 3: A 25-year-old G1P0 woman at an estimated gestational age of 9 weeks presents for her first prenatal visit following a positive home pregnancy test. She says she missed 2 periods but assumed it was due to stress at work. She has decided to continue with the pregnancy. Her past medical history is significant for migraine headaches, seizures, and asthma. She takes multiple medications for her condition. Physical examination is unremarkable. An ultrasound confirms a 9-week-old intrauterine pregnancy. Which of the following medications poses the greatest risk to the fetus?
- A. Valproic acid (Correct Answer)
- B. Budesonide
- C. Acetaminophen
- D. Sumatriptan
- E. Albuterol
Patient education topics Explanation: ***Valproic acid***
- **Valproic acid** is a known **teratogen** strongly associated with a high incidence of **neural tube defects** (e.g., spina bifida, anencephaly) when used during the first trimester of pregnancy.
- It can also lead to other malformations, including cardiac defects and facial dysmorphism, as part of **fetal valproate syndrome**.
*Budesonide*
- **Budesonide** is an inhaled corticosteroid commonly used for asthma, considered a relatively **safe medication** during pregnancy (FDA pregnancy category B).
- Studies have shown no increased risk of major congenital malformations with its use.
*Acetaminophen*
- **Acetaminophen** is a widely used analgesic and antipyretic considered **safe** for use throughout pregnancy at recommended doses.
- There is no strong evidence linking acetaminophen to an increased risk of birth defects.
*Sumatriptan*
- **Sumatriptan** is a serotonin receptor agonist used for migraine headaches. It is generally considered to be of **low risk** during pregnancy (FDA pregnancy category C).
- While some studies have suggested a minimal risk of certain birth defects, overall data supports its use when necessary.
*Albuterol*
- **Albuterol** is a short-acting beta-agonist used to treat asthma symptoms and is considered **safe** for use during pregnancy (FDA pregnancy category C).
- There is no evidence of teratogenicity, and the benefits of controlling asthma outweigh the potential risks.
Patient education topics US Medical PG Question 4: A 24-year-old woman visits her physician to seek preconception advice. She is recently married and plans to have a child soon. Menses occur at regular 28-day intervals and last 5 days. She has sexual intercourse only with her husband and, at this time, they consistently use condoms for birth control. The patient consumes a well-balanced diet with moderate intake of meat and dairy products. She has no history of serious illness and takes no medications currently. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. The patient’s history reveals no birth defects or severe genetic abnormalities in the family. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Pelvic examination indicates a normal vagina, cervix, uterus, and adnexa. To decrease the likelihood of fetal neural-tube defects in her future pregnancy, which of the following is the most appropriate recommendation for initiation of folic acid supplementation?
- A. As soon as her pregnancy is confirmed
- B. No folic acid supplement is required as nutritional sources are adequate
- C. As soon as possible (Correct Answer)
- D. When off contraception
- E. In the second half of pregnancy
Patient education topics Explanation: ***As soon as possible***
- Folic acid supplementation is crucial for preventing **neural tube defects (NTDs)**, which occur very early in pregnancy, often before a woman even knows she is pregnant.
- To be effective, supplementation should begin at least **one month prior to conception** and continue through the first trimester.
*As soon as her pregnancy is confirmed*
- This timing is too late because **neurulation** (the formation of the neural tube) is completed by the **28th day post-conception**, often before a pregnancy is confirmed.
- Delaying supplementation until confirmation significantly reduces its preventative effect against neural tube defects.
*No folic acid supplement is required as nutritional sources are adequate*
- While a balanced diet contains some folic acid, it is generally **insufficient** to reach the protective levels needed to prevent NTDs.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and other health organizations recommend universal folic acid supplementation for all women of childbearing age, regardless of diet.
*When off contraception*
- Although discontinuing contraception indicates an intent to conceive, starting folic acid *only* at this point might still be too late.
- It's recommended to start supplementation at least **1 month before attempting conception** to ensure adequate folate levels at the critical time of neural tube closure.
*In the second half of pregnancy*
- Supplementing in the second half of pregnancy is **too late** to prevent neural tube defects.
- By this stage, the neural tube has already fully developed or failed to close, and supplementation will not reverse any existing defects.
Patient education topics US Medical PG Question 5: A 35-year-old woman gravida 2, para 1, comes to the physician for her first prenatal visit. Pregnancy and delivery of her first child were uncomplicated. She is not sure about the date of her last menstrual period. Pelvic examination shows a uterus consistent in size with a 10-week gestation. An ultrasound examination confirms the gestational age and shows one fetus with no indication of multiple gestations. During counseling on pregnancy risks and possible screening and diagnostic tests, the patient states she would like to undergo screening for Down syndrome. She would prefer immediate and secure screening with a low risk to herself and the fetus. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management at this time?
- A. Nuchal translucency, pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A, human chorionic gonadotropin
- B. Maternal serum α-fetoprotein, human chorionic gonadotropin, unconjugated estriol, and inhibin A
- C. Chorionic villus sampling
- D. Amniocentesis
- E. Cell-free fetal DNA testing (Correct Answer)
Patient education topics Explanation: ***Cell-free fetal DNA testing***
- This is the most appropriate choice given the patient's desire for **immediate and secure screening with low risk** because it is a **non-invasive prenatal screening (NIPS)** method offering high sensitivity and specificity for Down syndrome, particularly in higher-risk pregnancies.
- It involves a simple maternal blood draw and can be performed as early as **10 weeks of gestation**, perfectly aligning with the patient's current gestational age and desire for early screening.
*Nuchal translucency, pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A, human chorionic gonadotropin*
- This combination represents the **first-trimester combined screen**, which is typically performed between 11 and 14 weeks of gestation. While suitable for early screening, **cell-free DNA testing offers higher detection rates and lower false-positive rates** for Down syndrome.
- The patient specifically asked for the most **secure and least risky** screening, and NIPS outperforms the combined screen in terms of diagnostic accuracy for aneuploidies.
*Maternal serum α-fetoprotein, human chorionic gonadotropin, unconjugated estriol, and inhibin A*
- This refers to the **quad screen**, which is typically performed in the **second trimester (15-20 weeks)**, making it too late for the patient's desire for immediate screening at 10 weeks gestational age.
- While a widely used screening tool, the quad screen has a **lower detection rate** for Down syndrome compared to cell-free DNA testing.
*Chorionic villus sampling*
- **Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)** is a **diagnostic, invasive procedure** that carries a small risk of miscarriage (approximately 1 in 455 or 0.22%) and is not a screening test.
- Although it can be performed earlier (typically between 10 and 13 weeks), the patient specifically requested a **low-risk screening** option, which CVS is not.
*Amniocentesis*
- **Amniocentesis** is also an **invasive diagnostic procedure** with a risk of miscarriage (approximately 1 in 900 or 0.11%) and is typically performed in the **second trimester (15-20 weeks)**.
- This option is unsuitable because the patient is at 10 weeks gestation and desires **immediate and low-risk screening**, not a diagnostic procedure with procedural risks a few weeks later.
Patient education topics US Medical PG Question 6: A 34-year-old gravida 2 para 1 woman at 16 weeks gestation presents for prenatal care. Her prenatal course has been uncomplicated. She takes no medications besides her prenatal vitamin which she takes every day, and she has been compliant with routine prenatal care. She has a 7-year-old daughter who is healthy. The results of her recent quadruple screen are listed below:
AFP: Low
hCG: Low
Estriol: Low
Inhibin-A: Normal
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step to confirm the diagnosis?
- A. Chorionic villus sampling
- B. Amniocentesis (Correct Answer)
- C. Ultrasound for nuchal translucency
- D. Folic acid supplementation
- E. Return to clinic in 4 weeks
Patient education topics Explanation: ***Amniocentesis***
- The presented quad screen results (low AFP, low hCG, low estriol, normal Inhibin-A) are highly suggestive of **trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome)**. Amniocentesis is a **definitive diagnostic test** that can confirm aneuploidy by providing a fetal karyotype.
- While typically performed between **15 and 20 weeks gestation**, it can differentiate between trisomy 18 and trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), which usually presents with high hCG and high Inhibin-A.
*Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)*
- **CVS** is typically performed earlier in pregnancy, between **10 and 13 weeks gestation**, meaning it is too late to perform at 16 weeks gestation.
- While it can provide a fetal karyotype for genetic diagnosis, the gestational age presented in the vignette makes this option currently inappropriate.
*Ultrasound for nuchal translucency*
- **Nuchal translucency (NT)** is part of the first-trimester screening, usually measured between **11 and 14 weeks gestation**.
- At 16 weeks gestation, measuring NT would be **outside the appropriate timeframe**, and the second-trimester quad screen has already been completed, making further screening rather than diagnosis less useful.
*Folic acid supplementation*
- **Folic acid supplementation** is crucial before and during early pregnancy to prevent neural tube defects, which would be associated with high AFP.
- The patient is already taking prenatal vitamins (which contain folic acid), and her quad screen results are not indicative of a neural tube defect but rather a chromosomal abnormality.
*Return to clinic in 4 weeks*
- The abnormal quad screen results indicate a **high risk for aneuploidy**, specifically trisomy 18, which requires immediate follow-up and definitive diagnosis.
- Delaying further assessment for 4 weeks would be clinically inappropriate and could increase patient anxiety and potentially reduce options for further management.
Patient education topics US Medical PG Question 7: A 31-year-old G1P0000 presents to her obstetrician for her first prenatal visit after having a positive home pregnancy test one week ago. She states that her last menstrual period was 8 weeks ago. The patient has a past medical history of type I diabetes mellitus since childhood and is on insulin. Her hemoglobin A1c two weeks ago was 13.7%. At that time, she was also found to have microalbuminuria on routine urinalysis, and her primary care provider prescribed lisinopril but the patient has not yet started taking it. The patient’s brother is autistic, but family history is otherwise unremarkable. At this visit, her temperature is 98.6°F (37.0°C), blood pressure is 124/81 mmHg, pulse is 75/min, and respirations are 14/min. Exam is unremarkable. This fetus is at increased risk for which of the following?
- A. Post-term delivery
- B. Oligohydramnios
- C. Neural tube defect (Correct Answer)
- D. Aneuploidy
- E. Neonatal hyperglycemia
Patient education topics Explanation: ***Neural tube defect***
- The patient's **poorly controlled type 1 diabetes mellitus** is evidenced by her **HbA1c of 13.7%**. Uncontrolled maternal hyperglycemia during organogenesis significantly increases the risk for fetal malformations, including neural tube defects due to impaired folate metabolism.
- This risk is highest when hyperglycemia occurs during the first 8 weeks of gestation, a period crucial for neural tube closure, which aligns with this patient's presentation at 8 weeks' gestation.
*Post-term delivery*
- **Uncontrolled maternal diabetes** is typically associated with **macrosomia and polyhydramnios**, which can lead to complications such as **shoulder dystocia, premature rupture of membranes (PROM)**, and often precipitates **earlier induction of labor** rather than post-term delivery.
- While exact delivery timing can vary, the direct causal link between uncontrolled diabetes and post-term delivery is not primary; rather, such pregnancies are often managed with earlier interventions.
*Oligohydramnios*
- Poorly controlled maternal diabetes, particularly type 1, is generally associated with **polyhydramnios** due to fetal polyuria caused by hyperglycemia, not oligohydramnios.
- **Oligohydramnios** can be associated with severe **placental insufficiency**, prolonged rupture of membranes, or fetal renal agenesis, none of which are directly indicated by uncontrolled maternal diabetes alone.
*Aneuploidy*
- The primary risk factor for **aneuploidy** (e.g., Down syndrome) is **advanced maternal age**, which is not present in this 31-year-old patient.
- **Maternal diabetes** itself is not a direct risk factor for aneuploidy; genetic factors related to nondisjunction are the main cause.
*Neonatal hyperglycemia*
- Maternal hyperglycemia leads to fetal hyperglycemia, causing **fetal hyperinsulinemia**. After birth, the neonate's elevated insulin levels, in the absence of maternal glucose supply, result in **neonatal hypoglycemia**, not hyperglycemia.
- **Neonatal hyperglycemia** is rare and usually associated with specific genetic defects or administration of excessive glucose postnatally, not maternal diabetes.
Patient education topics US Medical PG Question 8: A 26-year-old woman presents to the women’s health clinic with a 9-week delay in menses. The patient has a history of grand mal seizures, and was recently diagnosed with acute sinusitis. She is prescribed lamotrigine and amoxicillin. The patient smokes one-half pack of cigarettes every day for 10 years, and drinks socially a few weekends every month. Her mother died of breast cancer when she was 61 years old. The vital signs are stable during the current office visit. Physical examination is grossly normal. The physician orders a urine beta-hCG that comes back positive. Abdominal ultrasound shows an embryo consistent in dates with the first day of last menstrual period. Given the history of the patient, which of the following would most likely decrease congenital malformations in the newborn?
- A. Decrease alcohol consumption
- B. Switching to cephalexin
- C. Folic acid supplementation (Correct Answer)
- D. Smoking cessation
- E. Switching to another antiepileptic medication
Patient education topics Explanation: ***Folic acid supplementation***
- **Folic acid** (vitamin B9) is crucial in early pregnancy for **neural tube development** and significantly reduces the risk of **neural tube defects** and other congenital malformations.
- Given the patient’s history of **lamotrigine** use, which can increase the risk of neural tube defects, folic acid supplementation is even more critical.
*Decrease alcohol consumption*
- While **alcohol cessation** is important to prevent **fetal alcohol syndrome** and other alcohol-related developmental issues, it primarily affects neurological development and facial dysmorphology rather than primarily preventing
- The effects of alcohol are typically more pronounced with **chronic heavy consumption**, and while any reduction is beneficial, it is not the most likely intervention to decrease general congenital malformations.
*Switching to cephalexin*
- **Amoxicillin** is considered **safe in pregnancy** and is a penicillin-class antibiotic, while **cephalexin** is a cephalosporin.
- Switching antibiotics from one safe drug to another without a clear medical indication (e.g., allergy, resistance) would **not decrease the risk of congenital malformations**.
*Smoking cessation*
- **Smoking cessation** is vital during pregnancy as it reduces the risk of **low birth weight**, **preterm birth**, and other complications like placental abruption.
- However, the primary link of smoking is not directly with **congenital malformations** like neural tube defects, but rather with growth restriction and adverse perinatal outcomes.
*Switching to another antiepileptic medication*
- This patient is on **lamotrigine**, which is considered one of the **safer antiepileptic drugs (AEDs)** in pregnancy, especially compared to others like **valproic acid**.
- Switching to an alternative AED might even carry a **higher risk for congenital malformations** and is generally not recommended unless lamotrigine is ineffective or contraindicated.
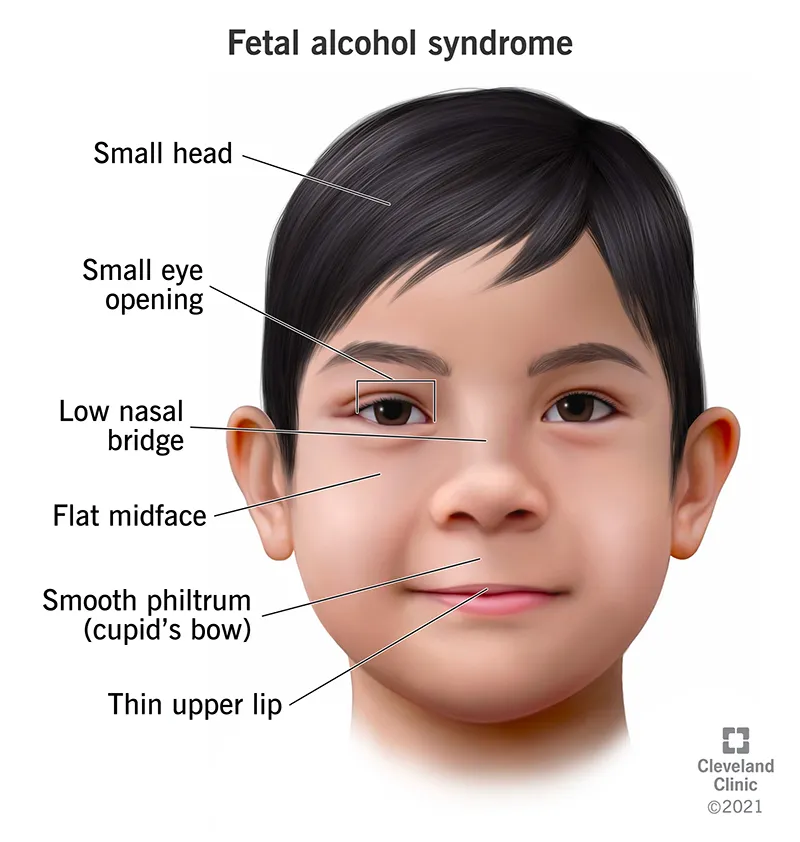
Patient education topics US Medical PG Question 9: A 26-year-old gravida 3 para 1 is admitted to labor and delivery with uterine contractions. She is at 37 weeks gestation with no primary care provider or prenatal care. She gives birth to a boy after an uncomplicated vaginal delivery with APGAR scores of 7 at 1 minute and 8 at 5 minutes. His weight is 2.2 kg (4.4 lb) and the length is 48 cm (1.6 ft). The infant has weak extremities and poor reflexes. The physical examination reveals microcephaly, palpebral fissures, thin lips, and a smooth philtrum. A systolic murmur is heard on auscultation. Identification of which of the following factors early in the pregnancy could prevent this condition?
- A. Phenytoin usage
- B. Maternal hypothyroidism
- C. Alcohol consumption (Correct Answer)
- D. Physical abuse
- E. Maternal toxoplasmosis
Patient education topics Explanation: ***Alcohol consumption***
- The constellation of **microcephaly**, **palpebral fissures**, **thin lips**, **smooth philtrum**, and **cardiac defects** (systolic murmur) in an infant points to **Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS)**.
- **FAS** is entirely preventable if alcohol is avoided during pregnancy, especially early in gestation, as there is no safe amount or time to drink alcohol during pregnancy.
*Phenytoin usage*
- **Phenytoin** is associated with **fetal hydantoin syndrome**, which can present with microcephaly, distinct facial features (e.g., broad nasal bridge, epicanthal folds), and hypoplastic nails, but typically not the specific facial features of FAS.
- While it is a teratogen, preventing its use would not specifically address the described clinical picture, which strongly aligns with alcohol exposure.
*Maternal hypothyroidism*
- **Untreated maternal hypothyroidism** can lead to **neurodevelopmental delays** and **cognitive impairment** in the child.
- It does not, however, cause the characteristic facial dysmorphology or cardiac defects seen in FAS.
*Physical abuse*
- **Physical abuse** does not cause congenital malformations or a specific syndrome evident at birth like FAS.
- While it is a serious concern for maternal and fetal well-being, it is not a direct teratogenic cause of the described neonatal findings.
*Maternal toxoplasmosis*
- **Congenital toxoplasmosis** can cause hydrocephalus, chorioretinitis, and intracranial calcifications.
- It does not cause the specific facial dysmorphology, cardiac defects, or microcephaly seen in this infant.
Patient education topics US Medical PG Question 10: A 34-year-old primigravid woman comes to the physician for a prenatal visit at 37-weeks' gestation because of worsening back pain for 3 weeks. The pain is worse with extended periods of walking, standing, and sitting. She has not had any changes in bowel movements or urination. Her mother has rheumatoid arthritis. Examination of the back shows bilateral pain along the sacroiliac joint area as a posterior force is applied through the femurs while the knees are flexed. She has difficulty actively raising either leg while the knee is extended. Motor and sensory function are normal bilaterally. Deep tendon reflexes are 2+. Babinski sign is absent. Pelvic examination shows a uterus consistent in size with a 37-weeks' gestation. There is no tenderness during abdominal palpation. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this patient's symptoms?
- A. Spinal cord compression
- B. Relaxation of the pelvic girdle ligaments (Correct Answer)
- C. Vertebral bone compression fracture
- D. Placental abruption
- E. Rheumatoid arthritis
Patient education topics Explanation: ***Relaxation of the pelvic girdle ligaments***
- During pregnancy, **hormonal changes** (especially relaxin) lead to the relaxation of **ligaments** in the **pelvic girdle**, including those around the sacroiliac joint. This can cause instability and pain, particularly with prolonged activity and in the third trimester.
- The exam findings of **bilateral pain along the sacroiliac joint** with posterior force and **difficulty raising extended legs** (suggesting weakness related to pelvic instability) are consistent with increased ligamentous laxity.
*Spinal cord compression*
- This would typically present with **neurological deficits** such as significant motor weakness, sensory changes, or bowel/bladder dysfunction, which are absent in this patient.
- The patient's **normal motor and sensory function** and **intact deep tendon reflexes** do not support spinal cord compression.
*Vertebral bone compression fracture*
- A compression fracture would likely result in **acute, severe, localized pain** often exacerbated by movement, and it is uncommon in healthy pregnant women without significant trauma or underlying bone pathology.
- The patient's symptoms are chronic (3 weeks), bilateral, and related to activity, which is not characteristic of an acute compression fracture.
*Placental abruption*
- This is characterized by **acute, severe abdominal pain**, **vaginal bleeding**, and signs of **fetal distress**, none of which are present in this patient.
- The pain is described as back pain, and the abdominal examination is normal, ruling out placental abruption.
*Rheumatoid arthritis*
- Although the patient's mother has rheumatoid arthritis, this condition primarily affects **small, peripheral joints** symmetrically and would not typically present with isolated sacroiliac pain in late pregnancy.
- Rheumatoid arthritis usually involves morning stiffness that improves with activity and is associated with systemic inflammatory symptoms, which are not described.
More Patient education topics US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.