Multiple gestation management US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Multiple gestation management. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Multiple gestation management US Medical PG Question 1: A 30-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 12 weeks' gestation comes to the physician for a prenatal visit. She feels well. Pregnancy and vaginal delivery of her first child were uncomplicated. Five years ago, she was diagnosed with hypertension but reports that she has been noncompliant with her hypertension regimen. The patient does not smoke or drink alcohol. She does not use illicit drugs. Medications include methyldopa, folic acid, and a multivitamin. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 80/min, and blood pressure is 145/90 mm Hg. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies, including serum glucose level, and thyroid-stimulating hormone concentration, are within normal limits. The patient is at increased risk of developing which of the following complications?
- A. Placenta previa
- B. Abruptio placentae (Correct Answer)
- C. Spontaneous abortion
- D. Polyhydramnios
- E. Uterine rupture
Multiple gestation management Explanation: ***Abruptio placentae***
- The patient's history of **chronic hypertension** (145/90 mmHg) and her noncompliance with antihypertensive medication significantly increase her risk for **abruptio placentae**. Hypertension is a major risk factor for this condition.
- Abruptio placentae involves the **premature separation of the placenta** from the uterine wall, which can lead to severe maternal hemorrhage, fetal distress, and preterm birth.
*Placenta previa*
- **Placenta previa** is characterized by the placenta covering the cervical os and is primarily associated with risk factors like **previous C-section**, multiple gestations, or advanced maternal age.
- While a serious complication, it is **not directly linked to chronic hypertension** in the same manner as abruptio placentae.
*Spontaneous abortion*
- **Spontaneous abortion** typically occurs in the **first trimester** and is often due to chromosomal abnormalities, endocrine disorders, or uterine anomalies.
- While hypertension could theoretically contribute to some pregnancy complications, it is **not a primary risk factor** for spontaneous abortion at 12 weeks gestation.
*Polyhydramnios*
- **Polyhydramnios** is an excessive accumulation of amniotic fluid, often associated with **maternal diabetes**, fetal anomalies (e.g., GI obstruction, anencephaly), or multiple gestations.
- Maternal hypertension is **not a direct risk factor** for polyhydramnios.
*Uterine rupture*
- **Uterine rupture** is a rare but catastrophic event, most commonly associated with a **previous uterine scar** (e.g., from a prior C-section or myomectomy).
- The patient's history of a prior vaginal delivery and absence of uterine surgery means she is **not at increased risk** for uterine rupture at this stage.
Multiple gestation management US Medical PG Question 2: A 2250-g (5.0-lb) male newborn and a 2900-g (6.4-lb) male newborn are delivered at 36 weeks' gestation to a 24-year-old, gravida 1, para 1 woman. The mother had no prenatal care. Examination of the smaller newborn shows low-set ears, retrognathia, and right-sided clubfoot. The hematocrit is 41% for the smaller newborn and 69% for the larger newborn. This pregnancy was most likely which of the following?
- A. Monochorionic-monoamniotic monozygotic
- B. Conjoined twins
- C. Dichorionic-diamniotic monozygotic
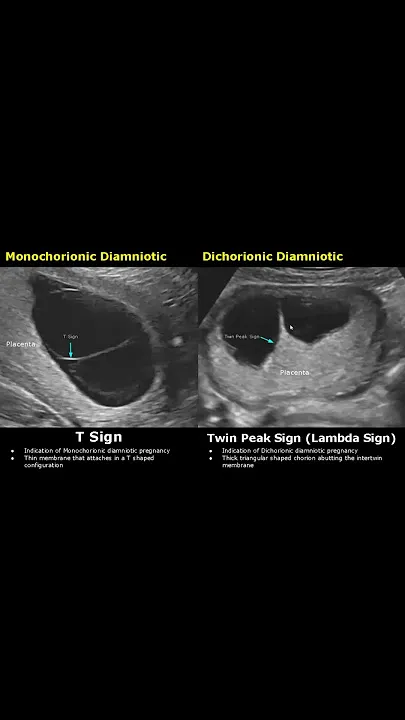
- D. Monochorionic-diamniotic monozygotic (Correct Answer)
- E. Dichorionic-monoamniotic monozygotic
Multiple gestation management Explanation: ***Monochorionic-diamniotic monozygotic***
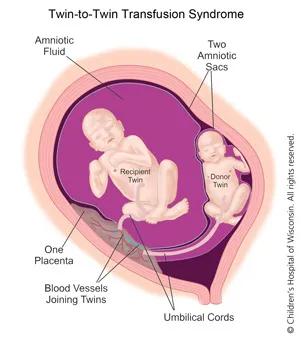
- This is the most likely scenario given the significant **weight discordance**, **malformations** in one twin (low-set ears, retrognathia, clubfoot), and divergent hematocrit values suggesting **twin-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS)**.
- **Monochorionic** indicates a shared placenta, allowing for vascular anastomoses that cause TTTS; **diamniotic** means separate amniotic sacs, which is typical for division between days 4-8 post-fertilization.
*Monochorionic-monoamniotic monozygotic*
- This type of twinning occurs with division after day 8-13 post-fertilization and would result in **both twins sharing the same amniotic sac**, increasing the risk of cord entanglement.
- While it's monochorionic and thus prone to TTTS, the presence of two distinct newborns without signs of cord entanglement makes diamniotic more likely.
*Conjoined twins*
- **Conjoined twins** result from incomplete separation of a monozygotic embryo after day 13, leading to physically connected infants.
- The description of two distinct newborns, despite the size and health differences, rules out physical fusion.
*Dichorionic-diamniotic monozygotic*
- While dichorionic-diamniotic twins can be monozygotic (splitting within the first 3 days post-fertilization), they typically have **separate placentas** or at least separate chorions.
- This arrangement significantly **reduces the risk of TTTS**, which is strongly suggested by the differing hematocrits and growth discordance.
*Dichorionic-monoamniotic monozygotic*
- **Dichorionic** means two separate chorions, implying separate placentas or at least separate chorionic membranes, making the significant vascular connection for TTTS unlikely.
- **Monoamniotic** (sharing one amniotic sac) with two chorions is a rare and highly unusual combination for monozygotic twins; it usually implies a very early split before chorion differentiation but without separate amnions.
Multiple gestation management US Medical PG Question 3: A 32-year-old primigravid woman with a history of seizures comes to the physician because she had a positive pregnancy test at home. Medications include valproic acid and a multivitamin. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. A urine pregnancy test is positive. Her baby is at increased risk for requiring which of the following interventions?
- A. Lower spinal surgery (Correct Answer)
- B. Kidney transplantation
- C. Arm surgery
- D. Cochlear implantation
- E. Respiratory support
Multiple gestation management Explanation: ***Lower spinal surgery***
- Maternal use of **valproic acid** during pregnancy significantly increases the risk of neural tube defects, particularly **spina bifida**, which often requires surgical correction of the lower spine in affected infants.
- **Spina bifida** results from the incomplete closure of the neural tube, leading to exposed spinal cord or meninges, and frequently necessitates surgical intervention to prevent further neurological damage and infection.
*Kidney transplantation*
- While some fetal anomalies can involve the kidneys, **valproic acid** exposure is not primarily associated with renal agenesis or severe kidney malformations requiring transplantation.
- Birth defects affecting the kidneys are more commonly linked to genetic syndromes or other teratogens, not specifically valproic acid.
*Arm surgery*
- **Valproic acid** has been associated with limb defects, but these are typically minor and do not usually directly necessitate extensive arm surgery.
- **Phocomelia** (shortened or absent limbs) is more typically associated with **thalidomide** exposure, not valproic acid.
*Cochlear implantation*
- Although **valproic acid** exposure has been occasionally linked to some congenital anomalies, it is not a primary risk factor for **severe hearing loss** requiring cochlear implantation.
- Hearing loss requiring such intervention is more often due to genetic factors, congenital infections, or other specific teratogens.
*Respiratory support*
- While a variety of congenital conditions can lead to respiratory compromise, **valproic acid** exposure does not specifically cause severe pulmonary hypoplasia or other defects that commonly necessitate prolonged or intense neonatal respiratory support.
- Respiratory distress in neonates is often related to prematurity, meconium aspiration, or other direct pulmonary issues.
Multiple gestation management US Medical PG Question 4: Immediately following prolonged delivery of the placenta at 40 weeks gestation, a 32-year-old multiparous woman develops vaginal bleeding. Other than mild asthma, the patient’s pregnancy has been uncomplicated. She has attended many prenatal appointments and followed the physician's advice about screening for diseases, laboratory testing, diet, and exercise. Previous pregnancies were uncomplicated. She has no history of a serious illness. She is currently on intravenous infusion of oxytocin. Her temperature is 37.2°C (99.0°F), blood pressure is 108/60 mm Hg, pulse is 88/min, and respirations are 17/min. Uterine palpation reveals a soft enlarged fundus that extends above the umbilicus. Based on the assessment of the birth canal and placenta, which of the following options is the most appropriate initial step in patient management?
- A. Intramuscular carboprost
- B. Manual exploration of the uterus
- C. Discontinuing oxytocin
- D. Intravenous methylergonovine
- E. Uterine fundal massage (Correct Answer)
Multiple gestation management Explanation: ***Uterine fundal massage***
- The patient presents with **postpartum hemorrhage** indicated by vaginal bleeding and a **soft, enlarged fundus** after placental delivery, suggesting **uterine atony**.
- **Uterine fundal massage** is the **first-line intervention** to encourage uterine contraction and reduce bleeding by expelling clots and compressing vessels.
*Intramuscular carboprost*
- **Carboprost** is a **prostaglandin F2 alpha analog** used to treat **uterine atony** when initial measures like uterine massage and oxytocin are insufficient.
- It is contraindicated in patients with **asthma** due to its bronchoconstrictive effects, which this patient has.
*Manual exploration of the uterus*
- **Manual exploration of the uterus** is indicated when there is suspicion of **retained placental fragments** or **uterine rupture**.
- While these can cause postpartum hemorrhage, the primary finding of a soft, boggy uterus points more strongly to atony, making massage the immediate priority.
*Discontinuing oxytocin*
- The patient is already on an **intravenous oxytocin infusion**, which is a uterotonic agent used to prevent and treat uterine atony.
- Discontinuing it would worsen **uterine atony** and increase blood loss, directly contradicting the goal of management.
*Intravenous methylergonovine*
- **Methylergonovine** is an **ergot alkaloid** used to treat **uterine atony**, but it is contraindicated in patients with **hypertension**, which is not explicitly present here, but it is a potent vasoconstrictor and second-line.
- It is often used as a **second-line agent** if oxytocin and massage are ineffective and there are no contraindications.
Multiple gestation management US Medical PG Question 5: A 28-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 30 weeks' gestation comes to the physician because of headache for the past 5 days. Her pregnancy has been uncomplicated to date. Pregnancy and vaginal delivery of her first child were uncomplicated. The patient does not smoke or drink alcohol. She does not use illicit drugs. Medications include folic acid and a multivitamin. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 82/min, and blood pressure is 150/92 mm Hg. Physical examination reveals 2+ pitting edema in the lower extremities. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 11.8 g/dL
Platelet count 290,000/mm3
Urine
pH 6.3
Protein 2+
WBC negative
Bacteria occasional
Nitrites negative
The patient is at increased risk of developing which of the following complications?
- A. Abruptio placentae (Correct Answer)
- B. Polyhydramnios
- C. Uterine rupture
- D. Spontaneous abortion
- E. Placenta previa
Multiple gestation management Explanation: ***Abruptio placentae***
- The patient presents with **preeclampsia** (new-onset hypertension after 20 weeks gestation, proteinuria, and edema), which is a significant risk factor for **placental abruption**.
- Preeclampsia can lead to **vasoconstriction** and **decidual hemorrhage**, causing premature separation of the placenta from the uterine wall.
*Polyhydramnios*
- **Polyhydramnios** is an excess of amniotic fluid, typically associated with **fetal anomalies** (e.g., esophageal atresia, anencephaly) or **maternal diabetes**, none of which are indicated here.
- While it can complicate pregnancy, it is not directly linked to preeclampsia as a primary complication.
*Uterine rupture*
- **Uterine rupture** is a rare but catastrophic event, most commonly associated with a **prior Cesarean section**, extensive uterine surgery, or **traumatic injury**.
- This patient had an uncomplicated vaginal delivery previously, and there are no signs suggesting a heightened risk for uterine rupture.
*Spontaneous abortion*
- **Spontaneous abortion** occurs before 20 weeks of gestation. This patient is at **30 weeks' gestation**, making spontaneous abortion highly unlikely.
- The term for pregnancy loss after 20 weeks is stillbirth, which is also not the most immediate or direct complication linked to preeclampsia for the mother.
*Placenta previa*
- **Placenta previa** occurs when the placenta covers the cervical os, a condition diagnosed by **ultrasound** and presenting with **painless vaginal bleeding**.
- Preeclampsia does not directly cause placenta previa; these are distinct obstetric complications with different etiologies.
Multiple gestation management US Medical PG Question 6: A 29-year-old G1P0 female at 32 weeks gestation presents to the emergency department with vaginal bleeding. She has had minimal prenatal care to-date with only an initial visit with an obstetrician after a positive home pregnancy test. She describes minimal spotting that she noticed earlier today that has progressed to larger amounts of blood; she estimates 30 mL of blood loss. She denies any cramping, pain, or contractions, and she reports feeling continued movements of the baby. Ultrasound and fetal heart rate monitoring confirm the presence of a healthy fetus without any evidence of current or impending complications. The consulted obstetrician orders blood testing for Rh-status of both the mother as well as the father, who brought the patient to the hospital. Which of the following represents the best management strategy for this situation?
- A. After 28 weeks gestation, administration of RhoGAM will have no benefit
- B. If mother is Rh-positive and father is Rh-negative then administer RhoGAM
- C. If mother is Rh-negative and father is Rh-negative then administer RhoGAM
- D. If mother is Rh-negative and father is Rh-positive, RhoGAM administration is not needed
- E. If mother is Rh-negative and father is Rh-positive then administer RhoGAM (Correct Answer)
Multiple gestation management Explanation: ***If mother is Rh-negative and father is Rh-positive then administer RhoGAM***
- This combination creates a risk for **Rh incompatibility**, meaning the fetus could be Rh-positive and the mother's immune system could form antibodies against fetal red blood cells, which can harm the fetus in future pregnancies.
- **RhoGAM (Rh immunoglobulin)** administration prevents the mother from forming these antibodies when there's a risk of maternal-fetal blood mixing, as indicated by vaginal bleeding.
*After 28 weeks gestation, administration of RhoGAM will have no benefit*
- This statement is incorrect; **RhoGAM is routinely administered around 28 weeks gestation** as prophylaxis in Rh-negative mothers, even without bleeding episodes, to prevent sensitization.
- In cases of potential fetal-maternal hemorrhage, such as vaginal bleeding, RhoGAM is indicated regardless of gestational age beyond the first trimester.
*If mother is Rh-positive and father is Rh-negative then administer RhoGAM*
- This scenario does not pose a risk for **Rh incompatibility hemolytic disease of the newborn**, as the mother already possesses the Rh antigen.
- RhoGAM is specifically given to Rh-negative mothers to prevent their immune system from reacting to an Rh-positive fetus.
*If mother is Rh-negative and father is Rh-negative then administer RhoGAM*
- In this case, both parents are **Rh-negative**, meaning the fetus will also be Rh-negative.
- There is no risk of **Rh incompatibility** or sensitization, so RhoGAM administration is not indicated.
*If mother is Rh-negative and father is Rh-positive, RhoGAM administration is not needed*
- This statement is incorrect and represents a critical misunderstanding of **Rh incompatibility prophylaxis**.
- This specific genetic combination creates the highest risk for **Rh sensitization** during pregnancy, especially with events like vaginal bleeding, making RhoGAM administration essential.
Multiple gestation management US Medical PG Question 7: A 37-year-old primigravid woman comes to the physician at 13 weeks' gestation for a prenatal visit. She feels well. Her only medication is folic acid. Vital signs are within normal limits. Pelvic examination shows a uterus consistent in size with a 13-week gestation. Ultrasonography shows a nuchal translucency above the 99th percentile. Maternal serum pregnancy-associated plasma protein A is decreased and human chorionic gonadotropin concentrations are elevated to 2 times the median level. Which of the following is most likely to confirm the diagnosis?
- A. Chorionic villus sampling (Correct Answer)
- B. Cell-free DNA testing
- C. Triple screening test
- D. Amniocentesis
- E. Quadruple marker test
Multiple gestation management Explanation: ***Chorionic villus sampling***
- This procedure can be performed between **10 to 13 weeks of gestation** to obtain fetal cells for genetic analysis, which is within the patient's gestational age.
- It provides a definitive diagnosis of **chromosomal abnormalities** by directly sampling placental tissue, which shares the same genetic material as the fetus.
*Cell-free DNA testing*
- While it has high sensitivity and specificity for various **aneuploidies**, it is a **screening test**, not a diagnostic one.
- An abnormal result from cell-free DNA testing still requires **confirmatory diagnostic testing** such as CVS or amniocentesis.
*Triple screening test*
- This test is typically performed between **15 and 20 weeks of gestation**, which is too late to confirm the findings presented at 13 weeks gestation.
- It measures **AFP, hCG, and unconjugated estriol**, and an abnormal result would indicate a need for further diagnostic testing.
*Amniocentesis*
- This procedure is generally performed later in pregnancy, typically between **15 and 20 weeks gestation**, so it would require waiting several more weeks.
- While it provides definitive genetic results, **chorionic villus sampling is preferred at 13 weeks** due to earlier diagnostic potential.
*Quadruple marker test*
- This test is also performed between **15 and 20 weeks of gestation** and measures **AFP, hCG, unconjugated estriol, and inhibin A**.
- It is a **screening test**, similar to the triple screen, and does not provide a definitive diagnosis, requiring further confirmatory testing if abnormal.
Multiple gestation management US Medical PG Question 8: A 21-year-old female presents to her primary care doctor for prenatal counseling before attempting to become pregnant for the first time. She is an avid runner, and the physician notes her BMI of 17.5. The patient complains of chronic fatigue, which she attributes to her busy lifestyle. The physician orders a complete blood count that reveals a Hgb 10.2 g/dL (normal 12.1 to 15.1 g/dL) with an MCV 102 µm^3 (normal 78 to 98 µm^3). A serum measurement of a catabolic derivative of methionine returns elevated. Which of the following complications is the patient at most risk for if she becomes pregnant?
- A. Placenta abruptio (Correct Answer)
- B. Placenta previa
- C. Placenta accreta
- D. Neural tube defects
- E. Gestational diabetes
Multiple gestation management Explanation: **Placenta abruptio**
* The patient presents with several risk factors for **placental abruption**, including **low BMI**, **anemia** (Hgb 10.2), and **elevated homocysteine** (indicated by elevated catabolic derivative of methionine, implying **folate or B12 deficiency**, which leads to high homocysteine).
* **Anemia** and **folate deficiency** are associated with an increased risk of placental abruption.
*Placenta previa*
* **Placenta previa** is characterized by the placenta covering the cervical os, typically associated with risk factors like **previous C-section**, **multiparity**, and **advanced maternal age**.
* The patient's profile (first pregnancy, young) does not align with the typical risk factors for placenta previa.
*Placenta accreta*
* **Placenta accreta** involves abnormal placental adherence to the uterine wall, most commonly linked to **prior uterine surgery** (especially C-sections) and **placenta previa**.
* The patient has no history of uterine surgery, making placenta accreta an unlikely primary risk.
*Neural tube defects*
* **Neural tube defects** are associated with **folate deficiency**, which is likely present given the **macrocytic anemia** (MCV 102) and elevated homocysteine.
* However, the question asks for the complication the patient is *most* at risk for due to her overall profile including her low BMI and anemia, and while NTDs are a risk, the combination of factors points more strongly to placental abruption.
*Gestational diabetes*
* **Gestational diabetes** is linked to risk factors like **obesity**, **family history of diabetes**, and **advanced maternal age**.
* The patient's **low BMI** (17.5) and young age make gestational diabetes an unlikely significant risk.
Multiple gestation management US Medical PG Question 9: A 28-year-old G2P1 female is concerned that she may give birth to another child with Down syndrome. She states that she may not be able to take care of another child with this disorder. Which of the following tests can confirm the diagnosis of Down syndrome in utero?
- A. Ultrasound
- B. Triple marker test
- C. Integrated test
- D. Quadruple marker test
- E. Amniocentesis (Correct Answer)
Multiple gestation management Explanation: ***Amniocentesis***
- **Amniocentesis** is a **diagnostic procedure** that involves collecting amniotic fluid to obtain fetal cells for **karyotyping**, which can definitively confirm the presence of an extra chromosome 21, the cause of Down syndrome.
- This test is typically performed between **15 and 20 weeks of gestation** and carries a small risk of complication but offers conclusive results.
*Ultrasound*
- **Ultrasound** is a **screening tool** that can detect anatomical features suggestive of Down syndrome, such as **nuchal translucency** or heart defects, but it cannot definitively diagnose the condition.
- It identifies **markers** that increase the suspicion of Down syndrome, prompting further diagnostic testing, but does not provide genetic confirmation.
*Triple marker test*
- The **triple marker test** is a **screening test** that measures levels of **alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)**, **unconjugated estriol (uE3)**, and **human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)** in maternal blood.
- While it can estimate the risk of Down syndrome, it is not a diagnostic test and only provides a **risk assessment**, not a definitive diagnosis.
*Integrated test*
- The **integrated test** combines results from first-trimester screening (nuchal translucency and PAPP-A) and second-trimester screening (quadruple marker test) to provide a **single risk assessment**.
- Like other screening tests, it calculates a **risk probability** for Down syndrome but does not offer a definitive diagnosis.
*Quadruple marker test*
- The **quadruple marker test** measures AFP, uE3, hCG, and **inhibin A** in maternal blood during the second trimester.
- It is a **screening test** used to assess the risk of Down syndrome and open neural tube defects, but it is not a diagnostic tool.
Multiple gestation management US Medical PG Question 10: A 31-year-old G6P6 woman with a history of fibroids gives birth to twins via vaginal delivery. Her pregnancy was uneventful, and she reported having good prenatal care. Both placentas are delivered immediately after the birth. The patient continues to bleed significantly over the next 20 minutes. Her temperature is 97.0°F (36.1°C), blood pressure is 124/84 mmHg, pulse is 95/min, respirations are 16/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Continued vaginal bleeding is noted. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial step in management?
- A. Oxytocin
- B. Blood product transfusion
- C. Uterine artery embolization
- D. Hysterectomy
- E. Bimanual massage (Correct Answer)
Multiple gestation management Explanation: ***Bimanual massage***
- The patient is experiencing **postpartum hemorrhage (PPH)**, indicated by significant bleeding post-delivery. **Uterine atony** is the most common cause of PPH, and bimanual massage helps stimulate uterine contractions to reduce bleeding.
- This is a **first-line, non-pharmacological intervention** that can be rapidly initiated to manage uterine atony.
*Oxytocin*
- While **oxytocin** is a uterotonic agent used to treat PPH, the initial step is typically **bimanual massage** to physically stimulate the uterus while preparing for medication administration.
- Oxytocin infusion would be administered concurrent with or immediately following bimanual massage, but manual compression is often initiated first.
*Blood product transfusion*
- Blood product transfusion is indicated for significant blood loss and hemodynamic instability, but it is a **supportive measure** rather than an initial intervention to stop the bleeding.
- The patient's current **blood pressure (124/84 mmHg)** and **pulse (95/min)** do not immediately suggest severe hypovolemic shock requiring immediate transfusion as the *first* step before attempting to control the source of bleeding.
*Uterine artery embolization*
- **Uterine artery embolization** is a highly invasive procedure typically reserved for cases where conservative measures, including uterotonic agents and bimanual compression, have failed to control PPH.
- It is not an appropriate initial step, as it requires specialized equipment and personnel and would delay immediate management of active bleeding.
*Hysterectomy*
- **Hysterectomy** is a last-resort intervention for intractable PPH that cannot be controlled by all other methods, including uterotonics, uterine massage, and other surgical or interventional radiology techniques.
- It is a highly invasive procedure with significant morbidity and is not considered an initial management step.
More Multiple gestation management US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.