Childhood immunization schedule US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Childhood immunization schedule. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Childhood immunization schedule US Medical PG Question 1: A 40-year-old pregnant woman, G4 P3, visits your office at week 30 of gestation. She is very excited about her pregnancy and wants to be the healthiest she can be in preparation for labor and for her baby. What vaccination should she receive at this visit?
- A. Measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR)
- B. Varicella vaccine
- C. Herpes zoster vaccine
- D. Live attenuated influenza vaccine
- E. Tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis (Tdap) (Correct Answer)
Childhood immunization schedule Explanation: ***Tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis (Tdap)***
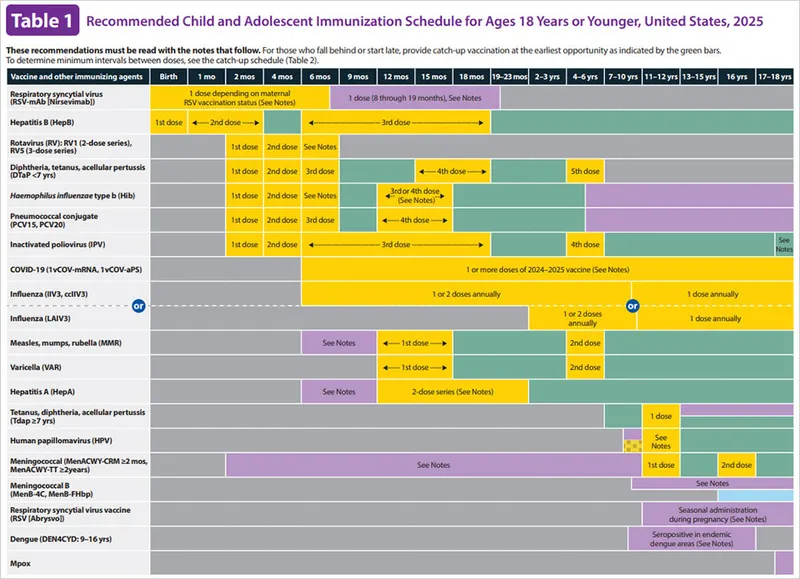
- The Tdap vaccine is recommended during each pregnancy, preferably between **27 and 36 weeks of gestation**, to maximize maternal antibody response and passive antibody transfer to the fetus.
- This provides critical protection against **pertussis (whooping cough)** for the newborn, who is too young to be vaccinated.
*Measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR)*
- The **MMR vaccine is a live vaccine** and is **contraindicated during pregnancy** due to the theoretical risk of congenital rubella syndrome, although no cases have been reported.
- It should be administered **postpartum** if the mother is not immune to rubella.
*Varicella vaccine*
- The **varicella vaccine is a live vaccine** and is **contraindicated during pregnancy** due to the theoretical risk of congenital varicella syndrome.
- Like MMR, it should be offered in the **postpartum period** if the woman is not immune.
*Herpes zoster vaccine*
- The herpes zoster vaccine is typically recommended for **older adults** (50 years and older) for shingles prevention.
- It is **not routinely recommended during pregnancy**, and its safety and efficacy in this population have not been sufficiently established.
*Live attenuated influenza vaccine*
- The **live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV)** is **contraindicated during pregnancy** due to its live virus content.
- Pregnant women should receive the **inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV)**, which is safe and recommended during any trimester.
Childhood immunization schedule US Medical PG Question 2: An 11-year-old boy is brought to his pediatrician by his parents for the routine Tdap immunization booster dose that is given during adolescence. Upon reviewing the patient’s medical records, the pediatrician notes that he was immunized according to CDC recommendations, with the exception that he received a catch-up Tdap immunization at the age of 8 years. When the pediatrician asks the boy’s parents about this delay, they inform the doctor that they immigrated to this country 3 years ago from Southeast Asia, where the child had not been immunized against diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis. Therefore, he received a catch-up series at 8 years of age, which included the first dose of the Tdap vaccine. Which of the following options should the pediatrician choose to continue the boy’s immunization schedule?
- A. A single dose of Td vaccine at 18 years of age
- B. A single dose of Td vaccine now
- C. No further vaccination needed
- D. A single dose of Tdap vaccine now
- E. A single dose of Tdap vaccine at 13 years of age (Correct Answer)
Childhood immunization schedule Explanation: ***A single dose of Tdap vaccine at 13 years of age***
- The CDC recommends a **minimum interval of 5 years** between Tdap doses when Tdap is given as part of a catch-up series.
- Since this patient received his first Tdap at age 8, the earliest he should receive the adolescent booster is at **age 13** (5 years later).
- This timing ensures adequate spacing while still providing the recommended adolescent booster for **pertussis, tetanus, and diphtheria** protection.
- The 5-year interval prevents excessive antigen exposure and optimizes immune response.
*A single dose of Tdap vaccine now*
- Giving Tdap now would result in only a **3-year interval** from the previous Tdap dose at age 8.
- This violates the CDC recommendation of a **minimum 5-year interval** between Tdap doses.
- Shorter intervals may increase local reactogenicity without improving protection.
*A single dose of Td vaccine now*
- While this would provide tetanus and diphtheria protection, it would **not protect against pertussis**, which is a critical component of adolescent vaccination.
- The Tdap vaccine is specifically recommended for adolescents to boost waning pertussis immunity.
- Additionally, giving it now would still be earlier than the recommended 5-year interval from the previous pertussis-containing vaccine.
*A single dose of Td vaccine at 18 years of age*
- This option would result in a **10-year gap** from the last pertussis-containing vaccine, leaving the adolescent vulnerable during high-risk years.
- The adolescent Tdap booster is specifically timed for ages 11-13 to protect during peak transmission periods in middle and high school.
- Waiting until 18 would miss the critical window for pertussis protection.
*No further vaccination needed*
- While the patient completed a catch-up series, the CDC still recommends an **adolescent Tdap booster** even for those who received Tdap in a catch-up series.
- The adolescent booster is important to maintain immunity against pertussis, which wanes significantly over time.
- The booster should be given at age 13 to maintain the 5-year minimum interval.
Childhood immunization schedule US Medical PG Question 3: A 24-year-old woman with HIV infection comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. She has been inconsistently taking combined antiretroviral therapy for the past 5 years. She did not receive any childhood vaccinations because her parents were against them. During the consultation, the patient says that she wants to catch up on the missed vaccinations. Laboratory studies show a CD4+ T lymphocyte cell count of 180/mm3. Administration of the vaccine against which of the following agents should be avoided in this patient?
- A. Clostridium tetani
- B. Human papillomavirus
- C. Varicella zoster virus (Correct Answer)
- D. Bordetella pertussis
- E. Haemophilus influenzae
Childhood immunization schedule Explanation: ***Varicella zoster virus***
- The **varicella zoster vaccine is a live attenuated vaccine**, which is generally contraindicated in individuals with severe **immunodeficiency**, such as HIV patients with a **CD4+ count below 200 cells/mm³**.
- Administering a live vaccine to an immunocompromised patient can lead to **uncontrolled viral replication** and potentially cause the disease it is meant to prevent.
*Clostridium tetani*
- The **tetanus vaccine** is a **toxoid vaccine**, meaning it contains inactivated bacterial toxins, not live organisms.
- It is **safe and recommended** for individuals with HIV, regardless of their CD4+ count, to provide protection against tetanus.
*Human papillomavirus*
- The **HPV vaccine** is a **recombinant vaccine**, consisting of viral-like particles (VLPs) and containing no live virus.
- It is **safe and recommended** for HIV-positive individuals and helps prevent HPV-related cancers.
*Bordetella pertussis*
- The **pertussis vaccine** (part of DTaP or Tdap) is an **acellular vaccine**, containing purified bacterial components, not live bacteria.
- It is **safe and recommended** for HIV patients to protect against whooping cough.
*Haemophilus influenzae*
- The **Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccine** is a **conjugate vaccine**, made from bacterial capsular polysaccharide linked to a carrier protein.
- It is **safe and recommended** for HIV-positive individuals, as they are at increased risk for invasive Hib disease.
Childhood immunization schedule US Medical PG Question 4: A 4-month-old boy is brought to the physician by his parents for a well-child examination. He has cystic fibrosis diagnosed by newborn screening. His parents report frequent feedings and large-volume and greasy stools. His 4-year-old brother has autism. Current medications include bronchodilators, pancreatic enzyme supplements, and fat-soluble vitamins. He is at the 18th percentile for height and 15th percentile for weight. Scattered wheezes are heard throughout both lung fields. Examination shows a distended and tympanic abdomen with no tenderness or guarding. Which of the following is a contraindication for administering one or more routine vaccinations?
- A. Allergy to egg protein
- B. History of cystic fibrosis
- C. History of febrile seizures
- D. Fever of 38.2°C (100.7°F) following previous vaccinations
- E. History of intussusception (Correct Answer)
Childhood immunization schedule Explanation: ***History of intussusception***
- A history of **intussusception** is a **contraindication for rotavirus vaccine** administration, as the vaccine itself has a small risk of intussusception, particularly with the first dose.
- The rotavirus vaccine is part of routine childhood immunizations, so this would be a contraindication for one of the routine vaccines.
*Allergy to egg protein*
- Egg allergy is a contraindication primarily for yellow fever vaccine and some influenza vaccines, which are typically not routine vaccinations for a 4-month-old. Many flu vaccines are egg-free or can be safely administered to those with egg allergy under supervision.
- The MMR vaccine is generally safe for those with egg allergy since the amount of egg protein is negligible.
*History of cystic fibrosis*
- **Cystic fibrosis** itself is **not a contraindication** to routine vaccinations; in fact, patients with chronic conditions like CF are often *more* encouraged to receive vaccinations to prevent severe infections.
- The patient's symptoms (poor growth, greasy stools, wheezing) are manifestations of CF, not reasons to defer vaccination.
*History of febrile seizures*
- A history of **febrile seizures** is generally **not a contraindication** to routine vaccinations.
- Parents should be counseled on fever management after vaccination, but the risk of recurrent febrile seizures is not increased by vaccination to a level that warrants deferral.
*Fever of 38.2°C (100.7°F) following previous vaccinations*
- A **low-grade fever** after vaccination is a common and **expected immune response**, not a contraindication for future doses.
- Only a **severe allergic reaction** (e.g., anaphylaxis) to a previous dose of a vaccine or one of its components is a contraindication to subsequent doses of that specific vaccine.
Childhood immunization schedule US Medical PG Question 5: A 20-year-old primigravid woman comes to the physician in October for her first prenatal visit. She has delayed the visit because she wanted a “natural birth” but was recently convinced to get a checkup after feeling more tired than usual. She feels well. Menarche was at the age of 12 years and menses used to occur at regular 28-day intervals and last 3–7 days. The patient emigrated from Mexico 2 years ago. Her immunization records are unavailable. Pelvic examination shows a uterus consistent in size with a 28-week gestation. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 12.4 g/dL
Leukocyte count 8,000/mm3
Blood group B negative
Serum
Glucose 88 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.1 mg/dL
TSH 3.8 μU/mL
Rapid plasma reagin negative
HIV antibody negative
Hepatitis B surface antigen negative
Urinalysis shows no abnormalities. Urine culture is negative. Chlamydia and gonorrhea testing are negative. A Pap smear is normal. Administration of which of the following vaccines is most appropriate at this time?
- A. Varicella and influenza
- B. Varicella and Tdap
- C. Influenza only
- D. Tdap and influenza (Correct Answer)
- E. Hepatitis B and MMR
Childhood immunization schedule Explanation: ***Tdap and influenza***
- The **Tdap vaccine** is recommended for pregnant women during each pregnancy, preferably between **27 and 36 weeks gestation**, to provide passive immunity to the newborn against pertussis. The patient is at 28 weeks gestation.
- The **influenza vaccine** is recommended for all pregnant women, regardless of trimester, during flu season (October in this case) to protect both the mother and the newborn.
*Varicella and influenza*
- The **varicella vaccine is contraindicated in pregnancy** because it is a live attenuated vaccine.
- While influenza vaccine is appropriate, administering varicella vaccine is not.
*Varicella and Tdap*
- As mentioned, the **varicella vaccine is contraindicated in pregnancy** due to its live attenuated nature.
- Although Tdap is appropriate, varicella is not.
*Influenza only*
- While the **influenza vaccine is appropriate**, the **Tdap vaccine** is also indicated for this patient given her gestational age and the benefits for the newborn.
- Administering only influenza would miss an opportunity to provide crucial pertussis protection.
*Hepatitis B and MMR*
- The **Hepatitis B vaccine** is safe in pregnancy if indicated, but the patient tested **Hepatitis B surface antigen negative**, suggesting no current infection and no immediate need for vaccination based on the provided information.
- The **MMR vaccine is contraindicated in pregnancy** because it is a live attenuated vaccine.
Childhood immunization schedule US Medical PG Question 6: A 28-year-old woman gives birth to a 2.2 kg child while on vacation. The mother's medical records are faxed to the hospital and demonstrate the following on hepatitis panel: hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg) positive, anti-hepatitis B core antigen (anti-HbcAg) positive, hepatitis C RNA is detected, hepatitis C antibody is reactive. Which of the following should be administered to the patient's newborn child?
- A. Hepatitis B vaccine, ledipasvir/sofosbuvir
- B. Hepatitis B IVIG and vaccine (Correct Answer)
- C. Hepatitis B IVIG, hepatitis B vaccine and ledipasvir/sofosbuvir
- D. Hepatitis B IVIG now, hepatitis B vaccine in one month
- E. Hepatitis B vaccine
Childhood immunization schedule Explanation: ***Hepatitis B IVIG and vaccine***
- The mother is **HBsAg positive** and **anti-HBcAg positive**, indicating a **chronic hepatitis B infection**. To prevent vertical transmission, the neonate must receive both **Hepatitis B Immune Globulin (HBIG)** and the **Hepatitis B vaccine** within 12 hours of birth.
- While the mother also has **Hepatitis C (HCV) RNA detected** and **HCV antibody reactive**, there is currently no preventative measure for HCV transmission to the newborn at birth, as antiviral medications like ledipasvir/sofosbuvir are not administered to neonates for this purpose.
*Hepatitis B vaccine, ledipisvir/sofosbuvir*
- Administering ledipasvir/sofosbuvir to the newborn is **not indicated** for preventing vertical transmission of Hepatitis C; these antivirals are used for treating HCV infection in adults and older children.
- While the Hepatitis B vaccine is necessary, it is **insufficient alone** for preventing perinatal HBV transmission in infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers.
*Hepatitis B IVIG, hepatitis B vaccine and ledipisvir/sofosbuvir*
- **Ledipasvir/sofosbuvir** is not a recommended prophylactic or treatment measure for newborns to prevent hepatitis C infection.
- While HBIG and the vaccine are correct for Hepatitis B, the addition of HCV antivirals for the neonate is **inappropriate**.
*Hepatitis B IVIG now, hepatitis B vaccine in one month*
- Both **HBIG** and the **first dose of the Hepatitis B vaccine** must be given **within 12 hours of birth** to be maximally effective in preventing perinatal HBV transmission. Delaying the vaccine dose significantly reduces its protective efficacy.
- This regimen would leave the newborn **unprotected** for a crucial period during which HBV transmission is most likely.
*Hepatitis B vaccine*
- Giving only the **Hepatitis B vaccine** is **insufficient** for an infant born to an HBsAg-positive mother.
- In such cases, **HBIG** is also required to provide immediate passive immunity and maximize protection against perinatal HBV infection, which has a high risk of chronicity.
Childhood immunization schedule US Medical PG Question 7: A 20-year-old man who is a biology major presents to his physician for a simple check-up. He is informed that he hasn't received a hepatitis B vaccine. When the first injection is applied, the medical professional informs him that he will need to come back 2 more times on assigned days, since the vaccine is given in 3 doses. Which of the following antibodies is produced first in the college student as a result of the first vaccination?
- A. IgE
- B. IgG
- C. IgM (Correct Answer)
- D. IgD
- E. IgA
Childhood immunization schedule Explanation: ***IgM***
- Upon initial exposure to an antigen (like in the first vaccine dose), **IgM antibodies** are the first class to be produced and secreted by plasma cells.
- This **primary immune response** is characterized by a rapid, but short-lived, **IgM** peak.
*IgE*
- **IgE antibodies** are primarily involved in **allergic reactions** and defense against parasites, not the initial response to vaccination.
- Their production is typically triggered by exposure to specific allergens or parasites and mediated by Th2 helper T cells.
*IgG*
- **IgG antibodies** are the most abundant class in serum and are produced later in the primary response and predominantly during the **secondary immune response**.
- They provide **long-term immunity** and can cross the placenta, but are not the first antibody produced after initial antigen exposure.
*IgD*
- **IgD antibodies** are mainly found on the surface of **naive B cells** and act as B-cell receptors, playing a role in B-cell activation.
- They are not secreted in significant amounts into the serum and thus are not the first circulating antibody produced after vaccination.
*IgA*
- **IgA antibodies** are primarily found in **mucosal secretions** (e.g., saliva, tears, breast milk, gastrointestinal fluid) and play a key role in mucosal immunity.
- They are not the first antibody produced systemically in response to an initial vaccine exposure.
Childhood immunization schedule US Medical PG Question 8: A 15-month-old girl is brought to her primary care physician for a follow-up visit to receive the 4th dose of her DTaP vaccine. She is up-to-date on her vaccinations. She received her 1st dose of MMR, 1st dose of varicella, 3rd dose of HiB, 4th dose of PCV13, and 3rd dose of polio vaccine 3 months ago. Thirteen days after receiving these vaccinations, the child developed a fever up to 40.5°C (104.9°F) and had one generalized seizure that lasted for 2 minutes. She was taken to the emergency department. The girl was sent home after workup for the seizure was unremarkable and her temperature subsided with acetaminophen therapy. She has not had any other symptoms since then. She has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. Her mother is concerned about receiving further vaccinations because she is afraid of the girl having more seizures. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate recommendation at this time?
- A. Administration of the DTaP vaccine as scheduled (Correct Answer)
- B. Administration of the DTaP vaccine with valproic acid
- C. Administration of a reduced-dose DTaP vaccine
- D. Refrain from administration of the DTaP vaccine
- E. Administration of the DTaP vaccine with prophylactic aspirin
Childhood immunization schedule Explanation: ***Administration of the DTaP vaccine as scheduled***
- The seizure experienced by the child was a **febrile seizure**, triggered by a fever following vaccination, and not a contraindication to future DTaP doses.
- The timing of the seizure (**13 days post-vaccination**) suggests it was most likely related to the **MMR vaccine**, which commonly causes delayed fever (5-12 days) and febrile seizures, rather than the pertussis component or other vaccines given simultaneously.
- Since the child did **not receive DTaP** at the visit when the febrile seizure occurred, there is no evidence that pertussis-containing vaccines trigger seizures in this patient.
- The **unremarkable workup** and the child's return to normal health indicate the seizure was benign and not indicative of an underlying seizure disorder or severe adverse reaction.
- **Simple febrile seizures are not a contraindication** to DTaP vaccination per CDC/ACIP guidelines.
*Administration of the DTaP vaccine with valproic acid*
- **Valproic acid** is an anti-epileptic drug and is not indicated for the prevention of simple febrile seizures following vaccination.
- Prophylactic use of anti-epileptic drugs for vaccination-related febrile seizures is generally not recommended due to potential side effects and lack of clear benefit.
*Administration of a reduced-dose DTaP vaccine*
- There is **no such thing as a reduced-dose DTaP vaccine** for standard administration in children of this age.
- Reducing the vaccine dose would compromise its efficacy and protective immunity.
*Refrain from administration of the DTaP vaccine*
- **Febrile seizures are not a contraindication** to receiving further DTaP vaccination.
- Withholding the vaccine would leave the child unprotected against **diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis**, which are serious and potentially life-threatening diseases.
*Administration of the DTaP vaccine with prophylactic aspirin*
- **Aspirin is contraindicated in children** due to the risk of **Reye's syndrome**, especially during viral illnesses or when fever is present.
- It should not be used as a prophylactic measure for vaccination-related fever or seizures.
Childhood immunization schedule US Medical PG Question 9: A 19-year-old male arrives to student health for an annual check up. He is up to date on his infant and childhood vaccinations up to age 10. At age 12, he received a single dose of the tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis vaccine, and a quadrivalent meningococcal conjugate vaccine. A month ago, he received the influenza vaccine. The patient has no significant medical history. He takes over the counter ibuprofen for occasional headaches. He has a father with hypertension and hyperlipidemia, and his brother has asthma. He is sexually active with his current girlfriend. He denies tobacco use, illicit drug use, and recent or future travel. The patient’s temperature is 98°F (36.7°C), blood pressure is 118/78 mmHg, pulse is 70/min, and respirations are 14/min with an oxygen saturation of 99% O2 on room air. A physical examination is normal. What of the following is the best recommendation for vaccination?
- A. Human papillomavirus vaccine (Correct Answer)
- B. Hepatitis A vaccine
- C. Herpes zoster vaccine
- D. Pneumococcal vaccine
- E. Tetanus and reduced diphtheria toxoid booster
Childhood immunization schedule Explanation: ***Human papilloma virus***
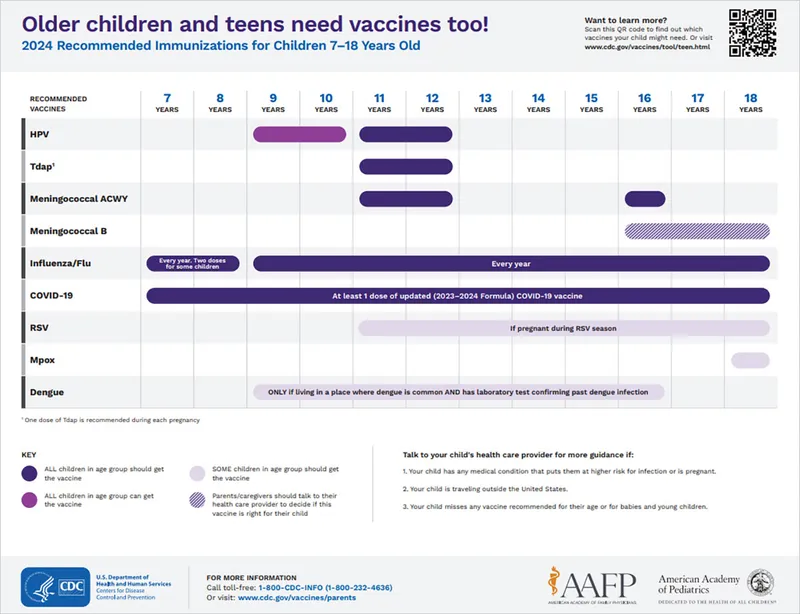
- This patient, being 19 years old and **sexually active**, is a prime candidate for the **HPV vaccine** to prevent infections that can lead to various cancers.
- The CDC recommends routine HPV vaccination at age 11-12, but catch-up vaccination is recommended for individuals up to age 26 if not adequately vaccinated previously.
*Hepatitis A vaccine*
- The Hepatitis A vaccine is generally recommended for individuals at **increased risk** of infection, such as travelers to endemic areas, men who have sex with men, or those with chronic liver disease, none of which apply to this patient.
- There is no indication for routine vaccination without specific risk factors in this otherwise healthy young male.
*Herpes zoster vaccine*
- The herpes zoster (shingles) vaccine is recommended for adults **age 50 years and older** to prevent shingles.
- This patient is only 19 years old, making him too young for this vaccine recommendation.
*Pneumococcal vaccine*
- Pneumococcal vaccines (PCV13 and PPSV23) are typically recommended for **young children**, adults **65 years and older**, or individuals with **certain underlying medical conditions** (e.g., chronic heart, lung, or kidney disease, or immunocompromised states).
- This 19-year-old patient has no such risk factors for pneumococcal disease.
*Tetanus and reduced diphtheria toxoid booster*
- The patient received a Tdap vaccine at age 12. A Td booster is recommended **every 10 years** for adults.
- Since it has been only 7 years since his last Tdap vaccine, he is not due for a Td booster at this time.
Childhood immunization schedule US Medical PG Question 10: A 12-year-old child is exposed to pollen while playing outside. The allergen stimulates TH2 cells of his immune system to secrete a factor that leads to B-cell class switching to IgE. What factor is secreted by the TH2 cell?
- A. IL-4 (Correct Answer)
- B. IL-22
- C. TGF-beta
- D. IL-17
- E. IFN-gamma
Childhood immunization schedule Explanation: ***IL-4***
- **Interleukin-4 (IL-4)** is a key cytokine produced by **TH2 cells** that promotes **B-cell class switching to IgE**, central to allergic reactions.
- It also stimulates the differentiation of naive T cells into **TH2 cells**, further amplifying the **allergic response**.
*IL-22*
- **IL-22** is primarily involved in maintaining **epithelial barrier integrity** and promoting **tissue repair**, especially in the gut and skin.
- It does not play a direct role in **IgE class switching** or the pathogenesis of type I hypersensitivity.
*TGF-beta*
- **TGF-beta (Transforming Growth Factor-beta)** is a pleiotropic cytokine involved in **cell growth**, differentiation, apoptosis, and immune regulation, particularly promoting **Treg cell development** and IgA class switching.
- It primarily suppresses rather than promotes **allergic reactions** and IgE production.
*IL-17*
- **IL-17** is a cytokine predominantly produced by **TH17 cells** and is crucial in protection against **extracellular bacteria and fungi**.
- It is associated with **autoimmune diseases** and inflammation but not directly with IgE-mediated allergic responses.
*IFN-gamma*
- **Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma)** is a critical **TH1 cytokine** that activates macrophages, enhances natural killer cell activity, and promotes the cell-mediated immune response.
- It typically **inhibits TH2 responses** and IgE production, thus working against the development of allergic reactions.
More Childhood immunization schedule US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.