Coagulation disorders in obstetrics US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Coagulation disorders in obstetrics. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Coagulation disorders in obstetrics US Medical PG Question 1: A 27-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 26 weeks' gestation comes to the emergency department because of vaginal bleeding and epistaxis for the past 2 days. She missed her last prenatal visit 2 weeks ago. Physical examination shows blood in the posterior pharynx and a uterus consistent in size with 23 weeks' gestation. Her hemoglobin concentration is 7.2 g/dL. Ultrasonography shows an intrauterine pregnancy with a small retroplacental hematoma and absent fetal cardiac activity. Further evaluation is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Decreased fibrinogen concentration (Correct Answer)
- B. Increased antithrombin concentration
- C. Increased factor V concentration
- D. Increased platelet count
- E. Decreased prothrombin time
Coagulation disorders in obstetrics Explanation: ***Decreased fibrinogen concentration***
- The patient's presentation with **vaginal bleeding**, **epistaxis**, a **small retroplacental hematoma**, and **absent fetal cardiac activity** strongly suggests **abruptio placentae** complicated by **disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)**.
- In DIC, widespread activation of the **coagulation cascade** leads to consumption of clotting factors, including **fibrinogen**, resulting in **decreased plasma levels**.
*Increased antithrombin concentration*
- **Antithrombin** is a natural anticoagulant that inhibits activated clotting factors; its concentration is typically **decreased** in DIC due to its consumption in an attempt to control widespread coagulation.
- An increase in antithrombin would generally **reduce** clot formation, which is contrary to the hypercoagulable state seen initially in DIC.
*Increased factor V concentration*
- **Factor V** is a procoagulant factor that is **consumed** during DIC, leading to **decreased** rather than increased concentrations.
- Increased factor V would promote clotting, which is overridden by the massive consumption of factors and platelets in DIC.
*Increased platelet count*
- **Platelets** are actively consumed in the widespread microthrombi formation characteristic of DIC, leading to **thrombocytopenia** (decreased platelet count), not an increase.
- An increased platelet count would be protective against bleeding, which is not the case here.
*Decreased prothrombin time*
- **Prothrombin time (PT)** measures the extrinsic and common coagulation pathways; in DIC, the consumption of coagulation factors, including **prothrombin**, leads to a **prolonged (increased)** PT, not a decreased one.
- A decreased PT would indicate a hypercoagulable state with enhanced clotting factor activity, which is eventually exhausted in DIC.
Coagulation disorders in obstetrics US Medical PG Question 2: A 28-year-old woman, gravida 1, para 0, at 32 weeks' gestation is evaluated for vaginal bleeding. Five days ago, she was admitted to the hospital and started on treatment for a deep vein thrombosis in the right leg. Her pulse is 125/min and blood pressure is 95/67 mm Hg. Physical examination shows large hematomas on the upper limbs and swelling in the right calf. There is a large amount of bright red blood in the vaginal vault. Laboratory studies show a hemoglobin of 8.9 mg/dL, platelet count of 185,000/mm3, and activated partial thromboplastin time of 160 seconds. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy to rapidly reverse this patient's coagulopathy?
- A. Vitamin K
- B. Prothrombin complex concentrate
- C. Fresh frozen plasma
- D. Protamine sulfate (Correct Answer)
- E. Alteplase
Coagulation disorders in obstetrics Explanation: ***Protamine sulfate***
- The patient's prolonged **aPTT (160 seconds)**, combined with recent treatment for DVT, strongly suggests **heparin overdose** or sensitivity.
- **Protamine sulfate** is the specific antidote for **heparin**, forming a stable salt that neutralizes its anticoagulant effect.
*Vitamin K*
- **Vitamin K** is the antidote for **warfarin** and helps in the synthesis of clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X.
- It would not reverse the effects of **heparin**, which works by activating antithrombin and inhibiting thrombin and factor Xa.
*Prothrombin complex concentrate*
- **PCC** contains factors II, VII, IX, and X and is used to rapidly reverse the effects of **warfarin** or in cases of severe bleeding due to factor deficiencies.
- While it could theoretically help with general coagulopathy, it is not the specific or most direct antagonist for **heparin**.
*Fresh frozen plasma*
- **FFP** contains all coagulation factors and is used for broad reversal of coagulopathy, especially in cases of **liver disease**, DIC, or multiple factor deficiencies.
- While it could provide factors, it would not directly antagonize the high levels of **heparin** that are likely causing the bleeding.
*Alteplase*
- **Alteplase** is a **thrombolytic agent** used to break down existing blood clots by converting plasminogen to plasmin.
- Administering alteplase would worsen the patient's severe bleeding and is contraindicated in this scenario.
Coagulation disorders in obstetrics US Medical PG Question 3: A 25-year-old pregnant woman at 28 weeks gestation presents with a headache. Her pregnancy has been managed by a nurse practitioner. Her temperature is 99.0°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 164/104 mmHg, pulse is 100/min, respirations are 22/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Physical exam is notable for a comfortable appearing woman with a gravid uterus. Laboratory tests are ordered as seen below.
Hemoglobin: 12 g/dL
Hematocrit: 36%
Leukocyte count: 6,700/mm^3 with normal differential
Platelet count: 100,500/mm^3
Serum:
Na+: 141 mEq/L
Cl-: 101 mEq/L
K+: 4.4 mEq/L
HCO3-: 25 mEq/L
BUN: 21 mg/dL
Glucose: 99 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1.0 mg/dL
AST: 32 U/L
ALT: 30 U/L
Urine:
Color: Amber
Protein: Positive
Blood: Negative
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. HELLP syndrome
- B. Acute fatty liver disease of pregnancy
- C. Preeclampsia
- D. Severe preeclampsia (Correct Answer)
- E. Eclampsia
Coagulation disorders in obstetrics Explanation: ***Severe preeclampsia***
- The patient exhibits **hypertension** (BP 164/104 mmHg), **proteinuria** (positive urine protein), and **thrombocytopenia** (platelet count 100,500/mm^3). The elevated BUN and creatinine also suggest **renal dysfunction**.
- The blood pressure reading 164/104 mmHg meets the criteria for **severe range blood pressure** (systolic ≥160 mmHg or diastolic ≥110 mmHg), classifying this as severe preeclampsia. Headaches are also a symptom of severe preeclampsia.
*HELLP syndrome*
- While **thrombocytopenia** is present, the **liver enzymes (AST/ALT)** are not elevated (AST 32 U/L, ALT 30 U/L), which would be a primary diagnostic criterion for HELLP (Hemolysis, Elevated Liver enzymes, Low Platelets).
- There is no evidence of **hemolysis**, such as elevated bilirubin or schistocytes on a peripheral smear, which is also required for HELLP diagnosis.
*Acute fatty liver disease of pregnancy*
- This condition presents with significantly elevated **liver enzymes**, **jaundice**, and often severe **hypoglycemia** and **coagulopathy**, none of which are evident in this patient's lab results.
- While it can cause elevated BUN and creatinine, it typically involves **more prominent liver dysfunction** than seen here.
*Preeclampsia*
- This patient meets the criteria for preeclampsia (hypertension and proteinuria), but her **blood pressure** (164/104 mmHg), **thrombocytopenia** (platelet count 100,500/mm^3), and elevated **creatinine** (1.0 mg/dL) all point to features that classify it as *severe* preeclampsia.
- Preeclampsia without severe features generally involves blood pressure values below 160/110 mmHg and no evidence of significant organ dysfunction or severe laboratory abnormalities.
*Eclampsia*
- Eclampsia is defined as the occurrence of new-onset **grand mal seizures** in a woman with preeclampsia.
- The patient presents with a **headache** but is described as "comfortable appearing" and there is no mention of seizures.
Coagulation disorders in obstetrics US Medical PG Question 4: A 27-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, at 41 weeks' gestation is admitted to the hospital in active labor. Her pregnancy has been uncomplicated. Both of her prior children were delivered by vaginal birth. She has a history of asthma. Current medications include iron and vitamin supplements. After a prolonged labor, she undergoes vaginal delivery. Shortly afterwards, she begins to have heavy vaginal bleeding with clots. Her temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F), pulse is 90/min, respirations are 17/min, and blood pressure is 130/72 mm Hg. Examination shows a soft, enlarged, and boggy uterus on palpation. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 10.8 g/dL
Hematocrit 32.3%
Leukocyte Count 9,000/mm3
Platelet Count 140,000/mm3
Prothrombin time 14 seconds
Partial thromboplastin time 38 seconds
Her bleeding continues despite bimanual uterine massage and administration of oxytocin. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Administer methylergonovine (Correct Answer)
- B. Transfuse blood
- C. Perform hysterectomy
- D. Administer carboprost tromethamine
- E. Perform curettage
Coagulation disorders in obstetrics Explanation: ***Administer methylergonovine***
- The patient is likely experiencing **postpartum hemorrhage (PPH)** due to **uterine atony**, characterized by a soft, enlarged, and boggy uterus after delivery, with continued bleeding despite initial measures (massage, oxytocin).
- Given her history of **asthma**, carboprost tromethamine (prostaglandin F2-alpha) is **contraindicated** due to its potential to cause severe bronchospasm, making methylergonovine (an ergot alkaloid) the appropriate next uterotonic agent.
*Transfuse blood*
- While blood transfusions may eventually be necessary if bleeding is severe and leads to significant hemodynamic instability or severe anemia, it is **not the immediate next step** in managing the underlying cause of the hemorrhage (uterine atony).
- **Uterotonic agents** should be tried first to contract the uterus and stop the bleeding, as indicated by the patient's current vital signs being relatively stable (pulse 90/min, BP 130/72 mm Hg).
*Perform hysterectomy*
- **Hysterectomy** is a drastic measure considered only after all less invasive medical and surgical interventions (e.g., uterotonic agents, uterine tamponade, suturing techniques) have failed to control severe PPH.
- It would be **premature** to proceed directly to hysterectomy without attempting additional medical management for uterine atony.
*Administer carboprost tromethamine*
- **Carboprost tromethamine** is a prostaglandin analog that is effective in treating uterine atony but is **contraindicated in patients with asthma** due to its known side effect of inducing bronchospasm.
- The patient's history of asthma makes this a **dangerous option**, and an alternative uterotonic like methylergonovine should be chosen.
*Perform curettage*
- **Curettage** (removing retained placental fragments) would be appropriate if the cause of PPH was **retained placental tissue**.
- However, the examination finding of a **soft, enlarged, and boggy uterus** is characteristic of uterine atony, not retained placenta, and the initial management of atony involves uterotonic agents.
Coagulation disorders in obstetrics US Medical PG Question 5: A 38-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 32 weeks' gestation comes to the physician because of a 1-day history of dyspnea and left-sided chest pain that is worse when she breathes deeply. One week ago, she returned from a trip to Chile, where she had a 3-day episode of flu-like symptoms that resolved without treatment. Pregnancy and delivery of her first child were uncomplicated. She has no history of serious illness. Her temperature is 37.2°C (99°F), pulse is 118/min, respirations are 28/min and slightly labored, and blood pressure is 110/76 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 91%. Examination shows jugular venous distention and bilateral pitting edema below the knees that is worse on the left-side. There is decreased breath sounds over the left lung base. The uterus is consistent in size with a 32-week gestation. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Further evaluation of this patient is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Protein dipstick test of 2+ on urinalysis
- B. Depression of the PR segment on electrocardiography
- C. Decreased fibrinogen levels on serum analysis
- D. Decreased myocardial perfusion on a cardiac PET scan
- E. Noncompressible femoral vein on ultrasonography (Correct Answer)
Coagulation disorders in obstetrics Explanation: **Noncompressible femoral vein on ultrasonography**
- The patient's symptoms (dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, tachypnea, tachycardia, hypoxemia, JVD, and unilateral leg edema) are highly suggestive of **pulmonary embolism (PE)**, especially given her recent travel and pregnancy. A noncompressible femoral vein on ultrasonography indicates a **deep vein thrombosis (DVT)**, which is the most common cause of PE.
- Pregnancy is a **hypercoagulable state**, increasing the risk of venous thromboembolism. The unilateral leg edema further supports the presence of a DVT.
*Protein dipstick test of 2+ on urinalysis*
- While preeclampsia can manifest with dyspnea due to pulmonary edema, her **blood pressure of 110/76 mm Hg is normal**, and she has no other signs of preeclampsia.
- **Proteinuria** would be a key finding in preeclampsia, but it is not directly linked to the acute pleuritic chest pain and hypoxemia seen here.
*Depression of the PR segment on electrocardiography*
- **PR segment depression** can be seen in **pericarditis**, which typically causes sharp, pleuritic chest pain that improves when leaning forward and is associated with a pericardial friction rub.
- The patient's presentation, particularly the unilateral leg edema and hypoxemia, is not typical for pericarditis.
*Decreased fibrinogen levels on serum analysis*
- **Decreased fibrinogen levels** are characteristic of **disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)**, which is a severe complication and would present with widespread bleeding or thrombotic events.
- While DIC can occur in pregnancy complications, it does not typically cause isolated acute PE symptoms and would not be the most likely initial finding in this scenario.
*Decreased myocardial perfusion on a cardiac PET scan*
- **Decreased myocardial perfusion** indicates **myocardial ischemia or infarction**, which usually presents with substernal chest pain, often radiating, and characteristic ECG changes.
- Although PE can cause right ventricular strain, the primary pathology is in the pulmonary vasculature, not directly in myocardial perfusion as the leading cause of her acute symptoms.
Coagulation disorders in obstetrics US Medical PG Question 6: A 32-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 38 weeks' gestation comes to the emergency department because of vaginal bleeding for the past hour. The patient reports that she felt contractions prior to the onset of the bleeding, but the contractions stopped after the bleeding started. She also has severe abdominal pain. Her first child was delivered by lower segment transverse cesarean section because of a nonreassuring fetal heart rate. Her pulse is 110/min, respirations are 17/min, and blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg. Examination shows diffuse abdominal tenderness with no rebound or guarding; no contractions are felt. The fetal heart rate shows recurrent variable decelerations. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Uterine inertia
- B. Amniotic fluid embolism
- C. Uterine rupture (Correct Answer)
- D. Vasa previa
- E. Abruptio placentae
Coagulation disorders in obstetrics Explanation: ***Uterine rupture***
- The patient's history of a prior **cesarean section**, sudden onset of **vaginal bleeding** and **severe abdominal pain**, resolution of contractions, and signs of **hypovolemic shock** (tachycardia, hypotension) coupled with fetal distress (variable decelerations) are highly indicative of uterine rupture.
- Diffuse abdominal tenderness without rebound or guarding, and no palpable contractions, are also consistent with rupture.
*Uterine inertia*
- This condition is characterized by **weak or uncoordinated uterine contractions** leading to prolonged labor, but it does not typically present with acute vaginal bleeding, sudden severe abdominal pain, or hypovolemic shock.
- Fetal distress in uterine inertia would more likely be due to prolonged labor rather than acute compromise following a sudden event.
*Amniotic fluid embolism*
- This is a rare, life-threatening obstetric emergency characterized by sudden **cardiovascular collapse, respiratory distress**, and **coagulopathy**, often occurring during labor or immediately postpartum.
- While it can cause fetal distress, vaginal bleeding and severe abdominal pain are not primary presenting symptoms.
*Vasa previa*
- Characterized by **painless vaginal bleeding** when fetal vessels within the membranes cross the internal cervical os, making them vulnerable to rupture during cervical dilation or amniotomy.
- The bleeding is typically fetal blood, and fetal distress occurs rapidly, but the mother would not experience severe abdominal pain or signs of hypovolemic shock unless the bleeding is substantial and prolonged.
*Abruptio placentae*
- This involves the **premature separation of the placenta**, causing painful vaginal bleeding, uterine tenderness, and frequent, strong contractions.
- While it can cause hypovolemic shock and fetal distress, the description of contractions stopping after bleeding started, along with a previous C-section scar, points more specifically to uterine rupture rather than an abruption.
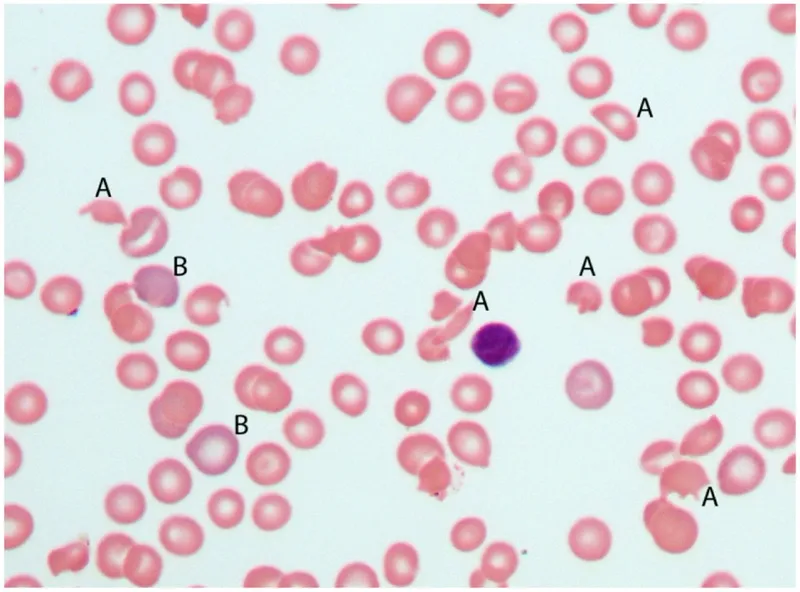
Coagulation disorders in obstetrics US Medical PG Question 7: A 33-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department after she was involved in a high-speed motor vehicle collision. She reports severe pelvic pain. Her pulse is 124/min and blood pressure is 80/56 mm Hg. Physical examination shows instability of the pelvic ring. As part of the initial emergency treatment, she receives packed red blood cell transfusions. Suddenly, the patient starts bleeding from peripheral venous catheter insertion sites. Laboratory studies show decreased platelets, prolonged prothrombin time and partial thromboplastin time, and elevated D-dimer. A peripheral blood smear of this patient is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Grouped erythrocytes with a stacked-coin appearance
- B. Erythrocytes with a bullseye appearance
- C. Crescent-shaped, fragmented erythrocytes (Correct Answer)
- D. Erythrocytes with cytoplasmic hemoglobin inclusions
- E. Erythrocytes with irregular, thorny projections
Coagulation disorders in obstetrics Explanation: ***Crescent-shaped, fragmented erythrocytes***
- The clinical picture of **hypotension**, **tachycardia**, **pelvic instability**, and widespread bleeding, along with laboratory findings of **decreased platelets**, **prolonged PT/PTT**, and **elevated D-dimer**, is highly suggestive of **Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)**.
- **Fragmented erythrocytes** (schistocytes) are a hallmark of **DIC** on peripheral blood smear, as red blood cells are mechanically sheared while passing through areas of microvascular thrombosis.
*Grouped erythrocytes with a stacked-coin appearance*
- This describes **rouleaux formation**, commonly seen in conditions with **elevated plasma proteins**, such as multiple myeloma or severe inflammation.
- While inflammation can be part of trauma, the specific constellation of lab findings points more strongly to DIC, where rouleaux is not a primary diagnostic feature.
*Erythrocytes with a bullseye appearance*
- This describes **target cells**, which are characteristic of **thalassemia**, **liver disease**, or **postsplenectomy states**.
- These conditions are not indicated by the patient's acute presentation or laboratory results.
*Erythrocytes with cytoplasmic hemoglobin inclusions*
- These are **Heinz bodies**, which are denatured hemoglobin precipitates seen in conditions like **G6PD deficiency** or **unstable hemoglobin variants**.
- This patient's symptoms are acute and related to trauma and hemorrhage, not a chronic hemolytic disorder.
*Erythrocytes with irregular, thorny projections*
- This describes **acanthocytes** (spur cells), typically associated with **severe liver disease** or **abetalipoproteinemia**.
- These findings are not consistent with an acute presentation of trauma-induced coagulopathy.
Coagulation disorders in obstetrics US Medical PG Question 8: A 34-year-old G3P2 is admitted to the hospital after being physically assaulted by her husband. She developed severe vaginal bleeding and abdominal pain. She is at 30 weeks gestation. Her previous pregnancies were uncomplicated, as has been the course of the current pregnancy. The vital signs are as follows: blood pressure, 80/50 mmHg; heart rate, 117/min and irregular; respiratory rate, 20/min; and temperature, 36.2℃ (97.1). The fetal heart rate is 103/min. On physical examination, the patient is pale and lethargic. Abdominal palpation reveals severe uterine tenderness and tetanic contractions. The perineum is grossly bloody. There are no vaginal or cervical lesions. There is active heavy bleeding with blood clots passing through the cervix. An ultrasound shows a retroplacental hematoma with a volume of approximately 400 ml.
Laboratory workup shows the following findings:
Red blood cells count: 3.0 millions/mL
Hb%: 7.2 g/dL
Platelet count: 61,000/mm3
Prothrombin time: 310 seconds (control 20 seconds)
Partial prothrombin time: 420 seconds
Serum fibrinogen: 16 mg/dL
Elevated levels of which of the following laboratory markers is characteristic for this patient’s complication?
- A. C-reactive protein
- B. D-dimer (Correct Answer)
- C. Creatinine
- D. Pro-brain natriuretic peptide
- E. Procalcitonin
Coagulation disorders in obstetrics Explanation: *** **D-dimer***
- This patient's presentation with **severe vaginal bleeding**, **abdominal pain**, **uterine tenderness**, **tetanic contractions**, and **fetal distress** following trauma, along with the ultrasound finding of a **retroplacental hematoma**, is highly suggestive of **abruptio placentae**.
- The abnormal coagulation panel (low platelets, prolonged PT/PTT, low fibrinogen) indicates **disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)**, a common complication of severe placental abruption due to extensive activation of the coagulation cascade and subsequent breakdown of clots. **D-dimer levels** are characteristically **elevated** in DIC as they are degradation products of **fibrin** from enhanced fibrinolysis.
*C-reactive protein*
- **C-reactive protein (CRP)** is an **acute-phase reactant** primarily elevated in response to **inflammation** or **infection**.
- While trauma could induce some inflammation, very high CRP levels are not specific for **DIC** or the direct complications of **placental abruption** described.
*Creatinine*
- **Creatinine** is a marker of **renal function**. While severe shock and hypoperfusion from significant bleeding could lead to **acute kidney injury** and elevated creatinine, it is not a direct or characteristic marker of the **coagulopathy** or **DIC** seen in this patient.
- The primary issue presented is one of **bleeding and coagulation abnormalities**, not primarily renal dysfunction.
*Pro-brain natriuretic peptide*
- **Pro-brain natriuretic peptide (pro-BNP)** is a biomarker primarily used to assess **cardiac stretch** and **heart failure**.
- There are no clinical signs or symptoms presented that suggest **cardiac dysfunction** as the primary or most characteristic complication in this setting.
*Procalcitonin*
- **Procalcitonin** is a biomarker that is significantly elevated in **bacterial infections** and **sepsis**.
- Although the patient's condition is critical, the clinical picture strongly points towards **hemorrhage** and **DIC** due to **placental abruption** rather than a primary **bacterial infection**.
Coagulation disorders in obstetrics US Medical PG Question 9: The patient declines the use of oxytocin or any other further testing and decides to await a spontaneous delivery. Five weeks later, she comes to the emergency department complaining of vaginal bleeding for 1 hour. Her pulse is 110/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 112/76 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 97%. Pelvic examination shows active vaginal bleeding. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 12.8 g/dL
Leukocyte count 10,300/mm3
Platelet count 105,000/mm3
Prothrombin time 26 seconds (INR=1.8)
Serum
Na+ 139 mEq/L
K+ 4.1 mEq/L
Cl- 101 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen 42 mg/dL
Creatinine 2.8 mg/dL
Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Infection with gram-negative bacteria
- B. Thromboplastin in maternal circulation (Correct Answer)
- C. Amniotic fluid in maternal circulation
- D. Separation of the placenta from the uterus
- E. Decreased synthesis of coagulation factors
Coagulation disorders in obstetrics Explanation: ***Thromboplastin in maternal circulation***
* This patient's presentation with **vaginal bleeding**, **elevated PT/INR**, and **thrombocytopenia** is highly suggestive of **disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)**, which can be triggered by placental abruption or retained products of conception releasing tissue thromboplastin.
* The prior history of a prolonged gestation and refusal of intervention suggests potential for **placental insufficiency** or **intrauterine fetal demise**, both of which can lead to release of **thromboplastin** into the maternal circulation, activating the coagulation cascade and consuming clotting factors and platelets.
* *Infection with gram-negative bacteria*
* While **sepsis** from gram-negative bacteria can cause DIC, there are no overt signs of infection like fever, chills, or a significant rise in leukocyte count disproportionate to bleeding stress.
* The primary presentation is bleeding and coagulopathy, not systemic signs of infection.
* *Amniotic fluid in maternal circulation*
* **Amniotic fluid embolism** is a rare and catastrophic event, typically presenting with sudden **cardiovascular collapse**, **respiratory distress**, and **DIC**.
* This patient's vital signs and oxygen saturation are relatively stable, and she lacks the acute cardiorespiratory symptoms characteristic of amniotic fluid embolism.
* *Separation of the placenta from the uterus*
* **Placental abruption** (separation of the placenta) can cause vaginal bleeding and may
cause DIC by releasing tissue factor from the decidua into the maternal circulation.
* However, DIC itself is the mechanism of the coagulopathy, and the release of thromboplastin from the abrupted tissue is the more direct underlying cause of the coagulation cascade activation.
* *Decreased synthesis of coagulation factors*
* Conditions causing **decreased synthesis of coagulation factors** (e.g., severe **liver disease** or severe **vitamin K deficiency**) typically lead to coagulopathy over time.
* This patient's acute presentation with evidence of platelet consumption (thrombocytopenia) points towards a consumptive coagulopathy like DIC rather than impaired production.
Coagulation disorders in obstetrics US Medical PG Question 10: A 9-year-old girl is admitted to the hospital with a one-day history of acute abdominal pain and vomiting. She also has a two-day history of fever, headache, and neck pain. Her immunizations are up-to-date. She is confused and oriented only to place and person. Her temperature is 39.7°C (103.5°F), pulse is 148/min, blood pressure is 90/50 mm Hg, and respiratory rate is 28/min. Cervical range of motion is limited by pain. The remainder of the neurologic examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 10.9 g/dL
Leukocyte count 44,000/mm3
Serum
pH 7.33
Na+ 130 mEq/L
Cl- 108 mEq/L
K+ 6.1 mEq/L
HCO3- 20 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen 34 mg/dL
Glucose 180 mg/dL
Creatinine 2.4 mg/dL
Urine ketones negative
A CT scan of the head shows enhancement of the arachnoid and pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis shows a leukocyte count of 3,400/μL (90% neutrophils), a glucose concentration of 50 mg/dL, protein concentration of 81 mg/dL, and no erythrocytes. Gram stain of the CSF shows gram-negative diplococci. This patient is at increased risk for which of the following complications?
- A. Vesicular skin eruptions
- B. Adrenal hemorrhage (Correct Answer)
- C. Pancreatitis
- D. Temporal lobe inflammation
- E. Deep neck abscess
Coagulation disorders in obstetrics Explanation: **Adrenal hemorrhage**
- The clinical picture of **fever, acute abdominal pain, confusion, hypotension, and a high WBC count (44,000/mm³)**, along with **Gram-negative diplococci in CSF**, indicates **meningococcal meningitis with sepsis**. This rapidly progressive infection by *Neisseria meningitidis* can lead to **Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome**, characterized by **adrenal hemorrhage** and profound shock.
- The **elevated potassium (6.1 mEq/L)** and **hyponatremia (130 mEq/L)** are consistent with **adrenal insufficiency** resulting from adrenal hemorrhage.
*Vesicular skin eruptions*
- **Vesicular skin eruptions** are characteristic of viral infections such as **herpes simplex virus (HSV)** or **varicella-zoster virus**, which would present differently (e.g., HSV encephalitis often causes temporal lobe involvement).
- While various infections can cause skin rashes, this specific presentation with extensive meningeal inflammation and septic shock points away from typical vesicular eruptions.
*Pancreatitis*
- **Pancreatitis** is characterized by severe epigastric pain radiating to the back, often with nausea and vomiting, and elevated lipase/amylase. While **abdominal pain** is present, other symptoms like **neck stiffness, confusion, and CSF findings of bacterial meningitis** are not typical for pancreatitis.
- There is no specific evidence, such as imaging findings or elevated pancreatic enzymes, to suggest pancreatitis in this case.
*Temporal lobe inflammation*
- **Temporal lobe inflammation** is a hallmark of **HSV encephalitis**, which often presents with seizures, bizarre behavior, and specific MRI findings in the temporal lobes. While a CT scan showed arachnoid and pia mater enhancement, this indicates **meningeal inflammation**, not specifically temporal lobe parenchymal inflammation (encephalitis).
- The presence of **Gram-negative diplococci in the CSF** strongly indicates bacterial meningitis, not viral encephalitis, making temporal lobe inflammation less likely.
*Deep neck abscess*
- A **deep neck abscess** would typically cause localized neck pain, swelling, dysphagia, and stridor, potentially with fever, but would not explain the widespread CNS symptoms (confusion, meningeal signs, CSF findings) or systemic signs of shock and coagulopathy seen here.
- While the patient has neck pain, it is due to **meningismus**, not a localized abscess, and there is no mention of local swelling or airway compromise.
More Coagulation disorders in obstetrics US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.