Pneumococcal disease US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Pneumococcal disease. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
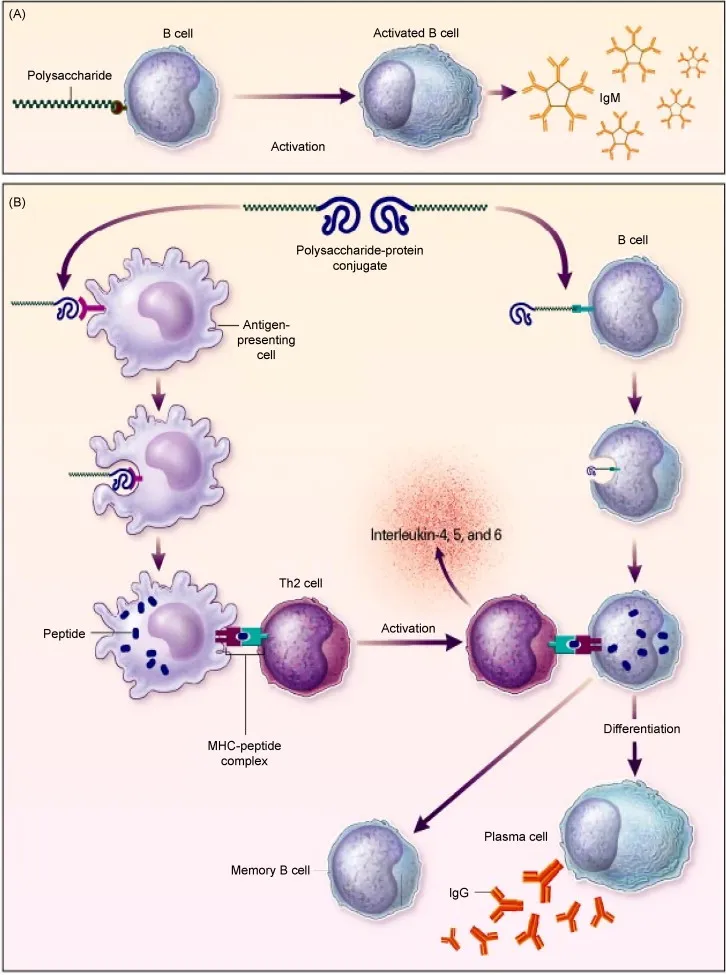
Pneumococcal disease US Medical PG Question 1: A 2-year-old boy is brought in by his parents to his pediatrician. The boy was born by spontaneous vaginal delivery at 39 weeks and 5 days after a normal pregnancy. The boy has received all age-appropriate vaccinations as of his last visit at 18 months of age. Of note, the boy has confirmed sickle cell disease and the only medication he takes is penicillin prophylaxis. The parents state that they plan on enrolling their son in a daycare, which requires documentation of up-to-date vaccinations. The pediatrician states that their son needs an additional vaccination at this visit, which is a polysaccharide vaccine that is not conjugated to protein. Which of the following matches this description?
- A. Pneumovax (Correct Answer)
- B. Menactra
- C. Prevnar
- D. Hib vaccine
- E. Live attenuated influenza vaccine
Pneumococcal disease Explanation: ***Pneumovax***
- **Pneumovax** (PCV23, PPSV23) is a **polysaccharide vaccine** that is not conjugated to a protein carrier. Children with **sickle cell disease** should receive this vaccine due to their immunocompromised state and increased risk of encapsulated bacterial infections.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends PPSV23 for children aged 2 years and older with chronic medical conditions such as **sickle cell disease**, usually administered 8 weeks after their last PCV13 dose.
*Menactra*
- **Menactra** is a **quadrivalent meningococcal conjugate vaccine** (MCV4), meaning it contains a polysaccharide antigen conjugated to a protein carrier.
- This vaccine primarily targets *Neisseria meningitidis* and is different from the pneumococcal vaccine required here.
*Prevnar*
- **Prevnar** (PCV13) is a **pneumococcal conjugate vaccine**, meaning its polysaccharide antigens are conjugated to a protein carrier.
- While important for children with sickle cell disease, the question specifically asks for a vaccination that is a **polysaccharide vaccine that is not conjugated to protein**.
*Hib vaccine*
- The **Hib vaccine** (against *Haemophilus influenzae* type b) is a **conjugate vaccine**, meaning its polysaccharide capsule is linked to a protein carrier to enhance immunogenicity, particularly in infants.
- This vaccine is typically given earlier in childhood and is not the "additional" unconjugated polysaccharide vaccine described.
*Live attenuated influenza vaccine*
- The **live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV)** is a live virus vaccine, not a polysaccharide vaccine.
- It is also contraindicated in individuals with certain immunocompromising conditions, such as some patients with sickle cell disease.
Pneumococcal disease US Medical PG Question 2: A 72-year-old man is admitted to the hospital with productive cough and fever. A chest radiograph is obtained and shows lobar consolidation. The patient is diagnosed with pneumonia. He has a history of penicillin allergy. The attending physician orders IV levofloxacin as empiric therapy. On morning rounds the next day, the team discovers that the patient was administered ceftriaxone instead of levofloxacin. The patient has already received a full dose of ceftriaxone and had no signs of allergic reaction, and his pneumonia appears to be improving clinically. What is the most appropriate next step?
- A. Administer diphenhydramine as prophylaxis against allergic reaction
- B. Continue with ceftriaxone as empiric therapy
- C. Switch the patient to oral azithromycin in preparation for discharge and home therapy
- D. Switch the patient back to levofloxacin and discuss the error with the patient
- E. Continue with ceftriaxone and add azithromycin as inpatient empiric pneumonia therapy (Correct Answer)
Pneumococcal disease Explanation: ***Continue with ceftriaxone and add azithromycin as inpatient empiric pneumonia therapy***
- This is the **guideline-recommended approach** for hospitalized community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) according to ATS/IDSA guidelines.
- Ceftriaxone (beta-lactam) plus azithromycin (macrolide) provides **dual coverage** for typical bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae) and atypical organisms (Mycoplasma, Chlamydophila, Legionella).
- Since the patient has already tolerated ceftriaxone without allergic reaction despite penicillin allergy history, continuing it is safe, and **adding azithromycin completes appropriate empiric therapy** for a 72-year-old hospitalized patient.
- The cross-reactivity between penicillins and cephalosporins is low (1-3%), and the patient's tolerance of ceftriaxone confirms safety.
*Continue with ceftriaxone as empiric therapy*
- While the patient is improving on ceftriaxone and tolerated it without allergic reaction, **monotherapy with a beta-lactam alone is suboptimal** for hospitalized CAP.
- Guidelines recommend dual therapy (beta-lactam + macrolide) or fluoroquinolone monotherapy for hospitalized non-ICU patients to ensure adequate atypical coverage.
- Continuing ceftriaxone alone misses potential atypical pathogens that may be contributing to the pneumonia.
*Switch the patient to oral azithromycin in preparation for discharge and home therapy*
- It is **premature to switch to oral therapy** or consider discharge after only one day of treatment for a 72-year-old with pneumonia requiring hospitalization.
- The patient should remain on IV therapy until clinically stable (afebrile, hemodynamically stable, improving oxygenation) for an appropriate duration.
*Administer diphenhydramine as prophylaxis against allergic reaction*
- Since the patient has already tolerated a full dose of ceftriaxone without any allergic reaction, **prophylactic antihistamines are unnecessary**.
- The low cross-reactivity between penicillins and third-generation cephalosporins, combined with the successful first dose, indicates minimal risk.
*Switch the patient back to levofloxacin and discuss the error with the patient*
- Switching back to levofloxacin is **unnecessary and potentially disruptive** given that the patient is clinically improving on ceftriaxone and has demonstrated tolerance to it.
- While the original plan was levofloxacin (appropriate fluoroquinolone monotherapy), the inadvertent use of ceftriaxone has proven safe and provides an opportunity to implement the preferred dual-therapy regimen.
- While discussing medication errors is important for transparency, the immediate medical priority is optimizing pneumonia treatment.
Pneumococcal disease US Medical PG Question 3: A patient is hospitalized for pneumonia. Gram-positive cocci in clusters are seen on sputum gram stain. Which of the following clinical scenarios is most commonly associated with this form of pneumonia?
- A. Elderly patient who has trouble swallowing and poor dentition
- B. An alcoholic with evidence of empyema and "currant jelly sputum"
- C. An otherwise healthy young adult with a week of mild fatigue, chills, and cough
- D. Hospitalized adult with development of pneumonia symptoms 2 weeks following a viral illness (Correct Answer)
- E. HIV positive adult with a CD4 count less than 150 and an impaired diffusion capacity
Pneumococcal disease Explanation: ***Hospitalized adult with development of pneumonia symptoms 2 weeks following a viral illness***
- Gram-positive cocci in clusters suggests **Staphylococcus aureus**, which is a common cause of secondary bacterial pneumonia, often following **viral illnesses** (e.g., influenza).
- This scenario represents a classic presentation of **secondary bacterial pneumonia**, where the initial viral infection compromises the respiratory defenses, allowing bacterial superinfection.
*Elderly patient who has trouble swallowing and poor dentition*
- This scenario points towards **aspiration pneumonia**, often caused by a **polymicrobial infection** that includes oral anaerobes, not typically dominated by Gram-positive cocci in clusters.
- While *S. aureus* can cause aspiration pneumonia, the primary concern in this context would be **anaerobic bacteria**, given the aspiration risk factors.
*An alcoholic with evidence of empyema and \"currant jelly sputum\"*
- This description is highly suggestive of **Klebsiella pneumoniae** infection, which typically presents with thick, gelatinous, and often **blood-tinged sputum**.
- **Klebsiella** is a Gram-negative rod, not Gram-positive cocci in clusters.
*An otherwise healthy young adult with a week of mild fatigue, chills, and cough*
- This presentation is more consistent with **atypical pneumonia** caused by organisms like **Mycoplasma pneumoniae** or **Chlamydophila pneumoniae**, which would not show Gram-positive cocci in clusters on sputum stain.
- **Streptococcus pneumoniae** (Gram-positive cocci in chains) can also cause community-acquired pneumonia in otherwise healthy individuals, but the "clusters" indicate **Staphylococcus aureus**.
*HIV positive adult with a CD4 count less than 150 and an impaired diffusion capacity*
- This clinical picture strongly suggests **Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP)**, which is common in severely immunocompromised HIV patients.
- *P. jirovecii* is a fungus and would not be seen as Gram-positive cocci in clusters on a routine Gram stain.
Pneumococcal disease US Medical PG Question 4: A 2-month-old girl is brought to the physician by her father for a routine well-child examination. She is given a vaccine that contains polyribosylribitol phosphate conjugated to a toxoid carrier. The vaccine is most likely to provide immunity against which of the following pathogens?
- A. Haemophilus influenzae (Correct Answer)
- B. Neisseria meningitidis
- C. Bordetella pertussis
- D. Streptococcus pneumoniae
- E. Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Pneumococcal disease Explanation: **Haemophilus influenzae**
- The vaccine described, containing **polyribosylribitol phosphate (PRP)** conjugated to a toxoid carrier, is characteristic of the **Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccine**.
- PRP is the **polysaccharide capsule** of *H. influenzae* type b, and conjugating it to a protein (toxoid carrier) allows for T-cell dependent immunity, effective in infants.
*Neisseria meningitidis*
- While *N. meningitidis* also has a **polysaccharide capsule** and vaccines are available, their capsular components differ (e.g., serogroups A, C, Y, W-135, or B outer membrane protein).
- The description of **polyribosylribitol phosphate** is specific to *H. influenzae* type b.
*Bordetella pertussis*
- Vaccines against *Bordetella pertussis* are typically **acellular pertussis vaccines (aP)**, which contain purified components like pertussis toxoid, filamentous hemagglutinin, and pertactin, not a PRP conjugate.
- These vaccines target bacterial toxins and adhesins, not a polysaccharide capsule unique to PRP.
*Streptococcus pneumoniae*
- Vaccines for *S. pneumoniae* (pneumococcal vaccines) use **capsular polysaccharides** from various serotypes, often conjugated to a protein carrier (e.g., diphtheria toxoid), but the specific polysaccharide is not PRP.
- The structure and serotypes of pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides are distinct from PRP.
*Corynebacterium diphtheriae*
- The vaccine for *C. diphtheriae* is the **diphtheria toxoid**, which is an inactivated form of the diphtheria toxin, not a polysaccharide conjugate.
- It provides immunity by inducing antibodies against the toxin, preventing its harmful effects.
Pneumococcal disease US Medical PG Question 5: A 71-year-old woman presents with high-grade fever and chills, difficulty breathing, and a productive cough with rust-colored sputum. She complains of a sharp left-sided chest pain. Physical examination reveals increased fremitus, dullness to percussion, and bronchial breath sounds on the lower left side. A chest X-ray shows left lower lobe consolidation. The offending organism that was cultured from the sputum was catalase-negative and had a positive Quellung reaction. The organism will show which gram stain results?
- A. Gram-negative diplococci
- B. Cannot be seen with gram staining since the organism lacks a cell wall
- C. Gram-positive cocci in clusters
- D. Gram-negative rod
- E. Gram-positive diplococci (Correct Answer)
Pneumococcal disease Explanation: ***Gram-positive diplococci***
- The clinical presentation (high fever, chills, productive cough with **rust-colored sputum**, sharp chest pain, signs of **consolidation**) is classic for **pneumococcal pneumonia**.
- The organism responsible for pneumococcal pneumonia, *Streptococcus pneumoniae*, is a **Gram-positive, catalase-negative diplococcus** that exhibits a **positive Quellung reaction** due to its polysaccharide capsule.
*Gram-negative diplococci*
- This describes organisms such as **Neisseria meningitidis** or **Neisseria gonorrhoeae**, which cause meningitis or gonorrhea, respectively, not typical pneumonia.
- While *Moraxella catarrhalis* is a Gram-negative diplococcus that can cause respiratory infections, it typically causes otitis media or sinusitis and less commonly severe pneumonia with rust-colored sputum.
*Cannot be seen with gram staining since the organism lacks a cell wall*
- This description typically refers to **Mycoplasma pneumoniae**, which causes **atypical pneumonia** and lacks a cell wall, rendering it unstainable by Gram stain.
- Mycoplasma pneumonia usually presents with a more indolent course, a non-productive cough, and rarely causes rust-colored sputum or lobar consolidation seen on X-ray.
*Gram-positive cocci in clusters*
- This morphology is characteristic of **staphylococci**, such as *Staphylococcus aureus*, which can cause pneumonia, often in immunocompromised individuals or as a complication of influenza.
- However, *Staphylococcus aureus* is **catalase-positive**, and its pneumonia presentation can be more fulminant, often leading to abscess formation, differing from the typical presentation of pneumococcal pneumonia.
*Gram-negative rod*
- This morphology is characteristic of various bacteria including **Klebsiella pneumoniae**, **Pseudomonas aeruginosa**, or **Haemophilus influenzae**.
- **Klebsiella pneumoniae** can cause severe pneumonia with **currant jelly sputum** but is a Gram-negative rod and would not exhibit a Quellung reaction in the same manner as *S. pneumoniae*.
Pneumococcal disease US Medical PG Question 6: While testing various strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae, a researcher discovers that a certain strain of this bacteria is unable to cause disease in mice when deposited in their lungs. What physiological test would most likely deviate from normal in this strain of bacteria as opposed to a typical strain?
- A. Quellung reaction (Correct Answer)
- B. Hemolytic reaction when grown on sheep blood agar
- C. Bile solubility
- D. Optochin sensitivity
- E. Motility
Pneumococcal disease Explanation: ***Quellung reaction***
- The **Quellung reaction** tests for the presence of the **polysaccharide capsule**, which is the primary virulence factor of *S. pneumoniae*.
- An **avirulent strain** that cannot cause disease would most likely lack the capsule and show a **negative Quellung reaction** (no capsular swelling), deviating from the **positive reaction** seen in typical encapsulated pathogenic strains.
- The capsule enables *S. pneumoniae* to evade phagocytosis and complement-mediated killing, which is essential for establishing infection in the lungs.
*Hemolytic reaction when grown on sheep blood agar*
- Both virulent and avirulent strains of *S. pneumoniae* typically exhibit **alpha-hemolysis** (partial hemolysis, producing a greenish discoloration) on sheep blood agar due to the production of pneumolysin.
- This characteristic does not differentiate between pathogenic and non-pathogenic strains in terms of disease-causing ability.
*Bile solubility*
- *S. pneumoniae* is characteristically **bile-soluble** due to the presence of autolysin enzymes that are activated by bile salts, leading to cellular lysis.
- This property is a **species characteristic** present in both virulent and avirulent strains, thus it would not explain the inability to cause disease.
*Optochin sensitivity*
- *S. pneumoniae* is universally **sensitive to optochin**, a chemical agent that inhibits its growth and is used for laboratory identification.
- This characteristic is used for **species identification** but does not correlate with strain virulence or disease-causing ability.
*Motility*
- *Streptococcus pneumoniae* is a **non-motile** bacterium; it lacks flagella.
- This characteristic is consistent across all strains and is not a virulence factor for this species.
Pneumococcal disease US Medical PG Question 7: A 13-year-old boy is brought by his mother to the emergency department because he has had fever, chills, and severe coughing for the last two days. While they originally tried to manage his condition at home, he has become increasingly fatigued and hard to arouse. He has a history of recurrent lung infections and occasionally has multiple foul smelling stools. On presentation, his temperature is 102.2 °F (39 °C), blood pressure is 106/71 mmHg, pulse is 112/min, and respirations are 20/min. Physical exam reveals scattered rhonchi over both lung fields, rales at the base of the right lung base and corresponding dullness to percussion. The most likely organism responsible for this patient's symptoms has which of the following characteristics?
- A. Mixed anaerobic rods
- B. Lancet-shaped diplococci
- C. Mucoid lactose-fermenting rod
- D. Green gram-negative rod (Correct Answer)
- E. Coagulase-positive, gram-positive cocci
Pneumococcal disease Explanation: ***Green gram-negative rod***
- The patient's history of **recurrent lung infections** and **foul-smelling stools (malabsorption)** is highly suggestive of **cystic fibrosis (CF)**.
- **Pseudomonas aeruginosa**, a **green gram-negative rod** (due to pyocyanin pigment), is a common cause of severe pulmonary infections in CF patients and is a significant contributor to morbidity and mortality.
*Mixed anaerobic rods*
- This typically causes **aspiration pneumonia**, often involving the posterior segments of the upper lobes or superior segments of the lower lobes.
- While patients with CF can have aspiration, the **recurrent nature** and specific **malabsorption symptoms** point more strongly to *Pseudomonas*.
*Lancet-shaped diplococci*
- This describes **Streptococcus pneumoniae**, a common cause of **community-acquired pneumonia**.
- While possible, it does not explain the recurrent infections or the patient's underlying condition of malabsorption and is less specific for CF-related pneumonia than *Pseudomonas*.
*Mucoid lactose-fermenting rod*
- This describes **Klebsiella pneumoniae**, which can cause severe pneumonia, often with **currant jelly sputum**.
- While *Klebsiella* can cause lung infections, it is not as characteristic of recurrent infections in CF patients as *Pseudomonas*, and the malabsorption connection is weaker.
*Coagulase-positive, gram-positive cocci*
- This describes **Staphylococcus aureus**, which is another common pathogen in CF, especially in younger patients.
- However, the description of a "green" gram-negative rod in the correct option points more specifically to *Pseudomonas aeruginosa*, which becomes increasingly prevalent and problematic in older CF patients.
Pneumococcal disease US Medical PG Question 8: A 1-year-old immigrant girl has not received any recommended vaccines since birth. She attends daycare and remains healthy despite her daily association with several other children for the past 3 months at a home day-care facility. Which of the following phenomena explains why she has not contracted any vaccine-preventable diseases such as measles, diphtheria, or pertussis?
- A. Herd immunity (Correct Answer)
- B. Immune evasion
- C. Tolerance
- D. Genetic drift
- E. Genetic shift
Pneumococcal disease Explanation: ***Herd immunity***
- **Herd immunity** occurs when a significant portion of a population is immune to a disease, providing **indirect protection** to unvaccinated individuals.
- In a daycare setting with vaccinated children, the low prevalence of disease agents protects the unvaccinated girl.
*Immune evasion*
- **Immune evasion** refers to mechanisms used by pathogens to **avoid detection** and destruction by the host immune system.
- This concept describes how a pathogen survives in an infected individual, not why an uninfected individual avoids disease.
*Tolerance*
- **Tolerance** in immunology is a state of **unresponsiveness to antigens**, preventing the immune system from attacking self-components or harmless foreign substances.
- It does not explain protection from infectious diseases; rather, it's about not mounting an immune response when one is usually expected.
*Genetic drift*
- **Genetic drift** is a change in the frequency of an existing gene variant (allele) in a population due to **random sampling** of organisms.
- This is a concept in population genetics that does not explain an individual's protection from infectious disease.
*Genetic shift*
- **Genetic shift** (antigenic shift) refers to an **abrupt, major change** in the influenza virus, leading to new hemagglutinin and/or neuraminidase proteins.
- This phenomenon explains the emergence of new influenza strains, not the protection of an individual from vaccine-preventable diseases.
Pneumococcal disease US Medical PG Question 9: A 47-year-old patient returns to his primary care physician after starting aspirin two weeks ago for primary prevention of coronary artery disease. He complains that he wakes up short of breath in the middle of the night and has had coughing "attacks" three times. After discontinuing aspirin, what medication is most appropriate for prevention of similar symptoms in this patient?
- A. Prednisone
- B. Montelukast (Correct Answer)
- C. Albuterol
- D. Fluticasone
- E. Tiotropium
Pneumococcal disease Explanation: ***Montelukast***
- The patient is experiencing symptoms consistent with **aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD)**, characterized by asthma symptoms, nasal polyps, and aspirin sensitivity.
- **Montelukast**, a **leukotriene receptor antagonist**, is effective in preventing these symptoms by blocking the inflammatory effects of leukotrienes, which are overproduced in AERD.
*Prednisone*
- While **oral corticosteroids** like prednisone can treat acute exacerbations of AERD, they are not suitable for long-term primary prevention due to significant side effects.
- Long-term use of prednisone is associated with issues like **osteoporosis**, **diabetes**, and **hypertension**.
*Albuterol*
- **Albuterol** is a **short-acting beta-agonist (SABA)** used for rescue relief of acute asthma symptoms and bronchospasm, not for long-term prevention.
- It does not address the underlying inflammatory pathway triggered by aspirin in AERD.
*Fluticasone*
- **Fluticasone** is an **inhaled corticosteroid (ICS)** primarily used for long-term control of asthma by reducing airway inflammation.
- While it can help with some asthma symptoms, it does not specifically prevent the aspirin-induced bronchospasm seen in AERD as effectively as leukotriene modifiers.
*Tiotropium*
- **Tiotropium** is a **long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA)** primarily used in the maintenance treatment of **COPD** and sometimes for severe asthma.
- It works by bronchodilation but does not target the specific leukotriene pathway involved in AERD.
Pneumococcal disease US Medical PG Question 10: A 7-month-old boy is brought by his parents to the pediatrician’s office. His mother says the child has been weakening progressively and is not as active as he used to be when he was born. His condition seems to be getting worse, especially over the last month. He was born at 41 weeks through normal vaginal delivery. There were no complications observed during the prenatal period. He was progressing well over the 1st few months and achieving the appropriate milestones. On examination, his abdomen appears soft with no liver enlargement. The patient appears to be dehydrated and lethargic. The results of a fundoscopic examination are shown in the picture. A blood test for which of the following enzymes is the next best assay to evaluate this patient's health?
- A. Acid alpha-glucosidase
- B. Hexosaminidase (Correct Answer)
- C. Sphingomyelinase
- D. Glucocerebrosidase
- E. Arylsulfatase A
Pneumococcal disease Explanation: ***Hexosaminidase***
- The symptoms and history suggest **Tay-Sachs disease**, characterized by progressive weakness and developmental delay, often linked to **deficiency in hexosaminidase A**.
- A fundoscopic exam typically reveals a **cherry-red spot**, consistent with this condition, making hexosaminidase testing essential for diagnosis.
- Tay-Sachs results from accumulation of **GM2 ganglioside** in neurons due to hexosaminidase A deficiency.
*Glucocerebrosidase*
- This enzyme is primarily associated with **Gaucher's disease**, which does not match the clinical features presented here.
- Symptoms of Gaucher's disease include **hepatosplenomegaly** and bone pain, not primarily weakness or lethargy in a young infant.
*Acid alpha-glucosidase*
- Generally tested for **Pompe disease**, which typically presents with **muscle weakness and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy**, not solely lethargy and failure to thrive.
- The clinical presentation in this case does not indicate glycogen storage disorder symptoms.
*Arylsulfatase A*
- This enzyme deficiency relates to **metachromatic leukodystrophy**, which often features neurological decline rather than isolated lethargy in infants.
- The specific symptoms and age do not align with the typical findings of this condition.
*Sphingomyelinase*
- Linked to **Niemann-Pick disease**, characterized by **hepatosplenomegaly** and neurological deterioration, absent in this scenario.
- The presentation of weakness does not match the classic signs expected with sphingomyelinase deficiency.
More Pneumococcal disease US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.