Uterotonics - The Tone Tighteners
-
First-Line: Oxytocin (Pitocin)
- Stimulates upper uterine segment to contract.
- Dose: 20-40 units in 1L crystalloid IV infusion.
-
Second-Line Agents:
- Methylergonovine (Methergine)
- Ergot alkaloid; causes generalized smooth muscle contraction.
- Dose: 0.2 mg IM.
- ⚠️ Contraindication: Hypertension, preeclampsia.
- Carboprost Tromethamine (Hemabate)
- Prostaglandin F2α analog.
- Dose: 0.25 mg IM.
- ⚠️ Contraindication: Asthma.
- Misoprostol (Cytotec)
- Prostaglandin E1 analog.
- Dose: 800-1000 mcg per rectum.
- Methylergonovine (Methergine)
-
Adjunct Therapy: Tranexamic Acid (TXA)
- Antifibrinolytic; prevents clot breakdown.
- Dose: 1 g IV, given within 3 hours of delivery.
⭐ Methylergonovine is contraindicated in patients with hypertension or preeclampsia due to its potent vasoconstrictive effects, which can precipitate a hypertensive crisis.
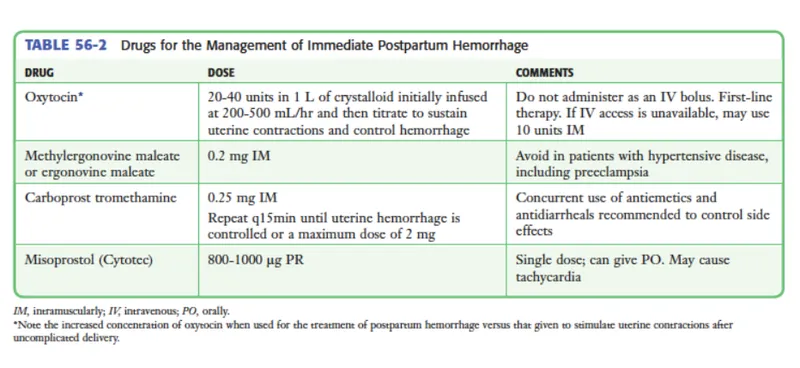
Adjunctive Meds - The Backup Brigade
- When oxytocin isn't enough, these second-line agents are crucial. Administer sequentially if bleeding persists.
| Medication | Class | Dose & Route | Key Contraindication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Methylergonovine | Ergot Alkaloid | 0.2 mg IM | Hypertension / Preeclampsia |
| Carboprost (Hemabate) | Prostaglandin F2α | 0.25 mg IM/Intramyometrial | Asthma ⚠️ |
| Misoprostol (Cytotec) | Prostaglandin E1 | 800-1000 mcg PR | - |
| Tranexamic Acid (TXA) | Antifibrinolytic | 1 g IV over 10 min | Hx of thromboembolic disease |
| %%{init: {'flowchart': {'htmlLabels': true}}}%% | |||
| flowchart TD |
A["🩺 Persistent Atony
• Uterine hemorrhage• Failure to contract"]
B["📋 Oxytocin Failed
• 1st line failed• Bleeding persists"]
C["💊 2nd Line Step
• Start uterotonics• Escalate therapy"]
D["💊 Specific Meds
• Methylergonovine• Carboprost dose"]
E["📋 Still Bleeding?
• Vital assessment• Ongoing PPH"]
F["💊 Add TXA
• Tranexamic acid• Antifibrinolytic"]
A --> B B --> C C --> D D --> E E -->|Yes| F
style A fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8 style B fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style C fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style D fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style E fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style F fill:#FDF4F3, stroke:#FCE6E4, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#B91C1C
> ⭐ **Exam Favorite:** Always check for a history of asthma before administering Carboprost (Hemabate). Prostaglandin F2α is a potent bronchoconstrictor and can trigger a severe asthma attack.
## Management Algorithm - PPH Playbook
* **Initial Steps:** Fundal massage, IV access, call for help.
* Administer Tranexamic Acid (TXA) **1g** IV within **3 hours** of birth.
```mermaid
%%{init: {'flowchart': {'htmlLabels': true}}}%%
flowchart TD
START["<b>⚠️ PPH Confirmed</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Maternal bleeding</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Postpartum hemorrhage</span>"]
OXY["<b>💊 1st Line: Oxytocin</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Uterotonic agent</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Promote contraction</span>"]
PERSIST{"<b>📋 Bleeding?</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Evaluate response</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Assess stability</span>"}
MONITOR["<b>👁️ Monitor</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Vital signs check</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Ongoing assess</span>"]
SECOND["<b>💊 2nd Line Drugs</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Uterotonic options</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Check CI's first</span>"]
METHYL["<b>💊 Methylergonovine</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• CI: Hypertension</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Ergot alkaloid</span>"]
CARBO["<b>💊 Carboprost</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• CI: Asthma</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Prostaglandin F2a</span>"]
MISO["<b>💊 Misoprostol</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• PGE1 analogue</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Rectal or subling</span>"]
START --> OXY
OXY --> PERSIST
PERSIST -->|No| MONITOR
PERSIST -->|Yes| SECOND
SECOND --> METHYL
SECOND --> CARBO
SECOND --> MISO
style START fill:#FDF4F3, stroke:#FCE6E4, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#B91C1C
style OXY fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534
style PERSIST fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E
style MONITOR fill:#EEFAFF, stroke:#DAF3FF, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#0369A1
style SECOND fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534
style METHYL fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534
style CARBO fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534
style MISO fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534
📌 Mnemonic (Uterotonics): Oh My Heavy Menses (Oxytocin, Methylergonovine, Hemabate, Misoprostol)
⭐ In cases of uterine atony, if oxytocin fails, the next step is typically a second-line uterotonic like methylergonovine or carboprost, keeping their contraindications (hypertension and asthma, respectively) in mind.
High‑Yield Points - ⚡ Biggest Takeaways
- Uterine atony is the #1 cause of PPH; always start with uterine massage and oxytocin.
- Refractory atony requires second-line agents like methylergonovine, carboprost, or misoprostol.
- Methylergonovine is contraindicated in hypertension and preeclampsia due to its vasoconstrictive effects.
- Carboprost tromethamine (a prostaglandin) is contraindicated in asthma due to the risk of bronchoconstriction.
- Tranexamic acid (TXA), an antifibrinolytic, is crucial if initial uterotonics fail to control the bleeding.

