Preterm labor management US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Preterm labor management. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Preterm labor management US Medical PG Question 1: A 27-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 37 weeks' gestation is admitted to the hospital in active labor. She has received routine prenatal care, but she has not been tested for group B streptococcal (GBS) colonization. Pregnancy and delivery of her first child were complicated by an infection with GBS that resulted in sepsis in the newborn. Current medications include folic acid and a multivitamin. Vital signs are within normal limits. The abdomen is nontender and contractions are felt every 4 minutes. There is clear amniotic fluid pooling in the vagina. The fetus is in a cephalic presentation. The fetal heart rate is 140/min. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Obtain vaginal-rectal swab for nucleic acid amplification testing
- B. Obtain vaginal-rectal swab for GBS culture
- C. Administer intrapartum intravenous penicillin (Correct Answer)
- D. Reassurance
- E. Obtain vaginal-rectal swab for GBS culture and nucleic acid amplification testing
Preterm labor management Explanation: ***Administer intrapartum intravenous penicillin***
- This patient has a **previous infant with invasive GBS disease**, which is a strong indication for **intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis (IAP)** regardless of current GBS colonization status.
- Penicillin is the **first-line agent** for GBS prophylaxis during labor to prevent vertical transmission to the newborn.
*Obtain vaginal-rectal swab for nucleic acid amplification testing*
- While **NAAT** can provide rapid results, the presence of a prior infant with invasive GBS disease is an **absolute indication** for IAP, making testing unnecessary.
- Waiting for NAAT results would **delay necessary antibiotic administration**, increasing the risk of GBS transmission.
*Obtain vaginal-rectal swab for GBS culture*
- A **GBS culture** typically takes 24-48 hours for results, which is too long given the patient is in active labor and requires immediate management.
- As with NAAT, a prior affected infant means that **IAP is indicated regardless of current culture results**.
*Reassurance*
- Reassurance alone is **insufficient** given the patient's history of a previous infant with GBS sepsis, which places her current fetus at high risk.
- **Active intervention** with antibiotics is crucial to prevent recurrence of GBS disease in the newborn.
*Obtain vaginal-rectal swab for GBS culture and nucleic acid amplification testing*
- Performing both tests is **unnecessary and delays treatment** in a patient with a clear indication for intrapartum antibiotics.
- The patient's history of a prior infant with GBS sepsis is classified as a **high-risk factor, necessitating immediate antibiotic prophylaxis** without waiting for test results.
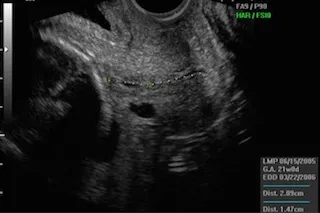
Preterm labor management US Medical PG Question 2: A 29-year-old G1P0 presents to her obstetrician for her first prenatal care visit at 12 weeks gestation by last menstrual period. She states that her breasts are very tender and swollen, and her exercise endurance has declined. She otherwise feels well. She is concerned about preterm birth, as she heard that certain cervical procedures increase the risk. The patient has a gynecologic history of loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) for cervical dysplasia several years ago and has had negative Pap smears since then. She also has mild intermittent asthma that is well controlled with occasional use of her albuterol inhaler. At this visit, this patient’s temperature is 98.6°F (37.0°C), pulse is 69/min, blood pressure is 119/61 mmHg, and respirations are 13/min. Cardiopulmonary exam is unremarkable, and the uterine fundus is just palpable at the pelvic brim. Pelvic exam reveals normal female external genitalia, a closed and slightly soft cervix, a 12-week-size uterus, and no adnexal masses. Which of the following is the best method for evaluating for possible cervical incompetence in this patient?
- A. Transabdominal ultrasound in the first trimester
- B. Transvaginal ultrasound in the first trimester
- C. Serial transvaginal ultrasounds starting at 16 weeks gestation
- D. Transabdominal ultrasound at 18 weeks gestation
- E. Transvaginal ultrasound at 18 weeks gestation (Correct Answer)
Preterm labor management Explanation: ***Transvaginal ultrasound at 18 weeks gestation***
- A history of **LEEP** is a risk factor for **cervical incompetence** and warrants screening with transvaginal ultrasound.
- The optimal timing for **cervical length** screening in women with a history of cervical procedures is typically between **18 and 24 weeks gestation**, as the risk of cervical shortening usually manifests during this period.
*Transabdominal ultrasound in the first trimester*
- **Transabdominal ultrasound** is generally not ideal for precise **cervical length measurement** due to potential shadowing from the fetus or maternal obesity.
- **First-trimester cervical length measurement** is not typically recommended for routine screening of cervical incompetence, as changes are less pronounced early in pregnancy.
*Transvaginal ultrasound in the first trimester*
- While more accurate than transabdominal, **first-trimester transvaginal ultrasound** for cervical length is not standard for predicting cervical incompetence.
- Significant cervical shortening due to incompetence often occurs later in the second trimester, so early screening may miss the condition.
*Serial transvaginal ultrasounds starting at 16 weeks gestation*
- While **serial transvaginal ultrasounds** starting at 16 weeks can be part of a management plan for high-risk patients, the most critical single assessment typically occurs at **18-24 weeks**.
- Starting serial scans too early may not be necessary if the cervix is long and closed at the initial key screening, unless there are other strong indications.
*Transabdominal ultrasound at 18 weeks gestation*
- Similar to first-trimester transabdominal ultrasound, **transabdominal imaging** at 18 weeks is generally **less accurate** than transvaginal for measuring cervical length.
- **Transvaginal ultrasound** offers a clearer and more precise view of the cervix, which is crucial for assessing potential shortening or funneling.
Preterm labor management US Medical PG Question 3: A 23-year-old G1P0 primigravid woman at 28 weeks estimated gestational age presents for a prenatal checkup. She says she has been having occasional headaches but is otherwise fine. The patient says she feels regular fetal movements and mild abdominal pain at times. Her past medical history is unremarkable. Current medications are a prenatal multivitamin and the occasional acetaminophen. Her blood pressure is 148/110 mm Hg today. On her last visit at 24 weeks of gestation, her blood pressure was 146/96 mm Hg. On physical exam, the fundus measures 28 cm above the pubic symphysis. Laboratory findings are significant for the following:
Serum Glucose (fasting) 88 mg/dL
Sodium 142 mEq/L
Potassium 3.9 mEq/L
Chloride 101 mEq/L
Serum Creatinine 0.9 mg/dL
Blood Urea Nitrogen 10 mg/dL
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) 18 U/L
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) 16 U/L
Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) 85 fL
Leukocyte count 4,200/mm3
Reticulocyte count 1%
Erythrocyte count 5.1 million/mm3
Platelet count 95,000mm3
Urinalysis show:
Proteins 2+
Glucose negative
Ketones negative
Leucocytes negative
Nitrites negative
Red Blood Cells (RBCs) negative
Casts negative
Which of the following medications would be the next best step in the treatment of this patient?
- A. Magnesium sulfate (Correct Answer)
- B. Phenobarbital
- C. Valproic acid
- D. Ethosuximide
- E. Diazepam
Preterm labor management Explanation: ***Magnesium sulfate***
- The patient presents with **gestational hypertension**, **proteinuria (2+)**, **thrombocytopenia (platelets 95,000/mm³)**, and **headaches at 28 weeks gestation**, indicating severe preeclampsia.
- **Magnesium sulfate** is the drug of choice for the prevention and treatment of **eclampsia-related seizures** in women with severe preeclampsia.
*Phenobarbital*
- **Phenobarbital** is an anticonvulsant but is generally reserved for refractory seizures or in situations where magnesium sulfate is contraindicated.
- It has a risk of **fetal respiratory depression** and neonatal withdrawal symptoms if used close to delivery.
*Valproic acid*
- **Valproic acid** is an anticonvulsant that carries a significant risk of **teratogenicity**, including **neural tube defects**, especially if used in early pregnancy.
- It is not the preferred agent for acute seizure prophylaxis in preeclampsia.
*Ethosuximide*
- **Ethosuximide** is primarily used for **absence seizures** and has no role in the management or prevention of seizures in preeclampsia.
- It would not address the underlying pathology or provide seizure prophylaxis in this patient.
*Diazepam*
- While **diazepam** can be used to abort an active seizure, it is not recommended for routine seizure prophylaxis in preeclampsia due to its **sedative effects** and potential for **fetal depression**.
- Magnesium sulfate is more effective and has a better safety profile for seizure prevention in preeclampsia.
Preterm labor management US Medical PG Question 4: A 31-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 32 weeks' gestation comes to the emergency department for sudden leakage of clear vaginal fluid. Her pregnancy has been uncomplicated. Her first child was born at term by vaginal delivery. She has no history of serious illness. She does not drink alcohol or smoke cigarettes. Current medications include vitamin supplements. Her temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F), pulse is 70/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 128/82 mm Hg. Speculum examination demonstrates clear fluid in the cervical canal. The fetal heart rate is reactive at 160/min with no decelerations. Tocometry shows uterine contractions. Nitrazine testing is positive. She is started on indomethacin. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Administer betamethasone and ampicillin (Correct Answer)
- B. Administer betamethasone, ampicillin, and proceed with cesarean section
- C. Administer betamethasone, ampicillin, and proceed with induction of labor
- D. Administer ampicillin and perform amnioinfusion
- E. Administer ampicillin and test amniotic fluid for fetal lung maturity
Preterm labor management Explanation: ***Administer betamethasone and ampicillin***
- This patient presents with **preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM)** at 32 weeks' gestation, indicated by clear vaginal fluid and positive nitrazine test. Given the preterm status, **antenatal corticosteroids (betamethasone)** are crucial for fetal lung maturity, and **antibiotics (ampicillin)** are necessary to prevent intrauterine infection.
- She is not in active labor and the fetus is stable, so conservative management with these medications is appropriate, allowing for continued gestation while mitigating risks associated with prematurity and infection.
*Administer betamethasone, ampicillin, and proceed with cesarean section*
- While betamethasone and ampicillin are appropriate, **proceeding directly with a cesarean section** is not indicated as the patient is not in active labor and there are no signs of fetal distress or immediate need for delivery.
- Cesarean section carries maternal risks and is reserved for specific indications such as non-reassuring fetal status, malpresentation, or contraindications to vaginal delivery.
*Administer betamethasone, ampicillin, and proceed with induction of labor*
- Administering betamethasone and ampicillin is correct, but **inducing labor immediately** is not the most appropriate step at 32 weeks with PPROM in a stable patient without chorioamnionitis.
- The goal at this gestational age is typically to prolong the pregnancy to allow for further fetal development, unless there are complications that necessitate delivery, such as chorioamnionitis or non-reassuring fetal testing.
*Administer ampicillin and perform amnioinfusion*
- Ampicillin is appropriate for infection prophylaxis in PPROM, but **amnioinfusion** is generally reserved for cases of **oligohydramnios** with umbilical cord compression, particularly during labor.
- While oligohydramnios can result from PPROM, amnioinfusion is not a standard or primary intervention in the initial management of PPROM before labor onset.
*Administer ampicillin and test amniotic fluid for fetal lung maturity*
- Ampicillin is appropriate, but **testing amniotic fluid for fetal lung maturity** is less critical in this scenario, as corticosteroids will be administered regardless.
- Given the 32-week gestation, fetal lungs are unlikely to be fully mature, and waiting for test results would delay essential interventions (i.e., corticosteroids) that improve fetal outcomes.
Preterm labor management US Medical PG Question 5: A P2G1 diabetic woman is at risk of delivering at 29 weeks gestation. Her obstetrician counsels her that there is a risk the baby could have significant pulmonary distress after it is born. However, she states she will give the mother corticosteroids, which will help prevent this from occurring. Additionally, the obstetrician states she will perform a test on the amniotic fluid which will indicate the likelihood of the infant being affected by this syndrome. Which of the following ratios would be most predictive of the infant having pulmonary distress?
- A. lecithin:phosphatidylserine < 1.5
- B. lecithin:sphingomyelin < 1.5 (Correct Answer)
- C. lecithin:sphingomyelin > 1.5
- D. lecithin:phosphatidylserine > 3.0
- E. lecithin:sphingomyelin > 3.0
Preterm labor management Explanation: ***lecithin:sphingomyelin < 1.5***
- A lecithin:sphingomyelin (L:S) ratio less than 2:1 (or 1.5 in some clinical contexts) indicates **fetal lung immaturity** and a **high risk for respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)**.
- The **lecithin level increases** significantly in the amniotic fluid during the third trimester as fetal lungs mature, while **sphingomyelin levels remain relatively constant**.
*lecithin:phosphatidylserine < 1.5*
- While **phosphatidylserine** is a component of surfactant, the **Lecithin:Sphingomyelin (L:S) ratio** is the established and most commonly used marker for fetal lung maturity.
- There is **no widely recognized or clinically validated threshold** for a lecithin:phosphatidylserine ratio in predicting respiratory distress syndrome.
*lecithin:sphingomyelin > 1.5*
- An L:S ratio **greater than 2:1 (or 1.5, in some labs)** generally indicates **fetal lung maturity** and a low risk for respiratory distress syndrome.
- Therefore, this ratio would suggest a **lower likelihood of pulmonary distress**, which contradicts the aim of identifying risk.
*lecithin:phosphatidylserine > 3.0*
- As with an L:S ratio, a higher ratio would generally indicate **lung maturity**, not increased risk for pulmonary distress.
- There is **no clinical standard for lecithin:phosphatidylserine ratio** to assess lung maturity for preventing RDS.
*lecithin:sphingomyelin > 3.0*
- An L:S ratio of **greater than 2:1 (or 3.0 in certain clinical scenarios)** is a strong indicator of **fetal lung maturity**, meaning the risk of respiratory distress syndrome is low.
- The question asks for a ratio that would be **predictive of pulmonary distress**, whereas this ratio indicates the opposite.
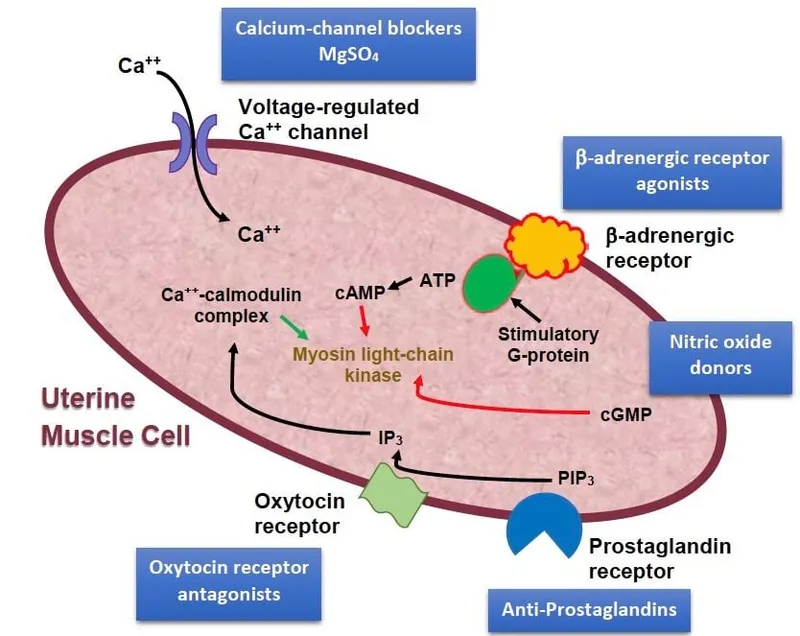
Preterm labor management US Medical PG Question 6: A P1G0 diabetic woman is at risk of delivering at 30 weeks gestation. Her obstetrician counsels her that there is a risk the baby could have significant pulmonary distress after it is born. However, she states she will administer a drug to the mother to help prevent this from occurring. By what action will this drug prevent respiratory distress in the premature infant?
- A. Increasing the secretory product of type II alveolar cells (Correct Answer)
- B. Promoting increased surface tension of alveoli
- C. Suppressing the neonatal immune system
- D. Preventing infection of immature lungs
- E. Reducing the secretory product of type II alveolar cells
Preterm labor management Explanation: ***Increasing the secretory product of type II alveolar cells***
- The drug administered is likely a **corticosteroid**, which **accelerates fetal lung maturation** by stimulating the production and release of **surfactant** from **type II alveolar cells**.
- **Surfactant** is crucial for reducing surface tension within the alveoli, preventing their collapse and ensuring proper lung function in premature infants.
*Promoting increased surface tension of alveoli*
- This option is incorrect because premature infants suffer from **respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)** due to **insufficient surfactant**, which leads to **high surface tension** and alveolar collapse.
- The goal of treatment is to **reduce surface tension**, not increase it.
*Suppressing the neonatal immune system*
- While corticosteroids do have **immunosuppressive effects**, this is not the primary mechanism by which they prevent **respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)** in premature infants.
- The main goal in this context is lung maturation, not immune modulation.
*Preventing infection of immature lungs*
- Although premature infants are susceptible to infections, the primary purpose of administering corticosteroids in this scenario is to promote **lung maturation** and prevent **respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)** due to **surfactant deficiency**, not to directly prevent infection.
- Antibiotics would be used for infection prevention or treatment.
*Reducing the secretory product of type II alveolar cells*
- This statement is incorrect because the problem in premature infants is a **deficiency of surfactant**, the secretory product of **type II alveolar cells**.
- The treatment aims to **increase** this secretory product to facilitate lung function.
Preterm labor management US Medical PG Question 7: A 26-year-old gravida 1 at 36 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department by her husband complaining of contractions lasting up to 2 minutes. The contractions are mostly in the front of her abdomen and do not radiate. The frequency and intensity of contractions have not changed since the onset. The patient worries that she is in labor. The blood pressure is 125/80 mm Hg, the heart rate is 96/min, the respiratory rate is 15/min, and the temperature 36.8°C (98.2℉). The physical examination is unremarkable. The estimated fetal weight is 3200 g (6.6 lb). The fetal heart rate is 146/min. The cervix is not dilated. The vertex is at the -4 station. Which of the following would be proper short-term management of this woman?
- A. Reassurance, hydration, and ambulation (Correct Answer)
- B. Admit to the Obstetrics Department for observation
- C. Manage with terbutaline
- D. Admit to the Obstetrics Department in preparation for labor induction
- E. Perform an ultrasound examination
Preterm labor management Explanation: ***Reassurance, hydration, and ambulation***
- This patient is experiencing **Braxton-Hicks contractions**, which are irregular, do not cause cervical change, and often resolve with hydration and rest or light activity.
- Given her stable vital signs, normal fetal heart rate, and undilated cervix, these interventions are appropriate to differentiate from true labor and provide comfort.
*Admit to the Obstetrics Department for observation*
- Admission for observation is unnecessary as there are no signs of **true labor** (cervical dilation or effacement) or fetal distress.
- The contractions are described as not changing in frequency or intensity and are localized to the anterior abdomen, consistent with **false labor**.
*Manage with terbutaline*
- **Terbutaline** is a tocolytic used to stop or prevent premature labor, but this patient is at 36 weeks gestation, which is near term, and not in true labor.
- Using a tocolytic for **Braxton-Hicks contractions** is not indicated and can have adverse effects.
*Admit to the Obstetrics Department in preparation for labor induction*
- There is no indication for **labor induction** as the patient is not in active labor and has not reached her due date.
- Labor induction is reserved for medical or obstetric indications, which are not present here.
*Perform an ultrasound examination*
- An ultrasound has already provided an estimated fetal weight and the fetal heart rate is normal, suggesting no immediate need for further **ultrasound evaluation**.
- There are no clinical signs to suggest fetal distress or other complications that would warrant an **urgent ultrasound**.
Preterm labor management US Medical PG Question 8: A 30-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 38 weeks' gestation comes to the hospital for regular, painful contractions that have been increasing in frequency. Her pregnancy has been complicated by gestational diabetes treated with insulin. Pelvic examination shows the cervix is 50% effaced and 4 cm dilated; the vertex is at -1 station. Ultrasonography shows no abnormalities. A tocometer and Doppler fetal heart monitor are placed on the patient's abdomen. The fetal heart rate monitoring strip shows a baseline heart rate of 145/min with a variability of ≥ 15/min. Within a 20-minute recording, there are 7 uterine contractions, 4 accelerations, and 3 decelerations that have a nadir occurring within half a minute. The decelerations occur at differing intervals relative to the contractions. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
- A. Vibroacoustic stimulation
- B. Routine monitoring (Correct Answer)
- C. Administer tocolytics
- D. Emergent cesarean delivery
- E. Placement of fetal scalp electrode
Preterm labor management Explanation: ***Routine monitoring***
- The presented FHR tracing exhibits a **normal baseline rate** (145/min), **moderate variability** (≥15/min), and the presence of **accelerations**, indicating a reassuring fetal status.
- The described decelerations are **variable decelerations** due to their sudden onset, nadir within 30 seconds, and variable relationship to contractions, which are generally benign unless prolonged, deep, or repetitive. Given the otherwise reassuring status, continued routine monitoring is appropriate.
*Vibroacoustic stimulation*
- This intervention is used to elicit **fetal accelerations** or movement during non-stress tests (NSTs) when the fetus is quiet or shows a non-reactive pattern.
- In this case, the fetus is already showing **accelerations** and moderate variability, so stimulation is not needed to assess fetal well-being.
*Administer tocolytics*
- **Tocolytics** are used to stop or slow down labor, typically in cases of preterm labor or uterine tachysystole causing fetal distress.
- This patient is at **38 weeks' gestation** and in active labor, and there are no signs of fetal distress warranting the cessation of contractions.
*Emergent cesarean delivery*
- **Emergent cesarean delivery** is indicated for acute fetal distress, such as prolonged decelerations, significant bradycardia, or absent variability in conjunction with other concerning FHR patterns.
- The FHR tracing described is largely reassuring with moderate variability and accelerations, and the variable decelerations are not indicative of immediate threat, making emergent delivery unnecessary.
*Placement of fetal scalp electrode*
- A **fetal scalp electrode** provides a more accurate and continuous measure of the FHR, often used when external monitoring is difficult or when there are concerns about the reliability of the tracing.
- While it can be useful in some situations, the current tracing is **interpretable as reassuring**, making invasive monitoring currently unnecessary.
Preterm labor management US Medical PG Question 9: A 33-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 26 weeks' gestation comes to the emergency department because of frequent contractions. The contractions are 40 seconds each, occurring every 2 minutes, and increasing in intensity. Her first child was delivered by lower segment transverse cesarean section because of a nonreassuring fetal heart rate. Her current medications include folic acid and a multivitamin. Her temperature is 36.9°C (98.4°F), heart rate is 88/min, and blood pressure is 126/76 mm Hg. Contractions are felt on the abdomen. There is clear fluid in the vulva and the introitus. The cervix is dilated to 5 cm, 70% effaced, and station of the head is -2. A fetal ultrasound shows polyhydramnios, a median cleft lip, and fused thalami. The corpus callosum, 3rd ventricle, and lateral ventricles are absent. The spine shows no abnormalities and there is a four chamber heart. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Initiate misoprostol therapy
- B. Allow vaginal delivery (Correct Answer)
- C. Perform dilation and evacuation
- D. Initiate nifedipine therapy
- E. Perform cesarean delivery
Preterm labor management Explanation: ***Allow vaginal delivery***
- The presence of severe fetal anomalies, including **holoprosencephaly** (median cleft lip, fused thalami, absent corpus callosum, 3rd and lateral ventricles), indicates that the fetus is **incompatible with life**.
- Given the prognosis, the most appropriate and safest approach for the mother is to **allow vaginal delivery**, as there is no benefit to delaying delivery or attempting a surgical intervention that might pose more risks to the mother.
*Initiate misoprostol therapy*
- **Misoprostol** is a prostaglandin analog used to induce labor or abortion, particularly in cases of uterine atony or to ripen the cervix.
- While it aids in cervical ripening and uterine contractions, the cervix is already 5 cm dilated and 70% effaced, indicating a **rapidly progressing labor** not requiring additional induction.
*Perform dilation and evacuation*
- **Dilation and evacuation (D&E)** is typically performed in the second trimester for fetal demise or termination of pregnancy, usually before 24 weeks' gestation.
- At 26 weeks' gestation with advanced labor and significant cervical dilation, D&E is a **high-risk procedure** for the mother and less appropriate than vaginal delivery.
*Initiate nifedipine therapy*
- **Nifedipine is a tocolytic** used to suppress preterm labor by relaxing the uterine muscles.
- Given the **lethal fetal anomalies** and the advanced stage of labor (5 cm dilated, 70% effaced, intense contractions), stopping labor would only prolong a non-viable pregnancy and increase maternal risk.
*Perform cesarean delivery*
- **Cesarean delivery** would expose the mother to surgical risks (e.g., infection, hemorrhage, future pregnancy complications) without any benefit to the fetus, who has anomalies **incompatible with survival**.
- A previous cesarean section does not preclude a vaginal delivery in this context, especially when **fetal viability is not a concern**.
Preterm labor management US Medical PG Question 10: A 30-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 31 weeks' gestation is admitted to the hospital because her water broke one hour ago. Pregnancy has been complicated by iron deficiency anemia and hypothyroidism treated with iron supplements and L-thyroxine, respectively. The patient followed-up with her gynecologist on a regular basis throughout the pregnancy. Pregnancy and delivery of her first child were uncomplicated. Pulse is 90/min, respirations are 17/min, and blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg. The abdomen is nontender. She has had 8 contractions within the last hour. Pelvic examination shows cervical dilation of 3 cm. The fetal heart rate is 140/min with no decelerations. In addition to administration of dexamethasone and terbutaline, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
- A. Administer prophylactic azithromycin
- B. Emergency cesarean delivery
- C. Administration of anti-RhD immunoglobulin
- D. Cervical cerclage
- E. Administration of magnesium sulfate (Correct Answer)
Preterm labor management Explanation: ***Administration of magnesium sulfate***
- This patient is experiencing **preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM)** at 31 weeks and is in **preterm labor** (contractions with cervical changes).
- **Magnesium sulfate** is administered for **fetal neuroprotection** in cases of anticipated preterm birth before 32 weeks' gestation, reducing the risk of cerebral palsy.
*Administer prophylactic azithromycin*
- **Prophylactic antibiotics** are indicated in PPROM to prolong latency and prevent infection, but **broad-spectrum antibiotics** (e.g., ampicillin and erythromycin) are typically used, not solely azithromycin.
- While azithromycin might be part of an antibiotic regimen for PPROM, it is not the *most appropriate next single step* given the immediate need for neuroprotection and labor inhibition.
*Emergency cesarean delivery*
- An emergency cesarean delivery is not indicated at this time as the **fetal heart rate is reassuring** (140/min with no decelerations) and there are no signs of fetal distress or maternal compromise.
- The primary goal is to **delay delivery** to allow for fetal lung maturity and neuroprotection, rather than immediate delivery.
*Administration of anti-RhD immunoglobulin*
- **Anti-RhD immunoglobulin** is administered to Rh-negative mothers to prevent alloimmunization, typically at 28 weeks' gestation and postpartum.
- While administration may be due at this stage for an Rh-negative patient, it is not the **most critical next step** in the *acute management* of preterm labor and PPROM.
*Cervical cerclage*
- **Cervical cerclage** is a procedure to reinforce the cervix and is performed to prevent preterm birth in patients with **cervical insufficiency**, usually in the late first or early second trimester.
- It is **contraindicated** once membranes have ruptured and the patient is in active labor due to the risk of infection and uterine rupture.
More Preterm labor management US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.