Postpartum hemorrhage protocols US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Postpartum hemorrhage protocols. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Postpartum hemorrhage protocols US Medical PG Question 1: A 38-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 35 weeks' gestation comes to the emergency department because of an episode of vaginal bleeding that morning. The bleeding has subsided. She has had no prenatal care. Her previous child was delivered with a caesarean section because of a breech presentation. Her temperature is 37.1°C (98.8°F), pulse is 88/min, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 125/85 mm Hg. The abdomen is nontender and the size of the uterus is consistent with a 35-week gestation. No contractions are felt. The fetal heart rate is 145/min. Her hemoglobin concentration is 12 g/dL, leukocyte count is 13,000/mm3, and platelet count is 350,000/mm3. Transvaginal ultrasound shows that the placenta covers the internal os. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Schedule elective cesarean delivery (Correct Answer)
- B. Observation only
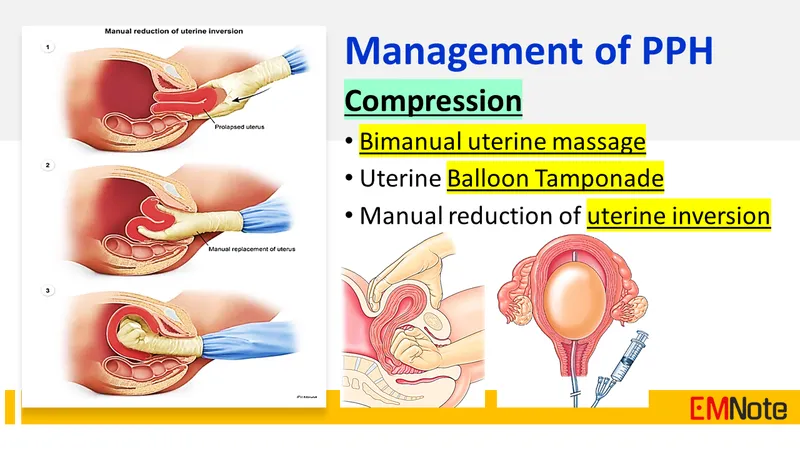
- C. Perform bimanual pelvic examination
- D. Perform emergency cesarean delivery
- E. Administer oxytocin to induce labor
Postpartum hemorrhage protocols Explanation: ***Schedule elective cesarean delivery***
- The ultrasound finding of the **placenta covering the internal os** confirms **placenta previa**. Given the patient is at **35 weeks' gestation** and has experienced **vaginal bleeding**, an elective cesarean delivery is the safest management to avoid further bleeding episodes and ensure maternal and fetal well-being.
- An elective cesarean delivery is typically scheduled between **36 and 37 weeks' gestation** for placenta previa to minimize the risk of spontaneous labor and potentially catastrophic hemorrhage.
*Observation only*
- This is inappropriate given the diagnosis of **placenta previa** and the history of **vaginal bleeding**. Observation alone carries a significant risk of recurrent, potentially severe hemorrhage.
- While the bleeding has subsided, the underlying condition remains and warrants active management to prevent future complications.
*Perform bimanual pelvic examination*
- A **bimanual pelvic examination** is **contraindicated** in cases of suspected or confirmed **placenta previa**.
- Performing such an examination can **disrupt the placenta** and precipitate a massive, life-threatening hemorrhage.
*Perform emergency cesarean delivery*
- An emergency cesarean delivery is indicated if the patient presents with **severe, active bleeding** or signs of **fetal distress**.
- In this case, the bleeding has subsided, the patient is hemodynamically stable, and the fetal heart rate is normal, so an immediate emergency delivery is not warranted.
*Administer oxytocin to induce labor*
- **Induction of labor with oxytocin** is **contraindicated** in **placenta previa**.
- Stimulating contractions would lead to **cervical dilation**, causing further placental separation and severe hemorrhage, putting both mother and fetus at extreme risk.
Postpartum hemorrhage protocols US Medical PG Question 2: A 35-year-old patient is brought into the emergency department post motor vehicle crash. Stabilization of the patient in the trauma bay requires endotracheal intubation. The patient has a laceration on the femoral artery from shrapnel and seems to have lost large quantities of blood. The patient is transfused with 13 units of packed red blood cells. His vitals are T 96.5, HR 150, BP 90/40. Even with the direct pressure on the femoral artery, the patient continues to bleed. Results of labs drawn within the last hour are pending. Which of the following is most likely to stop the bleeding in this patient?
- A. Normal saline
- B. Fresh frozen plasma and platelets (Correct Answer)
- C. Whole blood
- D. Dextrose
- E. Cryoprecipitate
Postpartum hemorrhage protocols Explanation: ***Fresh frozen plasma and platelets***
- This patient is experiencing **dilutional coagulopathy** due to massive transfusion of packed red blood cells, which lack clotting factors and platelets.
- **Fresh frozen plasma (FFP)** provides essential clotting factors, while **platelets** directly address thrombocytopenia, both crucial for **hemostasis**.
- This represents **standard component therapy** readily available in emergency departments.
*Normal saline*
- Administering normal saline would further dilute the remaining clotting factors and platelets, potentially **worsening the coagulopathy**.
- While essential for **volume resuscitation**, it does not provide any clotting components needed to stop bleeding.
*Whole blood*
- While **whole blood** contains red blood cells, plasma, and platelets in physiologic ratios, it is **not readily available** in most civilian trauma centers.
- Modern practice uses **component therapy** (FFP + platelets + PRBCs) which is more widely accessible and allows for targeted resuscitation.
- Low-titer O whole blood programs exist in some centers but are not universally available.
*Dextrose*
- **Dextrose solutions** primarily provide free water and glucose, used for hydration and hypoglycemia.
- It has **no hemostatic properties** and would further dilute clotting factors, exacerbating the bleeding.
*Cryoprecipitate*
- **Cryoprecipitate** is rich in **fibrinogen, factor VIII, factor XIII, and von Willebrand factor**.
- While useful for specific factor deficiencies or when fibrinogen is critically low in massive transfusions, it **does not replace all clotting factors or platelets** comprehensively as FFP and platelets would.
- Typically used as **adjunctive therapy** when fibrinogen levels are known to be low.
Postpartum hemorrhage protocols US Medical PG Question 3: A 34-year-old primigravida was brought to an obstetric clinic with a chief complaint of painless vaginal bleeding. She was diagnosed with placenta praevia and transfused with 2 units of whole blood. Five hours after the transfusion, she developed a fever and chills. How could the current situation be prevented?
- A. Administering prophylactic epinephrine
- B. ABO grouping and Rh typing before transfusion
- C. Transfusing leukocyte reduced blood products (Correct Answer)
- D. Performing Coombs test before transfusion
- E. Administering prophylactic immunoglobulins
Postpartum hemorrhage protocols Explanation: ***Transfusing leukocyte reduced blood products***
- The patient's symptoms of **fever and chills** occurring hours after transfusion are characteristic of a **febrile non-hemolytic transfusion reaction (FNHTR)**.
- FNHTRs are caused by residual **donor leukocytes** in the transfused blood product, which release **cytokines** during storage or react with recipient antibodies, and can be prevented by using **leukoreduced blood products**.
*Administering prophylactic epinephrine*
- **Epinephrine** is used to treat severe **anaphylactic and allergic reactions** but does not prevent the underlying mechanism of FNHTRs.
- Its prophylactic administration is not a standard practice for preventing transfusion reactions like FNHTRs.
*ABO grouping and Rh typing before transfusion*
- **ABO grouping and Rh typing** are crucial for preventing **acute hemolytic transfusion reactions**, which are much more severe and involve erythrocyte incompatibility.
- These tests would not prevent a **febrile non-hemolytic transfusion reaction (FNHTR)** caused by leukocyte components.
*Performing Coombs test before transfusion*
- The **Coombs test (Direct Antiglobulin Test)** detects antibodies attached to red blood cells and is primarily used to diagnose **autoimmune hemolytic anemia** or delayed hemolytic transfusion reactions.
- It does not prevent FNHTRs, which are unrelated to red blood cell incompatibility or antibody-mediated hemolysis.
*Administering prophylactic immunoglobulins*
- **Prophylactic immunoglobulins** are used in specific situations like **immunodeficiency** or **Rh incompatibility (RhoGAM)** to prevent alloimmunization, but not for preventing FNHTRs.
- This intervention would not target the mechanism leading to fever and chills caused by donor leukocyte interactions.
Postpartum hemorrhage protocols US Medical PG Question 4: A 34-year-old G5P5 woman gave birth to a healthy infant 30 minutes ago by vacuum-assisted vaginal delivery and is now experiencing vaginal bleeding. The placenta was delivered spontaneously and was intact upon examination. The infant weighed 5.2 kg and had Apgar scores of 8 and 9. No perineal tear or intentional episiotomy occurred. The patient has type 1 diabetes. She had good glycemic control throughout her pregnancy. She took a prenatal vitamin daily. Blood pressure is 135/72 mmHg, pulse is 102/min, and respirations are 18/min. Upon physical examination, the uterine fundus is soft and palpated 4 cm above the umbilicus. There are 3-cm blood clots on the patient’s bed pad. Which of the following is the next best step in management for the patient’s bleeding?
- A. Administer misoprostol
- B. Manually remove retained placental fragments
- C. Perform uterine massage and administer oxytocin (Correct Answer)
- D. Perform uterine artery embolization
- E. Perform hysterectomy
Postpartum hemorrhage protocols Explanation: ***Perform uterine massage and administer oxytocin***
- The patient's presentation of a **soft, boggy uterus** palpated 4 cm above the umbilicus after delivery, along with significant vaginal bleeding and clots, is highly indicative of **uterine atony**.
- **Uterine massage** and administration of **oxytocin** are the first-line interventions to stimulate uterine contractions and reduce bleeding by compressing placental site blood vessels.
*Administer misoprostol*
- **Misoprostol** is a prostaglandin analog that can be used for uterine atony when oxytocin is insufficient or contraindicated, but it is not the *first-line* treatment.
- Its onset of action may be slower than immediate uterine massage and IV oxytocin, which are preferred for initial management of acute uterine atony.
*Manually remove retained placental fragments*
- The question states that the **placenta was delivered spontaneously and was intact upon examination**, which makes retained placental fragments less likely as the primary cause of bleeding.
- While retained fragments can cause postpartum hemorrhage, the boggy uterus points more strongly to atony, and manual removal is indicated *after* confirming retained placental tissue.
*Perform uterine artery embolization*
- **Uterine artery embolization** is an interventional radiology procedure typically reserved for cases of postpartum hemorrhage that are refractory to conventional medical and surgical management.
- It is an invasive procedure and not the appropriate *next best step* for initial management of suspected uterine atony.
*Perform hysterectomy*
- **Hysterectomy** is a last-resort, life-saving measure for intractable postpartum hemorrhage when all other medical and surgical options have failed.
- It is a highly invasive and irreversible procedure, certainly not the *next best step* in a patient who has just begun to bleed.
Postpartum hemorrhage protocols US Medical PG Question 5: Five minutes after initiating a change of position and oxygen inhalation, the oxytocin infusion is discontinued. A repeat CTG that is done 10 minutes later shows recurrent variable decelerations and a total of 3 uterine contractions in 10 minutes. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Restart oxytocin infusion
- B. Emergent Cesarean section
- C. Administer terbutaline
- D. Monitor without intervention
- E. Amnioinfusion (Correct Answer)
Postpartum hemorrhage protocols Explanation: ***Amnioinfusion***
- **Recurrent variable decelerations** persisting after discontinuing oxytocin and changing maternal position often indicate **cord compression**, which can be relieved by amnioinfusion.
- Adding fluid to the amniotic cavity **cushions the umbilical cord**, reducing compression during uterine contractions.
*Restart oxytocin infusion*
- Reinitiating oxytocin would likely **worsen the recurrent variable decelerations** by increasing uterine contraction frequency and intensity, thereby exacerbating cord compression.
- The goal is to alleviate fetal distress, not to intensify uterine activity that is already causing issues.
*Emergent Cesarean section*
- While an emergent Cesarean section is indicated for **unresolved fetal distress**, it's usually considered after less invasive measures, such as amnioinfusion, have failed.
- There is still an opportunity for a simpler intervention to resolve the issue before resorting to surgery.
*Administer terbutaline*
- Terbutaline is a **tocolytic agent** used to reduce uterine contractions, which can be helpful in cases of tachysystole or hyperstimulation.
- In this scenario, the contraction frequency is low (3 in 10 minutes), so reducing contractions is not the primary aim; rather, the focus is on resolving the cord compression causing decelerations.
*Monitor without intervention*
- **Recurrent variable decelerations** are an concerning sign of **fetal distress** and require intervention to prevent potential harm to the fetus.
- Simply monitoring without intervention would be inappropriate and could lead to worsening fetal hypoxemia and acidosis.
Postpartum hemorrhage protocols US Medical PG Question 6: Thirty minutes after normal vaginal delivery of twins, a 35-year-old woman, gravida 5, para 4, has heavy vaginal bleeding with clots. Physical examination shows a soft, enlarged, and boggy uterus. Despite bimanual uterine massage, administration of uterotonic drugs, and placement of an intrauterine balloon for tamponade, the bleeding continues. A hysterectomy is performed. Vessels running through which of the following structures must be ligated during the surgery to achieve hemostasis?
- A. Suspensory ligament
- B. Round ligament
- C. Ovarian ligament
- D. Uterosacral ligament
- E. Cardinal ligament (Correct Answer)
Postpartum hemorrhage protocols Explanation: ***Cardinal ligament***
- The **uterine artery** and **uterine vein**, which supply the uterus, run through the **cardinal ligament** (also known as the transverse cervical ligament).
- Ligation of these vessels is crucial during a hysterectomy to control bleeding from the uterus.
*Suspensory ligament*
- The **suspensory ligament of the ovary** contains the **ovarian artery** and vein, which primarily supply the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
- While these may be ligated during a hysterectomy if the ovaries are removed, they are not the primary vessels causing uterine bleeding in postpartum hemorrhage.
*Round ligament*
- The **round ligament of the uterus** extends from the uterus to the labia majora and contains relatively small vessels, primarily contributing to uterine support.
- Ligation of this ligament alone would not effectively control heavy uterine bleeding.
*Ovarian ligament*
- The **ovarian ligament** connects the ovary to the uterus and contains small vessels that mainly supply the ovary.
- It does not house the major blood supply to the uterus itself.
*Uterosacral ligament*
- The **uterosacral ligaments** primarily provide support to the uterus by connecting it to the sacrum and contain small nerves and vessels.
- Ligation of these ligaments would not control the main arterial supply to the uterus.
Postpartum hemorrhage protocols US Medical PG Question 7: A 31-year-old G6P6 woman with a history of fibroids gives birth to twins via vaginal delivery. Her pregnancy was uneventful, and she reported having good prenatal care. Both placentas are delivered immediately after the birth. The patient continues to bleed significantly over the next 20 minutes. Her temperature is 97.0°F (36.1°C), blood pressure is 124/84 mmHg, pulse is 95/min, respirations are 16/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Continued vaginal bleeding is noted. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial step in management?
- A. Oxytocin
- B. Blood product transfusion
- C. Uterine artery embolization
- D. Hysterectomy
- E. Bimanual massage (Correct Answer)
Postpartum hemorrhage protocols Explanation: ***Bimanual massage***
- The patient is experiencing **postpartum hemorrhage (PPH)**, indicated by significant bleeding post-delivery. **Uterine atony** is the most common cause of PPH, and bimanual massage helps stimulate uterine contractions to reduce bleeding.
- This is a **first-line, non-pharmacological intervention** that can be rapidly initiated to manage uterine atony.
*Oxytocin*
- While **oxytocin** is a uterotonic agent used to treat PPH, the initial step is typically **bimanual massage** to physically stimulate the uterus while preparing for medication administration.
- Oxytocin infusion would be administered concurrent with or immediately following bimanual massage, but manual compression is often initiated first.
*Blood product transfusion*
- Blood product transfusion is indicated for significant blood loss and hemodynamic instability, but it is a **supportive measure** rather than an initial intervention to stop the bleeding.
- The patient's current **blood pressure (124/84 mmHg)** and **pulse (95/min)** do not immediately suggest severe hypovolemic shock requiring immediate transfusion as the *first* step before attempting to control the source of bleeding.
*Uterine artery embolization*
- **Uterine artery embolization** is a highly invasive procedure typically reserved for cases where conservative measures, including uterotonic agents and bimanual compression, have failed to control PPH.
- It is not an appropriate initial step, as it requires specialized equipment and personnel and would delay immediate management of active bleeding.
*Hysterectomy*
- **Hysterectomy** is a last-resort intervention for intractable PPH that cannot be controlled by all other methods, including uterotonics, uterine massage, and other surgical or interventional radiology techniques.
- It is a highly invasive procedure with significant morbidity and is not considered an initial management step.
Postpartum hemorrhage protocols US Medical PG Question 8: Two days after being admitted to the hospital because of severe peripartum vaginal bleeding during a home birth, a 40-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 3, has a 30-second generalized convulsive seizure followed by unconsciousness. Prior to the event she complained of acute onset of sweating and uncontrollable shivering. She was hemodynamically unstable and required several liters of intravenous fluids and 5 units of packed red blood cells in the intensive care unit. The patient's two prior pregnancies, at ages 33 and 35, were uncomplicated. She is otherwise healthy. Prior to admission, her only medication was a daily prenatal vitamin. Temperature is 37.5°C (99.5°F), pulse is 120/min, respirations are 18/min, blood pressure is 101/61 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 96%. Examination shows very little milk expression from the breasts bilaterally. Finger-stick glucose level is 36 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's condition?
- A. Lactotrophic adenoma
- B. Hypothalamic infarction
- C. Pituitary ischemia (Correct Answer)
- D. Adrenal hemorrhage
- E. Hypoactive thyroid
Postpartum hemorrhage protocols Explanation: ***Pituitary ischemia***
- The patient's history of **severe peripartum hemorrhage** followed by **hypotension** and **seizure** is highly suggestive of **Sheehan syndrome**, which is caused by pituitary ischemia and necrosis.
- The inability to lactate (**little milk expression**) and **hypoglycemia** (finger-stick glucose 36 mg/dL) are consistent with deficiencies of **prolactin** and **adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)**, respectively, due to pituitary damage.
*Lactotrophic adenoma*
- A lactotrophic adenoma would typically cause **hyperprolactinemia** leading to **galactorrhea** (excessive milk production), not decreased milk expression.
- While it can cause headaches and visual field defects, it does not explain the peripartum onset with hemorrhage or the subsequent hypoglycemia.
*Hypothalamic infarction*
- While hypothalamic damage can lead to endocrine dysfunction, an isolated hypothalamic infarction is a less common cause of this constellation of symptoms immediately following severe hemorrhage.
- **Pituitary infarction** is a more direct and common consequence of profound peripartum hypotension.
*Adrenal hemorrhage*
- **Adrenal hemorrhage** can lead to adrenal insufficiency with symptoms like hypotension, hypoglycemia, and shock.
- However, it does not explain the specific symptom of **agalactorrhea** (little milk expression), which points to pituitary involvement.
*Hypoactive thyroid*
- A **hypoactive thyroid (hypothyroidism)** can cause fatigue, bradycardia, and sometimes hypoglycemia, but it typically does not present with an acute seizure or agalactorrhea in the immediate postpartum period following hemorrhage.
- The acute presentation here is more consistent with a sudden and severe endocrine insult affecting multiple axes.
Postpartum hemorrhage protocols US Medical PG Question 9: A 30-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, abortus 1, comes to the physician because of failure to conceive for 12 months. She is sexually active with her husband 2–3 times per week. Her first child was born at term after vaginal delivery 2 years ago. At that time, the postpartum course was complicated by hemorrhage from retained placental products, and the patient underwent dilation and curettage. Menses occur at regular 28-day intervals and previously lasted for 5 days with normal flow, but now last for 2 days with significantly reduced flow. She stopped taking oral contraceptives 1 year after the birth of her son. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Speculum examination shows a normal vagina and cervix. The uterus is normal in size, and no adnexal masses are palpated. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Hysteroscopy with potential adhesiolysis (Correct Answer)
- B. Measurement of serum FSH and LH concentrations
- C. Measurement of antisperm antibody concentration
- D. Dilation and curettage
- E. Estrogen/progestin withdrawal test
Postpartum hemorrhage protocols Explanation: ***Hysteroscopy with potential adhesiolysis***
- The patient's history of **postpartum hemorrhage** requiring D&C, followed by significantly **reduced menstrual flow**, strongly suggests **intrauterine adhesions (Asherman's syndrome)**.
- **Hysteroscopy** is the definitive diagnostic and therapeutic procedure for Asherman's syndrome, allowing direct visualization and surgical lysis of adhesions.
*Measurement of serum FSH and LH concentrations*
- This step is typically used to evaluate **ovarian reserve** or **hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis dysfunction** in cases of anovulation or primary ovarian insufficiency.
- Given the patient's regular menstrual cycles, ovulatory dysfunction is less likely to be the primary cause of her infertility symptoms.
*Measurement of antisperm antibody concentration*
- **Antisperm antibodies** are a cause of infertility in a small percentage of couples, affecting sperm function or fertilization.
- This test is usually pursued after more common causes of infertility have been ruled out, as there are stronger indicators for Asherman's syndrome in this case.
*Dilation and curettage*
- A **D&C** was previously performed and is the likely iatrogenic cause of her current symptoms (Asherman's syndrome).
- Performing another D&C without addressing the adhesions would likely worsen her condition and lead to further scarring.
*Estrogen/progestin withdrawal test*
- This test assesses the integrity of the **endometrium** and the presence of sufficient endogenous estrogen if a patient has **amenorrhea**, as bleeding after withdrawal indicates a responsive endometrium.
- The patient has regular, albeit reduced, menstrual cycles, making this test less relevant for her specific symptoms.
Postpartum hemorrhage protocols US Medical PG Question 10: Two days after vaginal delivery of a healthy newborn at term, a 32-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 2, is unable to breastfeed. Her labor was complicated by antepartum hemorrhage and she received two units of packed red blood cells. Her pulse is 99/min and blood pressure is 90/55 mm Hg. Further evaluation of this patient is most likely to show which of the following sets of serum findings?
$$$ ACTH %%% Aldosterone %%% Cortisol $$$
- A. ↑ ↓ ↓
- B. ↓ ↑ ↓
- C. ↑ normal ↑
- D. ↓ normal ↑
- E. ↓ normal ↓ (Correct Answer)
Postpartum hemorrhage protocols Explanation: ***↓ normal ↓***
- This scenario describes **Sheehan's syndrome**, caused by **postpartum pituitary necrosis** due to severe hemorrhage and hypotension during delivery.
- Decreased **ACTH** (adrenocorticotropic hormone) leads to secondary **adrenal insufficiency**, causing decreased **cortisol**. **Aldosterone** secretion, primarily regulated by the **renin-angiotensin system**, remains largely normal because only the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex, which produces aldosterone, is regulated directly by the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), whereas the pituitary regulates the zona fasciculata and zona reticularis.
*↑ ↓ ↓*
- This pattern (high ACTH, low aldosterone, low cortisol) suggests **primary adrenal insufficiency** (Addison's disease), where the adrenal glands themselves are failing, leading to a compensatory increase in ACTH. However, this patient's condition is due to pituitary damage.
- In primary adrenal insufficiency, both **cortisol** and **aldosterone** would be low, and **ACTH** would be elevated due to a lack of negative feedback.
*↓ ↑ ↓*
- This pattern (low ACTH, high aldosterone, low cortisol) is inconsistent with most common adrenal or pituitary pathologies. Low ACTH and low cortisol would suggest secondary adrenal insufficiency, but high aldosterone does not fit.
- **Hyperaldosteronism** with secondary adrenal insufficiency is rare and not indicated by the patient's presentation.
*↑ normal ↑*
- This pattern (high ACTH, normal aldosterone, high cortisol) suggests **Cushing's disease** (pituitary adenoma secreting ACTH), or an ectopic ACTH tumor, or a state of acute stress.
- The patient's **hypotension** and inability to breastfeed point away from Cushing's and towards hypopituitarism.
*↓ normal ↑*
- This pattern (low ACTH, normal aldosterone, high cortisol) could be seen in states of iatrogenic **exogenous corticosteroid use**, leading to suppressed ACTH and endogenous cortisol, or in an adrenal tumor producing cortisol independent of ACTH.
- This is inconsistent with the symptoms of postpartum hemorrhage and inability to lactate, which indicate a **deficit** rather than an excess of pituitary hormones.
More Postpartum hemorrhage protocols US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.