Viruses

On this page
🦠 Viral Architecture: The Molecular Invasion Blueprint
Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites that commandeer your cells' machinery to replicate, causing diseases ranging from the common cold to global pandemics. You'll master how these molecular invaders are structured, how they hijack cellular processes, and how clinicians recognize, diagnose, and combat viral infections through targeted antivirals and immune strategies. Understanding viral architecture, replication cycles, and pathogenesis transforms these invisible threats into predictable patterns you can identify and manage at the bedside.
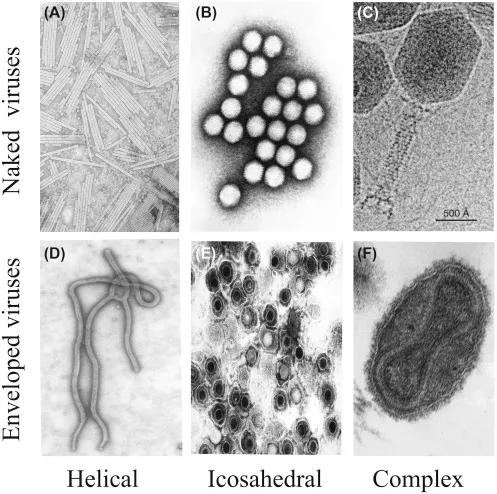
Viral Structural Hierarchy
- Nucleic Acid Core (20-250 kb genetic material)
- DNA viruses: 3-375 kb double or single-stranded
- RNA viruses: 7-30 kb positive, negative, or segmented
- Positive-sense: Direct translation (>80% RNA viruses)
- Negative-sense: Requires polymerase (<20% RNA viruses)
- Capsid Assembly (60-2,000 protein subunits)
- Icosahedral: 20 triangular faces, 12 vertices
- Helical: 16.3 subunits per turn (tobacco mosaic model)
- Complex: Combination architectures (<5% of viruses)
- Envelope Structure (present in 70% of human pathogens)
- Lipid bilayer: 4-6 nm thickness
- Glycoproteins: 10-15 spike proteins per 100 nm²
📌 Remember: DIVE for viral components - DNA/RNA core, Icosahedral/helical capsid, Viral proteins, Envelope (if present). Each component determines specific clinical characteristics and targeted therapeutic approaches.
| Structural Feature | Enveloped Viruses | Non-Enveloped | Clinical Impact | Survival Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Stability | Labile (<1 hour) | Stable (days-weeks) | Transmission route | Outbreak potential |
| Disinfection Sensitivity | 70% alcohol effective | Requires bleach/heat | Infection control | Hospital protocols |
| Host Cell Exit | Budding (non-lytic) | Lysis (100% cell death) | Disease severity | Tissue damage |
| Immune Evasion | Antigenic variation | Limited mutation | Vaccine efficacy | Reinfection risk |
| Size Range | 80-400 nm | 20-100 nm | Filtration needs | Diagnostic methods |
Understanding viral symmetry predicts assembly mechanisms and reveals therapeutic vulnerabilities through structural analysis.
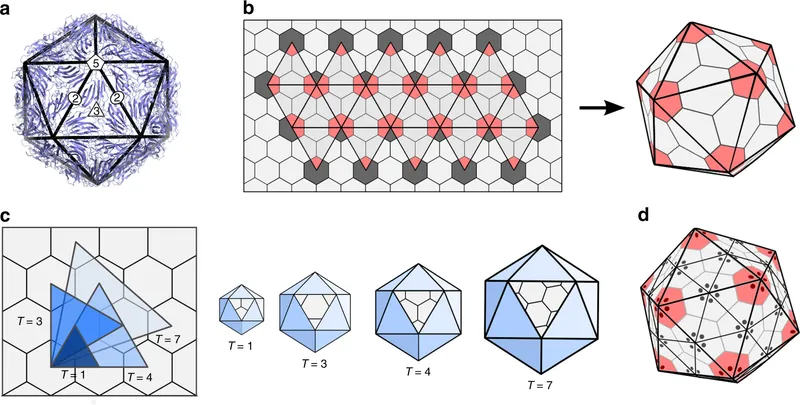
🦠 Viral Architecture: The Molecular Invasion Blueprint
⚙️ Viral Replication: The Cellular Hijacking Engine
Replication Strategy Classification
- DNA Virus Replication (nuclear for most families)
- dsDNA: Host polymerase utilization (>90% of DNA viruses)
- ssDNA: Conversion to dsDNA intermediate (100% requirement)
- Parvovirus: S-phase dependency (dividing cells only)
- Requires cellular DNA polymerase activation
- RNA Virus Replication (cytoplasmic predominance)
- Positive-sense: Direct ribosome binding (immediate translation)
- Negative-sense: RNA-dependent RNA polymerase essential
- Segmented genomes: reassortment potential (influenza model)
- Error rate: 10⁻³-10⁻⁵ mutations per nucleotide
📌 Remember: PENT for replication sites - Parvovirus (nucleus, S-phase), Enveloped RNA (cytoplasm/ER), Naked DNA (nucleus), Togavirus (cytoplasm). Location determines drug targeting and diagnostic timing.
| Replication Phase | Timeline | Key Events | Diagnostic Window | Therapeutic Target |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attachment | 0-30 min | Receptor binding | Pre-symptomatic | Entry inhibitors |
| Penetration | 30-60 min | Membrane fusion | PCR positive | Fusion blockers |
| Early Genes | 2-6 hours | Enzyme synthesis | Antigen detection | Polymerase inhibitors |
| Replication | 6-12 hours | Genome copying | Peak viral load | Nucleoside analogs |
| Assembly | 12-24 hours | Virion formation | Infectivity peak | Assembly inhibitors |
💡 Master This: Viral replication timing determines diagnostic sensitivity - PCR detects virus 2-4 hours post-infection, antigen tests require 6-12 hours, while antibodies appear 5-10 days later.
Replication mechanisms reveal why certain viruses cause acute versus chronic infections through distinct cellular interaction patterns.
⚙️ Viral Replication: The Cellular Hijacking Engine
🎯 Viral Recognition: The Clinical Pattern Matrix
Syndrome-Based Recognition Patterns
- Respiratory Viral Syndromes
- Upper respiratory: Rhinovirus (>50% of common colds)
- Bronchiolitis: RSV (70% in infants <2 years)
- Pneumonia: Influenza (15-30% of viral pneumonias)
- Influenza A: Epidemic potential, antigenic shift
- Influenza B: Endemic circulation, milder disease
- Exanthematous Viral Patterns
- Vesicular: VZV (>95% of chickenpox cases)
- Maculopapular: Measles (pathognomonic Koplik spots)
- Petechial: EBV (10-15% with ampicillin rash)
- Monospot positive: >90% in adolescents
- Atypical lymphocytes: >10% of total WBC count
📌 Remember: RASH for exanthem timing - Roseola (fever then rash), Adenovirus (fever with rash), Smallpox (fever before rash), HSV (vesicles without fever). Timing sequence predicts viral family with >85% accuracy.
| Viral Family | Incubation Period | Fever Pattern | Rash Characteristics | Diagnostic Clue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paramyxovirus | 10-14 days | High (>39°C) | Maculopapular, cephalocaudal | Koplik spots |
| Herpesviruses | 14-21 days | Variable | Vesicular, dermatomal | Unilateral distribution |
| Parvovirus B19 | 4-14 days | Low-grade | "Slapped cheek" erythema | Arthralgias in adults |
| Adenovirus | 2-14 days | Prolonged | Maculopapular, generalized | Conjunctivitis |
| Enterovirus | 3-6 days | Biphasic | Hand-foot-mouth pattern | Summer seasonality |
Neurotropic Viral Recognition
- Aseptic Meningitis (>85% viral etiology)
- Enterovirus: Summer predominance, benign course
- HSV-2: Recurrent episodes, genital association
- VZV: Immunocompromised hosts, dermatomal pain
- CSF pleocytosis: 10-1000 cells/μL (lymphocytic)
- Normal glucose: >60% of serum glucose
- Encephalitis (<15% viral CNS infections)
- HSV-1: Temporal lobe predilection, hemorrhagic necrosis
- Arbovirus: Geographic clustering, seasonal patterns
- Case fatality: 5-15% for HSV, 20-30% for Eastern equine
💡 Master This: CSF viral PCR has >95% sensitivity within 48 hours of symptom onset, but sensitivity drops to <70% after 7 days - early lumbar puncture is critical for diagnosis.
Pattern recognition frameworks enable rapid viral family identification and appropriate therapeutic intervention within critical time windows.

🎯 Viral Recognition: The Clinical Pattern Matrix
🔬 Viral Diagnostics: The Detection Arsenal
Molecular Diagnostic Hierarchy
- Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs)
- PCR sensitivity: 10-100 copies/mL (gold standard)
- Real-time PCR: Results in 2-4 hours (>99% specificity)
- Multiplex panels: 15-25 pathogens simultaneously
- Respiratory panel: >90% sensitivity for common viruses
- CNS panel: >95% sensitivity for neurotropic viruses
- Rapid Antigen Detection
- Influenza: 50-70% sensitivity, >95% specificity
- RSV: 80-90% sensitivity in infants (<2 years)
- SARS-CoV-2: 85-95% sensitivity with high viral loads
- Optimal timing: 1-5 days post-symptom onset
- False negative rate: 20-30% in asymptomatic patients
📌 Remember: RAPID for antigen test limitations - Reduced sensitivity (<80%), Asymptomatic poor detection, Peak viral load dependency, Influenza A/B cross-reactivity, Decreased accuracy after day 5.
| Diagnostic Method | Sensitivity | Specificity | Time to Result | Cost Factor | Clinical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT-PCR | >95% | >99% | 2-4 hours | High | Gold standard |
| Rapid Antigen | 50-85% | >95% | 15-30 min | Low | Point-of-care |
| Viral Culture | Variable | 100% | 3-14 days | High | Research/typing |
| Serology (IgM) | 70-90% | 85-95% | 1-2 hours | Moderate | Retrospective |
| Direct IF | 60-80% | >95% | 2-4 hours | Moderate | Specialized labs |
Serologic Interpretation Mastery
- IgM Response (acute infection marker)
- Appears: 5-10 days post-infection
- Peaks: 2-3 weeks, declines by 2-3 months
- False positives: Rheumatoid factor, cross-reactivity
- IgG Response (immunity indicator)
- Appears: 10-14 days post-infection
- Persists: Years to lifetime (memory response)
- Avidity testing: Low avidity = recent infection
💡 Master This: Four-fold rise in IgG titers between acute and convalescent sera (2-4 weeks apart) confirms recent viral infection with >95% specificity, even when IgM is negative.
Diagnostic timing optimization ensures maximum test sensitivity while minimizing false negative results during critical treatment windows.
🔬 Viral Diagnostics: The Detection Arsenal
💊 Antiviral Strategies: The Therapeutic Command Center
Mechanism-Based Therapeutic Categories
- Nucleoside/Nucleotide Analogs (DNA/RNA synthesis inhibitors)
- Acyclovir: HSV/VZV selective, >90% bioavailability (IV)
- Remdesivir: RNA polymerase inhibitor, broad-spectrum
- Tenofovir: Reverse transcriptase inhibitor, HIV/HBV
- Resistance barrier: High for tenofovir (>5 mutations)
- Renal monitoring: Creatinine every 3-6 months
- Protease Inhibitors (viral maturation blockers)
- Ritonavir: CYP3A4 inhibitor, boosting agent
- Nirmatrelvir: SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitor
- Drug interactions: >50 significant interactions
- Efficacy window: <5 days from symptom onset
📌 Remember: TIMER for antiviral efficacy - Timing (<48-72 hours), Immune status, Mechanism match, Early intervention, Resistance prevention. Late treatment reduces efficacy by >50% for most antivirals.
| Antiviral Class | Primary Targets | Efficacy Window | Resistance Rate | Monitoring Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleoside Analogs | HSV, VZV, CMV | <72 hours | <5% (immunocompetent) | Renal function |
| Neuraminidase Inhibitors | Influenza A/B | <48 hours | 1-5% (seasonal) | Respiratory status |
| Protease Inhibitors | HIV, SARS-CoV-2 | <5 days | Variable | Drug interactions |
| Polymerase Inhibitors | HCV, SARS-CoV-2 | <7 days | <1% (HCV) | Liver function |
| Entry Inhibitors | HIV, CMV | Prevention | <1% | Immune status |
Resistance Prevention Strategies
- Combination Therapy (HIV model)
- Triple therapy: >95% suppression rates
- Resistance barrier: Multiple simultaneous mutations required
- Adherence critical: >95% compliance for success
- Appropriate Duration (resistance minimization)
- HSV encephalitis: 14-21 days (prevent relapse)
- CMV retinitis: Induction + maintenance phases
- Induction: 2-3 weeks high-dose therapy
- Maintenance: Indefinite in AIDS patients
💡 Master This: Antiviral resistance develops in >30% of immunocompromised patients receiving prolonged therapy - genotypic testing guides salvage therapy selection with >80% success rates.
Therapeutic timing optimization ensures maximum antiviral efficacy while preventing resistance development through strategic intervention approaches.
💊 Antiviral Strategies: The Therapeutic Command Center
🌐 Viral Pathogenesis: The Disease Architecture Network
Host-Pathogen Interaction Matrix
- Viral Virulence Factors
- Immune evasion: >50 documented mechanisms across viral families
- Tissue tropism: Receptor specificity determines organ involvement
- Cytopathic effects: Direct vs immune-mediated tissue damage
- HSV: Direct neuronal destruction (>90% of damage)
- HBV: Immune-mediated hepatocyte killing (>80% of damage)
- Host Susceptibility Determinants
- Age extremes: <2 years and >65 years (highest mortality)
- Immunocompromised: 10-100x increased severe disease risk
- Genetic factors: HLA associations, receptor polymorphisms
- CCR5-Δ32: HIV resistance in 1% of population
- IFNL4 variants: HCV clearance 2-3x higher
📌 Remember: HAVOC for severe viral disease predictors - Host immunodeficiency, Age extremes, Viral load elevation, Organ dysfunction, Comorbidity burden. ≥3 factors predict severe disease with >85% accuracy.
| Host Factor | Risk Multiplier | Affected Viruses | Clinical Impact | Intervention Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age <2 years | 5-10x | RSV, rotavirus | Hospitalization | Passive immunization |
| Age >65 years | 3-5x | Influenza, SARS-CoV-2 | Mortality | Vaccination priority |
| Immunosuppression | 10-100x | CMV, EBV, VZV | Dissemination | Prophylactic antivirals |
| Pregnancy | 2-5x | Influenza, VZV | Maternal/fetal | Modified vaccines |
| Chronic disease | 2-10x | Respiratory viruses | Decompensation | Early treatment |
- Innate Immunity (first 96 hours)
- Interferon response: Type I (α/β) within 6-12 hours
- NK cell activation: Peak at 3-5 days post-infection
- Complement activation: Classical and alternative pathways
- Adaptive Immunity (5-14 days onset)
- T-cell responses: CD8+ cytotoxic (viral clearance)
- B-cell responses: Neutralizing antibodies (protection)
- Memory formation: Long-lived plasma cells (years)
- Cross-reactivity: Strain-specific vs broadly neutralizing
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Cytokine storm occurs in <5% of viral infections but accounts for >50% of severe disease - IL-6 levels >100 pg/mL predict critical illness with >90% specificity.
💡 Master This: Viral load correlates with disease severity in >80% of viral infections - log₁₀ increases predict exponential increases in complications and mortality risk.
Pathogenesis understanding enables personalized risk stratification and targeted therapeutic interventions based on individual host-pathogen interaction profiles.

🌐 Viral Pathogenesis: The Disease Architecture Network
🎯 Viral Mastery: The Clinical Command Arsenal
Essential Clinical Arsenal
- Rapid Recognition Patterns
- Syndrome-virus associations: >85% accuracy with key features
- Timing-based diagnosis: Incubation + symptom progression
- Epidemiologic clues: Season, geography, exposure history
- Diagnostic Decision Trees
- Symptom duration → Test selection (<48h = antigen, >48h = PCR)
- Risk stratification → Urgency level (high-risk = immediate)
- Cost-effectiveness → Targeted vs broad testing
📌 Remember: VIRAL mastery framework - Virus identification (<2 hours), Intervention timing (<48 hours), Risk assessment (immediate), Antiviral selection (appropriate), Long-term monitoring (complications).
| Clinical Scenario | Recognition Time | Diagnostic Approach | Treatment Window | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influenza-like illness | <30 minutes | Rapid antigen + clinical | <48 hours | >80% symptom reduction |
| Viral meningitis | <2 hours | CSF PCR panel | <6 hours | >95% diagnosis accuracy |
| HSV encephalitis | <1 hour | Emergency CSF PCR | <12 hours | >90% survival with treatment |
| Immunocompromised fever | <30 minutes | Broad viral panel | <24 hours | >70% mortality reduction |
| Neonatal viral sepsis | <15 minutes | Multi-platform testing | <6 hours | >85% improved outcomes |
- Multi-system viral effects recognition
- Resistance pattern anticipation and prevention
- Vaccine-preventable disease outbreak management
- Emerging viral threat assessment and response
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Early antiviral therapy (<48 hours) reduces hospitalization by >40% and complications by >60% across most viral infections - aggressive early intervention transforms outcomes.
💡 Master This: Viral medicine expertise combines rapid pattern recognition (<30 minutes), appropriate diagnostic selection (cost-effective), and timely therapeutic intervention (evidence-based) to achieve optimal patient outcomes with minimal resource utilization.
Clinical mastery frameworks enable confident viral medicine practice through systematic approaches that optimize patient care while minimizing diagnostic uncertainty and therapeutic delays.
🎯 Viral Mastery: The Clinical Command Arsenal
Practice Questions: Viruses
Test your understanding with these related questions
An HIV-positive 48-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a 3-month history of recurrent, painful mouth ulcers. This time, the pain is so severe that the patient cannot eat. He has a history of a seizure disorder but currently does not take any medications. He appears very ill. His temperature is 39.0°C (102.2°F). Physical examination shows numerous vesicular ulcerations on the lips and sloughing of the gums, buccal mucosa, and hard palate. Genetic analysis of the pathogen isolated from the lesions shows a mutation in a gene encoding viral phosphotransferases. Which of the following drugs is the most appropriate treatment?












