Trematodes (flukes) US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Trematodes (flukes). These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
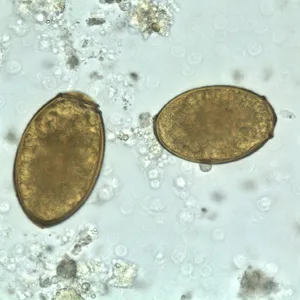
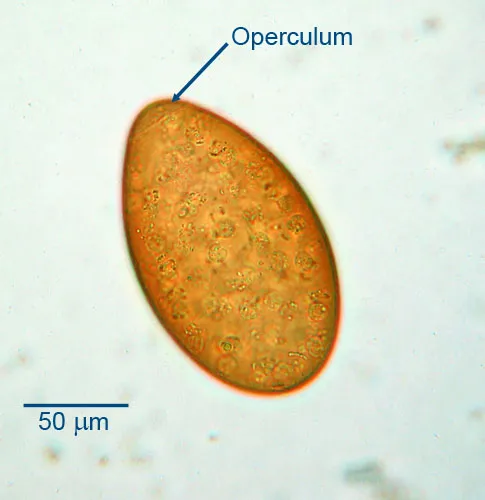
Trematodes (flukes) US Medical PG Question 1: A 7-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her mother because of a 4-week history of irritability, diarrhea, and a 2.2-kg (5-lb) weight loss that was preceded by a dry cough. The family returned from a vacation to Indonesia 2 months ago. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Abdominal examination shows mild tenderness with no guarding or rebound and increased bowel sounds. Her leukocyte count is 9,200/mm3 with 20% eosinophils. A photomicrograph of a wet stool mount is shown. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy?
- A. Diethylcarbamazine
- B. Metronidazole
- C. Albendazole (Correct Answer)
- D. Praziquantel
- E. Doxycycline
Trematodes (flukes) Explanation: ***Albendazole***
- The image shows a **hookworm egg**, characterized by its thin shell and developing larva inside; clinical features like **eosinophilia**, diarrhea, weight loss, and travel to an endemic area (Indonesia) are consistent with hookworm infection.
- **Albendazole** is the drug of choice for treating hookworm infections and other intestinal nematode infections.
*Diethylcarbamazine*
- This drug is primarily used for treating **lymphatic filariasis** (e.g., Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi) and **Loiasis** (African eye worm).
- It is not effective against hookworm infections.
*Metronidazole*
- **Metronidazole** is an antimicrobial agent effective against certain parasitic infections like **Giardia**, **Entamoeba histolytica**, and bacterial vaginosis.
- It is not indicated for the treatment of hookworm infections.
*Praziquantel*
- **Praziquantel** is an anthelminthic drug primarily used to treat infections caused by **flukes** (e.g., Schistosoma species) and **tapeworms** (e.g., Taenia species).
- It is not effective against hookworm infections.
*Doxycycline*
- **Doxycycline** is a tetracycline antibiotic with broad-spectrum activity against various bacterial infections and is also used in the treatment of some parasitic infections like **malaria prophylaxis** and **filariasis** (due to activity against Wolbachia endosymbionts).
- It is not a primary treatment for hookworm infections.
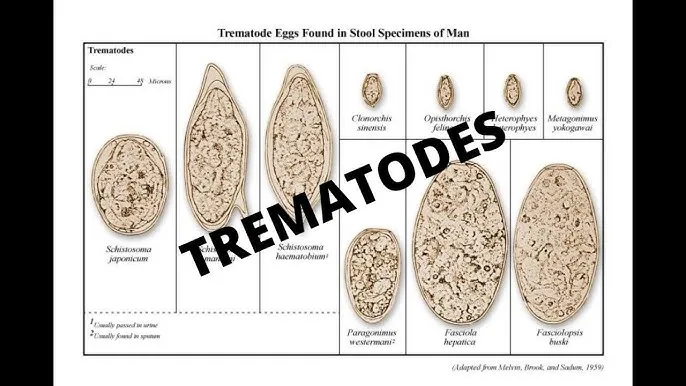
Trematodes (flukes) US Medical PG Question 2: A 19-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with chronic diarrhea, fatigue, and weakness. She also had mild lower extremity edema. On examination, she was noted to be pale. Blood testing revealed peripheral eosinophilia (60%) and a Hb concentration of 8 g/dL. The stool examination revealed Fasciolopsis buski eggs. Which of the following drugs would most likely be effective?
- A. Albendazole
- B. Oxamniquine
- C. Niclosamide
- D. Praziquantel (Correct Answer)
- E. Bithionol
Trematodes (flukes) Explanation: ***Praziquantel***
- **Praziquantel** is the **drug of choice** for treating trematode infections, including those caused by **Fasciolopsis buski**.
- Its mechanism of action involves increasing the permeability of the parasite's cell membrane to calcium, leading to paralysis and death of the fluke.
- It is highly effective, well-tolerated, and the standard first-line treatment.
*Albendazole*
- **Albendazole** is primarily used for various **nematode (roundworm)** infections, such as ascariasis, hookworm, and trichuriasis.
- While it has some activity against certain cestodes, it is not the first-line treatment for **Fasciolopsis buski**, a **trematode (fluke)**.
*Oxamniquine*
- **Oxamniquine** is an anthelmintic specifically used for the treatment of **schistosomiasis**, particularly against *Schistosoma mansoni*.
- It works by damaging the adult worms' teguments, but it is not effective against **Fasciolopsis buski**.
*Niclosamide*
- **Niclosamide** is an effective treatment for **cestode (tapeworm)** infections, such as *Taenia saginata* and *Hymenolepis nana*.
- Its mechanism involves inhibiting parasitic mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, but it is not active against **fluke** infections like **Fasciolopsis buski**.
*Bithionol*
- **Bithionol** is used primarily for treating **Fasciola hepatica** (the common liver fluke) and **Paragonimus westermani** (lung fluke) infections.
- While it has trematocidal activity, it is **not the drug of choice** for **Fasciolopsis buski**—**praziquantel** is preferred due to its superior efficacy, broader spectrum against intestinal flukes, better safety profile, and widespread availability.
Trematodes (flukes) US Medical PG Question 3: A 40-year-old woman presents to clinic with multiple complaints. She complains of swelling around her eyes (Image A) and generalized weakness. A complete blood count reveals eosinophilia. She recently returned from a trip to Asia where she reports having eaten street food, including pork. If this patient's disease is explained by a parasite that causes inflammation of skeletal muscle, what would be the appropriate treatment?
- A. Praziquantel
- B. Niridazole
- C. Albendazole or mebendazole (Correct Answer)
- D. Ivermectin
- E. Diethylcarbamazine
Trematodes (flukes) Explanation: ***Albendazole or mebendazole***
- The clinical presentation (periorbital edema, myalgia/weakness, eosinophilia, recent travel to Asia with consumption of pork) strongly suggests **trichinellosis**, caused by *Trichinella spiralis*.
- **Albendazole** or **mebendazole** (both benzimidazole anthelmintics) are the drugs of choice for treating trichinellosis by killing adult worms in the intestine and larvae in muscle tissue.
- Treatment is most effective when started early in the course of infection.
*Praziquantel*
- This agent is primarily used to treat infections caused by **trematodes** (flukes) and **cestodes** (tapeworms), such as schistosomiasis and taeniasis.
- It is **not effective** against *Trichinella spiralis*.
*Niridazole*
- Niridazole is an **older antischistosomal drug** that is now rarely used due to significant side effects.
- It has **no activity** against *Trichinella spiralis*.
*Ivermectin*
- Ivermectin is effective against various **nematodes**, including *Onchocerca volvulus* (river blindness) and *Strongyloides stercoralis*.
- While it has some activity against *Trichinella*, it is generally considered less effective than benzimidazoles and **not the first-line treatment** for trichinellosis.
*Diethylcarbamazine*
- This medication is primarily used to treat **lymphatic filariasis** (*Wuchereria bancrofti*, *Brugia malayi*) and **loiasis** (*Loa loa*).
- It is **not effective** against *Trichinella spiralis* infection.
Trematodes (flukes) US Medical PG Question 4: A 67-year-old male presents to his primary care physician for evaluation of fever and an unintended weight loss of 25 pounds over the last 4 months. He also has decreased appetite and complains of abdominal pain located in the right upper quadrant. The patient has not noticed any changes in stool or urine. He emigrated from Malaysia to the United States one year prior. Social history reveals that he smokes half a pack per day and has 5-7 drinks of alcohol per day. The patient is up to date on all of his vaccinations. Physical exam findings include mild jaundice as well as an enlarged liver edge that is tender to palpation. Based on clinical suspicion, biomarker labs are sent and show polycythemia and an elevated alpha fetoprotein level but a normal CA 19-9 level. Surface antigen for hepatitis B is negative. Ultrasound reveals a normal sized gallbladder. Given this presentation, which of the following organisms was most likely associated with the development of disease in this patient?
- A. Naked DNA virus
- B. Enveloped DNA virus
- C. Curved gram-negative bacteria
- D. Acute angle branching fungus
- E. Trematode from undercooked fish (Correct Answer)
Trematodes (flukes) Explanation: ***Trematode from undercooked fish***
- The patient's symptoms (fever, RUQ pain, weight loss, jaundice, hepatomegaly, elevated **AFP**, and normal CA 19-9) point strongly towards **hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)**.
- The history of emigration from Malaysia and the elevated **alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)** despite negative hepatitis B antigen, suggest a parasitic infection, specifically a liver fluke (trematode), as a risk factor for HCC. **Clonorchis sinensis** and **Opisthorchis viverrini** are trematodes acquired from undercooked freshwater fish, endemic to Southeast Asia, and are known to cause cholangiocarcinoma and, less commonly, HCC.
*Naked DNA virus*
- This typically refers to viruses like **human papillomavirus (HPV)** or **adenovirus**, which are not primary causes of the described liver pathology or HCC with this specific presentation.
- While some naked DNA viruses can cause human disease, they are not typically linked to the patient's specific symptoms and lab findings (elevated AFP) in the context of liver cancer from a Southeast Asian background.
*Enveloped DNA virus*
- This category includes viruses like **Herpesviruses** and **Hepatitis B virus (HBV)**. While HBV is a major cause of HCC, the patient's hepatitis B surface antigen is negative, ruling out active or chronic HBV infection as the direct cause in this case.
- Other enveloped DNA viruses do not commonly cause this specific cluster of symptoms and risk factors for HCC.
*Curved gram-negative bacteria*
- This description often refers to bacteria like **Campylobacter** or **Helicobacter pylori**. These can cause gastrointestinal issues but are not typically associated with liver masses, jaundice, and elevated AFP in the context of HCC.
- They do not explain the patient's risk factors or presentation that strongly suggests chronic liver inflammation leading to cancer.
*Acute angle branching fungus*
- This refers to fungi like **Aspergillus**, which can cause invasive infections, particularly in immunocompromised individuals.
- While Aspergillus can cause pulmonary infections and, less commonly, disseminate to other organs including the liver, it does not typically present with the described risk factors (Southeast Asian origin, undercooked fish consumption) or lab findings (elevated AFP) for HCC, nor does it fit the general clinical picture.
Trematodes (flukes) US Medical PG Question 5: A 78-year-old woman living in New Jersey is brought to the emergency department in July with a fever for 5 days. Lethargy is present. She has had bloody urine over the last 48 hours but denies any nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain. She has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. She has not traveled anywhere outside her city for the past several years. She appears ill. The temperature is 40.8℃ (105.4℉), the pulse is 108/min, the respiration rate is 20/min, and the blood pressure is 105/50 mm Hg. The abdominal exam reveals hepatosplenomegaly. Lymphadenopathy is absent. Petechiae are seen on the lower extremities. Laboratory studies show the following:
Laboratory test
Hemoglobin 8 g/dL
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) 98 µm3
Leukocyte count 4,200/mm3
Segmented neutrophils 32%
Lymphocytes 58%
Platelet count 108,000/mm3
Bilirubin, total 5.0 mg/dL
Direct 0.7 mg/dL
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) 51 U/L
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) 56 U/L
Alkaline phosphatase 180 U/L
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) 640 U/L (N = 140–280 U/L)
Haptoglobin 20 mg/dL (N = 30–200 mg/dL)
Urine
Hemoglobin +
Urobilinogen +
Protein +
A peripheral blood smear is shown (see image). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Babesiosis (Correct Answer)
- B. Leishmaniasis
- C. Lyme disease
- D. Malaria
- E. Plague
Trematodes (flukes) Explanation: ***Babesiosis***
- The patient's presentation with **fever, lethargy, hemolytic anemia** (low hemoglobin, elevated LDH, low haptoglobin, bilirubinemia, hemoglobinuria), **thrombocytopenia**, and **hepatosplenomegaly** is highly suggestive of babesiosis. The **peripheral blood smear showing intraerythrocytic parasites** (often described as ring forms or tetrads, "Maltese cross") is diagnostic. Living in **New Jersey** in **July** increases the likelihood of tick exposure, which transmits *Babesia microti*.
- Her age (78 years old) is a risk factor for severe babesiosis, and the **anemia and thrombocytopenia** are classic findings, with the elevated total bilirubin indicating significant hemolysis.
*Leishmaniasis*
- While leishmaniasis (specifically visceral leishmaniasis) can cause fever, hepatosplenomegaly, anemia, and thrombocytopenia, it is endemic to different regions (e.g., Mediterranean basin, South America, Asia, Africa) and is **not typically acquired in New Jersey**.
- Diagnosis is usually made by identifying **amastigotes in bone marrow, spleen, or lymph node aspirates**, not intraerythrocytic parasites on a peripheral smear.
*Lyme disease*
- Lyme disease, also transmitted by *Ixodes* ticks in New Jersey, typically presents with an **erythema chronicum migrans rash**, flu-like symptoms, and can lead to arthritis or cardiac/neurological manifestations.
- It **does not cause intraerythrocytic parasites or severe hemolytic anemia** with the lab findings described (elevated LDH, low haptoglobin, bilirubinemia, hemoglobinuria).
*Malaria*
- Malaria presents with fever, chills, anemia, and hepatosplenomegaly and is diagnosed by **intraerythrocytic parasites on a peripheral blood smear**. However, the patient has **not traveled to malaria-endemic regions** and has remained in her city for several years.
- While both *Babesia* and *Plasmodium* can appear as ring forms, the specific morphology (e.g., "Maltese cross" in *Babesia*) and geographic context strongly favor babesiosis in this case.
*Plague*
- Plague (caused by *Yersinia pestis*) typically presents as bubonic, septicemic, or pneumonic forms. **Bubonic plague** involves painful, swollen lymph nodes (buboes), which are absent in this patient.
- Although it can cause fever and systemic illness, it does not lead to **intraerythrocytic parasites or significant hemolytic anemia** as seen in this patient's lab results.
Trematodes (flukes) US Medical PG Question 6: A 30-year-old man presents to the physician after he discovered a raised, red, string-shaped lesion beneath the skin on his right foot. The lesion seems to move from one location to another over the dorsum of his foot from day to day. He says that the lesion is extremely itchy and has not responded to over the counter topical treatment. He and his wife recently returned from a honeymoon in southern Thailand, where they frequented the tropical beaches. The physician diagnoses him with a parasitic infection and prescribes albendazole for the patient. With which of the following organisms is the patient most likely infected?
- A. Ancylostoma braziliense (Correct Answer)
- B. Dracunculus medinensis
- C. Necator americanus
- D. Strongyloides stercoralis
- E. Wuchereria bancrofti
Trematodes (flukes) Explanation: ***Ancylostoma braziliense***
- This clinical presentation of a **pruritic, migratory, serpiginous rash** on the foot after exposure to contaminated sand (tropical beach in Thailand) is classic for **cutaneous larva migrans**, caused by hookworm larvae, predominantly *Ancylostoma braziliense*.
- The larvae penetrate the skin but cannot complete their life cycle in humans, instead migrating subcutaneously, causing the characteristic **"creeping eruption"**.
*Dracunculus medinensis*
- This parasite causes **dracunculiasis**, where the adult female worm migrates to the skin, creating a painful blister, often on the lower limbs, from which it emerges.
- It is acquired by ingesting **copepods** (water fleas) containing larvae, not by direct contact with contaminated sand, and the lesion typically ulcerates rather than migrating repeatedly.
*Necator americanus*
- This is a human hookworm that causes **iron deficiency anemia** and can lead to **cutaneous larva currens** from larval penetration, which is a rapidly advancing linear lesion, but it typically progresses to systemic infection where the worms reside in the small intestine.
- While it can cause an itchy rash at the site of penetration (ground itch), it does not cause the **chronic, migratory, serpiginous eruption** characteristic of cutaneous larva migrans.
*Strongyloides stercoralis*
- This parasite can cause **larva currens** (a rapidly moving linear skin eruption) and systemic complications, particularly in immunocompromised individuals.
- While it can cause skin lesions, the typical description is of a much faster-moving lesion that usually spreads from the anus and is less serpiginous and persistent in one area compared to the classic presentation of cutaneous larva migrans.
*Wuchereria bancrofti*
- This nematode causes **lymphatic filariasis** (elephantiasis), characterized by lymphedema, hydrocele, and chyluria, and is transmitted by **mosquito bites**.
- It does not cause cutaneous migratory lesions on the foot; its pathology relates to chronic lymphatic obstruction by adult worms.
Trematodes (flukes) US Medical PG Question 7: A 68-year-old man presents to his physician for symptoms of chronic weight loss, abdominal bloating, and loose stools. He notes that he has also been bothered by a chronic cough. The patient’s laboratory work-up includes a WBC differential, which is remarkable for an eosinophil count of 9%. Stool samples are obtained, with ova and parasite examination revealing roundworm larvae in the stool and no eggs. Which of the following parasitic worms is the cause of this patient’s condition?
- A. Taenia saginata
- B. Taenia solium
- C. Strongyloides stercoralis (Correct Answer)
- D. Necator americanus
- E. Ascaris lumbricoides
Trematodes (flukes) Explanation: ***Strongyloides stercoralis***
- The presence of **larvae (rhabditiform)** in the stool, **pulmonary symptoms** (chronic cough), **gastrointestinal symptoms** (weight loss, bloating, loose stools), and **eosinophilia** are classic findings for *Strongyloides stercoralis* infection.
- Unlike most other intestinal nematodes, *Strongyloides* can establish an **autoinfection cycle**, meaning larvae can reinfect the host, leading to persistent and potentially severe infections even in immunocompetent individuals, without the need for external re-exposure or eggs in stool.
*Taenia saginata*
- This is a **tapeworm (cestode)** that causes taeniasis and is acquired by consuming undercooked beef.
- Diagnosis is typically made by finding **proglottids** or **eggs** in the stool, not larvae, and pulmonary symptoms are not characteristic.
*Taenia solium*
- This is another **tapeworm (cestode)**, acquired by consuming undercooked pork; it can cause taeniasis (intestinal infection) and cysticercosis (tissue infection).
- Similar to *T. saginata*, diagnosis involves finding **proglottids** or **eggs** in stool for intestinal infection, and it does not typically present with lung involvement or larvae in stool.
*Necator americanus*
- This is a **hookworm** that causes iron-deficiency anemia due to blood loss in the intestines.
- While it can cause some pulmonary symptoms as larvae migrate through the lungs, and gastrointestinal symptoms, the diagnostic hallmark is finding **eggs** in the stool, not larvae.
*Ascaris lumbricoides*
- This is the **giant roundworm**; infections are common and often asymptomatic, but heavy worm burdens can cause intestinal obstruction or malnutrition.
- While **pulmonary symptoms (Loeffler's syndrome)** can occur during larval migration, and eosinophilia is present, the diagnosis is confirmed by finding characteristic **mammillated eggs** in the stool, not larvae.
Trematodes (flukes) US Medical PG Question 8: A 40-year-old man presents to the office with complaints of epigastric discomfort for the past 6 months. He adds that the discomfort is not that bothersome as it does not interfere with his daily activities. He does not have any other complaints at the moment. The past medical history is insignificant. He is a non-smoker and does not consume alcohol. He recently came back from a trip to South America where he visited a relative who owned a sheep farm. On physical examination, he has a poorly palpable epigastric non-tender mass with no organomegaly. The hepatitis B and C serology are negative. The liver CT scan and MRI are shown. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Echinococcosis (Correct Answer)
- B. Liver abscess
- C. Hepatocellular carcinoma
- D. Tuberculosis
- E. Hemangioma
Trematodes (flukes) Explanation: ***Echinococcosis (Correct Answer)***
- The patient's history of travel to **South America** and contact with a **sheep farm** is highly suggestive of exposure to *Echinococcus granulosus*, the causative agent of hydatid disease.
- The **CT scan image** shows a large, well-defined cyst with a **calcified wall** and internal septations, consistent with the characteristic appearance of a **hydatid cyst** in the liver.
- This presentation is classic for **hepatic echinococcosis**: chronic indolent course, epidemiological exposure, and pathognomonic imaging findings.
*Liver abscess (Incorrect)*
- Liver abscesses typically present with more acute symptoms such as **fever, chills, and significant pain**, which are absent in this case.
- Imaging usually reveals a **hypo-dense lesion** with a rim of enhancement, possibly gas formation, and less commonly a calcified wall.
*Hepatocellular carcinoma (Incorrect)*
- This patient lacks typical risk factors for HCC, such as **chronic hepatitis B or C infection** (serology is negative) or cirrhosis.
- HCC imaging typically shows an **enhancing mass** that washes out on delayed phases, without the calcified, multi-loculated appearance seen here.
*Tuberculosis (Incorrect)*
- Hepatic tuberculosis typically presents with fever, weight loss, and multiple **small, hypo-dense lesions** on imaging, often with an associated pulmonary or extra-pulmonary focus.
- The single, large, calcified cystic lesion seen on imaging is not characteristic of hepatic tuberculosis.
*Hemangioma (Incorrect)*
- Hepatic hemangiomas are benign vascular tumors that often present as **incidental findings** and are typically asymptomatic.
- On CT scans, they show characteristic **peripheral nodular enhancement** that fills in centripetally on delayed phases, which is different from the calcified cyst observed.
Trematodes (flukes) US Medical PG Question 9: A 32-year-old woman presents to your office with abdominal pain and bloating over the last month. She also complains of intermittent, copious, non-bloody diarrhea over the same time. Last month, she had a cough that has since improved but has not completely resolved. She has no sick contacts and has not left the country recently. She denies any myalgias, itching, or rashes. Physical and laboratory evaluations are unremarkable. Examination of her stool reveals the causative organism. This organism is most likely transmitted to the human host through which of the following routes?
- A. Insect bite
- B. Penetration of skin (Correct Answer)
- C. Sexual contact
- D. Inhalation
- E. Animal bite
Trematodes (flukes) Explanation: ***Penetration of skin***
- The symptoms of **abdominal pain**, **bloating**, **intermittent copious non-bloody diarrhea**, and a recent **cough** are highly suggestive of a **hookworm infection**.
- Hookworm larvae (filariform larvae) primarily penetrate the skin, usually through bare feet, as their mode of entry into the human host.
*Insect bite*
- Although some parasitic infections are transmitted by insect bites (e.g., malaria, Chagas disease), hookworms are not transmitted this way.
- **Insect-borne diseases** typically present with different clinical manifestations or geographical associations.
*Sexual contact*
- **Sexually transmitted infections** involve direct contact of mucous membranes or body fluids during sexual activity.
- Hookworm infection transmission through sexual contact is not a recognized route.
*Inhalation*
- **Inhalation** is a route of transmission for respiratory pathogens (e.g., influenza, tuberculosis) or certain fungal infections, but not for hookworms.
- While hookworm larvae migrate through the lungs, the initial infection pathway is not via inhalation.
*Animal bite*
- **Animal bites** transmit diseases like rabies or certain bacterial infections, but not parasitic hookworms.
- Hookworm infection does not result from direct contact with an animal's saliva or puncture wound.
Trematodes (flukes) US Medical PG Question 10: A 45-year-old male presents to the emergency room complaining of severe nausea and vomiting. He returned from a business trip to Nigeria five days ago. Since then, he has developed progressively worsening fevers, headache, nausea, and vomiting. He has lost his appetite and cannot hold down food or water. He did not receive any vaccinations before traveling. His medical history is notable for alcohol abuse and peptic ulcer disease for which he takes omeprazole regularly. His temperature is 103.0°F (39.4°C), blood pressure is 100/70 mmHg, pulse is 128/min, and respirations are 22/min. Physical examination reveals scleral icterus, hepatomegaly, and tenderness to palpation in the right and left upper quadrants. While in the examination room, he vomits up dark vomitus. The patient is admitted and started on multiple anti-protozoal and anti-bacterial medications. Serology studies are pending; however, the patient dies soon after admission. The virus that likely gave rise to this patient’s condition is part of which of the following families?
- A. Togavirus
- B. Flavivirus (Correct Answer)
- C. Calicivirus
- D. Hepevirus
- E. Bunyavirus
Trematodes (flukes) Explanation: ***Flavivirus***
- The clinical presentation, including acute onset of **high fever**, headache, nausea, vomiting (**dark vomitus**), **scleral icterus**, and **hepatomegaly** following travel to Nigeria, is highly suggestive of **yellow fever**.
- Yellow fever is caused by the **yellow fever virus**, which is a **flavivirus** transmitted by mosquitoes, primarily *Aedes aegypti*.
*Togavirus*
- The Togavirus family includes viruses like **rubella virus** and **alphaviruses** (e.g., Eastern equine encephalitis virus).
- While some alphaviruses can cause fever and encephalitis, they typically do not present with the characteristic **hemorrhagic fever** and severe liver involvement seen in this case.
*Calicivirus*
- The Calicivirus family includes **Norovirus**, which is a common cause of **gastroenteritis** with vomiting and diarrhea.
- Norovirus infections are typically self-limiting and do not usually lead to the severe systemic symptoms, **jaundice**, or fatal outcome described here.
*Hepevirus*
- The Hepevirus family includes the **hepatitis E virus (HEV)**.
- HEV causes **acute viral hepatitis**, characterized by jaundice, nausea, and vomiting, but it rarely progresses to the rapid, severe, and fatal hemorrhagic form seen in this patient.
*Bunyavirus*
- The Bunyavirus family (now split into several families) includes viruses like Hantavirus and Rift Valley fever virus, which can cause **hemorrhagic fevers**.
- While some bunyaviruses are found in Africa, the specific constellation of symptoms, particularly the prominent **scleral icterus** and rapid progression to severe liver failure and death, is most consistent with **yellow fever**, a flavivirus.
More Trematodes (flukes) US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.