Viral diagnostics US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Viral diagnostics. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Viral diagnostics US Medical PG Question 1: A 23-year-old woman presents with vulvar ulcers and lymphadenopathy. Testing confirms primary HSV infection. Which of the following statements about HSV antibody development is correct?
- A. IgG appears immediately after infection
- B. IgG antibodies appear 2-3 weeks after infection and persist (Correct Answer)
- C. No antibody response occurs
- D. IgM and IgG appear simultaneously at 6 weeks
Viral diagnostics Explanation: ***IgG antibodies appear 2-3 weeks after infection and persist***
- Following primary HSV infection, the body mounts an immune response, with **IgG antibodies** typically becoming detectable approximately **2-3 weeks post-infection**. [1]
- These **IgG antibodies** persist for life, providing long-term immunity and serving as a marker of past or latent infection. [1]
*IgG appears immediately after infection*
- The immune system requires time to generate a robust antibody response, so **IgG antibodies** do not appear immediately following infection. [2]
- The initial immune response involves innate immunity and the production of **IgM antibodies** before IgG. [1], [2]
*No antibody response occurs*
- The body's immune system recognizes the viral antigens and mounts an antibody response to combat the infection.
- Absence of an antibody response would imply a complete failure of the adaptive immune system, which is not the case in immunocompetent individuals with primary HSV. [1]
*IgM and IgG appear simultaneously at 6 weeks*
- **IgM antibodies** are produced earlier in the immune response compared to **IgG**. [2]
- While both may be present at 6 weeks, their appearance is not simultaneous, with IgM preceding IgG, and IgG often detectable by 2-3 weeks, not waiting until 6 weeks. [1]
Viral diagnostics US Medical PG Question 2: If the genetic material were isolated and injected into the cytoplasm of a human cell, which of the following would produce viable, infectious virions?
- A. Lassa fever virus
- B. Rabies virus
- C. Rhinovirus (Correct Answer)
- D. Mumps virus
- E. Influenza virus
Viral diagnostics Explanation: ***Rhinovirus***
- **Rhinovirus** is a **positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus**. Its genetic material can directly serve as mRNA in the host cell cytoplasm, leading to immediate protein synthesis and viral replication without needing DNA intermediates or a nuclear phase.
- This direct translation allows for the production of viable, infectious virions upon cytoplasmic injection of the genetic material.
*Lassa fever virus*
- **Lassa fever virus** is an **ambisense RNA virus** and requires an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) to transcribe its genome into mRNA.
- This RdRp is packaged within the virion, meaning the injected genetic material alone is not sufficient to initiate replication without the viral proteins.
*Rabies virus*
- **Rabies virus** is a **negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus**. Its genome cannot directly act as mRNA.
- It requires a virion-associated **RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp)** to transcribe its negative-sense RNA into positive-sense mRNA, which is essential for protein synthesis.
*Mumps virus*
- **Mumps virus** is a **negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus** and, like rabies virus, cannot directly translate its genome into proteins.
- It also requires its own **virion-associated RNA-dependent RNA polymerase** to synthesize mRNA from its negative-sense genome.
*Influenza virus*
- **Influenza virus** is a **negative-sense segmented RNA virus**. Its replication cycle involves the nucleus, where its RNA genome is transcribed into mRNA.
- This process requires the viral **RNA-dependent RNA polymerase**, which is brought into the cell by the virion, and interaction with host nuclear machinery.
Viral diagnostics US Medical PG Question 3: A rapid diagnostic test has been developed amid a major avian influenza outbreak in Asia. The outbreak has reached epidemic levels with a very high attack rate. Epidemiologists are hoping to use the rapid diagnostic test to identify all exposed individuals and curb the rapid spread of disease by isolating patients with any evidence of exposure to the virus. The epidemiologists compared rapid diagnostic test results to seropositivity of viral antigen via PCR in 200 patients. The findings are represented in the following table:
Test result PCR-confirmed avian influenza No avian influenza
Positive rapid diagnostic test 95 2
Negative rapid diagnostic test 5 98
Which of the following characteristics of the rapid diagnostic test would be most useful for curbing the spread of the virus via containment?
- A. Positive predictive value of 95/97
- B. Specificity of 98/100
- C. Sensitivity of 95/100 (Correct Answer)
- D. Negative predictive value of 98/103
- E. Accuracy of 193/200
Viral diagnostics Explanation: ***Sensitivity of 95/100***
- In an epidemic with a **high attack rate** and the goal of **identifying all exposed individuals** to prevent spread, a test with **high sensitivity** is crucial.
- **Sensitivity** measures the proportion of true positives that are correctly identified (95/100 = 95%), meaning it correctly identifies those *with* the disease, thus minimizing **false negatives** and ensuring all infected individuals are isolated.
- When the primary objective is containment and preventing disease spread, missing even a few infected individuals (false negatives) could perpetuate the epidemic.
*Positive predictive value of 95/97*
- **Positive predictive value (PPV)** indicates the probability that a positive test result truly reflects the presence of the disease (95/97 = 97.9%).
- While important for confirming disease in individuals, it's less critical than sensitivity for the primary goal of **identifying all exposed individuals** in an epidemic to prevent further spread.
*Specificity of 98/100*
- **Specificity** measures the proportion of true negatives that are correctly identified (98/100 = 98%), meaning it correctly identifies those *without* the disease.
- In this scenario, while important to avoid unnecessary isolation, high specificity is secondary to high sensitivity when the main objective is to **curb rapid disease spread by finding all infected individuals**.
*Negative predictive value of 98/103*
- **Negative predictive value (NPV)** indicates the probability that a negative test result truly reflects the absence of the disease (98/103 = 95.1%).
- While valuable for ruling out disease, high NPV is not the most critical characteristic when the primary goal is to **identify all infected individuals** to contain an epidemic.
*Accuracy of 193/200*
- **Accuracy** represents the overall proportion of correct results, both positive and negative (193/200 = 96.5%).
- While accuracy provides an overall measure of test performance, it doesn't specifically address the critical need to **minimize false negatives** in a containment scenario where missing infected individuals is the primary concern.
Viral diagnostics US Medical PG Question 4: The occupational health department at a hospital implements new safety precautions to prevent laboratory-acquired infections. One of the new precautions includes disinfecting the microbiology laboratory benches with 70% ethanol before and after use. This measure is most likely to be effective in preventing the transmission of which of the following viruses?
- A. Hepatitis A virus
- B. Herpes simplex virus (Correct Answer)
- C. Poliovirus
- D. Parvovirus
- E. Polyomavirus
Viral diagnostics Explanation: ***Herpes simplex virus***
- Herpes simplex virus is an **enveloped virus**, meaning it has a lipid outer layer that is easily disrupted by disinfectants like **70% ethanol**.
- The disruption of its envelope renders the virus inactive and unable to infect host cells, making this a highly effective prevention strategy.
*Hepatitis A virus*
- Hepatitis A virus is a **non-enveloped virus**, making it relatively **resistant to many common disinfectants**, including alcohol-based ones.
- Its robust protein capsid protects its genetic material, requiring stronger disinfection methods than 70% ethanol for inactivation.
*Poliovirus*
- Poliovirus is another **non-enveloped virus** that exhibits significant **resistance to alcohol-based disinfectants** due to its stable protein capsid.
- Effective inactivation typically requires disinfectants with greater germicidal activity, such as chlorine-based solutions.
*Parvovirus*
- Parvovirus is one of the **most resistant non-enveloped viruses** to disinfection, including inactivation by 70% ethanol.
- Its small size and extremely stable capsid make it challenging to eliminate from surfaces, often necessitating harsh chemical treatments.
*Polyomavirus*
- Polyomaviruses are **non-enveloped DNA viruses** that are generally more **resistant to alcohol-based disinfectants** than enveloped viruses.
- Their lack of a lipid envelope provides protection against agents like ethanol that target lipid bilayers.
Viral diagnostics US Medical PG Question 5: A 41-year-old woman comes to the primary care physician’s office with a 7-day history of headaches, sore throat, diarrhea, fatigue, and low-grade fevers. The patient denies any significant past medical history, recent travel, or recent sick contacts. On review of systems, the patient endorses performing sex acts in exchange for money and recreational drugs over the last several months. You suspect primary HIV infection, but the patient refuses further evaluation. At a follow-up appointment 1 week later, she reports that she had been previously tested for HIV, and it was negative. Physical examination does not reveal any external abnormalities of her genitalia. Her heart and lung sounds are normal on auscultation. Her vital signs show a blood pressure of 123/82 mm Hg, heart rate of 82/min, and a respiratory rate of 16/min. Of the following options, which is the next best step in patient management?
- A. Retest with HIV antigen/antibody test in 1 year
- B. Perform VDRL
- C. Repeat rapid HIV at this office check-up
- D. Perform monospot test
- E. Retest with 4th generation HIV antigen/antibody test in 2-4 weeks and again in 3 months (Correct Answer)
Viral diagnostics Explanation: ***Retest with 4th generation HIV antigen/antibody test in 2-4 weeks and again in 3 months***
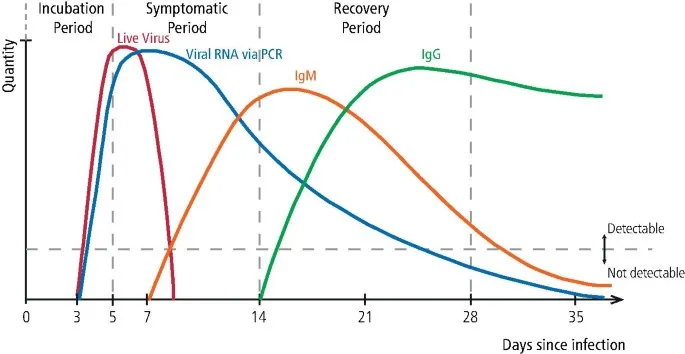
- This patient presents with symptoms highly suggestive of **acute retroviral syndrome** (primary HIV infection), including headaches, sore throat, diarrhea, fatigue, and low-grade fevers in the context of high-risk behavior (sex work and recreational drug use).
- A previous negative HIV test was likely obtained during the **window period**, when the infection was too recent to be detected. The **4th generation antigen/antibody immunoassay** detects both HIV antibodies and p24 antigen, reducing the window period to approximately **2-4 weeks** post-exposure.
- **Follow-up testing at 3 months** is recommended to definitively rule out HIV, as rare cases may have delayed seroconversion.
- Current **CDC guidelines** recommend 4th generation testing as the initial screening test for HIV.
*Retest with HIV antigen/antibody test in 1 year*
- Waiting a full year to retest would result in significant delay in diagnosis and treatment, potentially allowing disease progression to AIDS and increasing transmission risk.
- The patient's acute symptoms warrant more immediate re-evaluation within weeks, not months.
*Perform VDRL*
- **VDRL** (Venereal Disease Research Laboratory) tests for syphilis, not HIV.
- While co-infection with syphilis is possible in high-risk patients, it does not explain the constellation of symptoms typical of **acute retroviral syndrome**.
- Syphilis testing may be appropriate as part of comprehensive STI screening but is not the priority given the clinical presentation.
*Repeat rapid HIV at this office check-up*
- While **4th generation rapid tests** have improved sensitivity, repeating the test only **1 week** after the previous negative result and during the likely window period may still yield a false negative.
- The patient needs time for antibodies and/or antigen to develop to detectable levels (typically 2-4 weeks from exposure).
*Perform monospot test*
- A **monospot test** diagnoses **infectious mononucleosis** caused by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).
- While EBV can cause fatigue, sore throat, and low-grade fevers, the patient's high-risk sexual behavior, diarrhea, and acute presentation are more consistent with **acute HIV infection** than mononucleosis.
- EBV mononucleosis typically presents with prominent lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly, which are not mentioned here.
Viral diagnostics US Medical PG Question 6: A 45-year-old man visits the office with complaints of severe pain with urination for 5 days. In addition, he reports having burning discomfort and itchiness at the tip of his penis. He is also concerned regarding a yellow-colored urethral discharge that started a week ago. Before his symptoms began, he states that he had sexual intercourse with multiple partners at different parties organized by the hotel he was staying at. Physical examination shows edema and erythema concentrated around the urethral meatus accompanied by a mucopurulent discharge. Which of the following diagnostic tools will best aid in the identification of the causative agent for his symptoms?
- A. Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) (Correct Answer)
- B. Urethral biopsy
- C. Tzanck smear
- D. Leukocyte esterase dipstick test
- E. Gram stain
Viral diagnostics Explanation: ***Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs)***
- NAATs are the **most sensitive and specific diagnostic tools** for detecting common sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like **gonorrhea** and **chlamydia**, which present with urethral discharge, dysuria, and itching.
- They can identify the **genetic material** of the causative organisms directly from urine samples or urethral swabs, making them highly effective even with low bacterial loads.
*Urethral biopsy*
- A urethral biopsy is an **invasive procedure** generally reserved for investigating conditions like **strictures, tumors, or chronic inflammatory diseases** when other diagnostic methods are inconclusive.
- It is not a primary diagnostic tool for acute urethritis suspected to be an STI, as it carries risks and is unnecessary given the availability of less invasive options.
*Tzanck smear*
- The Tzanck smear is primarily used for diagnosing **herpes simplex virus (HSV) infections** by looking for multinucleated giant cells and intranuclear inclusions.
- While HSV can cause genital lesions, it typically does not present as a primary symptom of mucopurulent urethral discharge and dysuria without visible vesicles or ulcers, making it less likely in this scenario.
*Leukocyte esterase dipstick test*
- A leukocyte esterase dipstick test detects the presence of **white blood cells** in urine, indicating inflammation or infection in the urinary tract.
- While it can suggest urethritis, it is **not specific for the causative agent** and merely indicates inflammation, requiring further specific testing to identify the pathogen.
*Gram stain*
- A Gram stain of urethral discharge can rapidly identify Gram-negative intracellular diplococci suggestive of **gonorrhea** (Neisseria gonorrhoeae).
- However, its sensitivity for gonorrhea is lower than NAATs, especially in asymptomatic cases or for detecting other common causes of urethritis like **Chlamydia trachomatis**, which are not visible on Gram stain.
Viral diagnostics US Medical PG Question 7: Nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) of first-void urine confirms infection with Chlamydia trachomatis. Treatment with the appropriate pharmacotherapy is started. Which of the following health maintenance recommendations is most appropriate at this time?
- A. Take medication with food
- B. Avoid sun exposure
- C. Avoid drinking alcohol
- D. Avoid sexual activity for the next month (Correct Answer)
- E. Schedule an ophthalmology consultation
Viral diagnostics Explanation: ***Avoid sexual activity for the next month***
- **CDC guidelines** recommend abstinence from sexual activity until 7 days after treatment completion AND until all sexual partners have been treated and cured. The recommendation of "the next month" provides adequate time to ensure both conditions are met, as **partner notification**, testing, and treatment often takes several weeks.
- This is the **most important health maintenance recommendation** as preventing **reinfection** and further **transmission** is the primary public health concern, superseding medication-specific advice.
*Take medication with food*
- This recommendation is specific to certain antibiotics to reduce gastrointestinal upset or improve absorption, but it is not a universal health maintenance recommendation for all Chlamydia treatments (e.g., **azithromycin** can be taken with or without food; **doxycycline** should be taken with food to reduce GI upset, but not milk products).
- While relevant to **medication adherence**, it is not the most crucial health maintenance advice regarding preventing transmission or re-infection.
*Avoid sun exposure*
- This advice is primarily given for medications that cause **photosensitivity**, such as **doxycycline**, which is a common treatment for Chlamydia.
- However, it's not applicable to all Chlamydia treatments (e.g., **azithromycin**) and is not the most critical health recommendation in the context of preventing disease transmission.
*Avoid drinking alcohol*
- This is a general recommendation for many antibiotic treatments to prevent potential interactions or increased side effects, but it is not a specific contraindication for the primary antibiotics used for Chlamydia.
- **Metronidazole**, used for other STIs (e.g., trichomoniasis), has a strong interaction with alcohol. However, it's not the primary treatment for Chlamydia, making this recommendation less universally appropriate here.
*Schedule an ophthalmology consultation*
- While Chlamydia can cause **conjunctivitis** (ophthalmia neonatorum in newborns or adult inclusion conjunctivitis), it is not a typical complication requiring routine ophthalmology consultation unless specific **ocular symptoms** are present.
- This recommendation is not a standard health maintenance strategy for **uncomplicated Chlamydia infections**.
Viral diagnostics US Medical PG Question 8: A 17-year-old male comes to the physician because of painful genital sores, malaise, and fever for 3 days. He is sexually active with 3 female partners and does not use condoms consistently. His temperature is 38.3°C (101°F). Physical examination shows tender lymphadenopathy in the left inguinal region and multiple, punched-out ulcers over the penile shaft and glans. Microscopic examination of a smear from the ulcer is most likely to show which of the following?
- A. Bipolar-staining intracytoplasmic inclusions
- B. Eosinophilic intranuclear inclusions (Correct Answer)
- C. Eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions
- D. Basophilic intranuclear inclusions
- E. Basophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions
Viral diagnostics Explanation: ***Eosinophilic intranuclear inclusions***
- The patient's symptoms (painful genital sores, fever, malaise, tender lymphadenopathy, and punched-out ulcers) are highly suggestive of **herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection**, specifically HSV-2, which causes genital herpes.
- Microscopic examination of cells from HSV lesions often reveals **Cowdry type A intranuclear inclusions**, which are **eosinophilic** and represent viral replication within the nucleus, as well as **multinucleated giant cells**.
*Bipolar-staining intracytoplasmic inclusions*
- This description typically refers to the **safety pin appearance** of *Yersinia pestis* (the causative agent of plague) on Giemsa stain, which is a bacterial infection and has a completely different clinical presentation.
- This finding is not associated with genital ulcer disease.
*Eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions*
- While *eosinophilic inclusions* can be seen in some viral infections, they are typically **cytoplasmic** in diseases like **rabies** (Negri bodies) or some poxvirus infections, not HSV.
- HSV characteristically forms intranuclear inclusions.
*Basophilic intranuclear inclusions*
- **Basophilic intranuclear inclusions** are characteristic findings in infections caused by **cytomegalovirus (CMV)**, often described as an "owl's eye" appearance.
- CMV can cause genital ulcers but HSV is a more common cause of acute, painful, recurrent genital lesions and the inclusions are distinctly eosinophilic.
*Basophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions*
- **Basophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions** are seen in conditions such as **Chlamydia trachomatis infections** (e.g., in cells from conjunctivitis or cervical smears, known as elementary or reticulate bodies).
- While *Chlamydia* can cause genital ulcers (lymphogranuloma venereum), the inclusions are not intranuclear and the characteristic HSV inclusions are distinct.
Viral diagnostics US Medical PG Question 9: An investigator is processing a blood sample from a human subject. A reagent is added to the sample and the solution is heated to break the hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs. This solution is then cooled to allow artificial DNA primers in the solution to attach to the separated strands of the sample DNA molecules. An enzyme derived from the thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus is added and the solution is reheated. These steps are repeated multiple times until the aim of the test is achieved. The investigator most likely used which of the following laboratory procedures on the test sample?
- A. Northern blot
- B. Western blot
- C. Polymerase chain reaction (Correct Answer)
- D. Immunohistochemistry
- E. Fluorescence in-situ hybridization
Viral diagnostics Explanation: ***Polymerase chain reaction***
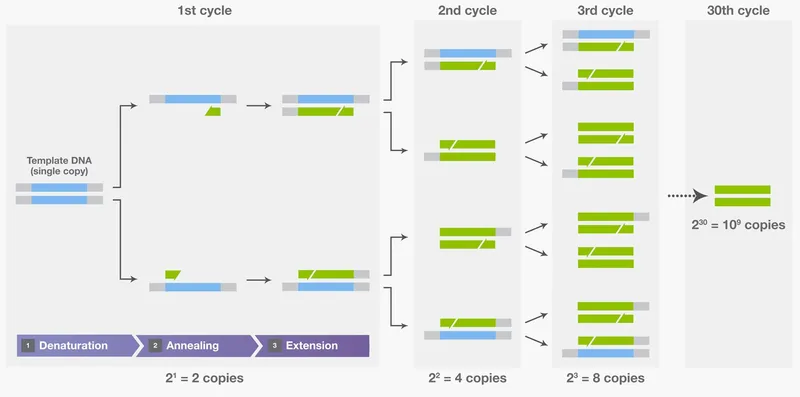
- The process described, including **denaturation** by heating, **annealing** of primers upon cooling, and **extension** by a heat-stable DNA polymerase (like from *Thermus aquaticus*), are the hallmark steps of **Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)**.
- PCR is used to **amplify specific DNA sequences** exponentially, making it possible to detect and analyze even minute amounts of genetic material.
*Northern blot*
- **Northern blot** is a laboratory technique used to detect specific **RNA molecules** among a mixture of RNA. It involves electrophoresis, transfer to a membrane, and hybridization with a probe.
- It does not involve repetitive heating, cooling, or the use of DNA primers and heat-stable polymerases for amplification.
*Western blot*
- **Western blot** is a widely used analytical technique in molecular biology and immunogenetics to detect specific **proteins** in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract.
- This method separates proteins by size using gel electrophoresis, transfers them to a membrane, and then detects the target protein using specific antibodies. It does not involve DNA denaturation or amplification.
*Immunohistochemistry*
- **Immunohistochemistry (IHC)** is a histological technique that uses the principle of specific antibody-antigen binding to **detect specific antigens (proteins) in cells or tissues**.
- It involves staining tissues with antibodies labeled with a chromogenic reporter or fluorophore to visualize the location and distribution of target proteins within preserved tissue sections.
*Fluorescence in-situ hybridization*
- **Fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH)** is a cytogenetic technique used to detect and **localize specific DNA or RNA sequences within cells or tissues** using fluorescent probes that bind to parts of the chromosome.
- While it involves hybridization, it is primarily for visualizing genetic material within its cellular context, not for amplifying DNA like PCR.
Viral diagnostics US Medical PG Question 10: A virology student is asked to identify a sample of virus. When subjected to a nonionic detergent, which disrupts lipid membranes, the virus was shown to lose infectivity. The student then purified the genetic material from the virus and subjected it to treatment with RNase, an enzyme that cleaves the phosphodiester linkages in the RNA backbone. A minute amount of the sample was then injected into a human cell line and was found to produce viral particles a few days later. Which of the following viruses was in the unknown sample?
- A. Togavirus
- B. Hepevirus
- C. Calicivirus
- D. Adenovirus
- E. Herpesvirus (Correct Answer)
Viral diagnostics Explanation: ***Herpesvirus***
- The loss of infectivity with nonionic detergents indicates the presence of a **lipid envelope**, a characteristic of herpesviruses.
- The genetic material survived **RNase treatment**, indicating it is **DNA** (not RNA), which is consistent with herpesviruses being DNA viruses.
- Under experimental conditions with **direct intracellular injection**, purified herpesvirus DNA can initiate viral replication by utilizing host cell transcription machinery, ultimately producing viral particles.
*Togavirus*
- Togaviruses are **enveloped RNA viruses**; they would lose infectivity with detergent treatment.
- However, their **RNA genome** would have been destroyed by RNase treatment, preventing any subsequent viral particle production.
*Hepevirus*
- Hepeviruses are **non-enveloped RNA viruses**; they would **not** lose infectivity with nonionic detergent, which contradicts the experimental observation.
- Additionally, their **RNA genome** would be destroyed by RNase, preventing viral replication.
*Calicivirus*
- Caliciviruses are **non-enveloped RNA viruses**, so they would not be inactivated by nonionic detergents.
- Their **RNA genome** would be susceptible to degradation by RNase, precluding viral production.
*Adenovirus*
- Adenoviruses are **non-enveloped DNA viruses**, meaning they would **not lose infectivity** when treated with nonionic detergent, which contradicts the first experimental result.
- Although they have a DNA genome that would survive RNase treatment, the lack of envelope rules them out.
More Viral diagnostics US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.