Fetal movement monitoring US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Fetal movement monitoring. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Fetal movement monitoring US Medical PG Question 1: You have been entrusted with the task of finding the causes of low birth weight in infants born in the health jurisdiction for which you are responsible. In 2017, there were 1,500 live births and, upon further inspection of the birth certificates, 108 of these children had a low birth weight (i.e. lower than 2,500 g), while 237 had mothers who smoked continuously during pregnancy. Further calculations have shown that the risk of low birth weight in smokers was 14% and in non-smokers, it was 7%, while the relative risk of low birth weight linked to cigarette smoking during pregnancy was 2%. In other words, women who smoked during pregnancy were twice as likely as those who did not smoke to deliver a low-weight infant. Using this data, you are also asked to calculate how much of the excess risk for low birth weight, in percentage terms, can be attributed to smoking. What is the attributable risk percentage for smoking leading to low birth weight?
- A. 40%
- B. 30%
- C. 20%
- D. 10%
- E. 50% (Correct Answer)
Fetal movement monitoring Explanation: ***50%***
- This value is calculated using the formula for **attributable risk percent (ARP)** in the exposed group: ARP = ((Risk in exposed - Risk in unexposed) / Risk in exposed) × 100.
- Given that the risk of low birth weight in smokers (exposed) is 14% and in non-smokers (unexposed) is 7%, the calculation is ((0.14 - 0.07) / 0.14) × 100 = (0.07 / 0.14) × 100 = **0.50 × 100 = 50%**.
*40%*
- This percentage does not align with the provided risk values for low birth weight in smokers (14%) and non-smokers (7%).
- A calculation of ((0.14 - 0.07) / 0.14) * 100 does not yield 40%.
*30%*
- This value is incorrect, as it would suggest a smaller difference in risk between the exposed and unexposed groups relative to the risk in the exposed group than what is presented in the problem.
- The calculated attributable risk percent is higher than 30%.
*20%*
- This option is significantly lower than the true attributable risk percent derived from the given risk figures.
- It would imply a much weaker association between smoking and low birth weight in terms of excess risk than what is calculated.
*10%*
- This value is substantially different from the correct calculation and would suggest a very minor attributable risk.
- The attributable risk percent for smoking leading to low birth weight is much higher than 10% based on the provided data.
Fetal movement monitoring US Medical PG Question 2: A 39-year-old woman, gravida 5, para 4, at 41 weeks' gestation is brought to the hospital because of regular uterine contractions that started 2 hours ago. Pregnancy has been complicated by iron deficiency anemia treated with iron supplements. Pelvic examination shows the cervix is 90% effaced and 7-cm dilated; the vertex is at -1 station. Fetal heart tracing is shown. The patient is repositioned, O2 therapy is initiated, and amnioinfusion is done. A repeat assessment after 20 minutes shows a similar cervical status, and no changes in the fetal heart tracing, and less than 5 contractions in a period of 10 minutes.What is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Emergent cesarean delivery (Correct Answer)
- B. Monitor without intervention
- C. Begin active pushing
- D. Retry maternal repositioning
- E. Administer tocolytics
Fetal movement monitoring Explanation: ***Emergent cesarean delivery***
- The fetal heart tracing shows **recurrent late decelerations** unresponsive to **intrauterine resuscitation** (repositioning, O2, amnioinfusion), indicating fetal distress and uteroplacental insufficiency.
- Given the fetal distress and persistent late decelerations despite interventions, **expedited delivery** via cesarean section is indicated to prevent further fetal compromise.
*Monitor without intervention*
- This approach is inappropriate as the fetal heart tracing indicates **fetal distress** with recurrent **late decelerations** that have not resolved with initial interventions.
- Continued monitoring without action would place the fetus at risk for **hypoxia** and acidosis.
*Begin active pushing*
- The cervix is 7-cm dilated, meaning the patient is still in the **active phase of labor** and has not reached **complete cervical dilation** (10 cm) necessary for effective pushing.
- Pushing at this stage is unlikely to resolve the fetal distress and can potentially worsen **fetal acidosis** and maternal exhaustion.
*Retry maternal repositioning*
- The patient has already been repositioned and received other intrauterine resuscitation measures (O2 therapy, amnioinfusion) without improvement in the fetal heart tracing.
- Repeated repositioning alone is unlikely to resolve the underlying cause of the **late decelerations** in this context.
*Administer tocolytics*
- Tocolytics are used to **reduce uterine contractions** and manage conditions like **uterine tachysystole** or arrested labor, which are not explicitly present as the primary problem here (less than 5 contractions in 10 minutes).
- While they can temporarily improve uterine blood flow, they do not address the persistent **fetal distress** indicated by the recurrent late decelerations unresponsive to other interventions.
Fetal movement monitoring US Medical PG Question 3: A 42-year-old G1P0 woman presents to an obstetrician for her first prenatal visit. She has been pregnant for about 10 weeks and is concerned about how pregnancy will affect her health. Specifically, she is afraid that her complicated medical history will be adversely affected by her pregnancy. Her past medical history is significant for mild polycythemia, obesity hypoventilation syndrome, easy bleeding, multiple sclerosis, and aortic regurgitation. Which of these disorders is most likely to increase in severity during the course of the pregnancy?
- A. Easy bleeding
- B. Hypoventilation (Correct Answer)
- C. Multiple sclerosis
- D. Polycythemia
- E. Heart murmur
Fetal movement monitoring Explanation: ***Hypoventilation***
- Pregnancy leads to increased **oxygen consumption** and **carbon dioxide production**, requiring increased ventilation.
- In a patient with **obesity hypoventilation syndrome**, the already compromised respiratory drive and mechanics can worsen, leading to increased **hypercapnia** and **hypoxia**.
*Easy bleeding*
- Pregnancy is a **hypercoagulable state**, which typically reduces the risk of bleeding.
- While certain pregnancy complications (e.g., placental abruption) can cause bleeding, the overall physiological changes tend to **decrease primary bleeding tendencies**.
*Multiple sclerosis*
- Pregnancy typically has an **immunomodulatory effect** that can lead to a decrease in the frequency of MS relapses, especially in the third trimester.
- Relapses may increase postpartum, but during pregnancy itself, the condition often **stabilizes or improves**.
*Polycythemia*
- Pregnancy increases **plasma volume** significantly, which can lead to a relative **hemodilution**.
- This physiological change would likely **ameliorate mild polycythemia** rather than worsen it.
*Heart murmur*
- The murmur is due to **aortic regurgitation**, and while pregnancy increases **cardiac output** and **blood volume**, severe aortic regurgitation can worsen.
- However, the overall physiological changes of pregnancy result in **increased minute ventilation**, making hypoventilation a more direct and universally worsened problem with existing **obesity hypoventilation syndrome**.
Fetal movement monitoring US Medical PG Question 4: A 27-year old primigravid woman at 37 weeks' gestation comes to the emergency department because of frequent contractions for 4 hours. Her pregnancy has been complicated by hyperemesis gravidarum which subsided in the second trimester. The contractions occur every 10–15 minutes and have been increasing in intensity and duration since onset. Her temperature is 37.1°C (98.8°F), pulse is 110/min, and blood pressure is 140/85 mm Hg. Uterine contractions are felt on palpation. Pelvic examination shows clear fluid in the vagina. The cervix is 50% effaced and 3 cm dilated. After 4 hours the cervix is 80% effaced and 6 cm dilated. Pelvic examination is inconclusive for the position of the fetal head. The fetal heart rate is reassuring. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
- A. Administer oxytocin
- B. Perform external cephalic version
- C. Administer misoprostol
- D. Perform Mauriceau-Smellie-Veit maneuver
- E. Perform ultrasonography (Correct Answer)
Fetal movement monitoring Explanation: ***Perform ultrasonography***
- The examination notes that the **pelvic examination is inconclusive for the position of the fetal head**, which is a critical piece of information needed for safe delivery. **Ultrasonography** is the most appropriate next step to ascertain the fetal presentation and position, especially given the dilated cervix.
- Determining fetal position is essential to rule out **malpresentation**, such as **breech** or **transverse lie**, which would significantly impact the delivery plan and potentially necessitate a **cesarean section**.
*Administer oxytocin*
- **Oxytocin** is used to induce or augment labor when contractions are insufficient or labor is prolonged, but in this case, the cervix is progressing well (from 3 cm to 6 cm dilation in 4 hours), indicating **active labor**.
- Without knowing the fetal presentation, administering oxytocin could exacerbate issues if there's a **malpresentation**, potentially leading to **fetal distress** or **uterine rupture**.
*Perform external cephalic version*
- **External cephalic version (ECV)** is performed to change a **breech presentation** to a **cephalic presentation** by external manipulation, typically done before labor onset or early in labor at term.
- This patient is already in **active labor** with significant cervical dilation (6 cm), making ECV less likely to be successful and potentially increasing risks like **placental abruption** or **umbilical cord compression**.
*Administer misoprostol*
- **Misoprostol** is a prostaglandin analog used for **cervical ripening** and **labor induction** in cases where the cervix is unfavorable or labor needs to be initiated.
- This patient is already in **active labor** with progressive cervical dilation, making misoprostol unnecessary and potentially harmful due to the risk of **uterine hyperstimulation**.
*Perform Mauriceau-Smellie-Veit maneuver*
- The **Mauriceau-Smellie-Veit maneuver** is a technique used during a **vaginal breech delivery** to deliver the fetal head, specifically in cases of **frank or complete breech** that are being delivered vaginally.
- This maneuver is only performed *during* delivery of a breech baby, and the fetal position is currently unknown. It would be premature and inappropriate to consider this maneuver without first confirming a **breech presentation** and the decision for vaginal delivery.
Fetal movement monitoring US Medical PG Question 5: A 15-month-old boy is brought to the pediatrician’s office by his mother due to abnormal muscle tone and an inability to walk. He was able to control his head at 5 months of age, roll at 8 months of age, sit at 11 months of age, and develop hand preference at 13 months of age. On physical exam, he is observed to asymmetrically crawl. He has a velocity-dependent increase in tone and 3+ biceps and patellar reflexes. His startle, asymmetric tonic neck, and Babinski reflexes are present. Which of the following is the most common risk factor for developing this patient’s clinical presentation?
- A. Intrauterine growth restriction
- B. Prematurity (Correct Answer)
- C. Perinatal hypoxic injury
- D. Multiparity
- E. Stroke
Fetal movement monitoring Explanation: ***Prematurity***
- **Cerebral palsy (CP)** is characterized by **delayed motor milestones**, **abnormal muscle tone (spasticity)**, **hyperreflexia**, and **persistent primitive reflexes** beyond the expected age.
- **Prematurity** (especially birth before 32 weeks' gestation) is the **most common risk factor** for CP overall, accounting for approximately 40-50% of cases.
- The developing brain of premature infants is particularly vulnerable to periventricular leukomalacia (PVL) and intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), which can lead to various CP subtypes.
- While this patient's **early hand preference** and **asymmetric crawling** suggest hemiplegic CP (often associated with stroke), the question asks for the most common risk factor **epidemiologically**, not the most likely cause in this specific case.
*Intrauterine growth restriction*
- While **IUGR** can be associated with developmental delays and is a risk factor for CP, it is less common than prematurity as the primary risk factor.
- IUGR alone without complications (like prematurity or hypoxia) accounts for a smaller proportion of CP cases.
*Perinatal hypoxic injury*
- **Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)** can cause CP, especially severe cases resulting in basal ganglia or watershed area damage.
- However, with modern obstetric monitoring and intervention, severe perinatal hypoxia accounts for only ~10% of CP cases—less common than prematurity.
*Multiparity*
- **Multiparity** (having multiple previous births) is generally not considered a direct or common risk factor for cerebral palsy.
- Any slight associations are typically due to confounding factors like increased risk of preterm birth in subsequent pregnancies, rather than multiparity itself.
*Stroke*
- **Perinatal stroke** can cause CP, typically presenting as **hemiplegic CP** with early hand preference and asymmetric motor findings—features seen in this patient.
- While stroke is a significant cause of hemiplegic CP specifically, it accounts for a smaller proportion of overall CP cases compared to prematurity, which causes various CP subtypes and is more prevalent.
Fetal movement monitoring US Medical PG Question 6: A 24-year-old primigravida at 28 weeks gestation presents to the office stating that she “can’t feel her baby kicking anymore.” She also noticed mild-to-moderate vaginal bleeding. A prenatal visit a few days ago confirmed the fetal cardiac activity by Doppler. The medical history is significant for GERD, hypertension, and SLE. The temperature is 36.78°C (98.2°F), the blood pressure is 125/80 mm Hg, the pulse is 70/min, and the respiratory rate is 14/min. Which of the following is the next best step in evaluation?
- A. Confirmation of cardiac activity by Doppler (Correct Answer)
- B. Order platelet count, fibrinogen, PT and PTT levels
- C. Abdominal delivery
- D. Speculum examination
- E. Misoprostol
Fetal movement monitoring Explanation: ***Confirmation of cardiac activity by Doppler***
- The patient presents with **decreased fetal movement** and **vaginal bleeding** at 28 weeks, which are concerning signs for complications like **placental abruption** or **fetal demise**.
- The immediate priority is to assess **fetal viability** by confirming the presence of a **fetal heartbeat**, with **Doppler ultrasonography** being the quickest and most accessible method.
*Order platelet count, fibrinogen, PT and PTT levels*
- While **coagulation studies** are important in cases of significant vaginal bleeding, especially if **placental abruption** is suspected, they are not the *next best step*.
- Assessing **fetal well-being** takes precedence, as the presence or absence of a **fetal heart rate** will guide subsequent emergency management.
*Abdominal delivery*
- **Abdominal delivery (C-section)** is a definitive intervention and should only be considered *after* an immediate assessment of **fetal status** and maternal stability.
- Delivery at 28 weeks gestation would be considered **preterm**, and careful evaluation is needed before making such a critical decision.
*Speculum examination*
- A **speculum examination** is used to investigate the source of vaginal bleeding, assess the cervix, and rule out causes such as **cervical lesions** or **cervical dilation**.
- However, given the *decreased fetal movement* and the potential for severe obstetrical emergencies, **fetal viability** must be confirmed first.
*Misoprostol*
- **Misoprostol** is a **prostaglandin analog** used to induce cervical ripening and uterine contractions, primarily for **labor induction** or **abortion**.
- It is not indicated as an initial diagnostic or therapeutic step in a patient with *decreased fetal movement* and *vaginal bleeding* without a clear diagnosis or indication for delivery.
Fetal movement monitoring US Medical PG Question 7: A 26-year-old G1P0 female who is 39 weeks pregnant presents to the emergency department in labor. She reports following her primary care physician’s recommendations throughout her pregnancy and has not had any complications. During delivery, the baby’s head turtled back into the vaginal canal and did not advance any further. The neonatal intensivist was called for shoulder dystocia and a baby girl was able to be delivered vaginally 6 minutes later. Upon initial assessment, the baby appeared pale throughout, had her arms and legs flexed without active motion, and had some flexion of extremities when stimulated. Her pulse is 120/min and had irregular respirations. What is this baby’s initial APGAR score?
- A. 5 (Correct Answer)
- B. 6
- C. 7
- D. 4
- E. 3
Fetal movement monitoring Explanation: ***5***
- The APGAR score is calculated based on five criteria: **Appearance**, **Pulse**, **Grimace**, **Activity**, and **Respiration**.
- This baby's score is calculated as follows: **Appearance** (pale all over) = 0, **Pulse** (120/min) = 2, **Grimace** (some flexion of extremities with stimulation) = 1, **Activity** (arms and legs flexed without active motion) = 1, and **Respiration** (irregular) = 1.
- Total score: 0 + 2 + 1 + 1 + 1 = **5 points**
- A score of 5 indicates **moderate neonatal compromise** requiring close monitoring and possible intervention.
*4*
- A score of 4 would indicate more severe compromise, such as absent respirations (0 points) rather than irregular respirations (1 point).
- This baby has irregular respirations present, which earns 1 point, not 0 points.
*6*
- A score of 6 would require improvement in at least one category, such as **acrocyanosis** (blue extremities but pink body = 1 point for appearance) instead of pallor throughout.
- This baby's complete pallor limits the score to 5.
*7*
- A score of 7 or higher is generally considered reassuring and indicates a **healthy transition** from intrauterine to extrauterine life.
- This baby's concerning signs, including **complete pallor**, **irregular respirations**, and **poor muscle tone**, are inconsistent with a score of 7.
*3*
- A score of 3 would indicate severe depression with findings such as **heart rate less than 100 bpm**, completely absent reflexes, or flaccid muscle tone.
- This baby has a reassuring pulse of 120/min (2 points), some reflex response (1 point), and some muscle tone (1 point), making the total score higher than 3.
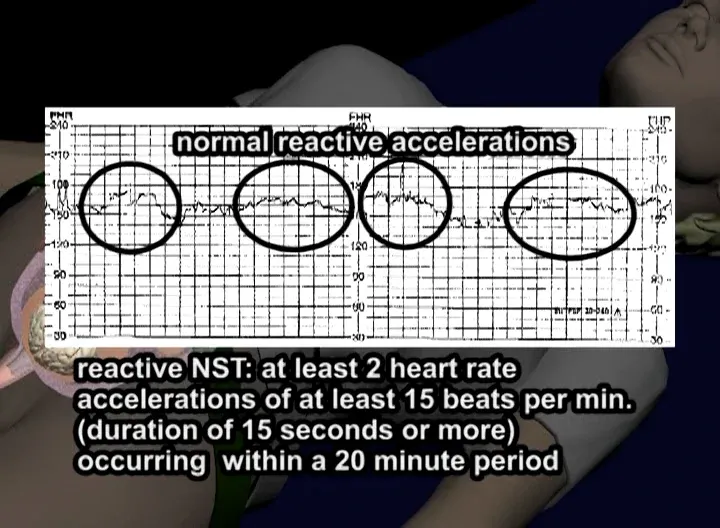
Fetal movement monitoring US Medical PG Question 8: A 30-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 38 weeks' gestation comes to the hospital for regular, painful contractions that have been increasing in frequency. Her pregnancy has been complicated by gestational diabetes treated with insulin. Pelvic examination shows the cervix is 50% effaced and 4 cm dilated; the vertex is at -1 station. Ultrasonography shows no abnormalities. A tocometer and Doppler fetal heart monitor are placed on the patient's abdomen. The fetal heart rate monitoring strip shows a baseline heart rate of 145/min with a variability of ≥ 15/min. Within a 20-minute recording, there are 7 uterine contractions, 4 accelerations, and 3 decelerations that have a nadir occurring within half a minute. The decelerations occur at differing intervals relative to the contractions. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
- A. Vibroacoustic stimulation
- B. Routine monitoring (Correct Answer)
- C. Administer tocolytics
- D. Emergent cesarean delivery
- E. Placement of fetal scalp electrode
Fetal movement monitoring Explanation: ***Routine monitoring***
- The presented FHR tracing exhibits a **normal baseline rate** (145/min), **moderate variability** (≥15/min), and the presence of **accelerations**, indicating a reassuring fetal status.
- The described decelerations are **variable decelerations** due to their sudden onset, nadir within 30 seconds, and variable relationship to contractions, which are generally benign unless prolonged, deep, or repetitive. Given the otherwise reassuring status, continued routine monitoring is appropriate.
*Vibroacoustic stimulation*
- This intervention is used to elicit **fetal accelerations** or movement during non-stress tests (NSTs) when the fetus is quiet or shows a non-reactive pattern.
- In this case, the fetus is already showing **accelerations** and moderate variability, so stimulation is not needed to assess fetal well-being.
*Administer tocolytics*
- **Tocolytics** are used to stop or slow down labor, typically in cases of preterm labor or uterine tachysystole causing fetal distress.
- This patient is at **38 weeks' gestation** and in active labor, and there are no signs of fetal distress warranting the cessation of contractions.
*Emergent cesarean delivery*
- **Emergent cesarean delivery** is indicated for acute fetal distress, such as prolonged decelerations, significant bradycardia, or absent variability in conjunction with other concerning FHR patterns.
- The FHR tracing described is largely reassuring with moderate variability and accelerations, and the variable decelerations are not indicative of immediate threat, making emergent delivery unnecessary.
*Placement of fetal scalp electrode*
- A **fetal scalp electrode** provides a more accurate and continuous measure of the FHR, often used when external monitoring is difficult or when there are concerns about the reliability of the tracing.
- While it can be useful in some situations, the current tracing is **interpretable as reassuring**, making invasive monitoring currently unnecessary.
Fetal movement monitoring US Medical PG Question 9: A 9-month-old boy is brought to the physician because of abnormal crawling and inability to sit without support. A 2nd-trimester urinary tract infection that required antibiotic use and a spontaneous preterm birth via vaginal delivery at 36 weeks’ gestation both complicated the mother’s pregnancy. Physical examination shows a scissoring posture of the legs when the child is suspended by the axillae. Examination of the lower extremities shows brisk tendon reflexes, ankle clonus, and upward plantar reflexes bilaterally. When encouraged by his mother, the infant crawls forward by using normal reciprocal movements of his arms, while his legs drag behind. A brain MRI shows scarring and atrophy in the white matter around the ventricles with ventricular enlargement. Which of the following is most likely associated with the findings in this child?
- A. Antenatal injury
- B. Genetic defect
- C. Postnatal head trauma
- D. Intrapartum asphyxia
- E. Preterm birth (Correct Answer)
Fetal movement monitoring Explanation: ***Preterm birth***
- The combination of **abnormal crawling**, **inability to sit without support**, **scissoring posture**, **spasticity**, and **periventricular white matter scarring** (periventricular leukomalacia, PVL) are classic signs of **spastic cerebral palsy**.
- **Preterm birth** is the most significant risk factor for **PVL** and the subsequent development of spastic cerebral palsy, particularly spastic diplegia.
- The **periventricular white matter** in preterm infants (especially <34 weeks, but also late preterm at 34-37 weeks) is highly vulnerable to ischemic injury due to immature vascular development and susceptibility to hypoxic-ischemic insults during the perinatal period.
- This infant was born at **36 weeks (late preterm)**, which is a known risk factor for PVL and cerebral palsy.
*Antenatal injury*
- While brain injury can occur in the antenatal period, the specific finding of **periventricular leukomalacia** is most characteristically associated with **prematurity** and perinatal/early postnatal events rather than purely antenatal injury.
- The term "antenatal injury" is too vague and doesn't capture the specific pathophysiology of PVL, which occurs around the time of birth in vulnerable preterm infants.
*Genetic defect*
- While some forms of cerebral palsy can have a genetic component, the clinical picture here, especially the MRI findings of **periventricular leukomalacia**, strongly points to an acquired brain injury rather than a primary genetic defect.
- Genetic conditions typically present with more widespread or specific neurodevelopmental abnormalities, often without the focal periventricular white matter scarring seen in PVL.
*Postnatal head trauma*
- **Postnatal head trauma** would typically present with a history of injury and more acute neurological deficits or focal lesions on imaging (e.g., subdural hematoma, contusions), rather than the characteristic **periventricular white matter scarring** observed here.
- The presentation is consistent with a developmental disorder from perinatal brain injury, not an acute traumatic event from infancy.
*Intrapartum asphyxia*
- **Intrapartum asphyxia** (hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy) in term infants characteristically leads to damage in the **deep grey matter** (e.g., basal ganglia, thalamus) and cortex, not primarily **periventricular white matter** as seen here.
- The MRI findings of **periventricular leukomalacia** are pathognomonic for **prematurity-related injury**, not term asphyxia.
Fetal movement monitoring US Medical PG Question 10: A 30-year-old primigravida schedules an appointment with her obstetrician for a regular check-up. She says that everything is fine, although she reports that her baby has stopped moving as much as previously. She is 22 weeks gestation. She denies any pain or vaginal bleeding. The obstetrician performs an ultrasound and also orders routine blood and urine tests. On ultrasound, there is no fetal cardiac activity or movement. The patient is asked to wait for 1 hour, after which the scan is to be repeated. The second scan shows the same findings. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Missed abortion
- B. Ectopic pregnancy
- C. Complete abortion
- D. Fetal demise (Correct Answer)
- E. Incomplete abortion
Fetal movement monitoring Explanation: ***Fetal demise***
- The absence of fetal cardiac activity and movement on repeated ultrasound scans at 22 weeks' gestation, after previously reporting fetal movement, is consistent with **fetal demise**.
- **Fetal demise** refers to the death of a fetus in utero at or after 20 weeks of gestation, or when the fetus weighs 350 grams or more.
*Missed abortion*
- **Missed abortion** (or missed miscarriage) is typically defined as a non-viable intrauterine pregnancy with a retained fetus or embryo without cardiac activity before 20 weeks of gestation.
- The patient is 22 weeks gestation, which places the condition beyond the general definition of a missed abortion.
*Ectopic pregnancy*
- In an **ectopic pregnancy**, the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tube, and would not have reached 22 weeks with reported fetal movement.
- An ectopic pregnancy would present with earlier symptoms like **abdominal pain** and **vaginal bleeding**, and an ultrasound would show an empty uterus or evidence of extrauterine pregnancy.
*Complete abortion*
- A **complete abortion** involves the complete expulsion of all products of conception from the uterus.
- This would be characterized by **heavy vaginal bleeding** and the passage of tissue, which the patient denies.
*Incomplete abortion*
- An **incomplete abortion** occurs when some, but not all, products of conception have been expelled from the uterus.
- Similar to complete abortion, an incomplete abortion would typically involve **vaginal bleeding** and retained tissue, accompanied by **cramping**, which are absent in this case.
More Fetal movement monitoring US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.