Rabies virus US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Rabies virus. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
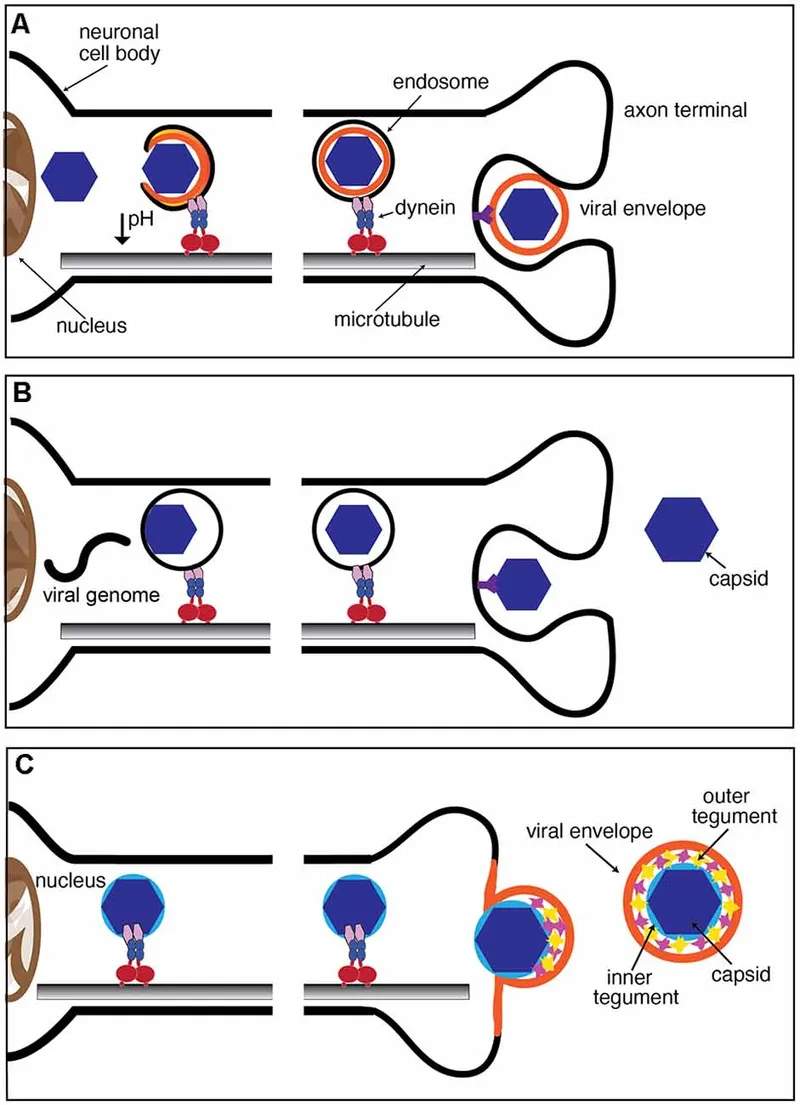
Rabies virus US Medical PG Question 1: An investigator is developing a drug that selectively inhibits the retrograde axonal transport of rabies virus towards the central nervous system. To achieve this effect, this drug must target which of the following?
- A. Dynein (Correct Answer)
- B. Tubulin
- C. Nidogen
- D. Kinesin
- E. Acetylcholine
Rabies virus Explanation: ***Dynein***
- **Dynein** is a microtubule-dependent motor protein responsible for **retrograde axonal transport**, moving cargo (like rabies virus) away from the axon terminals towards the cell body and ultimately the central nervous system.
- Inhibiting dynein would therefore prevent the **rabies virus** from traveling from the site of infection (e.g., muscle cell) to the central nervous system.
*Tubulin*
- **Tubulin** is the primary protein subunit that polymerizes to form **microtubules**, which serve as the tracks for axonal transport.
- Inhibiting tubulin polymerization would disrupt both **anterograde** and **retrograde transport** nonspecifically, leading to severe neurotoxicity rather than selective inhibition of rabies virus transport.
*Nidogen*
- **Nidogen** (also known as entactin) is a glycoprotein component of the **basal lamina**, an extracellular matrix structure.
- It plays a role in cell adhesion and tissue organization but is not directly involved in the intracellular motor processes of axonal transport.
*Kinesin*
- **Kinesin** is a microtubule-dependent motor protein primarily responsible for **anterograde axonal transport**, moving cargo from the cell body towards the axon terminals.
- Inhibiting kinesin would disrupt the outward movement of vesicles and organelles, but would not prevent the **inward retrograde transport** of the rabies virus.
*Acetylcholine*
- **Acetylcholine** is a neurotransmitter that plays a role in synaptic transmission in both the peripheral and central nervous systems.
- While rabies virus can affect neuronal function, acetylcholine itself is not a motor protein or a structural component directly involved in the physical process of **axonal transport**.
Rabies virus US Medical PG Question 2: If the genetic material were isolated and injected into the cytoplasm of a human cell, which of the following would produce viable, infectious virions?
- A. Lassa fever virus
- B. Rabies virus
- C. Rhinovirus (Correct Answer)
- D. Mumps virus
- E. Influenza virus
Rabies virus Explanation: ***Rhinovirus***
- **Rhinovirus** is a **positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus**. Its genetic material can directly serve as mRNA in the host cell cytoplasm, leading to immediate protein synthesis and viral replication without needing DNA intermediates or a nuclear phase.
- This direct translation allows for the production of viable, infectious virions upon cytoplasmic injection of the genetic material.
*Lassa fever virus*
- **Lassa fever virus** is an **ambisense RNA virus** and requires an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) to transcribe its genome into mRNA.
- This RdRp is packaged within the virion, meaning the injected genetic material alone is not sufficient to initiate replication without the viral proteins.
*Rabies virus*
- **Rabies virus** is a **negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus**. Its genome cannot directly act as mRNA.
- It requires a virion-associated **RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp)** to transcribe its negative-sense RNA into positive-sense mRNA, which is essential for protein synthesis.
*Mumps virus*
- **Mumps virus** is a **negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus** and, like rabies virus, cannot directly translate its genome into proteins.
- It also requires its own **virion-associated RNA-dependent RNA polymerase** to synthesize mRNA from its negative-sense genome.
*Influenza virus*
- **Influenza virus** is a **negative-sense segmented RNA virus**. Its replication cycle involves the nucleus, where its RNA genome is transcribed into mRNA.
- This process requires the viral **RNA-dependent RNA polymerase**, which is brought into the cell by the virion, and interaction with host nuclear machinery.
Rabies virus US Medical PG Question 3: A 3-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her parents because of a barking cough, a raspy voice, and noisy breathing for the last 3 days. Five days ago, she had a low-grade fever and runny nose. She attends daycare. Her immunizations are up-to-date. Her temperature is 37.8°C (100°F) and respirations are 33/min. Physical examination shows supraclavicular retractions. There is a high-pitched sound present on inspiration. Examination of the throat shows erythema without exudates. Which of the following is the most likely location of the anatomic narrowing causing this patient's symptoms?
- A. Bronchioles
- B. Pharynx
- C. Subglottic larynx (Correct Answer)
- D. Distal trachea
- E. Epiglottis
Rabies virus Explanation: ***Subglottic larynx***
- The patient's symptoms of **barking cough**, **raspy voice**, **stridor** (high-pitched inspiratory sound), and **supraclavicular retractions** are classic for **croup** (laryngotracheobronchitis), which is caused by inflammation and narrowing of the subglottic region of the larynx.
- The preceding low-grade fever and runny nose are typical of a viral upper respiratory infection, which commonly precedes croup.
*Bronchioles*
- Narrowing in the bronchioles typically causes **wheezing** (a high-pitched whistling sound on expiration) and **respiratory distress**, often seen in conditions like **bronchiolitis** or **asthma**.
- A barking cough and raspy voice are not characteristic symptoms of bronchiolar obstruction.
*Pharynx*
- Inflammation and narrowing of the pharynx primarily cause **sore throat**, **difficulty swallowing** (dysphagia), and sometimes **muffled voice**.
- It would not typically lead to a barking cough, stridor, or severe inspiratory distress.
*Distal trachea*
- While tracheal narrowing can cause stridor, the classic **barking cough** and **hoarseness** (raspy voice) are more specifically localized to the laryngeal area.
- Obstruction in the distal trachea would be less likely to affect voice quality as significantly as subglottic narrowing.
*Epiglottis*
- **Epiglottitis** presents as a rapidly progressive, life-threatening condition with **high fever**, **dysphagia**, **drooling**, and a **muffled "hot potato" voice**.
- The patient would typically appear toxic and prefer to sit in the **tripod position**, which is not described in this case, and her symptoms are less acute.
Rabies virus US Medical PG Question 4: A 20-year-old man is brought to the emergency department for evaluation of an animal bite. He was hiking earlier that day when he was bitten by a raccoon. He says the attack was unprovoked and the animal ran away after the encounter. He was bitten by a stray dog when he was 11 years old and received postexposure prophylaxis for rabies at that time. His immunizations are up-to-date. His immunization record shows he received 3 doses of diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis vaccine as a child and a tetanus-diphtheria-acellular pertussis vaccination at the age of 16. He is in no apparent distress. His temperature is 98.4°F (36.9°C), pulse is 72/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 124/75 mm Hg. He has a wound on his left lower extremity with actively bleeding puncture sites. The wound is thoroughly irrigated with normal saline and cleansed with antiseptic and a bandage is applied. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Rabies immunoglobulin and vaccine
- B. No action needed
- C. Rabies vaccination (Correct Answer)
- D. Tetanus booster, rabies immunoglobulin
- E. Tetanus booster
Rabies virus Explanation: ***Rabies vaccination***
- This patient has a history of receiving **post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP)** for rabies 9 years ago, meaning he has been previously immunized. For individuals with prior rabies vaccination, treatment for a new exposure consists solely of a **rabies vaccine** series.
- **Rabies immunoglobulin (RIG)** is not indicated for previously vaccinated individuals because their immune system is primed to produce antibodies rapidly upon re-exposure.
*Rabies immunoglobulin and vaccine*
- **Rabies immunoglobulin (RIG)** is administered as part of post-exposure prophylaxis for **unvaccinated individuals** to provide immediate passive immunity.
- Since this patient has a history of rabies PEP, he is considered previously vaccinated, making RIG unnecessary and potentially interfering with the active immune response.
*No action needed*
- An **unprovoked attack by a raccoon** is considered a high-risk exposure for rabies, requiring intervention even in previously vaccinated individuals.
- Despite prior vaccination, a **booster series of rabies vaccine** is indicated to rapidly reactivate the immune response and ensure protection.
*Tetanus booster, rabies immunoglobulin*
- The patient's tetanus immunization history (Tdap at age 16) indicates he is **up-to-date on tetanus** and would not require a booster for this wound unless more than 5 years had passed since the last dose and the wound was clean.
- As explained, **rabies immunoglobulin (RIG)** is not given to previously vaccinated individuals.
*Tetanus booster*
- The patient received a Tdap booster at age 16, and given he is 20, his tetanus immunization is **still considered current** (up to 10 years for clean wounds, 5 years for dirty wounds).
- While a tetanus booster might be considered depending on the exact timing of his last dose and wound characteristics, it is **not the primary or sole action needed** given the high-risk rabies exposure.
Rabies virus US Medical PG Question 5: A 50-year-old man comes to the emergency department for evaluation of right-sided facial weakness that he noticed after waking up. One month ago, he also experienced right-sided neck pain and headache that began after returning from a hunting trip to New Hampshire the week before. He took ibuprofen to relieve symptoms, which subsided a week later. He has a 5-year history of hypertension controlled with drug therapy. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 35 years and he drinks two beers daily. His vital signs are within the normal range. Physical examination shows right-sided drooping of the upper and lower half of the face. The patient has difficulties smiling and he is unable to close his right eye. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in diagnosis?
- A. Noncontrast CT
- B. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis
- C. Western blot
- D. Polymerase chain reaction of the facial skin
- E. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Correct Answer)
Rabies virus Explanation: ***Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay***
- The patient's presentation with **right-sided facial weakness affecting both upper and lower halves of the face**, along with a history of **neck pain and headache after a hunting trip to New Hampshire** (an endemic area for Lyme disease), strongly suggests **Lyme disease-associated Bell's palsy**.
- An **ELISA** is the appropriate initial test for **Lyme disease screening**, detecting antibodies against *Borrelia burgdorferi*.
*Noncontrast CT*
- A **noncontrast CT scan of the brain** is primarily used to rule out acute intracranial pathologies like **hemorrhage** or **large strokes**.
- In this case, the isolated facial paralysis without other focal neurological deficits or signs of acute stroke makes a CT less immediately relevant as the first diagnostic step.
*Cerebrospinal fluid analysis*
- **CSF analysis** would be considered if there were signs of **meningitis** or **encephalitis**, or if Lyme disease was strongly suspected but initial serological tests were negative.
- It is not the most appropriate initial diagnostic step for isolated facial palsy.
*Western blot*
- A **Western blot** is used as a **confirmatory test** for Lyme disease, typically performed after a positive or indeterminate **ELISA result**.
- It differentiates specific antibodies, but it is not the initial screening test.
*Polymerase chain reaction of the facial skin*
- **PCR of facial skin** is not a standard diagnostic test for facial palsy or Lyme disease, as the disease is systemic and not localized to a skin lesion in this context.
- **Skin biopsy PCR** might be used to confirm an erythema migrans rash, which is not present here.
Rabies virus US Medical PG Question 6: A 24-year-old college student presents to student health with 2 days of developing a sore throat, runny nose, and a cough that started today. He states that he has been getting mild fevers which began yesterday. On exam, his temperature is 102.0°F (38.9°C), blood pressure is 135/76 mmHg, pulse is 95/min, and respirations are 12/min. His physician recommends over-the-counter cold medications and reassures him that his symptoms are due to a viral infection that is self-limited. Which of the following best describes the most likely cause of his illness?
- A. Nonenveloped dsRNA virus
- B. Enveloped (+) ssRNA virus (Correct Answer)
- C. Nonsegmented, enveloped (-) ssRNA virus
- D. Segmented, enveloped (-) ssRNA
- E. Nonenveloped dsDNA virus
Rabies virus Explanation: ***Enveloped (+) ssRNA virus***
- The symptoms of **sore throat**, **runny nose**, **cough**, and **mild fevers** are characteristic of the **common cold**.
- While **rhinoviruses** (nonenveloped picornaviruses) are the most common cause overall, **coronaviruses** are **enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses** that frequently cause the common cold, accounting for approximately 15-20% of cases.
- Among the given viral classifications, **coronaviruses** best match this presentation of a self-limited upper respiratory infection in an otherwise healthy adult.
*Nonenveloped dsRNA virus*
- This describes **Rotavirus**, which causes **gastroenteritis** with severe diarrhea and vomiting, not upper respiratory symptoms.
- The patient's respiratory symptoms and lack of gastrointestinal complaints rule out this viral type.
*Nonsegmented, enveloped (-) ssRNA virus*
- This describes viruses like **Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)** or **parainfluenza virus**.
- While these cause respiratory infections, they more commonly cause **bronchiolitis** in infants and young children, or **croup** in children.
- In adults, they typically cause more severe lower respiratory symptoms than the mild cold presented here.
*Segmented, enveloped (-) ssRNA*
- This describes **influenza viruses**, which typically present with **abrupt onset**, **high fevers**, **severe myalgias**, **headache**, and **profound fatigue**.
- Influenza is generally **more severe** than the mild, self-limited illness described here.
- The gradual onset over 2 days and reassurance of self-limited disease argue against influenza.
*Nonenveloped dsDNA virus*
- This describes **adenoviruses**, which can cause upper respiratory infections, **conjunctivitis**, **pharyngitis**, and sometimes **gastroenteritis**.
- While adenoviruses can cause cold-like symptoms, the typical mild common cold presentation is more consistent with **coronaviruses** among the enveloped RNA virus options.
Rabies virus US Medical PG Question 7: A parent presents to her pediatrician requesting information about immunizations for her newborn. The pediatrician explains about basic principles of immunization, types of vaccines, possible adverse effects, and the immunization schedule. Regarding how immunizations work, the pediatrician explains that there are mainly 2 types of vaccines. The first type of vaccine provides stronger and more lasting immunity as it induces both cellular and humoral immune responses. The second type of vaccine produces mainly a humoral response only, and its overall efficacy is less as compared to the first type. Which of the following vaccines belongs to the first type of vaccine that the pediatrician is talking about?
- A. Hepatitis A vaccine
- B. Polio vaccine (Salk)
- C. Yellow fever vaccine (Correct Answer)
- D. Rabies vaccine
- E. Hepatitis B vaccine
Rabies virus Explanation: ***Yellow fever vaccine***
- The Yellow fever vaccine is a **live-attenuated vaccine**, which mimics natural infection and effectively stimulates both **cellular and humoral immune responses**, leading to strong and long-lasting immunity.
- Live-attenuated vaccines contain a weakened form of the pathogen, allowing for replication within the host and robust immune system activation.
*Hepatitis A vaccine*
- The Hepatitis A vaccine is an **inactivated vaccine**, which primarily induces a **humoral (antibody-mediated) immune response**.
- Inactivated vaccines generally do not stimulate a strong cellular immune response and often require booster doses to maintain protective immunity.
*Polio vaccine (Salk)*
- The Salk polio vaccine is an **inactivated polio vaccine (IPV)**, meaning it contains killed viral particles.
- As an inactivated vaccine, it mainly elicits a **humoral immune response** producing circulating antibodies but less mucosal or cellular immunity.
*Rabies vaccine*
- The Rabies vaccine is an **inactivated vaccine** given after exposure or for pre-exposure prophylaxis.
- It primarily induces a **humoral antibody response** rather than a strong cellular immune response.
*Hepatitis B vaccine*
- The Hepatitis B vaccine is a **recombinant vaccine**, containing only a portion of the viral antigen (HBsAg).
- This type of vaccine primarily stimulates a **humoral immune response** leading to antibody production, which is effective but does not typically induce a strong cellular response like live vaccines.
Rabies virus US Medical PG Question 8: A 13-year-old boy is brought to a physician with severe fevers and headaches for 3 days. The pain is constant and mainly behind the eyes. He has myalgias, nausea, vomiting, and a rash for one day. Last week, during an academic winter break, he traveled on a tour with his family to several countries, including Brazil, Panama, and Peru. They spent many evenings outdoors without any protection against insect bites. There is no history of contact with pets, serious illness, or use of medications. The temperature is 40.0℃ (104.0℉); the pulse is 110/min; the respiratory rate is 18/min, and the blood pressure is 110/60 mm Hg. A maculopapular rash is seen over the trunk and extremities. Several tender lymph nodes are palpated in the neck on both sides. A peripheral blood smear shows no organisms. Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient’s presentation?
- A. Chagas disease
- B. Zika virus
- C. Babesiosis
- D. Malaria
- E. Dengue fever (Correct Answer)
Rabies virus Explanation: ***Dengue fever***
- This patient's symptoms (fever, **retro-orbital headache**, myalgias, nausea, vomiting, rash, and travel history to endemic areas like **Brazil, Panama, and Peru**) are classic for dengue fever. The **high fever (40°C)** and rash are also highly suggestive.
- Exposure to mosquito bites in tropical regions, typical of travel during an academic break, is a common mode of transmission for this **flavivirus**.
*Chagas disease*
- Chagas disease, caused by **Trypanosoma cruzi**, is typically transmitted by the **reduviid bug** (kissing bug).
- Acute symptoms can include **fever**, **Romana's sign** (unilateral periorbital swelling), and sometimes a chagoma, but the widespread **maculopapular rash** and severe retro-orbital headache are less characteristic.
*Zika virus*
- Zika virus infection can present with **fever**, **rash**, **arthralgia**, and **conjunctivitis**.
- While the travel history fits, the **severe retro-orbital headache**, high fever, and myalgias are more prominent in dengue fever; Zika symptoms are generally milder in adults.
*Babesiosis*
- Babesiosis is a **tick-borne** illness caused by **Babesia parasites**, often presenting with **fever**, **fatigue**, chills, and **hemolytic anemia**.
- There is no mention of tick exposure, and the characteristic rash and retro-orbital headache are not typical features of babesiosis.
*Malaria*
- Malaria, caused by **Plasmodium parasites** transmitted by **Anopheles mosquitoes**, presents with cyclical fevers, chills, sweats, and fatigue.
- While the travel history to endemic areas is relevant, the **retro-orbital headache** and **maculopapular rash** as described are not typical for uncomplicated malaria; malaria is also detected on a peripheral blood smear, which was negative here.
Rabies virus US Medical PG Question 9: A scientist is studying the influenza A virus. He focuses on two strains – one from humans (H7N1) and one from horses (H3N8). He takes cells from chickens and coinfects these cells with both influenza strains. From these chicken cells, the scientist isolates a new strain and finds that this new strain can infect human cells. He further characterizes the new strain’s hemagglutinin and neuraminidase description as H7N8. What term best describes the process that underlies these experimental results?
- A. Transduction
- B. Antigenic drift
- C. Transformation
- D. Conjugation
- E. Antigenic shift (Correct Answer)
Rabies virus Explanation: ***Antigenic shift***
- **Antigenic shift** in influenza viruses refers to the process where two different influenza strains **coinfect** the same host cell, leading to a **reassortment** of their segmented genomes.
- This reassortment creates a novel viral strain with a new combination of hemagglutinin (H) and neuraminidase (N) antigens (e.g., H7N1 + H3N8 → H7N8), which can lead to pandemics.
*Transduction*
- **Transduction** is a process where foreign DNA is introduced into a cell by a virus or viral vector, primarily seen in bacteria.
- It involves the transfer of genetic material via **bacteriophages** and does not describe the reassortment of influenza virus segments.
*Antigenic drift*
- **Antigenic drift** involves small, gradual changes in the H and N antigens of influenza viruses due to **point mutations** during replication.
- These slow mutations lead to seasonal epidemics, but not the creation of a completely new subtype as described.
*Transformation*
- **Transformation** is the process by which a cell takes up naked DNA from its environment, incorporating it into its own genome.
- This mechanism is common in bacteria for acquiring new genetic traits and is not applicable to the reassortment of viral segments within a coinfected host cell.
*Conjugation*
- **Conjugation** is a process of genetic material transfer between bacteria through direct cell-to-cell contact, typically via a **pilus**.
- This mechanism is distinct from viral genetic reassortment and does not involve the coinfection of a host cell by different viral strains.
Rabies virus US Medical PG Question 10: A 15-year-old girl presents to her primary care physician with her parents. She is complaining of fever and a sore throat for the past 4 days. She was born at 39 weeks gestation via spontaneous vaginal delivery and is up to date on all vaccines and is meeting all developmental milestones. Her boyfriend at school has the same symptoms including fever and sore throat. Today, her heart rate is 90/min, respiratory rate is 17/min, blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg, and temperature is 38.2°C (100.8°F). Examination revealed cervical lymphadenopathy and mild hepatosplenomegaly. Oral exam reveals focal tonsillar exudate. A monospot test is positive. This patient is most likely infected with which of the following viruses?
- A. Varicella virus
- B. Cytomegalovirus
- C. Herpes simplex virus
- D. Epstein-Barr virus (Correct Answer)
- E. Variola virus
Rabies virus Explanation: ***Epstein-Barr virus***
- The symptoms of fever, sore throat, **cervical lymphadenopathy**, **hepatosplenomegaly**, and **tonsillar exudates** in an adolescent, coupled with a **positive Monospot test**, are highly characteristic of **infectious mononucleosis** caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
- The positive Monospot test detects **heterophile antibodies**, which are a hallmark of acute EBV infection and essentially confirms the diagnosis
*Varicella virus*
- Varicella virus (chickenpox) typically presents with a **pruritic vesicular rash** that progresses through different stages (macules → papules → vesicles → crusts), which is not described in this patient
- While fever can be present, the distinctive rash, rather than lymphadenopathy and tonsillar exudates, is the defining feature
*Cytomegalovirus*
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV) can cause a **mononucleosis-like syndrome** with similar clinical features
- However, CMV mononucleosis typically presents with **negative heterophile antibodies** (negative Monospot test), which distinguishes it from EBV
- This patient's positive Monospot test makes CMV unlikely as the primary cause
*Herpes simplex virus*
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV) infections typically cause **oral ulcers** (cold sores), **gingivostomatitis**, or **genital lesions**
- While HSV can cause fever and sore throat, it would not typically lead to the diffuse lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and positive Monospot test seen in this case
*Variola virus*
- Variola virus (smallpox) is characterized by a **distinctive rash** of deep-seated pustules that begin on the face and extremities, often with systemic symptoms like high fever and malaise
- Smallpox has been **eradicated worldwide since 1980**, making this diagnosis impossible in contemporary practice
- The presentation is distinctly different from the symptoms described, especially with the absence of the characteristic rash
More Rabies virus US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.