Hepatitis A and B vaccination US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Hepatitis A and B vaccination. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Hepatitis A and B vaccination US Medical PG Question 1: An 11-year-old boy is brought to his pediatrician by his parents for the routine Tdap immunization booster dose that is given during adolescence. Upon reviewing the patient’s medical records, the pediatrician notes that he was immunized according to CDC recommendations, with the exception that he received a catch-up Tdap immunization at the age of 8 years. When the pediatrician asks the boy’s parents about this delay, they inform the doctor that they immigrated to this country 3 years ago from Southeast Asia, where the child had not been immunized against diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis. Therefore, he received a catch-up series at 8 years of age, which included the first dose of the Tdap vaccine. Which of the following options should the pediatrician choose to continue the boy’s immunization schedule?
- A. A single dose of Td vaccine at 18 years of age
- B. A single dose of Td vaccine now
- C. No further vaccination needed
- D. A single dose of Tdap vaccine now
- E. A single dose of Tdap vaccine at 13 years of age (Correct Answer)
Hepatitis A and B vaccination Explanation: ***A single dose of Tdap vaccine at 13 years of age***
- The CDC recommends a **minimum interval of 5 years** between Tdap doses when Tdap is given as part of a catch-up series.
- Since this patient received his first Tdap at age 8, the earliest he should receive the adolescent booster is at **age 13** (5 years later).
- This timing ensures adequate spacing while still providing the recommended adolescent booster for **pertussis, tetanus, and diphtheria** protection.
- The 5-year interval prevents excessive antigen exposure and optimizes immune response.
*A single dose of Tdap vaccine now*
- Giving Tdap now would result in only a **3-year interval** from the previous Tdap dose at age 8.
- This violates the CDC recommendation of a **minimum 5-year interval** between Tdap doses.
- Shorter intervals may increase local reactogenicity without improving protection.
*A single dose of Td vaccine now*
- While this would provide tetanus and diphtheria protection, it would **not protect against pertussis**, which is a critical component of adolescent vaccination.
- The Tdap vaccine is specifically recommended for adolescents to boost waning pertussis immunity.
- Additionally, giving it now would still be earlier than the recommended 5-year interval from the previous pertussis-containing vaccine.
*A single dose of Td vaccine at 18 years of age*
- This option would result in a **10-year gap** from the last pertussis-containing vaccine, leaving the adolescent vulnerable during high-risk years.
- The adolescent Tdap booster is specifically timed for ages 11-13 to protect during peak transmission periods in middle and high school.
- Waiting until 18 would miss the critical window for pertussis protection.
*No further vaccination needed*
- While the patient completed a catch-up series, the CDC still recommends an **adolescent Tdap booster** even for those who received Tdap in a catch-up series.
- The adolescent booster is important to maintain immunity against pertussis, which wanes significantly over time.
- The booster should be given at age 13 to maintain the 5-year minimum interval.
Hepatitis A and B vaccination US Medical PG Question 2: Two months after giving birth to a boy, a 27-year-old woman comes to the physician with her infant for a well-child examination. She was not seen by a physician during her pregnancy. Physical examination of the mother and the boy shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show elevated titers of hepatitis B surface antigen in both the mother and the boy. Which of the following statements regarding the infant's condition is most accurate?
- A. Hepatitis B e antigen titer is likely undetectable
- B. Chronic infection is unlikely
- C. Lifetime risk of hepatocellular carcinoma is low
- D. Significant elevation of transaminases is not expected (Correct Answer)
- E. The viral replication rate is low
Hepatitis A and B vaccination Explanation: **Significant elevation of transaminases is not expected**
- Infants infected with HBV vertically are often **immunologically tolerant** to the virus, leading to low or normal levels of **alanine aminotransferase (ALT)** and **aspartate aminotransferase (AST)** despite high viral loads.
- This **immune tolerance** means their immune system does not actively attack infected hepatocytes, preventing inflammation and liver damage in the early stages.
*Hepatitis B e antigen titer is likely undetectable*
- In infants with **vertical transmission** of HBV, especially when not treated, the **HBeAg titer** is typically **HIGH** and detectable, indicating active viral replication.
- A detectable HBeAg in this scenario signifies a **highly infectious state** and is a marker of high viral load.
*Chronic infection is unlikely*
- Perinatal transmission of HBV has a very high — 70-90% — likelihood of leading to **chronic HBV infection** if the infant is not properly immunized at birth.
- The presence of **HBsAg in both mother and child** and lack of prenatal care strongly suggest chronic infection in the infant.
*Lifetime risk of hepatocellular carcinoma is low*
- Infants who acquire HBV perinatally and develop **chronic infection** have a significantly **increased lifetime risk** of developing **cirrhosis** and **hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)**.
- The immune tolerance and persistent viral replication in early life contribute to long-term liver disease progression.
*The viral replication rate is low*
- In infants with vertically transmitted HBV who are in the **immune-tolerant phase**, the **viral replication rate is high**, often characterized by very high HBV DNA levels.
- This high replication without significant immune response is why they are often asymptomatic but highly infectious.
Hepatitis A and B vaccination US Medical PG Question 3: A 28-year-old woman gives birth to a 2.2 kg child while on vacation. The mother's medical records are faxed to the hospital and demonstrate the following on hepatitis panel: hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg) positive, anti-hepatitis B core antigen (anti-HbcAg) positive, hepatitis C RNA is detected, hepatitis C antibody is reactive. Which of the following should be administered to the patient's newborn child?
- A. Hepatitis B vaccine, ledipasvir/sofosbuvir
- B. Hepatitis B IVIG and vaccine (Correct Answer)
- C. Hepatitis B IVIG, hepatitis B vaccine and ledipasvir/sofosbuvir
- D. Hepatitis B IVIG now, hepatitis B vaccine in one month
- E. Hepatitis B vaccine
Hepatitis A and B vaccination Explanation: ***Hepatitis B IVIG and vaccine***
- The mother is **HBsAg positive** and **anti-HBcAg positive**, indicating a **chronic hepatitis B infection**. To prevent vertical transmission, the neonate must receive both **Hepatitis B Immune Globulin (HBIG)** and the **Hepatitis B vaccine** within 12 hours of birth.
- While the mother also has **Hepatitis C (HCV) RNA detected** and **HCV antibody reactive**, there is currently no preventative measure for HCV transmission to the newborn at birth, as antiviral medications like ledipasvir/sofosbuvir are not administered to neonates for this purpose.
*Hepatitis B vaccine, ledipisvir/sofosbuvir*
- Administering ledipasvir/sofosbuvir to the newborn is **not indicated** for preventing vertical transmission of Hepatitis C; these antivirals are used for treating HCV infection in adults and older children.
- While the Hepatitis B vaccine is necessary, it is **insufficient alone** for preventing perinatal HBV transmission in infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers.
*Hepatitis B IVIG, hepatitis B vaccine and ledipisvir/sofosbuvir*
- **Ledipasvir/sofosbuvir** is not a recommended prophylactic or treatment measure for newborns to prevent hepatitis C infection.
- While HBIG and the vaccine are correct for Hepatitis B, the addition of HCV antivirals for the neonate is **inappropriate**.
*Hepatitis B IVIG now, hepatitis B vaccine in one month*
- Both **HBIG** and the **first dose of the Hepatitis B vaccine** must be given **within 12 hours of birth** to be maximally effective in preventing perinatal HBV transmission. Delaying the vaccine dose significantly reduces its protective efficacy.
- This regimen would leave the newborn **unprotected** for a crucial period during which HBV transmission is most likely.
*Hepatitis B vaccine*
- Giving only the **Hepatitis B vaccine** is **insufficient** for an infant born to an HBsAg-positive mother.
- In such cases, **HBIG** is also required to provide immediate passive immunity and maximize protection against perinatal HBV infection, which has a high risk of chronicity.
Hepatitis A and B vaccination US Medical PG Question 4: A 3-month-old African American boy presents to his pediatrician’s office for his routine well visit. He was born full-term from an uncomplicated vaginal delivery. He is exclusively breastfeeding and not receiving any medications or supplements. Today, his parents report no issues or concerns with their child. He is lifting his head for brief periods and smiling. He has received only 2 hepatitis B vaccines. Which of the following is the correct advice for this patient’s parents?
- A. He should be sleeping more.
- B. He should have his serum lead level checked to screen for lead intoxication.
- C. He should start vitamin D supplementation. (Correct Answer)
- D. He should start rice cereal.
- E. He needs a 3rd hepatitis B vaccine.
Hepatitis A and B vaccination Explanation: ***He should start vitamin D supplementation.***
- **Exclusively breastfed** infants, regardless of maternal vitamin D intake, require **vitamin D supplementation** due to insufficient amounts in breast milk.
- The recommended daily dose is **400 IU** starting from the first few days of life, to prevent **rickets** and promote bone health.
- **African American infants** have an additional risk factor due to increased skin melanin content, which reduces cutaneous vitamin D synthesis from sunlight exposure.
*He should be sleeping more.*
- A 3-month-old infant typically sleeps between **14-17 hours per day**, with **waking periods to feed** and interact.
- The case description does not indicate any concerns with the child's sleep patterns, and **developmental milestones** like lifting his head and smiling are being met.
*He should have his serum lead level checked to screen for lead intoxication.*
- **Lead screening** is not routinely recommended for all infants unless specific **risk factors** are present, such as living in an older home with lead paint, or having siblings with elevated lead levels.
- There are no reported risk factors for lead exposure in this patient's history.
*He should start rice cereal.*
- Introduction of solid foods, such as rice cereal, is typically recommended around **6 months of age**, when the infant shows signs of **developmental readiness**.
- These signs include **head control**, sitting with support, and showing interest in food.
*He needs a 3rd hepatitis B vaccine.*
- The **third dose of the hepatitis B vaccine** is typically administered between **6 and 18 months of age**.
- At 3 months old, the infant is not yet due for his third dose.
Hepatitis A and B vaccination US Medical PG Question 5: A 20-year-old man who is a biology major presents to his physician for a simple check-up. He is informed that he hasn't received a hepatitis B vaccine. When the first injection is applied, the medical professional informs him that he will need to come back 2 more times on assigned days, since the vaccine is given in 3 doses. Which of the following antibodies is produced first in the college student as a result of the first vaccination?
- A. IgE
- B. IgG
- C. IgM (Correct Answer)
- D. IgD
- E. IgA
Hepatitis A and B vaccination Explanation: ***IgM***
- Upon initial exposure to an antigen (like in the first vaccine dose), **IgM antibodies** are the first class to be produced and secreted by plasma cells.
- This **primary immune response** is characterized by a rapid, but short-lived, **IgM** peak.
*IgE*
- **IgE antibodies** are primarily involved in **allergic reactions** and defense against parasites, not the initial response to vaccination.
- Their production is typically triggered by exposure to specific allergens or parasites and mediated by Th2 helper T cells.
*IgG*
- **IgG antibodies** are the most abundant class in serum and are produced later in the primary response and predominantly during the **secondary immune response**.
- They provide **long-term immunity** and can cross the placenta, but are not the first antibody produced after initial antigen exposure.
*IgD*
- **IgD antibodies** are mainly found on the surface of **naive B cells** and act as B-cell receptors, playing a role in B-cell activation.
- They are not secreted in significant amounts into the serum and thus are not the first circulating antibody produced after vaccination.
*IgA*
- **IgA antibodies** are primarily found in **mucosal secretions** (e.g., saliva, tears, breast milk, gastrointestinal fluid) and play a key role in mucosal immunity.
- They are not the first antibody produced systemically in response to an initial vaccine exposure.
Hepatitis A and B vaccination US Medical PG Question 6: A 3255-g (7-lb) female newborn is delivered at term. Pregnancy and delivery were uncomplicated. On the day of her birth, she is given a routine childhood vaccine that contains a noninfectious glycoprotein. This vaccine will most likely help prevent infection by which of the following pathogens?
- A. Bordetella pertussis
- B. Rotavirus
- C. Poliovirus
- D. Haemophilus influenzae type b
- E. Hepatitis B virus (Correct Answer)
Hepatitis A and B vaccination Explanation: ***Hepatitis B virus***
- The **Hepatitis B vaccine** is routinely given at birth and contains a **noninfectious glycoprotein** (HBsAg) that elicits an immune response.
- This vaccine is crucial for preventing mother-to-child transmission and provides long-term protection against **Hepatitis B infection**.
*Bordetella pertussis*
- The vaccine for **Bordetella pertussis** (whooping cough) is part of the DTaP vaccine and is typically given at 2 months of age, not at birth.
- The DTaP vaccine usually contains **inactivated toxins** or acellular components, not solely a glycoprotein.
*Rotavirus*
- The **Rotavirus vaccine** is an **oral live-attenuated vaccine** administered in two or three doses, with the first dose typically given at 2 months of age.
- It does not contain a noninfectious glycoprotein.
*Poliovirus*
- The **Poliovirus vaccine** (IPV) is an **inactivated vaccine** given at 2 months of age, and the **oral poliovirus vaccine (OPV)** is a live-attenuated vaccine.
- Neither is routinely given at birth, nor described as a noninfectious glycoprotein.
*Haemophilus influenzae type b*
- The **Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccine** is a polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine, first administered at 2 months of age.
- While it contains a protein component, it is not typically given at birth.
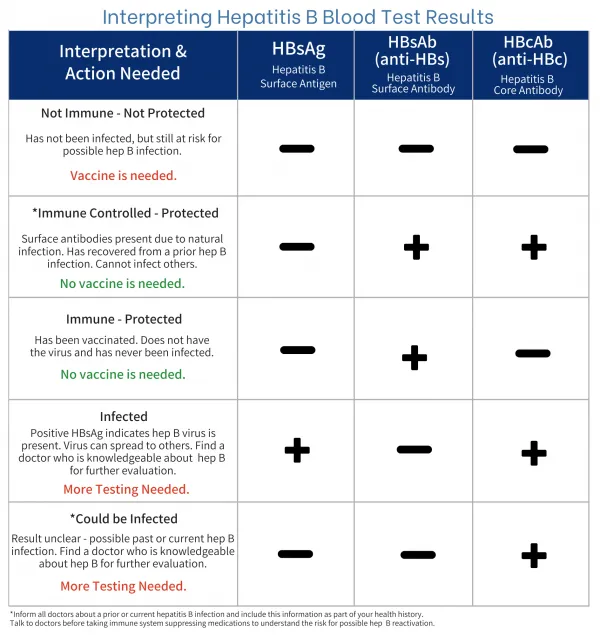
Hepatitis A and B vaccination US Medical PG Question 7: A 44-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with jaundice and diffuse abdominal pain. She denies any previous medical problems and says she does not take any medications, drugs, or supplements. Her temperature is 97.6°F (36.4°C), blood pressure is 133/87 mmHg, pulse is 86/min, respirations are 22/min, and oxygen saturation is 100% on room air. Physical exam is notable for sclera which are icteric and there is tenderness to palpation over the right upper quadrant. Laboratory studies are ordered as seen below.
Hepatitis B surface antigen: Positive
Hepatitis B surface antibody: Negative
Hepatitis B core antibody IgM: Negative
Hepatitis B core antibody IgG: Positive
Hepatitis B E antigen: Positive
Hepatitis B E antibody (anti-HBe): Negative
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Chronic hepatitis B infection (Correct Answer)
- B. Hepatitis B vaccination
- C. Acute hepatitis B infection
- D. Resolved hepatitis B infection
- E. No hepatitis B vaccination or infection
Hepatitis A and B vaccination Explanation: ### ***Chronic hepatitis B infection***
- The presence of **Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) positive** combined with **Hepatitis B core antibody IgG (anti-HBc IgG) positive** indicates infection that has persisted beyond 6 months.
- **Hepatitis B core antibody IgM (anti-HBc IgM) negative** rules out acute infection, as IgM antibodies appear early in acute hepatitis B.
- **Hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) positive** indicates active viral replication and high infectivity, consistent with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B.
- The clinical presentation with jaundice and RUQ pain suggests an acute flare of chronic hepatitis B infection.
### *Hepatitis B vaccination*
- Successful hepatitis B vaccination produces **anti-HBs positive** with **HBsAg negative** and **anti-HBc negative**.
- This patient has **HBsAg positive** and **anti-HBc IgG positive**, indicating actual infection rather than vaccine-induced immunity.
### *Acute hepatitis B infection*
- Acute hepatitis B is characterized by **HBsAg positive** with **anti-HBc IgM positive** (IgM appears first in acute infection).
- This patient has **anti-HBc IgM negative** and **anti-HBc IgG positive**, indicating the infection occurred more than 6 months ago, consistent with chronic rather than acute infection.
### *Resolved hepatitis B infection*
- Resolved infection shows **HBsAg negative**, **anti-HBs positive**, and **anti-HBc IgG positive**.
- This patient's **HBsAg positive** status directly indicates ongoing infection, not resolution.
### *No hepatitis B vaccination or infection*
- Complete absence of exposure would show **HBsAg negative**, **anti-HBs negative**, and **anti-HBc negative** (all markers negative).
- This patient has multiple positive markers including **HBsAg** and **anti-HBc IgG**, confirming hepatitis B infection.
Hepatitis A and B vaccination US Medical PG Question 8: A 1-year-old immigrant girl has not received any recommended vaccines since birth. She attends daycare and remains healthy despite her daily association with several other children for the past 3 months at a home day-care facility. Which of the following phenomena explains why she has not contracted any vaccine-preventable diseases such as measles, diphtheria, or pertussis?
- A. Herd immunity (Correct Answer)
- B. Immune evasion
- C. Tolerance
- D. Genetic drift
- E. Genetic shift
Hepatitis A and B vaccination Explanation: ***Herd immunity***
- **Herd immunity** occurs when a significant portion of a population is immune to a disease, providing **indirect protection** to unvaccinated individuals.
- In a daycare setting with vaccinated children, the low prevalence of disease agents protects the unvaccinated girl.
*Immune evasion*
- **Immune evasion** refers to mechanisms used by pathogens to **avoid detection** and destruction by the host immune system.
- This concept describes how a pathogen survives in an infected individual, not why an uninfected individual avoids disease.
*Tolerance*
- **Tolerance** in immunology is a state of **unresponsiveness to antigens**, preventing the immune system from attacking self-components or harmless foreign substances.
- It does not explain protection from infectious diseases; rather, it's about not mounting an immune response when one is usually expected.
*Genetic drift*
- **Genetic drift** is a change in the frequency of an existing gene variant (allele) in a population due to **random sampling** of organisms.
- This is a concept in population genetics that does not explain an individual's protection from infectious disease.
*Genetic shift*
- **Genetic shift** (antigenic shift) refers to an **abrupt, major change** in the influenza virus, leading to new hemagglutinin and/or neuraminidase proteins.
- This phenomenon explains the emergence of new influenza strains, not the protection of an individual from vaccine-preventable diseases.
Hepatitis A and B vaccination US Medical PG Question 9: A 52-year-old male patient with chronic alcoholism presents to an ambulatory medical clinic, where the hepatologist elects to perform comprehensive hepatitis B screening, in addition to several other screening and preventative measures. Given the following choices, which serologic marker, if positive, would indicate the patient’s immunity to the hepatitis B virus?
- A. HBeAb
- B. HBeAg
- C. HBsAb (Correct Answer)
- D. HBsAg
- E. HBcAb
Hepatitis A and B vaccination Explanation: ***HBsAb***
- A positive **HBsAb** (Hepatitis B surface antibody) indicates immunity to hepatitis B virus, either from successful **vaccination** or **recovery from past infection**.
- This antibody provides **protective immunity** against future HBV infection and is the definitive marker of immunity.
*HBeAb*
- **HBeAb** (Hepatitis B e antibody) indicates **seroconversion** from HBeAg during chronic HBV infection, suggesting lower viral replication.
- It does **not confer immunity** against the virus itself and only reflects a phase of chronic infection.
*HBeAg*
- **HBeAg** (Hepatitis B e antigen) indicates **active viral replication** with high infectivity during ongoing hepatitis B infection.
- Its presence signifies a **replicative phase** of infection and increased risk of transmission to others.
*HBsAg*
- **HBsAg** (Hepatitis B surface antigen) indicates **active hepatitis B infection**, whether acute or chronic.
- This antigen is the **first serologic marker** to appear following exposure and confirms presence of the virus.
*HBcAb*
- **HBcAb** (Hepatitis B core antibody) indicates **previous or current exposure** to hepatitis B virus.
- It does **not differentiate** between acute, chronic, or resolved infection and does not confer protective immunity.
Hepatitis A and B vaccination US Medical PG Question 10: A 52-year-old female presents to her primary care physician for medical evaluation prior to an elective hip replacement surgery. She has hypertension and diabetes, both of which are well controlled on oral medications. She also admits to occasional use of recreational injection drugs so a panel of serologies are obtained. Based on the results, the patient is found to have had a previous infection with hepatitis B from which she has fully recovered. Which of the following is a characteristic of the immunoglobulin subtype that most likely binds to hepatitis B core antigen in this patient?
- A. It exists as a dimer
- B. It is only activated by multivalent immunogens
- C. It exists as a pentamer
- D. It activates mast cells
- E. It exists as a monomer (Correct Answer)
Hepatitis A and B vaccination Explanation: ***It exists as a monomer***
- In a recovered hepatitis B infection, **anti-HBc IgG** antibodies are prominent, indicating past exposure and immunity.
- **IgG** is the most abundant immunoglobulin in serum and exists primarily as a **monomer**, providing long-term immunity.
*It exists as a dimer*
- This characteristic primarily describes **secretory IgA**, which is found in mucosal secretions like tears, saliva, and breast milk.
- While IgA can be involved in host defense, it's not the primary antibody subtype associated with sustained immunity after hepatitis B recovery, nor does it typically target the **core antigen** in this context.
*It is only activated by multivalent immunogens*
- This statement is more characteristic of **IgM**, which often requires multiple binding sites to activate complement efficiently due to its pentameric structure.
- **IgG** can bind to both univalent and multivalent antigens and is effective in neutralizing pathogens and activating other immune responses.
*It exists as a pentamer*
- This describes **IgM**, which is typically the first antibody produced during a primary immune response and is found on the surface of B cells.
- In a recovered infection, IgM would have largely subsided, replaced by **IgG**.
*It activates mast cells*
- This is a hallmark function of **IgE**, which binds to receptors on mast cells and basophils, triggering the release of histamine and other mediators in allergic reactions.
- **IgG** has different effector functions, such as opsonization, neutralization, and complement activation.
More Hepatitis A and B vaccination US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.