Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8). These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) US Medical PG Question 1: A father brings in his 7-year-old twin sons because they have a diffuse rash. They have several papules, vesicles, pustules, and crusts on their scalps, torso, and limbs. The skin lesions are pruritic. Other than that, the boys appear to be well. The father reports that several children in school have a similar rash. The family recently returned from a beach vacation but have not traveled internationally. Both boys have stable vital signs within normal limits. What is the most common complication of the infection the boys appear to have?
- A. Encephalitis
- B. Hepatitis
- C. Bacterial superinfection of skin lesions (Correct Answer)
- D. Cerebellar ataxia
- E. Pneumonia
Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) Explanation: ***Bacterial superinfection of skin lesions***
- The description of a **pruritic rash** with **papules, vesicles, pustules, and crusts** in various stages of healing, especially in young children with school exposure, is classic for **varicella (chickenpox)**.
- The most common complication of chickenpox is **secondary bacterial infection** of the skin lesions, often caused by *Staphylococcus aureus* or *Streptococcus pyogenes*, due to scratching compromising the skin barrier.
*Encephalitis*
- **Encephalitis** is a rare but severe neurological complication of varicella, occurring in less than 0.1% of cases.
- While possible, it is far less common than bacterial superinfection of the skin.
*Hepatitis*
- **Hepatitis** can occur with varicella, particularly in immunocompromised individuals or adults, but it is rare and not considered the most common complication in healthy children.
- The symptoms described do not suggest liver involvement.
*Cerebellar ataxia*
- **Cerebellar ataxia** is a known neurological complication of varicella, typically occurring acutely after the rash resolves.
- While it is a recognized complication, it is less common than bacterial skin infections and is usually self-limiting.
*Pneumonia*
- **Varicella pneumonia** is a serious complication, especially in adults, immunocompromised individuals, and neonates.
- In healthy children, however, it is much less common than bacterial superinfection of the skin lesions.
Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) US Medical PG Question 2: A 65-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for a rash. He states that for the past several days he has felt burning and itching around his eye. Yesterday, he noticed that a rash had formed. Review of systems is notable for mild diarrhea for the past week. The patient has a past medical history of diabetes, asthma, seasonal allergies, and hypertension. He is not currently taking any medications. Physical exam is notable for a vesicular rash surrounding the orbit. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
- A. Acyclovir (Correct Answer)
- B. Removal of gluten containing products from the diet
- C. Topical steroids
- D. Topical mupirocin
- E. Oral steroids
Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) Explanation: ***Acyclovir***
- The patient's symptoms of **burning, itching**, and a **vesicular rash around the orbit** are highly suggestive of **herpes zoster ophthalmicus**, a reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus (shingles).
- **Antiviral medications** like acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir are the mainstay of treatment and should be initiated promptly (within 72 hours of rash onset) to reduce the severity and duration of the rash, prevent new lesions, and decrease the risk of post-herpetic neuralgia and ocular complications.
*Removal of gluten-containing products from the diet*
- This intervention is appropriate for **dermatitis herpetiformis**, an intensely pruritic, vesicular rash associated with **celiac disease**.
- While the patient has mild diarrhea, his rash distribution and the characteristic burning/itching are inconsistent with dermatitis herpetiformis, and there is no evidence of underlying celiac disease.
*Topical steroids*
- Topical steroids are used for various inflammatory skin conditions but are **contraindicated** in viral infections like herpes zoster, especially around the eye, as they can worsen ocular involvement and viral replication.
- They would not address the underlying viral etiology and could delay healing or increase complications.
*Topical mupirocin*
- **Mupirocin is an antibiotic** used for bacterial skin infections, such as impetigo or secondary bacterial infections of skin lesions.
- The primary rash described is viral (vesicular), and there is no mention of signs of bacterial superinfection, such as pustules, purulent discharge, or increasing redness and warmth.
*Oral steroids*
- Oral steroids might be considered for severe cases of post-herpetic neuralgia or to reduce inflammation in specific circumstances, but they are generally **not recommended as primary therapy** for acute herpes zoster due to limited evidence of benefit and potential for adverse effects.
- They also do not treat the underlying viral cause and can potentially suppress the immune system, which is generally undesirable in a viral infection.
Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) US Medical PG Question 3: A 15-month-old girl is brought to the physician because of the sudden appearance of a rash on her trunk that started 6 hours ago and subsequently spread to her extremities. Four days ago, she was taken to the emergency department because of a high fever and vomiting. She was treated with acetaminophen and discharged the next day. The fever persisted for several days and abated just prior to appearance of the rash. Physical examination shows a rose-colored, blanching, maculopapular rash, and postauricular lymphadenopathy. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Roseola infantum (Correct Answer)
- B. Rubella
- C. Erythema infectiosum
- D. Drug allergy
- E. Nonbullous impetigo
Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) Explanation: ***Roseola infantum***
- The classic presentation includes several days of **high fever** that **abruptly resolves**, followed by the appearance of a **rose-colored, blanching maculopapular rash**, primarily on the trunk.
- This condition is most common in infants and young children, often accompanied by **postauricular lymphadenopathy**.
*Rubella*
- While rubella presents with a **maculopapular rash** and **postauricular lymphadenopathy**, the rash typically appears *with* or *shortly after* the fever, not after the fever has completely abated.
- The fever in rubella is usually milder than the high fever seen in roseola.
*Erythema infectiosum*
- This condition, also known as fifth disease, typically presents with a **"slapped cheek" rash** on the face, followed by a lacy rash on the extremities, often without the distinct pattern of high fever followed by rash offset.
- The fever is often low-grade or absent, unlike the high fever experienced by the patient.
*Drug allergy*
- A drug allergy could cause a rash, but it's less likely to selectively manifest several days after acetaminophen administration once the fever has disappeared, especially without other allergic symptoms like **pruritus** or **urticaria**.
- The precise sequence of high fever followed by rash resolution is not typical for most drug-induced rashes.
*Nonbullous impetigo*
- This is a **bacterial skin infection** characterized by **honey-crusted lesions**, most commonly around the nose and mouth, not a generalized maculopapular rash.
- It is typically not preceded by a systemic illness with high fever and vomiting in this manner.
Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) US Medical PG Question 4: A 12-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of fever, malaise, and a painful, itchy rash on the right shoulder for 2 weeks. The patient's mother says the boy's condition has worsened over the past 4 days. He has a history of atopic dermatitis. He has lived with his mother at several public shelters since she separated from his physically abusive father 2 months ago. His immunizations are up-to-date. There is cervical lymphadenopathy. Laboratory studies show no abnormalities. A photograph of the rash is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Bed bug bites
- B. Shingles
- C. Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- D. Eczema herpeticum (Correct Answer)
- E. Nonbullous impetigo
Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) Explanation: ***Eczema herpeticum***
- This diagnosis is highly likely given the patient's history of **atopic dermatitis**, which predisposes to widespread viral infections like **herpes simplex virus (HSV)**.
- The rash presents as **painful, itchy vesicles and punched-out erosions** over the existing eczematous skin, accompanied by fever, malaise, and cervical lymphadenopathy.
*Bed bug bites*
- Bed bug bites typically appear as **pruritic, erythematous papules or wheals** arranged in a linear pattern ("breakfast, lunch, and dinner") and are not associated with fever, malaise, or lymphadenopathy.
- While living in public shelters could increase exposure, the disseminated vesicular and erosive nature of this rash is inconsistent with bed bug bites.
*Shingles*
- Shingles (herpes zoster) presents as a **unilateral, dermatomal vesicular rash**, which is not seen here as the rash is widespread and not confined to a single dermatome.
- Although caused by a herpesvirus, the distribution and appearance differ significantly from the presented image.
*Stevens-Johnson syndrome*
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) is a severe mucocutaneous reaction characterized by **widespread epidermal necrosis, targetoid lesions, and mucositis**, often triggered by medications.
- The image does not show typical targetoid lesions or extensive skin detachment characteristic of SJS.
*Nonbullous impetigo*
- Nonbullous impetigo presents with **honey-colored crusted lesions** typically around the nose and mouth, often starting as small vesicles.
- While it can be itchy, the extensive, disseminated, and primarily vesicular/erosive nature of the rash, along with systemic symptoms like fever and malaise, is not typical for impetigo.
Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) US Medical PG Question 5: A 63-year-old man presents to his primary care physician because he has been having headaches and hearing loss. In addition, he says that he has been having difficulty opening his jaw to eat and recurrent middle ear infections. Physical exam reveals enlarged neck lymph nodes and a mass in the nasopharynx. Biopsy of the mass reveals undifferentiated squamous epithelial cells. The organism that is most likely associated with this patient's disease is also associated with which of the following disorders?
- A. Kaposi sarcoma
- B. Hepatocellular carcinoma
- C. Adult T-cell lymphoma
- D. Burkitt lymphoma (Correct Answer)
- E. Vulvar carcinoma
Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) Explanation: ***Burkitt lymphoma***
- The patient's symptoms (headaches, hearing loss, difficulty opening jaw, recurrent middle ear infections, nasopharyngeal mass, enlarged neck lymph nodes) and biopsy results (undifferentiated squamous epithelial cells) point to **nasopharyngeal carcinoma**.
- **Nasopharyngeal carcinoma** is strongly associated with the **Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)**. EBV is also a causative agent in **Burkitt lymphoma**.
*Kaposi sarcoma*
- **Kaposi sarcoma** is caused by **Human Herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8)**, not EBV.
- It typically presents as vascular skin lesions and can affect visceral organs, differing from the nasopharyngeal carcinoma described.
*Hepatocellular carcinoma*
- **Hepatocellular carcinoma** is primarily associated with **Hepatitis B virus (HBV)** and **Hepatitis C virus (HCV)** infection, as well as cirrhosis from other causes.
- There is no significant association between EBV and hepatocellular carcinoma.
*Adult T-cell lymphoma*
- **Adult T-cell lymphoma** is caused by the **Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1)**.
- This is a retrovirus distinct from EBV.
*Vulvar carcinoma*
- **Vulvar carcinoma** is most frequently associated with **Human Papillomavirus (HPV)** infection, especially high-risk strains like HPV 16 and 18.
- It is not typically linked to EBV.
Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) US Medical PG Question 6: A 67-year-old man presents to the emergency department with confusion. The patient is generally healthy, but his wife noticed him becoming progressively more confused as the day went on. The patient is not currently taking any medications and has no recent falls or trauma. His temperature is 102°F (38.9°C), blood pressure is 126/64 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, respirations are 17/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Physical exam is notable for a confused man who cannot participate in a neurological exam secondary to his confusion. No symptoms are elicited with flexion of the neck and jolt accentuation of headache is negative. Initial laboratory values are unremarkable and the patient's chest radiograph and urinalysis are within normal limits. An initial CT scan of the head is unremarkable. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
- A. CT angiogram of the head and neck
- B. Vancomycin, ceftriaxone, ampicillin, and dexamethasone
- C. Acyclovir (Correct Answer)
- D. PCR of the cerebrospinal fluid
- E. MRI of the head
Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) Explanation: ***Acyclovir***
- This patient presents with **acute confusion and fever** without an obvious infectious source, negative meningeal signs, and normal initial imaging, highly suggestive of **herpes simplex encephalitis (HSE)**.
- HSE is a **medical emergency** with high mortality (70-80%) if untreated, but mortality drops to 20-30% with early acyclovir therapy.
- **Empiric acyclovir must be started immediately** upon clinical suspicion of HSE, **without waiting for diagnostic confirmation**.
- Standard management includes obtaining CSF for PCR **concurrently** with starting acyclovir, but treatment should never be delayed for diagnostic testing.
- The best next step in **management** is initiating acyclovir; CSF PCR is obtained for confirmation but does not delay treatment.
*PCR of the cerebrospinal fluid*
- **CSF PCR for HSV** is the gold standard **diagnostic test** for HSE with high sensitivity (96%) and specificity (99%).
- While lumbar puncture should be performed to obtain CSF for PCR, this is a **diagnostic step** that should be done **concurrently** with starting acyclovir, not instead of it.
- The question asks for best next step in **management**, not diagnosis—acyclovir therapy takes precedence.
- Delaying acyclovir while awaiting diagnostic confirmation significantly increases morbidity and mortality.
*Vancomycin, ceftriaxone, ampicillin, and dexamethasone*
- This broad-spectrum antibiotic regimen is empiric therapy for **bacterial meningitis** and should be considered in patients with fever and altered mental status.
- However, the **absence of meningeal signs** (negative nuchal rigidity, negative jolt accentuation) makes bacterial meningitis less likely.
- In practice, when HSE is suspected but bacterial meningitis cannot be excluded, both antimicrobial regimens may be initiated empirically, but the primary concern here is HSE given the clinical presentation.
*MRI of the head*
- **MRI with FLAIR sequences** is highly sensitive for HSE and typically shows **temporal lobe involvement** (especially medial temporal lobes).
- However, MRI findings may be **normal early in the disease course** (first 48-72 hours).
- MRI is useful for supporting the diagnosis but should **not delay empiric acyclovir therapy**.
- Obtaining MRI before treatment would be inappropriate given the time-sensitive nature of HSE.
*CT angiogram of the head and neck*
- CT angiography evaluates vascular structures and is indicated for suspected **stroke, aneurysm, or vascular dissection**.
- This patient lacks focal neurological deficits, signs of acute stroke, or vascular risk factors that would prioritize vascular imaging.
- The presentation with fever and diffuse encephalopathy points toward an infectious/inflammatory process rather than a vascular etiology.
Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) US Medical PG Question 7: A 17-year-old male comes to the physician because of painful genital sores, malaise, and fever for 3 days. He is sexually active with 3 female partners and does not use condoms consistently. His temperature is 38.3°C (101°F). Physical examination shows tender lymphadenopathy in the left inguinal region and multiple, punched-out ulcers over the penile shaft and glans. Microscopic examination of a smear from the ulcer is most likely to show which of the following?
- A. Bipolar-staining intracytoplasmic inclusions
- B. Eosinophilic intranuclear inclusions (Correct Answer)
- C. Eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions
- D. Basophilic intranuclear inclusions
- E. Basophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions
Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) Explanation: ***Eosinophilic intranuclear inclusions***
- The patient's symptoms (painful genital sores, fever, malaise, tender lymphadenopathy, and punched-out ulcers) are highly suggestive of **herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection**, specifically HSV-2, which causes genital herpes.
- Microscopic examination of cells from HSV lesions often reveals **Cowdry type A intranuclear inclusions**, which are **eosinophilic** and represent viral replication within the nucleus, as well as **multinucleated giant cells**.
*Bipolar-staining intracytoplasmic inclusions*
- This description typically refers to the **safety pin appearance** of *Yersinia pestis* (the causative agent of plague) on Giemsa stain, which is a bacterial infection and has a completely different clinical presentation.
- This finding is not associated with genital ulcer disease.
*Eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions*
- While *eosinophilic inclusions* can be seen in some viral infections, they are typically **cytoplasmic** in diseases like **rabies** (Negri bodies) or some poxvirus infections, not HSV.
- HSV characteristically forms intranuclear inclusions.
*Basophilic intranuclear inclusions*
- **Basophilic intranuclear inclusions** are characteristic findings in infections caused by **cytomegalovirus (CMV)**, often described as an "owl's eye" appearance.
- CMV can cause genital ulcers but HSV is a more common cause of acute, painful, recurrent genital lesions and the inclusions are distinctly eosinophilic.
*Basophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions*
- **Basophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions** are seen in conditions such as **Chlamydia trachomatis infections** (e.g., in cells from conjunctivitis or cervical smears, known as elementary or reticulate bodies).
- While *Chlamydia* can cause genital ulcers (lymphogranuloma venereum), the inclusions are not intranuclear and the characteristic HSV inclusions are distinct.
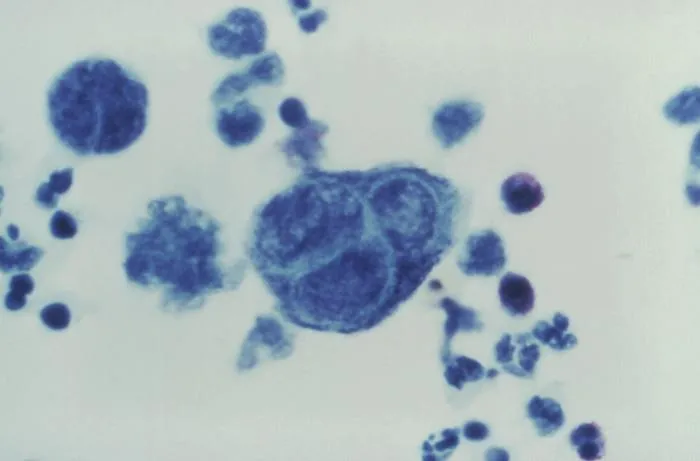
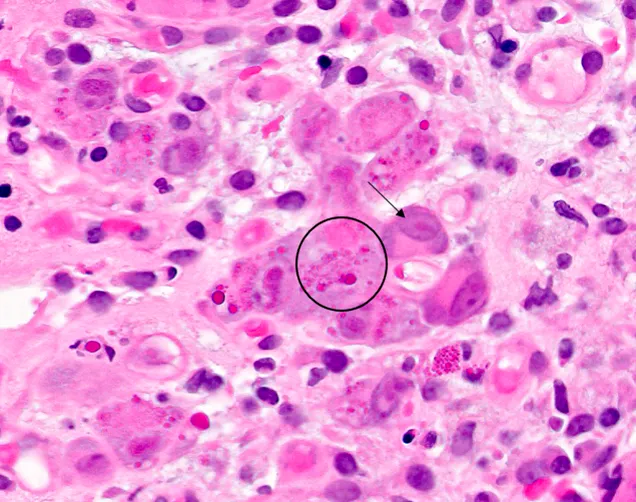
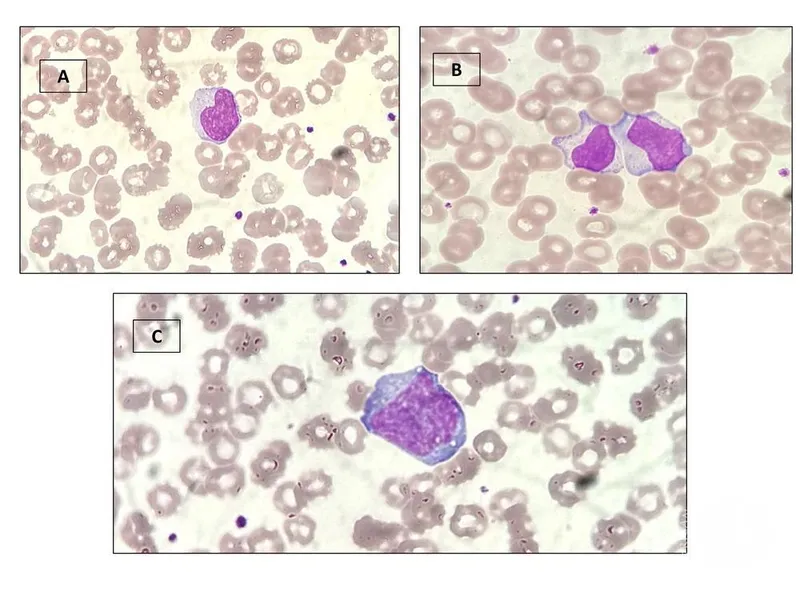
Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) US Medical PG Question 8: You are seeing an otherwise healthy 66-year-old male in clinic who is complaining of localized back pain and a new rash. On physical exam, his vital signs are within normal limits. You note a vesicular rash restricted to the upper left side of his back. In order to confirm your suspected diagnosis, you perform a diagnostic test. What would you expect to find on the diagnostic test that was performed?
- A. Gram negative bacilli
- B. Branching pseudohyphae
- C. Pear shaped motile cells
- D. Multinucleated giant cells (Correct Answer)
- E. Gram positive cocci
Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) Explanation: ***Multinucleated giant cells***
- The patient's presentation of a **unilateral, vesicular rash** in an older adult, along with localized back pain, is highly suggestive of **herpes zoster (shingles)**.
- A Tzanck smear, a common diagnostic test for vesicular lesions, would reveal **multinucleated giant cells** and **intranuclear inclusions**, characteristic cytopathic effects of herpesviruses like VZV.
*Gram negative bacilli*
- This finding would suggest a **bacterial infection**, typically not associated with vesicular rashes like shingles.
- Gram-negative bacilli are often implicated in conditions such as **urinary tract infections** or **sepsis**, not dermatological viral infections.
*Branching pseudohyphae*
- This microscopic feature is characteristic of **fungal infections**, specifically **Candida species**, which present as a candidiasis rash, not a dermatomal vesicular rash.
- Fungal rashes are typically erythematous and can be pruritic but do not usually form discrete vesicles in a dermatomal distribution.
*Pear shaped motile cells*
- This describes **Trichomonas vaginalis**, a parasite causing sexually transmitted infections, primarily **vaginitis** or **urethritis**.
- This finding would be completely unrelated to a vesicular skin rash or the suspected diagnosis of shingles.
*Gram positive cocci*
- This finding is indicative of a **bacterial infection**, such as those caused by **Staphylococcus aureus** or **Streptococcus pyogenes**.
- While these bacteria can cause skin infections (e.g., impetigo, cellulitis), they do not produce the classic unilateral vesicular rash of shingles and would not involve multinucleated giant cells on microscopy.
Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) US Medical PG Question 9: A 16-year-old male is brought to the clinic by his mother for the complaints of fever, nonproductive cough, fatigue, lack of appetite, and sore throat for the past 2 months. Several other students at his high school have had similar symptoms. Physical exam shows a whitish membrane in his oropharynx, bilateral enlarged cervical lymphadenopathy, and mild splenomegaly. Which of the following tests is most likely to diagnose his condition?
- A. Monospot test (Correct Answer)
- B. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- C. Throat culture
- D. Urine culture
- E. Chest X-ray
Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) Explanation: ***Monospot test***
- The Monospot test detects **heterophile antibodies**, which are commonly produced during an acute Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, the cause of **infectious mononucleosis**.
- The patient's symptoms (fever, fatigue, nonproductive cough, sore throat, cervical lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly) and the epidemiological context (several other students with similar symptoms) are highly suggestive of **infectious mononucleosis**.
*Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)*
- While ELISA can detect antibodies to various pathogens, including EBV-specific antigens, the **Monospot test** is the more common and rapid initial diagnostic tool for infectious mononucleosis.
- ELISA for EBV-specific antibodies (e.g., VCA-IgM, VCA-IgG) might be used if the Monospot test is negative but clinical suspicion remains high, especially in younger children or atypical presentations.
*Throat culture*
- A throat culture is used to identify bacterial infections, such as **Streptococcus pyogenes** (strep throat).
- Although the patient has a sore throat and a whitish membrane, his other systemic symptoms (fatigue, splenomegaly, lack of appetite for 2 months) are not typical for a bacterial pharyngitis which usually responds to antibiotics. A **nonproductive cough** also makes bacterial pharyngitis less likely.
*Urine culture*
- A urine culture is used to diagnose **urinary tract infections**.
- The patient's symptoms are not indicative of a urinary tract infection.
*Chest X-ray*
- A chest X-ray is used to evaluate the lungs for conditions such as **pneumonia**, **bronchitis**, or other respiratory pathologies.
- While the patient has a nonproductive cough, the predominant systemic symptoms (fever, fatigue, lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly) point towards a systemic viral infection rather than primarily a lung issue that would be definitively diagnosed by a chest X-ray.
Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) US Medical PG Question 10: A previously healthy 5-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of increasing weakness and a retroauricular rash that started 2 days ago. The rash spread rapidly and involves the trunk and extremities. Last week, he had a mild sore throat, pink eyes, and a headache. His family recently immigrated from Ethiopia. His immunization status is unknown. The patient appears severely ill. His temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F). Examination shows tender postauricular and suboccipital lymphadenopathy. There is a nonconfluent, maculopapular rash over the torso and extremities. Infection with which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Togavirus (Correct Answer)
- B. Human herpesvirus 6
- C. Parvovirus
- D. Varicella zoster virus
- E. Paramyxovirus
Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) Explanation: ***Togavirus***
- This patient's presentation is classic for **rubella** (German measles), caused by the **rubella virus**, a **togavirus**.
- The hallmark clinical finding is **tender postauricular and suboccipital lymphadenopathy**, which appears before the rash and is pathognomonic for rubella.
- The **maculopapular rash** begins on the face (retroauricular region) and spreads cephalocaudally to the trunk and extremities over 2-3 days.
- The prodrome includes **mild symptoms** (low-grade fever, sore throat, mild conjunctivitis, headache), which is characteristic of rubella.
- The patient's **unknown immunization status** and immigration from a region with lower vaccination coverage increases the likelihood of rubella infection.
*Paramyxovirus*
- **Measles virus** is a paramyxovirus that causes rubeola, but the clinical presentation differs significantly from this case.
- Measles typically presents with the **"3 Cs"**: severe **cough**, **coryza** (profuse nasal discharge), and **conjunctivitis** (more prominent than rubella).
- **Koplik spots** (white spots on buccal mucosa) are pathognomonic for measles and appear before the rash.
- Measles causes **higher fever** (often >40°C) and more severe systemic illness than described here.
- While measles can have lymphadenopathy, the **prominent postauricular and suboccipital nodes are characteristic of rubella, not measles**.
*Human herpesvirus 6*
- **HHV-6** causes **roseola infantum** (exanthem subitum), typically in infants 6-24 months old.
- The classic presentation is **high fever for 3-5 days** that suddenly resolves, followed immediately by a rash (**"fever then rash"**).
- This patient had prodromal symptoms followed by rash while still febrile, which does not fit roseola.
- Roseola does not cause significant lymphadenopathy or conjunctivitis.
*Parvovirus*
- **Parvovirus B19** causes **erythema infectiosum** (fifth disease), characterized by a **"slapped cheek"** facial erythema followed by a reticular (lacy) rash on the trunk and extremities.
- The rash pattern and prominent lymphadenopathy in this case are not consistent with fifth disease.
- Fifth disease typically causes mild or no fever and lacks the retroauricular distribution seen here.
*Varicella zoster virus*
- **VZV** causes **chickenpox**, which presents with a **pruritic, vesicular rash** that appears in successive crops and progresses through stages (macule → papule → vesicle → crust).
- This patient has a **maculopapular, nonconfluent rash** without vesicles, which is inconsistent with chickenpox.
- Chickenpox does not typically cause prominent postauricular lymphadenopathy.
More Herpesviruses (HSV, VZV, CMV, EBV, HHV-6/7/8) US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.