Substance use in pregnancy US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Substance use in pregnancy. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Substance use in pregnancy US Medical PG Question 1: A male newborn delivered at 32 weeks' gestation to a 41-year-old woman dies shortly after birth. The mother did not receive prenatal care and consistently consumed alcohol during her pregnancy. At autopsy, examination shows microcephaly, an eye in the midline, a cleft lip, and a single basal ganglion. Failure of which of the following processes is the most likely cause of this condition?
- A. Formation of the 1st branchial arch
- B. Closure of the rostral neuropore
- C. Cleavage of the forebrain (Correct Answer)
- D. Development of the metencephalon
Substance use in pregnancy Explanation: ***Cleavage of the forebrain***
- The combination of **microcephaly**, a **single midline eye (cyclopia)**, **cleft lip**, and a **single basal ganglion** is characteristic of **holoprosencephaly**.
- **Holoprosencephaly** results from the **failure of the embryonic forebrain (prosencephalon)** to properly divide into two cerebral hemispheres and associated structures.
*Formation of the 1st branchial arch*
- Defects in the **1st branchial arch** would primarily lead to malformations of the **mandible**, **maxilla**, and structures of the **external ear**, such as in **Treacher Collins syndrome**.
- This would not explain the severe midline brain and facial defects like a single basal ganglion or cyclopia.
*Closure of the rostral neuropore*
- Failure of the **rostral neuropore to close** results in **anencephaly** [1] or **encephalocele**, characterized by an incomplete skull and exposed brain tissue.
- While it involves the forebrain region, it presents with a different spectrum of defects than the observed holoprosencephaly.
*Development of the metencephalon*
- The **metencephalon** develops into the **pons** and **cerebellum** [2].
- Defects in its development would lead to **cerebellar malformations** or malformations of the posterior brain, which are not described in this constellation of symptoms.
Substance use in pregnancy US Medical PG Question 2: A 30-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 40 weeks' gestation is admitted to the hospital in active labor. Her first pregnancy and delivery were complicated by iron deficiency anemia and pregnancy-induced hypertension. She has had no routine prenatal care during this pregnancy but was diagnosed with oligohydramnios 4 weeks ago. The remainder of her medical history is not immediately available. A 2400-g (5.4-lb) female newborn is delivered vaginally. Examination of the newborn shows a short, mildly webbed neck and low-set ears. Ocular hypertelorism along with slanted palpebral fissures are noted. A cleft palate and hypoplasia of the nails and distal phalanges are present. There is increased coarse hair on the body and face. Which of the following best explains the clinical findings found in this newborn?
- A. Maternal phenytoin therapy (Correct Answer)
- B. Fetal X chromosome monosomy
- C. Fetal posterior urethral valves
- D. Maternal diabetes mellitus
- E. Maternal alcohol intake
Substance use in pregnancy Explanation: ***Maternal phenytoin therapy***
- The constellation of **craniofacial anomalies** (short, webbed neck, low-set ears, ocular hypertelorism, slanted palpebral fissures, cleft palate), **nail hypoplasia**, and **hirsutism** are characteristic features of **fetal hydantoin syndrome**, caused by **phenytoin exposure** in utero.
- Oligohydramnios can be associated with complications of antiepileptic drug use, such as **renal dysfunction**, further supporting this diagnosis.
*Fetal X chromosome monosomy*
- This condition, also known as **Turner syndrome**, is characterized by a **short webbed neck** and **low-set ears**, but typically presents with **gonadal dysgenesis**, **coarctation of the aorta**, and **lymphedema**, which are not mentioned.
- **Nail hypoplasia** and **hirsutism** are not typical features of Turner syndrome.
*Fetal posterior urethral valves*
- **Posterior urethral valves** cause **urinary tract obstruction** in male fetuses, leading to **oligohydramnios**, **pulmonary hypoplasia**, and characteristic facial features (Potter facies) due to decreased amniotic fluid pressure.
- The patient is female, and the specific facial anomalies and nail/hair findings are not consistent with **Potter sequence** but rather with a teratogenic exposure syndrome.
*Maternal diabetes mellitus*
- **Maternal diabetes** can cause a range of fetal complications, including **macrosomia**, **cardiac defects**, and **caudal regression syndrome**.
- While it can be associated with increased risk of certain birth defects and occasionally oligohydramnios, the specific combination of **craniofacial features**, **nail hypoplasia**, and **hirsutism** seen here is not characteristic of diabetic embryopathy.
*Maternal alcohol intake*
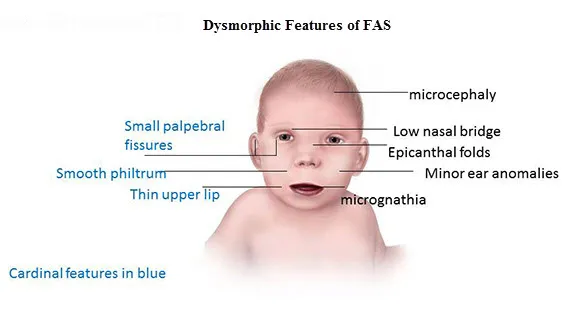
- **Maternal alcohol intake** leads to **fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS)**, characterized by **growth restriction**, **facial anomalies** (smooth philtrum, thin upper lip, short palpebral fissures), and **CNS dysfunction**.
- While some facial features might overlap, **nail hypoplasia** and **hirsutism** as described are not typical of FAS.
Substance use in pregnancy US Medical PG Question 3: A 31-year-old G3P0 is admitted to the hospital with profuse vaginal bleeding and abdominal pain at 34 weeks gestation. She reports passing bright blood with clots and no water in the discharge. She denies recent trauma or medical illnesses. She had no prenatal care. Her previous pregnancies culminated in spontaneous abortions in the second trimester. She has a 6-year history of drug abuse and cocaine smoking 2 hours prior to the onset of her symptoms. Her blood pressure is 160/90 mm Hg, the heart rate is 93/min, the respiratory rate is 19/min, and the temperature is 36.9℃ (98.4℉). The fetal heart rate is 110/min. On examination, the patient is lethargic. Her pupils are constricted, but reactive to light bilaterally. There are no signs of trauma. Abdominal palpation identifies lower abdominal tenderness and strong uterine contractions. The fundus of the uterus is between the xiphoid process and umbilicus. The patient’s perineum is grossly bloody. On pelvic examination, the vaginal canal is without lesions. The cervix is almost completely effaced and 2 cm dilated. Which of the following options is the most likely cause of the patient’s pregnancy-related condition?
- A. Thrombosis of the placental vessels
- B. Dramatic decrease in thrombocytes
- C. Premature rupture of the membranes
- D. Rupture of the placental vessels
- E. Abrupt constriction of maternal and placental vessels (Correct Answer)
Substance use in pregnancy Explanation: ***Abrupt constriction of maternal and placental vessels***
- The patient's presentation with **profuse vaginal bleeding**, **abdominal pain**, **strong uterine contractions**, **hypertension**, and a history of **cocaine use** strongly points to **placental abruption**. Cocaine causes abrupt and severe vasoconstriction, leading to placental detachment.
- The **firm and tender uterus**, coupled with **fetal distress** (fetal heart rate of 110/min), is characteristic of placental abruption due to the accumulation of blood behind the placenta and uterine hypertonicity.
*Thrombosis of the placental vessels*
- While thrombosis can affect the placenta, it typically leads to **placental insufficiency** and **fetal growth restriction**, not acute, profuse vaginal bleeding with contractions.
- **Thrombosis** alone does not explain the sudden onset of severe abdominal pain and uterine hypertonicity seen in this case.
*Dramatic decrease in thrombocytes*
- A dramatic decrease in thrombocytes (thrombocytopenia) would cause **generalized bleeding diathesis**, often with petechiae, purpura, or bleeding from other sites, not typically isolated profuse vaginal bleeding with uterine pain and contractions.
- While severe **placental abruption** can lead to **disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)** and secondary thrombocytopenia, the primary cause of bleeding here is the placental detachment, not a pre-existing low platelet count.
*Premature rupture of the membranes*
- **Premature rupture of membranes (PROM)** involves the leakage of **amniotic fluid** ("water breaking"), which the patient explicitly denies.
- Although PROM can precede preterm labor, it does not directly cause profuse vaginal bleeding, severe abdominal pain, and uterine hypertonicity in the absence of placental abruption.
*Rupture of the placental vessels*
- **Rupture of placental vessels** without abruption (e.g., vasa previa) typically presents with **painless vaginal bleeding** and rapid **fetal compromise**, but usually without significant maternal abdominal pain or strong uterine contractions.
- The context of **cocaine use** and its known effect on vasoconstriction directly points to placental abruption rather than isolated vessel rupture.
Substance use in pregnancy US Medical PG Question 4: A 5-year-old boy is brought to his neurologist for continued treatment of muscle spasms. His past medical history is significant for a brain abnormality that was detected neonatally when it presented with an enlarged posterior fossa as well as a malformed cerebellar vermis. Since birth, he has had developmental delay, high muscle tone, difficulty with coordination, and speech delay. He has been treated with a number of therapies to relax his muscle tone such as baclofen. Which of the following conditions is associated with this patient's most likely condition?
- A. Syringomyelia
- B. Hydrocephalus (Correct Answer)
- C. Fetal alcohol syndrome
- D. Polyhydramnios
- E. Vocal cord paralysis
Substance use in pregnancy Explanation: ***Hydrocephalus***
- The patient's presentation with an **enlarged posterior fossa** and a **malformed cerebellar vermis** indicates **Dandy-Walker malformation**, which is frequently complicated by **hydrocephalus**.
- Hydrocephalus results from impaired cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow due to the posterior fossa abnormalities, leading to increased intracranial pressure and worsening neurological symptoms.
*Syringomyelia*
- **Syringomyelia** is characterized by a **fluid-filled cyst (syrinx)** within the spinal cord, often associated with Chiari malformations, but it is not the primary abnormality described here.
- While it can cause neurological deficits, it doesn't directly explain the **enlarged posterior fossa** or **malformed cerebellar vermis**.
*Fetal alcohol syndrome*
- **Fetal alcohol syndrome** is caused by maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy and is associated with distinct facial features, growth restriction, and developmental delays, but not specifically with **Dandy-Walker malformation** or its characteristic brain abnormalities.
- It is a **teratogenic condition** with a different set of diagnostic criteria.
*Polyhydramnios*
- **Polyhydramnios** refers to an **excess amount of amniotic fluid** during pregnancy. While it can be associated with various fetal anomalies, it is a prenatal finding and not a direct neurological condition or complication of Dandy-Walker malformation itself.
- It is related to impaired fetal swallowing or increased urination, not inherently to specific brain malformations.
*Vocal cord paralysis*
- **Vocal cord paralysis** is a disorder affecting the movement of the vocal cords, which can be caused by various neurological conditions or injury, but it is not a direct or common association with **Dandy-Walker malformation**.
- It is a specific symptom rather than a primary condition linked to the broader neurological picture described.
Substance use in pregnancy US Medical PG Question 5: A 27-year-old homeless man presents to the emergency department with abdominal pain and vomiting. He has a known history of intravenous drug use and has been admitted to the hospital several times before. On physical examination his temperature is 99°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 130/85 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, respirations are 19/min, and pulse oximetry is 99% on room air. The patient is in obvious discomfort. There is increased salivation and lacrimation. Pupils are reactive to light and 5 mm bilaterally. Cardiopulmonary exam is unremarkable. There is diffuse abdominal tenderness to palpation with no rebound or guarding. Which of the following interventions would have prevented this patient’s current condition?
- A. Naltrexone
- B. Buprenorphine (Correct Answer)
- C. Lorazepam
- D. Naloxone
- E. Bupropion
Substance use in pregnancy Explanation: ***Buprenorphine***
- This patient is presenting with symptoms consistent with **opioid withdrawal** (abdominal pain, vomiting, increased salivation, lacrimation). **Buprenorphine** is used for **opioid dependence treatment** as it's a **partial opioid agonist** that helps manage withdrawal symptoms and cravings, thus preventing acute withdrawal episodes.
- By stabilizing opioid receptors, buprenorphine, often combined with naloxone (Suboxone), reduces the risk of relapse and prevents the cycle of **intravenous drug use** that leads to withdrawal.
*Naltrexone*
- **Naltrexone** is an **opioid antagonist** used to prevent relapse in individuals who have achieved abstinence from opioids. It blocks the effects of opioids.
- However, administering naltrexone to someone actively using opioids or in withdrawal would precipitate or worsen withdrawal symptoms, making it unsuitable for preventing this acute presentation.
*Lorazepam*
- **Lorazepam** is a **benzodiazepine** primarily used to treat **anxiety**, **insomnia**, and **seizures**, and it is often used in **alcohol withdrawal**.
- While it can help manage some anxiety associated with opioid withdrawal, it does not address the underlying opioid dependence or prevent the physical symptoms of withdrawal itself, nor does it prevent the underlying cause of withdrawal which is abstinence from opioids.
*Naloxone*
- **Naloxone** is a potent, short-acting **opioid antagonist** used to **reverse opioid overdose** by rapidly displacing opioids from receptors.
- It would not prevent withdrawal; in fact, administering naloxone to an opioid-dependent individual would acutely precipitate severe withdrawal.
*Bupropion*
- **Bupropion** is an **antidepressant** that also aids in **smoking cessation**. It works by inhibiting the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine.
- It has no role in the prevention or treatment of opioid withdrawal and would not have altered this patient's current condition.
Substance use in pregnancy US Medical PG Question 6: A 38-year-old primigravid woman at 34 weeks' gestation comes to the emergency department because of progressive shortness of breath for 3 hours. At a prenatal visit 2 weeks earlier, she was diagnosed with gestational hypertension. Amniocentesis with chromosomal analysis was performed at 16 weeks' gestation and showed no abnormalities. The patient has been otherwise healthy, except for a deep venous thrombosis 2 years ago that was treated with low molecular weight heparin. Her current medications include methyldopa and a multivitamin. She appears anxious. Her pulse is 90/min, respirations are 24/min, and blood pressure is 170/100 mm Hg. Crackles are heard over both lung bases. Pelvic examination shows a uterus consistent in size with a 32-week gestation. Examination of the heart, abdomen, and extremities shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's shortness of breath?
- A. Pulmonary edema (Correct Answer)
- B. Pulmonary metastases
- C. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- D. Pulmonary thromboembolism
- E. Amniotic fluid embolism
Substance use in pregnancy Explanation: ***Pulmonary edema***
- The patient presents with **gestational hypertension** and new-onset **shortness of breath** with **bilateral basal crackles**, a classic presentation for pulmonary edema, often precipitated by conditions like preeclampsia in pregnancy.
- Her elevated blood pressure (170/100 mm Hg) and rapid respiratory rate (24/min) further support increased **pulmonary hydrostatic pressure**, leading to fluid extravasation into the lung alveoli.
*Pulmonary metastases*
- This is unlikely given her young age, lack of a prior cancer diagnosis, and acute onset of symptoms.
- **Pulmonary metastases** typically present with a more gradual onset of symptoms and are less commonly associated with bilateral basal crackles in isolation.
*Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis*
- **Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis** is a chronic, progressive interstitial lung disease, typically affecting older individuals, and has a much slower, gradual onset of symptoms.
- The acute presentation of severe shortness of breath in a young, previously healthy pregnant woman does not fit the typical course of this disease.
*Pulmonary thromboembolism*
- While the patient has a history of **DVT** and is pregnant (a hypercoagulable state), the primary presentation with **bilateral crackles** and **hypertension** makes pulmonary edema more likely.
- A pulmonary embolism might cause sudden shortness of breath and an elevated pulse, but significant bilateral crackles are less typical unless there's associated right heart failure leading to pulmonary congestion.
*Amniotic fluid embolism*
- **Amniotic fluid embolism** is a rare but catastrophic event, typically presenting with sudden, severe respiratory distress, hemodynamic collapse, and coagulopathy, often occurring during labor or soon after delivery.
- This patient is not in labor, does not show signs of hemodynamic collapse or coagulopathy, and the onset is progressive over several hours rather than sudden.
Substance use in pregnancy US Medical PG Question 7: A 37-year-old woman presents to her physician with a newly detected pregnancy for the initial prenatal care visit. She is gravida 3 para 2 with a history of preeclampsia in her 1st pregnancy. Her history is also significant for arterial hypertension diagnosed 1 year ago for which she did not take any medications. The patient reports an 8-pack-year smoking history and states she quit smoking a year ago. On examination, the vital signs are as follows: blood pressure 140/90 mm Hg, heart rate 69/min, respiratory rate 14/min, and temperature 36.6°C (97.9°F). The physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following options is the most appropriate next step in the management for this woman?
- A. Methyldopa (Correct Answer)
- B. Magnesium sulfate
- C. Fosinopril
- D. Labetalol
- E. No medications needed
Substance use in pregnancy Explanation: ***Methyldopa***
- **Methyldopa** is a **centrally acting alpha-2 adrenergic agonist** that is considered a first-line agent for the treatment of **chronic hypertension in pregnancy**.
- Its **safety profile** and effectiveness in controlling blood pressure without significant fetal harm make it an appropriate choice.
*Magnesium sulfate*
- **Magnesium sulfate** is primarily used for the **prevention and treatment of seizures in preeclampsia** and **eclampsia**.
- It is not indicated for the chronic management of hypertension and is prescribed for specific acute indications during pregnancy.
*Fosinopril*
- **Fosinopril** is an **ACE inhibitor**, which is **contraindicated in pregnancy** due to its association with **fetal renal dysfunction**, **oligohydramnios**, and **malformations**, especially in the second and third trimesters.
- ACE inhibitors and ARBs should be avoided during pregnancy.
*Labetalol*
- **Labetalol** is an **alpha and beta-blocker that can be used for chronic hypertension in pregnancy**, but given the patient's history of asthma (implied through a history of smoking), **methyldopa** might be a slightly safer initial choice, although labetalol could also be considered.
- While generally safe, its use can be associated with **fetal growth restriction** and **neonatal bradycardia** if used indiscriminately, making methyldopa a preferred first-line agent in many cases.
*No medications needed*
- The patient has **chronic hypertension** (diagnosed 1 year ago) and previous **preeclampsia**, indicating a need for **antihypertensive management** to prevent adverse maternal and fetal outcomes.
- Not initiating treatment would put the patient at increased risk for **severe preeclampsia**, **placental abruption**, and other complications.
Substance use in pregnancy US Medical PG Question 8: A 35-year-old woman gravida 2, para 1, comes to the physician for her first prenatal visit. Pregnancy and delivery of her first child were uncomplicated. She is not sure about the date of her last menstrual period. Pelvic examination shows a uterus consistent in size with a 10-week gestation. An ultrasound examination confirms the gestational age and shows one fetus with no indication of multiple gestations. During counseling on pregnancy risks and possible screening and diagnostic tests, the patient states she would like to undergo screening for Down syndrome. She would prefer immediate and secure screening with a low risk to herself and the fetus. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management at this time?
- A. Nuchal translucency, pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A, human chorionic gonadotropin
- B. Maternal serum α-fetoprotein, human chorionic gonadotropin, unconjugated estriol, and inhibin A
- C. Chorionic villus sampling
- D. Amniocentesis
- E. Cell-free fetal DNA testing (Correct Answer)
Substance use in pregnancy Explanation: ***Cell-free fetal DNA testing***
- This is the most appropriate choice given the patient's desire for **immediate and secure screening with low risk** because it is a **non-invasive prenatal screening (NIPS)** method offering high sensitivity and specificity for Down syndrome, particularly in higher-risk pregnancies.
- It involves a simple maternal blood draw and can be performed as early as **10 weeks of gestation**, perfectly aligning with the patient's current gestational age and desire for early screening.
*Nuchal translucency, pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A, human chorionic gonadotropin*
- This combination represents the **first-trimester combined screen**, which is typically performed between 11 and 14 weeks of gestation. While suitable for early screening, **cell-free DNA testing offers higher detection rates and lower false-positive rates** for Down syndrome.
- The patient specifically asked for the most **secure and least risky** screening, and NIPS outperforms the combined screen in terms of diagnostic accuracy for aneuploidies.
*Maternal serum α-fetoprotein, human chorionic gonadotropin, unconjugated estriol, and inhibin A*
- This refers to the **quad screen**, which is typically performed in the **second trimester (15-20 weeks)**, making it too late for the patient's desire for immediate screening at 10 weeks gestational age.
- While a widely used screening tool, the quad screen has a **lower detection rate** for Down syndrome compared to cell-free DNA testing.
*Chorionic villus sampling*
- **Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)** is a **diagnostic, invasive procedure** that carries a small risk of miscarriage (approximately 1 in 455 or 0.22%) and is not a screening test.
- Although it can be performed earlier (typically between 10 and 13 weeks), the patient specifically requested a **low-risk screening** option, which CVS is not.
*Amniocentesis*
- **Amniocentesis** is also an **invasive diagnostic procedure** with a risk of miscarriage (approximately 1 in 900 or 0.11%) and is typically performed in the **second trimester (15-20 weeks)**.
- This option is unsuitable because the patient is at 10 weeks gestation and desires **immediate and low-risk screening**, not a diagnostic procedure with procedural risks a few weeks later.
Substance use in pregnancy US Medical PG Question 9: A 67-year-old man comes to the clinic for establishment of care. He recently retired and moved to Florida with his wife. His past medical history includes hypertension, diabetes, chronic back pain, and hyperlipidemia. According to the patient, he takes lisinopril, metformin, atorvastatin, acetaminophen, and methadone. His previous doctor prescribed methadone for breakthrough pain as he has been having more severe pain episodes due to the recent move. He is currently out of his methadone and asks for a refill on the prescription. A physical examination is unremarkable except for mild lower extremity edema bilaterally and diffuse lower back pain upon palpation. What is the best initial step in the management of this patient?
- A. Refer the patient to a pain management clinic
- B. Inform the patient that methadone is not the best option and do not prescribe
- C. Encourage the patient to switch to duloxetine
- D. Assess the patient's pain medication history (Correct Answer)
- E. Prescribe a limited dose of methadone for breakthrough back pain
Substance use in pregnancy Explanation: ***Assess the patient's pain medication history***
- It is crucial to gather a comprehensive **pain medication history** for a new patient on long-term opioids, especially when they are requesting a refill for a potentially high-risk medication like **methadone**. This includes understanding the duration of use, previous dosages, other medications tried, and the effectiveness of prior treatments.
- A comprehensive assessment helps to identify potential risks, such as **opioid tolerance**, dependence, or drug-drug interactions, and allows the physician to make an informed decision regarding the patient's ongoing pain management plan in accordance with **CDC guidelines** on opioid prescribing.
*Refer the patient to a pain management clinic*
- While referral to a pain management clinic may be appropriate later, the **initial step** should involve a thorough assessment by the primary care physician to understand the patient's immediate needs and history, especially given the new patient encounter.
- A direct referral without an initial evaluation could delay critical care decisions related to safe opioid prescribing and **withdrawal prevention**.
*Inform the patient that methadone is not the best option and do not prescribe*
- Simply refusing to prescribe methadone without a proper assessment and alternative plan can lead to **opioid withdrawal** and non-adherence to care, which can be dangerous for the patient.
- While methadone has significant risks, abruptly discontinuing it without a transition plan is generally discouraged, as it can cause severe **rebound pain** and withdrawal symptoms.
*Encourage the patient to switch to duloxetine*
- Duloxetine is an appropriate medication for **neuropathic pain** and **chronic musculoskeletal pain**, but it's not an immediate solution for breakthrough pain in a patient accustomed to methadone and should only be considered after a full assessment and discussion of risks and benefits.
- Switching to duloxetine without a clear understanding of the patient's current pain control, opioid dependence, and potential for withdrawal is premature and could exacerbate the patient's pain and lead to severe **withdrawal symptoms**.
*Prescribe a limited dose of methadone for breakthrough back pain*
- Prescribing methadone without a complete and thorough assessment of the patient's pain history, current dosage, and potential interactions with other medications is not safe practice, especially for a **new patient**.
- Methadone has a **long and variable half-life**, making it prone to accumulation and overdose, and requires careful titration and monitoring, which cannot be done without a full history.
Substance use in pregnancy US Medical PG Question 10: A 23-year-old primigravida presents to her physician’s office at 12 weeks gestation complaining of increased sweating and palpitations for the last week. She does not have edema or dyspnea, and had no pre-existing illnesses. The patient says that the symptoms started a few days after several episodes of vomiting. She managed the vomiting at home and yesterday the vomiting stopped, but the symptoms she presents with are persistent. The pre-pregnancy weight was 54 kg (119 lb). The current weight is 55 kg (121 lb). The vital signs are as follows: blood pressure 130/85 mm Hg, heart rate 113/min, respiratory rate 15/min, and temperature 37.0℃ (98.6℉). The physical examination is significant for diaphoresis, an irregular heartbeat, and a fine resting tremor of the hands. The neck is not enlarged and the thyroid gland is not palpable. The ECG shows sinus tachyarrhythmia. The thyroid panel is as follows:
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) < 0.1 mU/L
Total T4 178 nmol/L
Free T4 31 pmol/L
Which of the following is indicated?
- A. Recommend iodine radioablation
- B. Schedule a subtotal thyroidectomy
- C. Prescribe methimazole
- D. Manage with propylthiouracil
- E. Ensure proper hydration and prescribe a beta-blocker (Correct Answer)
Substance use in pregnancy Explanation: ***Ensure proper hydration and prescribe a beta-blocker***
- The patient's symptoms (sweating, palpitations, irregular heartbeat, tremor, tachycardia, low TSH, high T4) are consistent with **hyperthyroidism**. However, her symptoms started shortly after persistent vomiting (hyperemesis gravidarum), and the thyroid is not enlarged, suggesting **gestational transient thyrotoxicosis (GTT)** rather than Graves' disease. GTT is typically mild and self-limiting, often resolving by mid-gestation.
- Since the patient is pregnant, definitive treatments like **radioiodine ablation** or **thyroidectomy** are contraindicated. Antithyroid medications (methimazole, PTU) are also generally avoided in GTT unless symptoms are severe, due to potential side effects for both mother and fetus. The primary management for mild to moderate GTT involves supportive care, such as ensuring proper hydration and using **beta-blockers** (e.g., propranolol) to alleviate adrenergic symptoms like palpitations and tremors.
*Recommend iodine radioablation*
- **Radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy** for hyperthyroidism is absolutely **contraindicated in pregnancy** because radioactive iodine crosses the placenta and can destroy the fetal thyroid gland, leading to congenital hypothyroidism.
- This treatment is primarily used for definitive treatment of hyperthyroidism in non-pregnant patients, particularly for **Graves' disease** or toxic nodular goiter.
*Schedule a subtotal thyroidectomy*
- **Thyroidectomy** at 12 weeks gestation carries significant risks to both the mother (surgical complications) and the fetus (miscarriage, preterm labor). It is considered only in very rare cases of severe, uncontrolled hyperthyroidism refractory to medical management, typically in the second trimester.
- Given the suspicion of **gestational transient thyrotoxicosis (GTT)**, a self-limiting condition, surgical intervention is highly inappropriate.
*Prescribe methimazole*
- **Methimazole** is an antithyroid drug used to reduce thyroid hormone synthesis. While effective for hyperthyroidism, it is generally **avoided in the first trimester of pregnancy** due to its association with rare but severe fetal abnormalities, such as aplasia cutis.
- For gestational transient thyrotoxicosis, antithyroid drugs are typically not necessary because the condition is usually mild and self-limiting.
*Manage with propylthiouracil*
- **Propylthiouracil (PTU)** is another antithyroid drug that blocks thyroid hormone synthesis. It is typically **preferred over methimazole during the first trimester of pregnancy** when antithyroid medication is absolutely necessary, as it has a lower risk of teratogenicity during this period.
- However, PTU itself carries risks, including rare but severe **hepatotoxicity**, and is generally reserved for cases of severe hyperthyroidism where the benefits outweigh the risks. In mild to moderate gestational transient thyrotoxicosis, medications like PTU are usually not required.
More Substance use in pregnancy US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.