Measles, mumps, rubella US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Measles, mumps, rubella. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Measles, mumps, rubella US Medical PG Question 1: A 35-year-old woman from San Francisco has been refusing to vaccinate her children due to the claims that vaccinations may cause autism in children. Her 10-year-old male child began developing a low-grade fever with a rash that started on his face; as the rash began to spread to his limbs, it slowly disappeared from his face. When the child was taken to a clinic, the physician noticed swollen lymph nodes behind the ears of the child. Which of the following are characteristics of the virus causing these symptoms?
- A. Nonenveloped, DS segmented RNA
- B. Enveloped, SS - nonsegmented RNA
- C. Enveloped, SS + nonsegmented RNA (Correct Answer)
- D. Nonenveloped, SS linear DNA
- E. Enveloped, DS linear DNA
Measles, mumps, rubella Explanation: ***Enveloped, SS + nonsegmented RNA***
- The clinical presentation with a **low-grade fever**, a **rash** that starts on the face and spreads downwards while fading from the face, and **post-auricular lymphadenopathy** is highly characteristic of **Rubella** (German measles).
- Rubella virus is an **enveloped**, **single-stranded (SS)**, **positive-sense (+)**, **nonsegmented RNA virus** belonging to the *Togaviridae* family.
*Nonenveloped, DS segmented RNA*
- This description matches **Rotavirus** (a cause of gastroenteritis) or **Reoviruses**, which are **nonenveloped** and have **double-stranded (DS) segmented RNA** genomes.
- These viruses do not cause the described rubella-like symptoms with rash and lymphadenopathy.
*Enveloped, SS - nonsegmented RNA*
- This describes viruses like **measles, mumps, influenza, and rabies viruses**, which are **enveloped, single-stranded (SS) negative-sense (-) nonsegmented RNA viruses**.
- While measles causes a rash, it typically presents with a **high fever**, **Koplik spots**, and a rash that does not fade from the face as it spreads.
*Nonenveloped, SS linear DNA*
- This description is incorrect as DNA viruses are typically double-stranded. Single-stranded DNA viruses are rare, such as **Parvovirus B19**, which causes **Fifth disease** (erythema infectiosum).
- Parvovirus B19 causes a "slapped cheek" rash, which is distinct from the rubella rash described.
*Enveloped, DS linear DNA*
- This describes viruses such as **Herpesviruses** (e.g., Varicella-Zoster virus causing chickenpox, Herpes Simplex virus) or **Poxviruses**.
- While chickenpox involves an enveloped, DS linear DNA virus and a rash, the rash typically presents as **vesicles** and does not have the classic head-to-toe progression with fading on the face.
Measles, mumps, rubella US Medical PG Question 2: A 4-month-old boy is brought to the physician by his parents for a well-child examination. He has cystic fibrosis diagnosed by newborn screening. His parents report frequent feedings and large-volume and greasy stools. His 4-year-old brother has autism. Current medications include bronchodilators, pancreatic enzyme supplements, and fat-soluble vitamins. He is at the 18th percentile for height and 15th percentile for weight. Scattered wheezes are heard throughout both lung fields. Examination shows a distended and tympanic abdomen with no tenderness or guarding. Which of the following is a contraindication for administering one or more routine vaccinations?
- A. Allergy to egg protein
- B. History of cystic fibrosis
- C. History of febrile seizures
- D. Fever of 38.2°C (100.7°F) following previous vaccinations
- E. History of intussusception (Correct Answer)
Measles, mumps, rubella Explanation: ***History of intussusception***
- A history of **intussusception** is a **contraindication for rotavirus vaccine** administration, as the vaccine itself has a small risk of intussusception, particularly with the first dose.
- The rotavirus vaccine is part of routine childhood immunizations, so this would be a contraindication for one of the routine vaccines.
*Allergy to egg protein*
- Egg allergy is a contraindication primarily for yellow fever vaccine and some influenza vaccines, which are typically not routine vaccinations for a 4-month-old. Many flu vaccines are egg-free or can be safely administered to those with egg allergy under supervision.
- The MMR vaccine is generally safe for those with egg allergy since the amount of egg protein is negligible.
*History of cystic fibrosis*
- **Cystic fibrosis** itself is **not a contraindication** to routine vaccinations; in fact, patients with chronic conditions like CF are often *more* encouraged to receive vaccinations to prevent severe infections.
- The patient's symptoms (poor growth, greasy stools, wheezing) are manifestations of CF, not reasons to defer vaccination.
*History of febrile seizures*
- A history of **febrile seizures** is generally **not a contraindication** to routine vaccinations.
- Parents should be counseled on fever management after vaccination, but the risk of recurrent febrile seizures is not increased by vaccination to a level that warrants deferral.
*Fever of 38.2°C (100.7°F) following previous vaccinations*
- A **low-grade fever** after vaccination is a common and **expected immune response**, not a contraindication for future doses.
- Only a **severe allergic reaction** (e.g., anaphylaxis) to a previous dose of a vaccine or one of its components is a contraindication to subsequent doses of that specific vaccine.
Measles, mumps, rubella US Medical PG Question 3: A 2-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of the rash shown in the picture for 2 days. His mother says that the rash initially appeared on his face and neck. He has had fever, cough, and poor appetite for 5 days. The boy's family recently immigrated from Asia and is unable to provide his vaccination records. His temperature is 38.8°C (102.0°F), pulse is 105/min, and respiratory rate is 21/min. Physical examination shows fading of the rash over the face and neck without any desquamation. Examination of the oropharynx shows tiny rose-colored lesions on the soft palate. Enlarged tender lymph nodes are palpated in the suboccipital, postauricular and anterior cervical regions. The clinical presentation in this patient is most compatible with which of the following diseases?
- A. Mumps
- B. Rubella (Correct Answer)
- C. Roseola
- D. Parvovirus B19 infection
- E. Measles
Measles, mumps, rubella Explanation: ***Rubella***
- The description of a **maculopapular rash** that started on the face and neck, then faded without desquamation, along with **postauricular and suboccipital lymphadenopathy**, is highly characteristic of rubella (German measles).
- The presence of **tiny rose-colored lesions on the soft palate (Forchheimer spots)** further supports the diagnosis of rubella.
*Mumps*
- Mumps is primarily characterized by **parotitis (swelling of the salivary glands)**, which is not described in this patient.
- While mumps can cause fever and malaise, it typically does not present with a widespread rash or the specific lymphadenopathy described.
*Roseola*
- Roseola (human herpesvirus 6 and 7) typically presents with a **high fever for several days** followed by the abrupt appearance of a **rash as the fever breaks**.
- The rash of roseola is usually less pronounced on the face and is not associated with the prominent postauricular and suboccipital lymphadenopathy seen here.
*Parvovirus B19 infection*
- Parvovirus B19 infection (fifth disease) characteristically presents with a **"slapped cheek" rash** on the face, followed by a **lacy, reticular rash** on the trunk and extremities.
- It does not typically cause the prominent lymphadenopathy described, nor does it commonly produce palatal lesions.
*Measles*
- Measles (rubeola) typically presents with a prodrome of high fever, **cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis**, followed by the appearance of a **maculopapular rash** that spreads from the face downward.
- A key differentiating feature is the presence of **Koplik spots** on the buccal mucosa, which are not described here, and the rash of measles is usually more confluent and lasts longer, often with desquamation.
Measles, mumps, rubella US Medical PG Question 4: A 2-year-old boy presents to the pediatrician for evaluation of an elevated temperature, sore throat, runny nose, and lacrimation for the past week, and a rash which he developed yesterday. The rash began on the patient’s face and spread down to the trunk, hands, and feet. The patient’s mother gave him ibuprofen to control the fever. The child has not received mumps, measles, and rubella vaccinations because he was ill when the vaccine was scheduled and was later lost to follow-up. The vital signs include blood pressure 90/50 mm Hg, heart rate 110/min, respiratory rate 22/min, and temperature 37.8°C (100.0℉). On physical examination, the child was drowsy. His face, trunk, and extremities were covered with a maculopapular erythematous rash. Two irregularly-shaped red dots were also noted on the mucosa of the lower lip. The remainder of the physical examination was within normal limits. What is the probable causative agent for this child’s condition?
- A. Group A Streptococcus
- B. Rubulavirus
- C. Influenzavirus
- D. Morbillivirus (Correct Answer)
- E. Herpesvirus
Measles, mumps, rubella Explanation: ***Morbillivirus***
- The constellation of symptoms—**elevated temperature**, **sore throat**, **runny nose**, **lacrimation**, a **maculopapular erythematous rash** that began on the face and spread downward, and especially the **irregularly-shaped red dots on the mucosa of the lower lip** (likely **Koplik spots**)—are classic for **measles**, caused by Morbillivirus.
- The patient's **unvaccinated status** against MMR further supports measles as the most probable diagnosis, as it is a highly contagious disease prevented by vaccination.
*Group A Streptococcus*
- This bacterium causes **scarlet fever**, characterized by a **sandpaper-like rash** and **strawberry tongue**, not a maculopapular rash spreading from face to extremities with Koplik spots.
- While it can cause pharyngitis and fever, the specific rash progression and oral lesions rule out Group A Streptococcus.
*Rubulavirus*
- Rubulavirus causes **mumps**, which primarily presents with **parotitis** (swelling of parotid glands), fever, and headache.
- It does not typically cause a generalized maculopapular rash or Koplik spots, making it an unlikely cause for the described symptoms.
*Influenzavirus*
- Influenzavirus causes **influenza**, characterized by sudden onset of high fever, cough, myalgia, and headache.
- While it can cause fever and respiratory symptoms, it does not typically present with a widespread maculopapular rash or Koplik spots.
*Herpesvirus*
- Herpesviruses cause a variety of conditions, including **chickenpox** (Varicella-zoster virus), which presents with **vesicular lesions** that crust over, and **roseola infantum** (HHV-6/7), which primarily causes a high fever followed by a non-pruritic rash appearing *after* the fever subsides.
- Neither of these typically presents with Koplik spots or the specific maculopapular rash progression described.
Measles, mumps, rubella US Medical PG Question 5: A 3000-g (6.6-lb) female newborn is delivered at term to a 23-year-old primigravid woman. The mother has had no prenatal care. Immunization records are not available. Cardiac examination shows a continuous heart murmur. There are several bluish macules on the skin that do not blanch with pressure. Slit lamp examination shows cloudy lenses in both eyes. The newborn does not pass his auditory screening tests. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Congenital parvovirus infection
- B. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection
- C. Congenital rubella infection (Correct Answer)
- D. Congenital syphilis
- E. Congenital toxoplasmosis
Measles, mumps, rubella Explanation: ***Congenital rubella infection***
- The classic triad of congenital rubella includes **sensorineural hearing loss**, **ocular abnormalities** (e.g., cataracts, glaucoma), and **cardiac defects** (e.g., patent ductus arteriosus, pulmonary artery stenosis), all of which are present in this case.
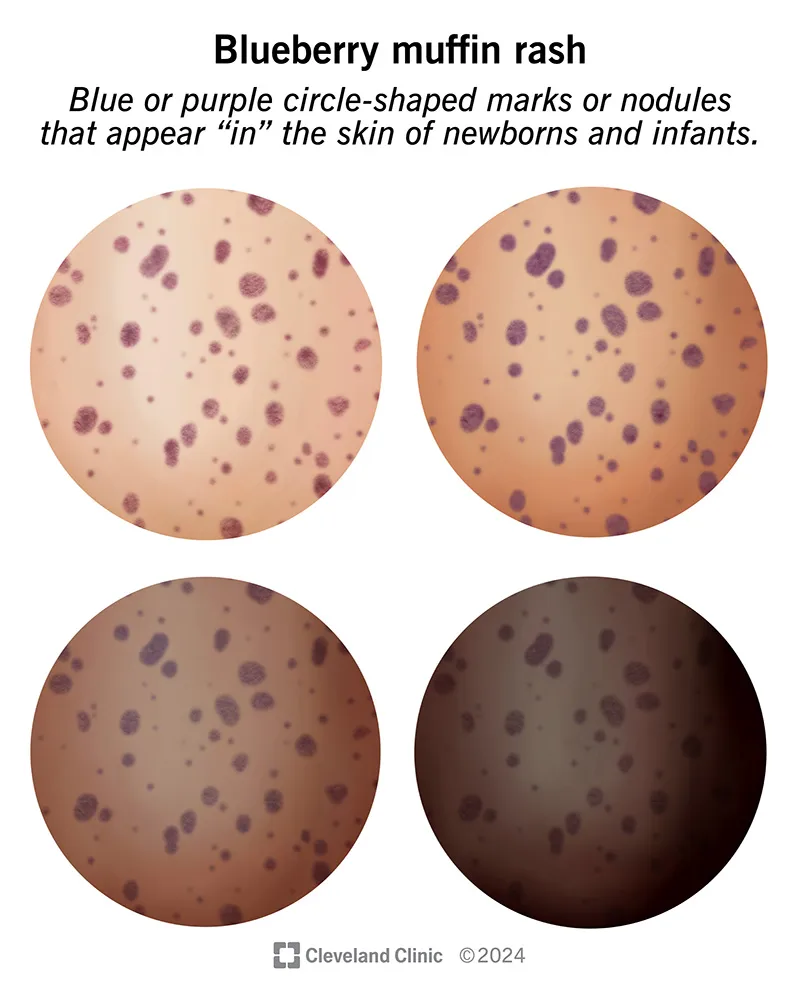
- The **blueberry muffin rash** (bluish macules) is also a characteristic, although non-specific, finding due to **extramedullary hematopoiesis**.
*Congenital parvovirus infection*
- Primarily causes **hydrops fetalis**, severe **anemia**, and fetal demise, often without the specific cardiac, ocular, and auditory defects described.
- While it can cause skin lesions, the constellation of findings strongly points away from parvovirus.
*Congenital cytomegalovirus infection*
- Can cause **sensorineural hearing loss** and central nervous system abnormalities (e.g., **periventricular calcifications**, microcephaly), but **cardiac defects** and **cataracts** are less common than with rubella.
- The typical skin lesions are often petechiae or purpura, not the distinct bluish macules seen here.
*Congenital syphilis*
- Presents with a wide range of manifestations, including **hepatosplenomegaly**, **rash** (often maculopapular or desquamating), **saddle nose deformity**, and bone abnormalities.
- While it can cause some ocular (e.g., interstitial keratitis) and auditory issues, the specific combination of **cataracts**, **patent ductus arteriosus**, and **sensorineural deafness** is not its hallmark.
*Congenital toxoplasmosis*
- Characterized by the classic triad of **chorioretinitis**, **hydrocephalus**, and **intracranial calcifications**.
- While it can cause hearing loss and some skin manifestations, the cardiac defect and cataracts described are not typical features.
Measles, mumps, rubella US Medical PG Question 6: A previously healthy 5-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of increasing weakness and a retroauricular rash that started 2 days ago. The rash spread rapidly and involves the trunk and extremities. Last week, he had a mild sore throat, pink eyes, and a headache. His family recently immigrated from Ethiopia. His immunization status is unknown. The patient appears severely ill. His temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F). Examination shows tender postauricular and suboccipital lymphadenopathy. There is a nonconfluent, maculopapular rash over the torso and extremities. Infection with which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Togavirus (Correct Answer)
- B. Human herpesvirus 6
- C. Parvovirus
- D. Varicella zoster virus
- E. Paramyxovirus
Measles, mumps, rubella Explanation: ***Togavirus***
- This patient's presentation is classic for **rubella** (German measles), caused by the **rubella virus**, a **togavirus**.
- The hallmark clinical finding is **tender postauricular and suboccipital lymphadenopathy**, which appears before the rash and is pathognomonic for rubella.
- The **maculopapular rash** begins on the face (retroauricular region) and spreads cephalocaudally to the trunk and extremities over 2-3 days.
- The prodrome includes **mild symptoms** (low-grade fever, sore throat, mild conjunctivitis, headache), which is characteristic of rubella.
- The patient's **unknown immunization status** and immigration from a region with lower vaccination coverage increases the likelihood of rubella infection.
*Paramyxovirus*
- **Measles virus** is a paramyxovirus that causes rubeola, but the clinical presentation differs significantly from this case.
- Measles typically presents with the **"3 Cs"**: severe **cough**, **coryza** (profuse nasal discharge), and **conjunctivitis** (more prominent than rubella).
- **Koplik spots** (white spots on buccal mucosa) are pathognomonic for measles and appear before the rash.
- Measles causes **higher fever** (often >40°C) and more severe systemic illness than described here.
- While measles can have lymphadenopathy, the **prominent postauricular and suboccipital nodes are characteristic of rubella, not measles**.
*Human herpesvirus 6*
- **HHV-6** causes **roseola infantum** (exanthem subitum), typically in infants 6-24 months old.
- The classic presentation is **high fever for 3-5 days** that suddenly resolves, followed immediately by a rash (**"fever then rash"**).
- This patient had prodromal symptoms followed by rash while still febrile, which does not fit roseola.
- Roseola does not cause significant lymphadenopathy or conjunctivitis.
*Parvovirus*
- **Parvovirus B19** causes **erythema infectiosum** (fifth disease), characterized by a **"slapped cheek"** facial erythema followed by a reticular (lacy) rash on the trunk and extremities.
- The rash pattern and prominent lymphadenopathy in this case are not consistent with fifth disease.
- Fifth disease typically causes mild or no fever and lacks the retroauricular distribution seen here.
*Varicella zoster virus*
- **VZV** causes **chickenpox**, which presents with a **pruritic, vesicular rash** that appears in successive crops and progresses through stages (macule → papule → vesicle → crust).
- This patient has a **maculopapular, nonconfluent rash** without vesicles, which is inconsistent with chickenpox.
- Chickenpox does not typically cause prominent postauricular lymphadenopathy.
Measles, mumps, rubella US Medical PG Question 7: A 32-year-old pregnant woman at 32 weeks gestation presents with a 2-day history of low-grade fever, headache, and myalgias. She works at a daycare where several children recently had 'slapped cheek' rash. Laboratory studies show hemoglobin 8.5 g/dL (baseline 12 g/dL), reticulocyte count 0.1%, and positive parvovirus B19 IgM. Fetal ultrasound shows hydrops fetalis with ascites, pleural effusions, and severe anemia on cordocentesis. Evaluate the pathophysiologic mechanism and management approach that best addresses both maternal and fetal complications.
- A. Vertical transmission causing fetal aplastic crisis; intrauterine transfusion with close monitoring (Correct Answer)
- B. Fetal cardiac failure from myocarditis; deliver immediately for neonatal intensive care
- C. Placental insufficiency from maternal viremia; administer antivirals and corticosteroids
- D. Maternal immune thrombocytopenia causing fetal bleeding; administer IVIG to mother
- E. Maternal-fetal ABO incompatibility exacerbated by viral infection; plasmapheresis
Measles, mumps, rubella Explanation: ***Vertical transmission causing fetal aplastic crisis; intrauterine transfusion with close monitoring***
- **Parvovirus B19** targets **erythroid progenitor cells** by binding to the **P antigen**, causing a temporary halt in RBC production known as **aplastic crisis**.
- In the fetus, this leads to **high-output heart failure** and **hydrops fetalis** (ascites, effusions); **intrauterine transfusion** is the definitive treatment to manage severe fetal anemia.
*Fetal cardiac failure from myocarditis; deliver immediately for neonatal intensive care*
- While Parvovirus can cause some direct **myocarditis**, the primary driver of hydrops is **anemia-induced failure**, not primary cardiac muscle death.
- Immediate delivery at 32 weeks carries risks of **prematurity**; treating the anemia **in utero** via transfusion usually allows the pregnancy to continue to a safer gestational age.
*Placental insufficiency from maternal viremia; administer antivirals and corticosteroids*
- The primary pathology is a direct viral attack on **fetal bone marrow**, not a failure of blood flow through the **placenta**.
- There are no specific **antiviral medications** proven effective against Parvovirus B19; management is strictly **supportive care** through transfusion.
*Maternal immune thrombocytopenia causing fetal bleeding; administer IVIG to mother*
- The presentation clearly shows **anemia** and **reticulocytopenia** (low RBC precursors), not a decrease in **platelets** (thrombocytopenia).
- While **IVIG** is used for chronic B19 infections in immunocompromised patients, it does not treat the acute **fetal hydrops** already visible on ultrasound.
*Maternal-fetal ABO incompatibility exacerbated by viral infection; plasmapheresis*
- Hydrops fetalis in this context is **nonimmune**, caused by viral destruction of RBCs, rather than **immune-mediated hemolysis** from ABO/Rh mismatch.
- **Plasmapheresis** is not indicated for Parvovirus B19 infection; it does nothing to restore the destroyed **erythroid progenitors** in the fetus.
Measles, mumps, rubella US Medical PG Question 8: A public health official must design a vaccination strategy for a refugee camp with 10,000 children under 5 years old. Resources allow for only one vaccine initially. Current diseases in the camp include measles (15 cases/week), diphtheria (5 cases/week), pertussis (20 cases/week), and rotavirus diarrhea (100 cases/week). Three children have died from measles, two from pertussis, and ten from dehydration due to diarrhea. Evaluate which vaccine should be prioritized and justify the decision.
- A. MMR vaccine because measles has the highest case fatality rate and transmission potential (Correct Answer)
- B. DTaP vaccine because pertussis has the highest incidence
- C. Oral rehydration therapy instead of vaccination to address immediate mortality
- D. Rotavirus vaccine because diarrhea has caused the most deaths
- E. Pneumococcal vaccine because it prevents the leading cause of childhood mortality globally
Measles, mumps, rubella Explanation: ***MMR vaccine because measles has the highest case fatality rate and transmission potential***
- In this scenario, **Measles** has the highest **Case Fatality Rate (CFR)** at 20% (3 deaths/15 cases), compared to pertussis (10%) and rotavirus (10%).
- Measles is prioritized in refugee settings due to its extreme **transmissibility (R0 of 12-18)** and its ability to cause **secondary immunosuppression**, which leads to further mortality from other infections.
*DTaP vaccine because pertussis has the highest incidence*
- While **pertussis** has a higher weekly incidence (20 cases/week), its **mortality rate** in this cohort is lower than that of measles.
- Public health prioritization in crisis settings focuses on **epidemic potential** and virulence; measles poses a greater risk for explosive, high-mortality outbreaks.
*Oral rehydration therapy instead of vaccination to address immediate mortality*
- **Oral Rehydration Therapy (ORT)** is a treatment modality for symptoms, not a **preventative vaccination strategy** as requested by the prompt.
- While ORT is critical for managing active diarrhea cases, it does not stop the transmission of **rotavirus** or provide the long-term community protection that a vaccine does.
*Rotavirus vaccine because diarrhea has caused the most deaths*
- Although **rotavirus** caused the highest absolute number of deaths (10), its **case fatality rate** (10/100 = 10%) is significantly lower than that of measles.
- Vaccination for measles is prioritized because it is a more effective single-dose intervention for preventing **explosive outbreaks** in overcrowded refugee conditions.
*Pneumococcal vaccine because it prevents the leading cause of childhood mortality globally*
- While the **Pneumococcal vaccine** addresses significant global mortality, it is not targeted toward the **active infectious outbreaks** (measles, pertussis, rotavirus) currently occurring in the camp.
- Resource allocation in an emergency must address the **current epidemiological profile** and immediate threats rather than general global health statistics.
Measles, mumps, rubella US Medical PG Question 9: A hospital infection control committee reviews a cluster of 5 cases of invasive pneumococcal disease over 6 months, all caused by serotype 19A, in vaccinated children aged 3-5 years who received all recommended doses of PCV13. All isolates show resistance to penicillin and macrolides. The committee must evaluate the outbreak and recommend interventions. Which factor most likely explains this outbreak despite appropriate vaccination?
- A. Serotype replacement with non-vaccine serotypes after PCV7 was replaced by PCV13
- B. Evolution of antibiotic resistance in serotype 19A reducing vaccine effectiveness
- C. Inadequate immune response in children with undiagnosed primary immunodeficiency
- D. Vaccine storage failure leading to loss of immunogenicity
- E. Serotype 19A strain with capsular switching evading vaccine-induced immunity (Correct Answer)
Measles, mumps, rubella Explanation: ***Serotype 19A strain with capsular switching evading vaccine-induced immunity***
- **Capsular switching** occurs when *Streptococcus pneumoniae* undergoes **horizontal gene transfer**, allowing a strain to express a capsule (like 19A) that may have slight antigenic variations or different genetic backgrounds from the vaccine strain.
- This evolutionary mechanism allows the bacteria to evade **vaccine-induced immunity** provided by **PCV13**, even though 19A is a covered serotype, leading to breakthrough invasive disease.
*Serotype replacement with non-vaccine serotypes after PCV7 was replaced by PCV13*
- **Serotype replacement** refers to an increase in disease caused by serotypes **not included** in the vaccine, whereas 19A is specifically included in PCV13.
- This phenomenon explained the rise of 19A after PCV7 usage, but it does not explain why 19A specifically is causing an outbreak in **PCV13-vaccinated** children.
*Evolution of antibiotic resistance in serotype 19A reducing vaccine effectiveness*
- **Antibiotic resistance** (to penicillin and macrolides) is a common feature of serotype 19A but does not directly impact **vaccine effectiveness**.
- The vaccine targets the **polysaccharide capsule**, and the immune response is independent of the bacterial mechanisms used to resist antibiotics.
*Inadequate immune response in children with undiagnosed primary immunodeficiency*
- While **immunodeficiency** can lead to vaccine failure, it is highly unlikely that a cluster of five unrelated children would all have the same undiagnosed condition.
- An outbreak or **cluster** suggests a factor related to the pathogen's evolution or the vaccine's delivery rather than host-specific immune defects.
*Vaccine storage failure leading to loss of immunogenicity*
- **Cold chain failure** or storage issues could lead to loss of potency, but this usually results in a broader lack of protection against many serotypes, not just 19A.
- Capsular switching is a more scientifically documented reason for **specific serotype breakthrough** in controlled clinical populations receiving the same vaccine profile.
Measles, mumps, rubella US Medical PG Question 10: A 65-year-old man with diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease presents with sudden onset right-sided facial weakness, inability to close his right eye, and loss of taste on the anterior two-thirds of his tongue. He has vesicular lesions in his right external auditory canal. He received varicella vaccine 20 years ago and had shingles on his trunk 5 years ago. Analyze the relationship between his current presentation and his varicella vaccination history.
- A. His previous shingles and current presentation both resulted from reactivation of wild-type VZV acquired before vaccination (Correct Answer)
- B. The varicella vaccine virus has reactivated to cause this condition
- C. This is a bacterial infection unrelated to varicella-zoster virus
- D. The current infection represents primary varicella despite previous vaccination
- E. Simultaneous reactivation of vaccine and wild-type VZV strains
Measles, mumps, rubella Explanation: ***His previous shingles and current presentation both resulted from reactivation of wild-type VZV acquired before vaccination***
- The patient presents with **Ramsay Hunt syndrome** (herpes zoster oticus), characterized by facial nerve palsy, ear canal vesicles, and taste loss, caused by **VZV reactivation** in the **geniculate ganglion**.
- Given his age, he likely contracted **wild-type VZV** (chickenpox) in childhood before the vaccine was available in 1995; subsequent adult vaccination does not eliminate already latent wild-type virus.
*The varicella vaccine virus has reactivated to cause this condition*
- While the **Oka strain** (live-attenuated vaccine) can establish latency, it is significantly less virulent and less likely to reactivate compared to the **wild-type strain**.
- Reactivation of vaccine-strain VZV is extremely rare in immunocompetent or even partially immunocompromised adults who had prior natural chickenpox.
*This is a bacterial infection unrelated to varicella-zoster virus*
- The combination of **vesicular lesions** and cranial nerve involvement is pathognomonic for a viral etiology, specifically a **herpetic infection**.
- Bacterial conditions like **otitis externa** or **malignant otitis externa** would present with different findings such as severe ear canal edema or bone destruction rather than specific taste loss and zoster-like vesicles.
*The current infection represents primary varicella despite previous vaccination*
- Primary varicella (chickenpox) presents as a **diffuse pruritic rash** in varying stages of development, not a localized dermatomal or cranial nerve distribution.
- The patient's history of prior shingles confirms he already had a latent **VZV infection**, making a "primary" infection (first exposure) impossible.
*Simultaneous reactivation of vaccine and wild-type VZV strains*
- There is no clinical evidence or common pathophysiological mechanism to support the **simultaneous reactivation** of two different VZV strains.
- The **wild-type virus** is the dominant latent pathogen that typically reactivates during periods of **immunocompromise** (like CKD and diabetes), suppressing any potential activity from the weaker vaccine strain.
More Measles, mumps, rubella US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.