Postpartum hemorrhage

On this page
🩸 The Obstetric Emergency: When Birth Becomes a Battle
Postpartum hemorrhage transforms a moment of joy into a life-threatening emergency within minutes, demanding split-second recognition and coordinated action. You'll master the physiologic cascade that leads to uncontrolled bleeding, build a systematic approach to rapid diagnosis, and execute evidence-based interventions that save lives. This lesson equips you with the clinical detective skills to identify subtle warning signs, the treatment algorithms to guide your team through crisis, and the multidisciplinary coordination framework that turns chaos into controlled response when every second counts.
📌 Remember: PPH = 4 T's - Tone (uterine atony 70%), Tissue (retained placenta 10%), Trauma (lacerations 15%), Thrombin (coagulopathy 5%)
The clinical definition centers on quantitative blood loss thresholds: ≥500mL after vaginal delivery or ≥1000mL after cesarean section. However, modern practice emphasizes cumulative blood loss ≥1000mL or bleeding with hemodynamic instability regardless of delivery mode.
-
Primary PPH (within 24 hours)
- Accounts for 85% of all PPH cases
- Peak incidence: first 4 hours postpartum
- Associated with 4 T's pathophysiology
- Uterine atony: inadequate myometrial contraction
- Retained tissue: incomplete placental separation
- Genital trauma: cervical/vaginal lacerations
- Coagulopathy: inherited or acquired bleeding disorders
-
Secondary PPH (24 hours to 12 weeks)
- Incidence: 0.5-2% of deliveries
- Common causes: retained products (60%), endometritis (30%)
- Peak timing: 7-14 days postpartum
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Blood loss estimation is notoriously inaccurate - visual estimates underestimate actual loss by 30-50%. Use quantitative measurement with calibrated drapes and weighing techniques.
| Risk Factor Category | Specific Factors | Relative Risk | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uterine Overdistension | Multiple gestation, Polyhydramnios, Macrosomia >4000g | 3.2-4.5x | Myometrial fiber overstretching |
| Previous PPH | Prior hemorrhage history | 2.3x | Highest single predictor |
| Prolonged Labor | Active phase >12h, 3rd stage >30min | 1.8-2.1x | Uterine exhaustion pattern |
| Placental Abnormalities | Previa, Accreta spectrum, Abruption | 5.2-15x | Surgical intervention required |
| Coagulopathy | Thrombocytopenia <100k, Factor deficiency | 4.1-8.3x | Medical management priority |
The hemodynamic response follows predictable patterns based on percentage blood volume lost:
- 15% loss (750mL): Minimal symptoms, compensated shock
- 15-30% loss (750-1500mL): Tachycardia >100, mild hypotension
- 30-40% loss (1500-2000mL): Severe tachycardia >120, hypotension <90 systolic
- >40% loss (>2000mL): Decompensated shock, altered mental status
⚠️ Warning: Pregnancy physiology masks early shock signs - 50% blood volume increase during pregnancy means 1500mL loss may present with minimal symptoms initially.
Understanding PPH pathophysiology through the 4 T's framework provides systematic approach to rapid diagnosis and targeted intervention, forming the foundation for all subsequent management decisions.
🩸 The Obstetric Emergency: When Birth Becomes a Battle
⚡ The Hemorrhage Cascade: When Hemostasis Fails
📌 Remember: HEMOSTASIS = 3 C's - Contraction (myometrial), Clots (platelet), Coagulation (fibrin cascade)
Uterine Atony Pathophysiology represents 70% of PPH cases through myometrial dysfunction:
-
Calcium Depletion Mechanism
- Prolonged labor depletes intracellular calcium stores
- Magnesium sulfate administration blocks calcium channels
- Results in inadequate actin-myosin interaction
- Spiral arteries remain uncompressed at 15-20mmHg instead of normal >80mmHg
-
Receptor Desensitization Pattern
- Oxytocin receptors downregulate after prolonged exposure
- Prostaglandin receptors become refractory with chorioamnionitis
- Beta-agonist tocolytics cause persistent uterine relaxation
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Uterine massage increases intrauterine pressure to 60-80mmHg, temporarily compressing spiral arteries while uterotonics take effect (2-5 minutes for IV oxytocin, 15-20 minutes for IM methylergonovine).
Coagulopathy Mechanisms affect 5-10% of PPH cases but carry highest mortality risk:
| Coagulopathy Type | Mechanism | Laboratory Pattern | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| DIC | Tissue factor release, consumption | ↓Platelets, ↓Fibrinogen, ↑D-dimer | Minutes to hours |
| Dilutional | Massive transfusion, crystalloids | ↓All factors proportionally | Hours |
| Hypofibrinogenemia | Consumption, abruption | Fibrinogen <200mg/dL | 30-60 minutes |
| Thrombocytopenia | HELLP, ITP, dilution | Platelets <100,000 | Variable |
| Factor Deficiency | Inherited, acquired | ↑PT/PTT, specific factor low | Pre-existing |
Retained Tissue Pathophysiology prevents effective uterine contraction through mechanical interference:
- Retained placental fragments occupy >10% of uterine cavity
- Adherent membranes create irregular contraction patterns
- Placenta accreta spectrum involves myometrial invasion requiring surgical management
Trauma-Related Bleeding follows different hemodynamic patterns:
- Arterial lacerations: pulsatile bleeding, rapid volume loss
- Venous tears: steady bleeding, slower decompensation
- Cervical injuries: bright red bleeding despite firm uterus
⚠️ Warning: Concealed bleeding into broad ligament hematomas can accumulate >1000mL without external signs. Monitor for flank pain, unilateral leg numbness, and unexplained hemodynamic instability.
The hemorrhage cascade accelerates through positive feedback loops: hypotension reduces uterine perfusion, acidosis impairs coagulation, hypothermia decreases platelet function, creating the lethal triad of coagulopathy, acidosis, and hypothermia.
Understanding these failure mechanisms enables targeted interventions that interrupt the cascade before irreversible shock develops, transforming PPH management from reactive to predictive clinical practice.
⚡ The Hemorrhage Cascade: When Hemostasis Fails
🎯 Recognition Mastery: The Clinical Detective Framework
📌 Remember: RECOGNIZE = 4 H's - Hemodynamics (vital signs), Hematocrit (trending), Hard uterus (tone), Hemorrhage (visual/quantitative)
Early Warning Pattern Recognition:
-
Hemodynamic Instability Patterns
- Pulse pressure narrowing <25mmHg (earliest sign)
- Heart rate increase >15 bpm from baseline
- Orthostatic changes: HR ↑20 or SBP ↓20 when sitting
- Delayed capillary refill >3 seconds
- Urine output <30mL/hour or 0.5mL/kg/hour
-
"Soft Signs" Recognition Framework
- Patient anxiety or sense of doom (sympathetic activation)
- Thirst and nausea (early hypovolemia)
- Skin pallor and cool extremities (peripheral vasoconstriction)
- Restlessness or altered mental status (cerebral hypoperfusion)
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Shock index (HR/SBP) >0.9 predicts severe PPH with 75% sensitivity. Values >1.1 indicate massive transfusion requirement with 85% specificity.
Systematic "See This, Think That" Correlations:
| Clinical Finding | Think This | Next Action | Time Frame |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boggy uterus + bleeding | Uterine atony | Massage + oxytocin | <2 minutes |
| Firm uterus + bright bleeding | Genital trauma | Immediate inspection | <5 minutes |
| Bleeding + shock + firm uterus | Concealed hemorrhage | Broad ligament hematoma | <10 minutes |
| Oozing + no clots | Coagulopathy | Labs + blood bank | <15 minutes |
| Incomplete placenta | Retained tissue | Manual exploration | <20 minutes |
- Visual estimation: Consistently underestimates by 30-50%
- Calibrated drapes: Accuracy within 15% for volumes >500mL
- Weighing method: 1g = 1mL blood (subtract dry weight)
- Hemoglobin trending: 1g/dL drop = approximately 500mL blood loss
💡 Master This: Blood on floor represents visible loss only. Hidden bleeding into broad ligaments, retroperitoneum, or uterine cavity can exceed 1500mL without external signs. Always correlate clinical findings with hemodynamic status.
Risk Stratification Integration:
-
High-Risk Profile (requires continuous monitoring)
- Previous PPH + current risk factors
- Placenta previa or accreta spectrum
- Multiple gestation + prolonged labor
- Coagulopathy + operative delivery
-
Moderate-Risk Profile (requires enhanced vigilance)
- Single major risk factor (macrosomia, polyhydramnios)
- Prolonged labor without other complications
- Previous cesarean with current vaginal delivery
-
Low-Risk Profile (requires standard monitoring)
- Uncomplicated pregnancy and delivery
- No significant risk factors
- Normal coagulation studies
Differential Recognition Patterns:
-
Uterine Atony Recognition
- Boggy, soft uterus on palpation
- Fundal height above umbilicus
- Continuous bleeding without clot formation
- Responds to massage and uterotonics
-
Genital Trauma Recognition
- Firm, well-contracted uterus
- Bright red, arterial bleeding
- Continuous bleeding despite uterine contraction
- Visible lacerations on inspection
-
Retained Tissue Recognition
- Incomplete placenta on inspection
- Irregular uterine contraction pattern
- Intermittent bleeding with clots
- Fundal height remains elevated
-
Coagulopathy Recognition
- Oozing from multiple sites (IV sites, episiotomy)
- Absence of clot formation
- Petechiae or ecchymoses
- Family history of bleeding disorders
⚠️ Warning: Normal vital signs do not exclude significant blood loss in young, healthy women. Pregnancy physiology maintains blood pressure until >30% blood volume is lost through increased cardiac output and peripheral vasoconstriction.
Technology-Enhanced Recognition:
- Continuous pulse oximetry: Pleth variability index >13% suggests hypovolemia
- Non-invasive hemoglobin monitoring: Real-time trending without blood draws
- Shock index monitoring: Automated calculation and trending
The clinical detective framework transforms subjective assessment into objective pattern recognition, enabling early intervention that prevents progression from manageable bleeding to life-threatening hemorrhage.
🎯 Recognition Mastery: The Clinical Detective Framework
🔬 Diagnostic Precision: Laboratory and Clinical Correlation
📌 Remember: LABS = 4 C's - CBC (hemoglobin trending), Coags (PT/PTT/INR), Chemistry (lactate/creatinine), Cross-match (blood bank)
Essential Laboratory Panel Timing and Interpretation:
| Test Category | Specific Tests | Normal Values | Critical Values | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hematologic | Hemoglobin, Hematocrit | Hgb 11-13 g/dL | Hgb <7 g/dL | Transfusion threshold |
| Coagulation | PT/PTT/INR, Fibrinogen | PT 11-13 sec, Fibrinogen 200-400 | PT >18 sec, Fib <150 | Coagulopathy diagnosis |
| Platelet Function | Platelet count, TEG/ROTEM | Platelets 150-400k | Platelets <50k | Bleeding risk assessment |
| Metabolic | Lactate, Base deficit | Lactate <2 mmol/L | Lactate >4 mmol/L | Tissue hypoperfusion |
| Renal Function | Creatinine, BUN | Creatinine 0.6-1.0 | Creatinine >1.5 | End-organ damage |
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Fibrinogen is the most sensitive early marker of consumptive coagulopathy. Values <200mg/dL predict massive transfusion requirement with 85% sensitivity, while <150mg/dL indicates immediate cryoprecipitate need.
Point-of-Care Testing Integration:
-
Thromboelastography (TEG) Interpretation
- R-time (reaction time): >8 minutes suggests factor deficiency
- K-time (kinetics): >3 minutes indicates fibrinogen dysfunction
- Alpha angle: <55 degrees shows impaired fibrin formation
- MA (maximum amplitude): <55mm suggests platelet dysfunction
- LY30 (lysis at 30 min): >8% indicates hyperfibrinolysis
-
Rotational Thromboelastometry (ROTEM) Patterns
- EXTEM CT >80 seconds: Factor VII deficiency or warfarin effect
- INTEM CT >240 seconds: Intrinsic pathway or heparin effect
- FIBTEM A10 <8mm: Fibrinogen deficiency requiring cryoprecipitate
- APTEM improvement: Hyperfibrinolysis requiring tranexamic acid
💡 Master This: Serial hemoglobin measurements every 30-60 minutes provide trending data more valuable than single values. A 2g/dL drop in 2 hours suggests ongoing bleeding requiring immediate intervention, regardless of absolute values.
Coagulopathy Classification and Management:
-
Consumptive Coagulopathy (DIC)
- Laboratory pattern: ↓Platelets, ↓Fibrinogen, ↑D-dimer, ↑PT/PTT
- Clinical triggers: Abruption, amniotic fluid embolism, sepsis
- Management priority: Treat underlying cause + component therapy
-
Dilutional Coagulopathy
- Laboratory pattern: Proportional decrease in all factors
- Clinical trigger: Massive crystalloid or colloid resuscitation
- Management priority: Balanced transfusion with plasma and platelets
-
Hyperfibrinolysis
- Laboratory pattern: ↑D-dimer, ↓Fibrinogen, TEG LY30 >8%
- Clinical triggers: Trauma, liver disease, certain medications
- Management priority: Tranexamic acid 1g IV immediately
Blood Bank Communication Protocol:
-
Type and Screen vs Type and Crossmatch
- Type and screen: Adequate for anticipated transfusion <4 units
- Type and crossmatch: Required for immediate transfusion or >4 units
- Emergency release: O-negative available in <10 minutes
-
Massive Transfusion Protocol (MTP) Activation
- Clinical triggers: >4 units in 1 hour or >10 units in 24 hours
- Laboratory triggers: Shock index >1.1 + ongoing bleeding
- Ratio strategy: 1:1:1 (RBC:FFP:Platelets) or 1:1:2
Advanced Diagnostic Considerations:
-
Factor-Specific Assays
- Factor XIII deficiency: Normal PT/PTT but poor clot stability
- von Willebrand studies: Bleeding time, ristocetin cofactor
- Antithrombin III: Heparin resistance pattern
-
Genetic Testing Indications
- Family history of bleeding disorders
- Unexplained coagulopathy with normal standard tests
- Recurrent PPH without obvious cause
⚠️ Warning: Normal coagulation studies do not exclude platelet dysfunction or factor XIII deficiency. Consider platelet aggregometry or TEG/ROTEM for unexplained bleeding with normal PT/PTT.
Monitoring Parameters During Treatment:
- Hemoglobin: Every 30-60 minutes during active bleeding
- Coagulation studies: Every 2-4 hours or after 4 units transfusion
- Platelet count: Before and after platelet transfusion
- Fibrinogen: Before and after cryoprecipitate administration
The diagnostic precision framework enables rapid identification of specific coagulopathy patterns, guiding targeted therapy that corrects underlying defects rather than empirical transfusion, optimizing patient outcomes while minimizing complications.
🔬 Diagnostic Precision: Laboratory and Clinical Correlation
⚕️ Treatment Algorithms: Evidence-Based Intervention Strategies
📌 Remember: TREAT = 4 S's - Stop bleeding (uterotonics), Support circulation (fluids/blood), Surgical options (if refractory), Systemic support (ICU care)
First-Line Medical Management Protocol:
| Intervention | Dosage | Onset Time | Duration | Contraindications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxytocin | 10-40 units IV or 10 units IM | 2-3 minutes IV | 30-60 minutes | None absolute |
| Methylergonovine | 0.2mg IM (avoid IV) | 5-10 minutes | 2-4 hours | Hypertension >140/90 |
| Misoprostol | 800-1000mcg sublingual/rectal | 15-30 minutes | 4-6 hours | Severe asthma |
| Tranexamic Acid | 1g IV over 10 minutes | 15-30 minutes | 6-8 hours | Thrombotic disease |
Advanced Medical Interventions:
-
Carboprost (Hemabate) Protocol
- Dosage: 250mcg IM every 15-90 minutes (maximum 8 doses)
- Mechanism: Prostaglandin F2α analog causing sustained uterine contraction
- Contraindications: Asthma, cardiac disease, hepatic/renal dysfunction
- Side effects: Bronchospasm, hypertension, hyperthermia
-
Recombinant Factor VIIa (rFVIIa)
- Dosage: 90mcg/kg IV (may repeat in 2-3 hours)
- Indications: Refractory bleeding with coagulopathy
- Prerequisites: Fibrinogen >150mg/dL, platelets >50,000
- Thrombotic risk: 2-5% incidence of arterial thrombosis
💡 Master This: Tranexamic acid reduces PPH mortality by 19% when given within 3 hours of delivery. Earlier administration (<1 hour) shows 31% mortality reduction. The WOMAN trial established this as standard care.
Surgical Intervention Hierarchy:
-
Balloon Tamponade (Second-line intervention)
- Success rate: 85-95% for uterine atony
- Balloon types: Bakri, BT-Cath, Foley catheter
- Inflation volume: 150-500mL saline (until bleeding stops)
- Duration: 12-24 hours maximum
- Complications: Uterine rupture (<1%), infection (5-10%)
-
Uterine Compression Sutures
- B-Lynch suture: Vertical compression technique
- Cho suture: Multiple square sutures for focal bleeding
- Hayman suture: Anterior-posterior compression without cavity entry
- Success rate: 75-85% for atony, lower for other causes
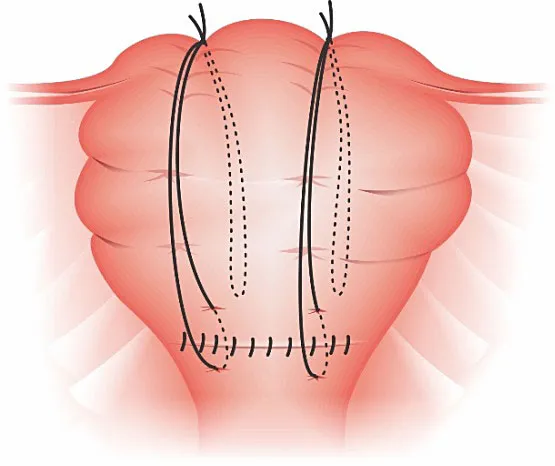
Vascular Intervention Options:
-
Uterine Artery Ligation
- Technique: Bilateral ligation at uterine artery origin
- Success rate: 80-85% when properly performed
- Preservation: Ovarian function maintained via collateral circulation
- Complications: Ureteral injury (<2%), bladder injury (<1%)
-
Internal Iliac Artery Ligation
- Indications: Failed uterine artery ligation or broad ligament hematoma
- Technique: Anterior division ligation 2cm distal to bifurcation
- Success rate: 70-80% for PPH control
- Complications: Buttock claudication (rare), nerve injury
-
Interventional Radiology
- Uterine artery embolization: 95% success rate in stable patients
- Balloon occlusion: Prophylactic in high-risk cases (accreta)
- Time requirement: 30-90 minutes for procedure completion
- Limitations: Requires stable patient and available expertise
Massive Transfusion Protocol Integration:
-
Activation Criteria
- Clinical: >4 units in 1 hour or anticipated >10 units
- Laboratory: Shock index >1.1 + ongoing bleeding
- Hemodynamic: SBP <90 despite 2L crystalloid
-
Transfusion Ratios
- 1:1:1 ratio: RBC:FFP:Platelets for massive bleeding
- 1:1:2 ratio: Alternative with higher platelet emphasis
- Cryoprecipitate: 1 unit per 10kg when fibrinogen <150mg/dL
⚠️ Warning: Hysterectomy should be considered early in refractory cases rather than last resort. Delayed decision-making increases morbidity and mortality due to prolonged shock and coagulopathy.
Quality Metrics and Outcomes:
- Time to intervention: <15 minutes for first-line therapy
- Blood loss reduction: >50% within 30 minutes of appropriate intervention
- Transfusion requirements: <4 units RBC in 85% of cases with early intervention
- ICU admission rate: <10% with protocol adherence
The evidence-based algorithm approach transforms chaotic emergency response into systematic intervention, ensuring optimal outcomes through standardized care that adapts to individual patient needs while maintaining therapeutic momentum.
⚕️ Treatment Algorithms: Evidence-Based Intervention Strategies
🔄 Systems Integration: Multidisciplinary Coordination Excellence
📌 Remember: TEAM = 4 R's - Roles (defined responsibilities), Resources (blood bank/OR), Recognition (early warning), Review (quality improvement)
Multidisciplinary Team Structure and Roles:
-
Primary Response Team (Immediate availability)
- Obstetrician: Clinical leadership, medical management, surgical decisions
- Anesthesiologist: Hemodynamic support, airway management, pain control
- Nursing: Medication administration, monitoring, family communication
- Blood bank technician: Product preparation, compatibility testing, inventory management
-
Secondary Response Team (15-30 minute activation)
- Maternal-fetal medicine: Complex case consultation, advanced procedures
- Interventional radiology: Embolization procedures, balloon occlusion
- Hematology: Coagulopathy management, factor replacement
- Critical care: ICU management, organ support, family counseling
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Closed-loop communication reduces medical errors by 75% during emergency situations. Use SBAR format (Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation) for all critical communications.
Communication Protocol Framework:
| Communication Type | Format | Timing | Recipients |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Alert | "PPH Alert - Room X" | <2 minutes | All team members |
| Status Updates | SBAR format | Every 15 minutes | Team leader + consultants |
| Blood Product Requests | Specific units + urgency | As needed | Blood bank + anesthesia |
| Surgical Consultation | Clinical summary + request | <10 minutes | Surgical team |
| Family Updates | Honest + supportive | Every 30 minutes | Designated family member |
-
Blood Bank Coordination
- Emergency release: O-negative RBC available <10 minutes
- Type-specific: ABO-compatible available <20 minutes
- Crossmatched: Full compatibility available <45 minutes
- MTP activation: 6-unit packs delivered every 30 minutes
-
Operating Room Readiness
- Emergency OR: Available <30 minutes for urgent cases
- Equipment check: Suction, electrocautery, compression devices
- Surgical instruments: Hysterectomy set, vascular clamps, balloon catheters
- Anesthesia preparation: Large-bore IV access, arterial line, blood warmer
💡 Master This: Simulation-based training improves team performance by 45% and reduces response times by 30%. Monthly drills maintain skill proficiency and identify system weaknesses before real emergencies.
Quality Improvement Integration:
-
Real-Time Monitoring
- Time metrics: Recognition to intervention intervals
- Resource utilization: Blood product usage patterns
- Communication effectiveness: Information transfer accuracy
- Patient outcomes: Morbidity and mortality tracking
-
Post-Event Analysis
- Hot wash: Immediate debrief within 24 hours
- Root cause analysis: System factors contributing to delays or complications
- Action items: Specific improvements with assigned responsibility
- Follow-up: Implementation tracking and effectiveness measurement
Technology Integration:
-
Electronic Health Records
- Real-time documentation: Vital signs, interventions, blood products
- Decision support: Automated alerts for critical values
- Communication tools: Secure messaging between team members
- Quality metrics: Automated data collection for performance analysis
-
Mobile Communication Systems
- Secure messaging: HIPAA-compliant team communication
- Alert systems: Push notifications for critical events
- Resource tracking: Real-time blood bank inventory
- Consultation platforms: Telemedicine for remote expertise
Risk Mitigation Strategies:
-
Anticipatory Planning
- High-risk identification: Prenatal and intrapartum screening
- Resource pre-positioning: Blood products and equipment preparation
- Team pre-briefing: Role clarification and contingency planning
- Family preparation: Informed consent for potential interventions
-
Failure Mode Analysis
- Communication breakdowns: Backup systems and redundant pathways
- Resource shortages: Alternative suppliers and emergency protocols
- Skill gaps: Competency assessment and continuing education
- Equipment failures: Maintenance schedules and backup devices
Performance Metrics and Benchmarking:
- Response time: <15 minutes from recognition to first intervention
- Team activation: <5 minutes for complete team assembly
- Blood availability: <20 minutes for type-specific products
- Surgical readiness: <30 minutes for emergency procedures
- Communication accuracy: >95% for critical information transfer
⚠️ Warning: System failures during PPH emergencies often result from communication breakdowns rather than clinical knowledge deficits. Regular team training and clear protocols prevent coordination failures that compromise patient safety.
Continuous Improvement Framework:
- Monthly case reviews: All PPH cases with >1000mL blood loss
- Quarterly metrics analysis: Trending of performance indicators
- Annual system assessment: Comprehensive evaluation of protocols and outcomes
- Best practice sharing: Inter-institutional collaboration and knowledge transfer
The systems integration approach transforms individual expertise into collective excellence, ensuring that every PPH case receives optimal care through coordinated team effort and systematic quality improvement.
🔄 Systems Integration: Multidisciplinary Coordination Excellence
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Rapid Reference and Decision Tools
📌 Remember: MASTER = 4 A's - Algorithms (decision trees), Arsenal (critical numbers), Assessment (rapid evaluation), Action (immediate intervention)
Essential Clinical Thresholds - The Critical Numbers:
| Parameter | Normal Range | Action Threshold | Critical Value | Immediate Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood Loss | <500mL vaginal | >500mL | >1000mL | MTP consideration |
| Hemoglobin | 11-13 g/dL | <9 g/dL | <7 g/dL | Transfusion required |
| Shock Index | <0.7 | >0.9 | >1.1 | Massive transfusion |
| Fibrinogen | 200-400 mg/dL | <200 mg/dL | <150 mg/dL | Cryoprecipitate now |
| Platelets | 150-400k | <100k | <50k | Platelet transfusion |
| Systolic BP | 110-140 mmHg | <100 mmHg | <90 mmHg | Vasopressor support |
Rapid Assessment Framework - The 60-Second Evaluation:
- 0-15 seconds: Vital signs + uterine tone + bleeding assessment
- 15-30 seconds: IV access + blood draw + team notification
- 30-45 seconds: Uterine massage + first-line uterotonic
- 45-60 seconds: Response evaluation + escalation decision
Uterotonic Quick Reference:
- Oxytocin: 10-40 units IV - First choice, no contraindications
- Methylergonovine: 0.2mg IM - Avoid if HTN >140/90
- Misoprostol: 800-1000mcg SL/PR - Safe in asthma
- Carboprost: 250mcg IM q15min - Avoid in asthma/cardiac disease
Surgical Decision Tree:
💡 Master This: The 15-Minute Rule - If bleeding continues despite appropriate medical management for 15 minutes, surgical intervention should be strongly considered rather than prolonging medical therapy.
Blood Product Decision Matrix:
-
RBC Transfusion
- Hemoglobin <7 g/dL: Transfuse immediately
- Hemoglobin 7-9 g/dL + ongoing bleeding: Transfuse
- Hemoglobin >9 g/dL + stable: Monitor closely
-
Plasma Transfusion
- PT/PTT >1.5x normal: 2-4 units FFP
- Massive transfusion: 1:1 ratio with RBC
- Coagulopathy + bleeding: Immediate administration
-
Platelet Transfusion
- Platelets <50k + bleeding: 1 unit per 10kg
- Platelets 50-100k + surgery planned: Consider transfusion
- Functional defect (aspirin, etc.): Regardless of count
Communication Scripts for Critical Situations:
-
MTP Activation: "This is [name] activating MTP for PPH in L&D Room [X]. Patient has lost >1000mL with ongoing bleeding. Need 6-pack now."
-
Surgical Consultation: "PPH case, failed medical management, patient [stable/unstable], considering [specific procedure]. Can you come now?"
-
Family Update: "Your wife is experiencing heavier bleeding than normal. We're giving medications and monitoring closely. The baby is fine. I'll update you in 15 minutes."
Quality Assurance Checklist:
- Team activated within 5 minutes
- IV access (2 large-bore) established
- Blood samples sent (CBC, coags, type & screen)
- First-line uterotonic administered
- Uterine massage performed
- Blood bank notified
- Response assessed at 15 minutes
- Escalation if no improvement
High-Yield Clinical Pearls for Mastery:
⭐ Pearl 1: Visual blood loss estimation is 50% accurate at best. Always use quantitative measurement and clinical correlation.
⭐ Pearl 2: Normal vital signs in young women do not exclude significant blood loss. Pregnancy physiology compensates until >30% volume loss.
⭐ Pearl 3: Fibrinogen is the first factor to become critically low. <200mg/dL predicts massive transfusion with 85% accuracy.
⭐ Pearl 4: Tranexamic acid within 3 hours reduces mortality by 19%. Earlier administration shows greater benefit.
⭐ Pearl 5: Hysterectomy should be considered early in refractory cases. Delayed decision increases morbidity and mortality.
Emergency Contact Quick List:
- Blood Bank: Extension [X] - 24/7 availability
- OR Charge: Extension [Y] - Emergency cases
- Anesthesia: Extension [Z] - Immediate response
- MFM Attending: [Phone number] - Complex cases
- IR On-call: [Pager] - Embolization procedures
The Clinical Mastery Arsenal transforms theoretical knowledge into practical expertise, ensuring rapid, evidence-based decision-making that optimizes outcomes through systematic excellence and immediate access to critical information.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Rapid Reference and Decision Tools
Practice Questions: Postpartum hemorrhage
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 38-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 35 weeks' gestation comes to the emergency department because of an episode of vaginal bleeding that morning. The bleeding has subsided. She has had no prenatal care. Her previous child was delivered with a caesarean section because of a breech presentation. Her temperature is 37.1°C (98.8°F), pulse is 88/min, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 125/85 mm Hg. The abdomen is nontender and the size of the uterus is consistent with a 35-week gestation. No contractions are felt. The fetal heart rate is 145/min. Her hemoglobin concentration is 12 g/dL, leukocyte count is 13,000/mm3, and platelet count is 350,000/mm3. Transvaginal ultrasound shows that the placenta covers the internal os. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?










