Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases US Medical PG Question 1: A 34-year-old man comes to the physician because of progressive swelling of the left lower leg for 4 months. One year ago, he had an episode of intermittent fever and tender lymphadenopathy that occurred shortly after he returned from a trip to India and resolved spontaneously. Physical examination shows 4+ nonpitting edema of the left lower leg. His leukocyte count is 8,000/mm3 with 25% eosinophils. A blood smear obtained at night confirms the diagnosis. Treatment with diethylcarbamazine is initiated. Which of the following is the most likely route of transmission of the causal pathogen?
- A. Penetration of the skin by hookworms in feces
- B. Penetration of the skin by cercariae from contaminated fresh water
- C. Deposition of larvae into the skin by a female black fly
- D. Ingestion of encysted larvae in undercooked pork
- E. Deposition of thread-like larvae into the skin by a female mosquito (Correct Answer)
Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases Explanation: ***Deposition of thread-like larvae into the skin by a female mosquito***
- The symptoms described, including progressive **nonpitting edema** (lymphedema), a history of **fever** and **lymphadenopathy** after travel to an endemic area (India), and significant **eosinophilia**, are classic for **lymphatic filariasis**.
- Lymphatic filariasis, caused by filarial worms like *Wuchereria bancrofti* or *Brugia malayi*, is transmitted by **mosquitoes** that deposit infectious larvae onto the skin during a blood meal.
*Penetration of the skin by hookworms in feces*
- This describes the transmission of **hookworm infection**, which causes **iron deficiency anemia** and gastrointestinal symptoms, not lymphedema or high eosinophilia with nocturnal microfilaremia.
- While hookworms can cause eosinophilia, the clinical presentation of chronic lymphedema and the need for a nocturnal blood smear point away from hookworm infection.
*Penetration of the skin by cercariae from contaminated fresh water*
- This is the transmission method for **schistosomiasis**, which can cause symptoms depending on the species and affected organs, such as **urinary tract disease**, **hepatic fibrosis**, or **intestinal inflammation**.
- Schistosomiasis does not typically present with the progressive lymphedema and episodic lymphadenitis characteristic of filariasis.
*Deposition of larvae into the skin by a female black fly*
- This describes the transmission of **onchocerciasis** (river blindness), caused by *Onchocerca volvulus*.
- Onchocerciasis primarily causes skin disease (intense **pruritus**, dermatitis) and **ocular lesions** leading to blindness, not extensive lymphedema of the limbs.
*Ingestion of encysted larvae in undercooked pork*
- This is the route of transmission for **trichinellosis**, caused by *Trichinella spiralis*.
- Trichinellosis involves **muscle pain**, fever, and periorbital edema, but not chronic lymphedema of the extremities or the specific nocturnal periodicity for diagnosis.
Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases US Medical PG Question 2: A 45-year-old man presents to the physician with complaints of fever with rigors, headache, malaise, muscle pains, nausea, vomiting, and decreased appetite for the past 3 days. He informs the physician that he had been backpacking on the Appalachian Trail in the woods of Georgia in the month of June, 2 weeks ago, and had been bitten by a tick there. His temperature is 39.0°C (102.3°F), pulse is 94/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 126/82 mm Hg. His physical exam does not reveal any significant abnormality except for mild splenomegaly. Laboratory studies show:
Total white blood cell count 3,700/mm3 (3.7 x 109/L)
Differential count
Neutrophils 85%
Lymphocytes 12%
Monocytes 2%
Eosinophils 1%
Basophils 0%
Platelet count 88,000/mm3 (95 x 109/L)
Serum alanine aminotransferase 140 IU/L
Serum aspartate aminotransferase 80 IU/L
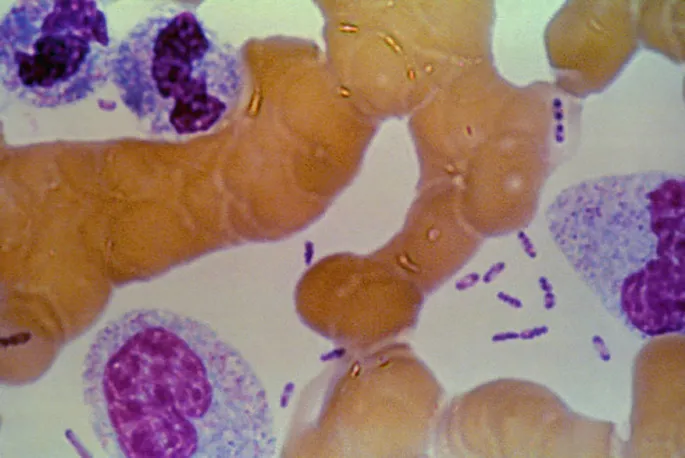
Microscopic examination of a peripheral blood smear stained with Wright-Giemsa stain shows the presence of morulae in the cytoplasm of leukocytes. In addition to drugs for symptomatic relief, what is the most appropriate initial step in the treatment of this patient?
- A. Doxycycline (Correct Answer)
- B. Ceftriaxone
- C. Rifampin
- D. Ciprofloxacin
- E. Daptomycin
Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases Explanation: ***Doxycycline***
- The patient's presentation with **fever, myalgia, headache, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, elevated liver enzymes**, a history of **tick bite** in an endemic area (Appalachian Trail, Georgia), and the presence of **morulae in leukocytes** strongly indicates **ehrlichiosis** or **anaplasmosis**.
- **Doxycycline** is the **first-line treatment** for all rickettsial diseases, including ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis, regardless of age or pregnancy status, due to its effectiveness in preventing severe complications.
*Ceftriaxone*
- While effective against many bacterial infections, **ceftriaxone** is **not effective** against intracellular bacteria like *Ehrlichia* or *Anaplasma*.
- It is typically used for conditions like Lyme disease (later stages), meningitis, or community-acquired pneumonia, which do not match the complete clinical picture here.
*Rifampin*
- **Rifampin** is sometimes used for treatment of ehrlichiosis in patients who **cannot tolerate doxycycline**, but it is **not the first-line agent**.
- Its primary uses are for tuberculosis and prophylaxis of meningococcal disease, making it an inappropriate initial choice given the classic presentation.
*Ciprofloxacin*
- **Ciprofloxacin** is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic primarily used for urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and some gastrointestinal infections.
- It has **no significant activity** against species of *Ehrlichia* or *Anaplasma* and is therefore not indicated for this condition.
*Daptomycin*
- **Daptomycin** is a lipopeptide antibiotic used for treating **Gram-positive bacterial infections**, especially those resistant to other antibiotics (e.g., MRSA).
- It is **ineffective** against the intracellular Gram-negative bacteria causing ehrlichiosis or anaplasmosis.
Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases US Medical PG Question 3: A 33-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a fever and fatigue. He states that he has not felt well since he returned from a hiking trip in Alabama. He is generally healthy and has no other medical conditions. His temperature is 101°F (38.3°C), blood pressure is 127/85 mmHg, pulse is 108/min, respirations are 14/min, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. Physical exam including a full dermatologic inspection is unremarkable. Laboratory studies are ordered as seen below.
Hemoglobin: 13 g/dL
Hematocrit: 39%
Leukocyte count: 2,200/mm^3 with normal differential
Platelet count: 77,000/mm^3
Serum:
Na+: 139 mEq/L
Cl-: 100 mEq/L
K+: 4.3 mEq/L
HCO3-: 24 mEq/L
BUN: 19 mg/dL
Glucose: 98 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1.3 mg/dL
Ca2+: 10.2 mg/dL
AST: 92 U/L
ALT: 100 U/L
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Lyme disease
- B. Babesiosis
- C. Influenza
- D. Ehrlichiosis (Correct Answer)
- E. Rocky Mountain spotted fever
Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases Explanation: ***Ehrlichiosis***
- This patient's symptoms (fever, fatigue), recent travel to an **endemic area** (Alabama), **leukopenia** (WBC 2,200/mm^3), **thrombocytopenia** (platelet 77,000/mm^3), and **elevated liver enzymes** (AST 92, ALT 100) are highly characteristic of ehrlichiosis, a **tick-borne disease**.
- The absence of a rash helps differentiate it from some other tick-borne illnesses.
*Lyme disease*
- While Lyme disease is also tick-borne, it typically presents with an **erythema migrans rash**, which is absent in this case.
- Lyme disease is less commonly associated with the **pronounced leukopenia** and **thrombocytopenia** seen here.
*Rocky Mountain spotted fever*
- Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF) is characterized by a **maculopapular rash** that often starts on the ankles and wrists and spreads centrally, involving the palms and soles. This rash is absent in the patient.
- While RMSF can cause thrombocytopenia and elevated liver enzymes, the **lack of rash is a key differentiator**.
*Babesiosis*
- Babesiosis is a tick-borne parasitic infection that causes **hemolytic anemia**, which is not clearly indicated by the patient's hemoglobin and hematocrit, and typically results in severe fatigue and sometimes splenomegaly.
- This condition is often seen in immunocompromised individuals or those without a spleen, and the labs here are more consistent with ehrlichiosis than babesiosis.
*Influenza*
- Influenza presents with fever, fatigue, myalgia, and respiratory symptoms, but it does not cause **thrombocytopenia**, **leukopenia**, or **elevated liver enzymes** to the extent seen in this patient.
- The symptoms are more indicative of a **tick-borne illness** given the travel history and specific lab abnormalities.
Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases US Medical PG Question 4: A 45-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with a headache, fevers with chills, rigors, and generalized joint pain for the past week. She also complains of a progressive rash on her left arm. She says that a few days ago she noticed a small, slightly raised lesion resembling an insect bite mark, which had a burning sensation. The medical and surgical histories are unremarkable. She recalls walking in the woods 2 weeks prior to the onset of symptoms, but does not recall finding a tick on her body. On examination, the temperature is 40.2°C (104.4°F). A circular red rash measuring 10 cm x 5 cm in diameter is noted on the left arm, as shown in the accompanying image. The remainder of her physical examination is unremarkable. The tick causing her disease is also responsible for the transmission of which of the following pathogens?
- A. Rickettsia rickettsii
- B. Babesia microti (Correct Answer)
- C. Rickettsia typhi
- D. Ehrlichia
- E. Plasmodium vivax
Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases Explanation: ***Babesia microti***
- The clinical picture of **headache**, **fever with chills**, **rigors**, **generalized joint pain**, and an **expanding erythematous rash (erythema migrans)** after a woodland exposure points to **Lyme disease**, caused by *Borrelia burgdorferi*.
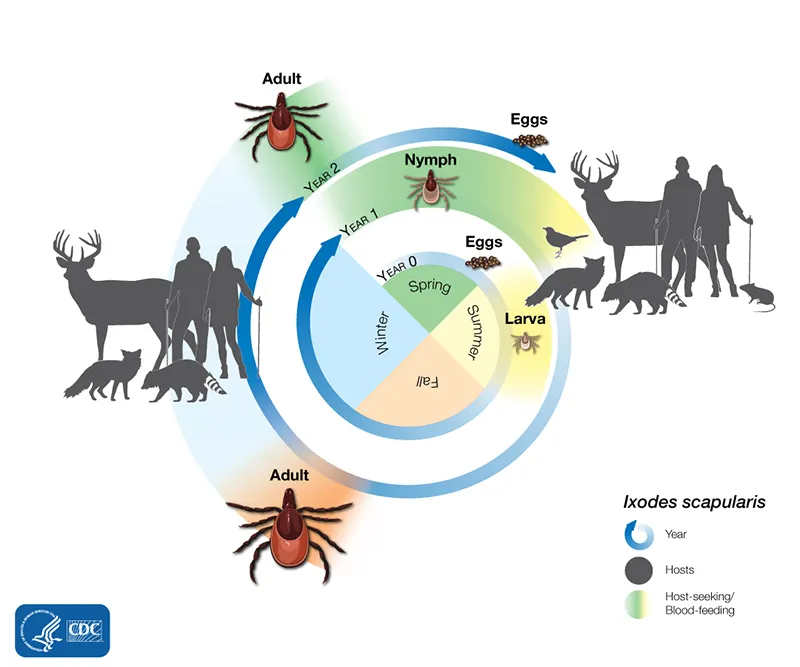
- **Both *Borrelia burgdorferi*** and ***Babesia microti*** are transmitted by the **deer tick** (*Ixodes scapularis*), making co-infection common in endemic areas.
*Rickettsia rickettsii*
- This pathogen causes **Rocky Mountain spotted fever**, which typically presents with a **maculopapular rash** that often becomes petechial and involves the palms and soles.
- The rash in this vignette is an **expanding erythematous lesion (erythema migrans)**, characteristic of Lyme disease, not RMSF.
*Rickettsia typhi*
- This bacterium causes **endemic (murine) typhus**, typically transmitted by the **infected flea** (*Xenopsylla cheopis*).
- Symptoms include fever, headache, and a **truncal maculopapular rash**, but it is not associated with a tick bite or erythema migrans.
*Ehrlichia*
- *Ehrlichia chaffeensis* causes **human monocytic ehrlichiosis**, transmitted by the **lone star tick** (*Amblyomma americanum*).
- While it can cause fever, headache, and myalgia, it does not typically present with the classic **erythema migrans rash** seen in Lyme disease.
*Plasmodium vivax*
- This protozoan causes **malaria**, transmitted by the **Anopheles mosquito**.
- Symptoms include cyclical fevers, chills, and headache but do not involve a tick bite or the characteristic **erythema migrans rash**.
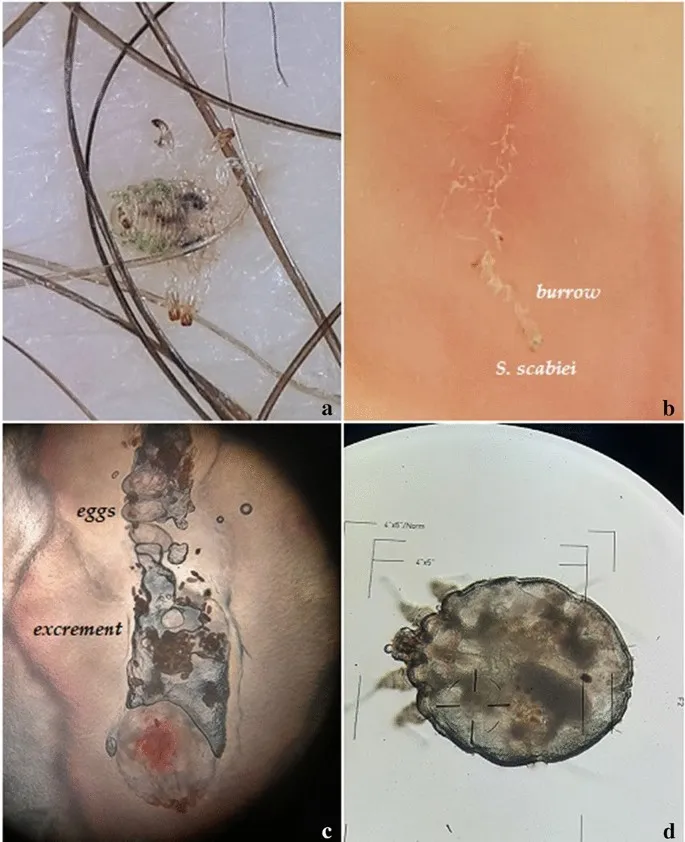
Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases US Medical PG Question 5: A 37-year-old woman with a history of systemic lupus erythematosus, on prednisone and methotrexate, presents to the dermatology clinic with three weeks of a diffuse, itchy rash. Physical exam is remarkable for small red papules in her bilateral axillae and groin and thin reddish-brown lines in her interdigital spaces. The following skin biopsy is obtained. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment?
- A. Capsaicin cream
- B. Ketoconazole cream
- C. Permethrin cream (Correct Answer)
- D. Hydrocortisone cream
- E. Nystatin cream
Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases Explanation: ***Permethrin cream***
- The patient's presentation with **diffuse itchy rash**, small red papules in the axillae and groin, and **reddish-brown lines in interdigital spaces (burrows)** is classic for **scabies**.
- **Permethrin 5% cream** is the **first-line treatment** for scabies due to its efficacy as a **scabicidal agent** by disrupting the parasite's nervous system.
- The patient's **immunocompromised status** (on prednisone and methotrexate) increases risk for **crusted (Norwegian) scabies**, but permethrin remains the primary topical treatment; severe cases may require addition of oral ivermectin.
*Capsaicin cream*
- Capsaicin cream is used for **neuropathic pain** and often causes a burning sensation, making it unsuitable for a pruritic rash caused by mites.
- It does not have any **antiparasitic properties** and would not treat the underlying cause of scabies.
*Ketoconazole cream*
- Ketoconazole is an **antifungal agent** used to treat conditions like candidiasis or tinea infections.
- The clinical presentation is not suggestive of a fungal infection, and ketoconazole would be ineffective against scabies mites.
*Hydrocortisone cream*
- Hydrocortisone is a **topical corticosteroid** used to reduce inflammation and itching associated with various dermatoses.
- While it may temporarily relieve itching, it would not eradicate the **scabies mites** and their eggs, leading to recurrence.
- Using corticosteroids alone in an **already immunocompromised patient** could worsen the infestation.
*Nystatin cream*
- Nystatin is another **antifungal medication** primarily used for cutaneous candidiasis.
- It has no activity against parasitic infestations such as scabies and would therefore be an inappropriate treatment.
Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases US Medical PG Question 6: A 32-year-old woman presents to your office with abdominal pain and bloating over the last month. She also complains of intermittent, copious, non-bloody diarrhea over the same time. Last month, she had a cough that has since improved but has not completely resolved. She has no sick contacts and has not left the country recently. She denies any myalgias, itching, or rashes. Physical and laboratory evaluations are unremarkable. Examination of her stool reveals the causative organism. This organism is most likely transmitted to the human host through which of the following routes?
- A. Insect bite
- B. Penetration of skin (Correct Answer)
- C. Sexual contact
- D. Inhalation
- E. Animal bite
Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases Explanation: ***Penetration of skin***
- The symptoms of **abdominal pain**, **bloating**, **intermittent copious non-bloody diarrhea**, and a recent **cough** are highly suggestive of a **hookworm infection**.
- Hookworm larvae (filariform larvae) primarily penetrate the skin, usually through bare feet, as their mode of entry into the human host.
*Insect bite*
- Although some parasitic infections are transmitted by insect bites (e.g., malaria, Chagas disease), hookworms are not transmitted this way.
- **Insect-borne diseases** typically present with different clinical manifestations or geographical associations.
*Sexual contact*
- **Sexually transmitted infections** involve direct contact of mucous membranes or body fluids during sexual activity.
- Hookworm infection transmission through sexual contact is not a recognized route.
*Inhalation*
- **Inhalation** is a route of transmission for respiratory pathogens (e.g., influenza, tuberculosis) or certain fungal infections, but not for hookworms.
- While hookworm larvae migrate through the lungs, the initial infection pathway is not via inhalation.
*Animal bite*
- **Animal bites** transmit diseases like rabies or certain bacterial infections, but not parasitic hookworms.
- Hookworm infection does not result from direct contact with an animal's saliva or puncture wound.
Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases US Medical PG Question 7: A 42-year-old man presents to a free dermatology clinic, complaining of itchy skin over the past several days. He has no insurance and lives in a homeless shelter. The patient has no significant medical history. Physical evaluation reveals 2 mm erythematous papules and vesicles on his back and groin, with linear excoriation marks. Careful observation of his hands reveals serpiginous, grayish, threadlike elevations in the superficial epidermis, ranging from 3–9 mm in length in the webbing between several digits. What should be the suggested treatment in this case?
- A. No medication should be administered, only proper hygiene.
- B. Antiviral medication
- C. Permethrin (Correct Answer)
- D. Antifungal medication
- E. Broad-spectrum antibiotic
Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases Explanation: ***Permethrin***
- This patient's symptoms, including intense itching, erythematous papules and vesicles, linear excoriations, and especially the **serpiginous, grayish, threadlike elevations (burrows)** in the web spaces of the fingers, are classic signs of **scabies**.
- **Permethrin cream** (5%) is the first-line treatment for scabies due to its high efficacy and safety profile, targeting the *Sarcoptes scabiei* mite.
*No medication should be administered, only proper hygiene.*
- While good hygiene is important for overall health, it is **insufficient** to eradicate a parasitic infestation like scabies.
- Scabies requires **specific pharmacologic intervention** to kill the mites and eggs, as they are not simply washed away.
*Antiviral medication*
- **Antiviral medications** are used to treat viral infections (e.g., herpes, varicella), which do not present with the characteristic burrows or respond to antiviral agents.
- The patient's symptoms are indicative of a **parasitic infestation**, not a viral one.
*Antifungal medication*
- **Antifungal medications** are indicated for fungal infections (e.g., ringworm, candidiasis), which typically present with a different morphology (e.g., annular lesions with raised borders) and lack the classic burrows seen in scabies.
- The clinical presentation points away from a fungal etiology.
*Broad-spectrum antibiotic*
- **Broad-spectrum antibiotics** treat bacterial infections. While secondary bacterial infections can occur due to scratching in scabies, the primary issue here is the mite infestation itself, which antibiotics do not address.
- Treating the primary scabies infestation is crucial to stop the itching and prevent further secondary infections.
Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases US Medical PG Question 8: A 20-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-day history of fever, myalgia, and swelling in his left groin after a recent camping trip in northern California. He appears acutely ill. Physical examination shows tender, left-sided inguinal lymphadenopathy and an enlarged, tender lymph node in the right axilla that is draining bloody necrotic material. Microscopic examination of a lymph node aspirate shows gram-negative coccobacilli with bipolar staining and a safety-pin appearance. This patient's condition is most likely caused by an organism with which of the following reservoirs?
- A. Squirrels (Correct Answer)
- B. Deer
- C. Bats
- D. Dogs
- E. Birds
Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases Explanation: ***Squirrels***
- The clinical presentation of **fever**, **myalgia**, **tender lymphadenopathy (buboes)**, especially with **bloody necrotic material drainage**, in a patient with recent outdoor exposure in **northern California**, is highly suggestive of **bubonic plague**.
- Microscopic examination revealing **gram-negative coccobacilli with bipolar staining** and a **safety-pin appearance** is **pathognomonic for *Yersinia pestis***, the causative agent of plague.
- The primary reservoir for *Y. pestis* is **wild rodents**, particularly **ground squirrels, prairie dogs, and rock squirrels** in the western United States, including California.
- Transmission occurs via flea bites from infected rodents, or through direct contact with infected animals.
*Deer*
- **Deer** are not reservoirs for *Yersinia pestis*.
- Deer serve as reservoirs for **Lyme disease** (*Borrelia burgdorferi*) transmitted by *Ixodes* ticks, which presents with erythema migrans, not buboes with bipolar-staining bacteria.
- Deer may also harbor ticks that transmit other diseases (ehrlichiosis, anaplasmosis), but none match this clinical picture.
*Bats*
- **Bats** are not associated with *Yersinia pestis* infection.
- Bats are reservoirs for **rabies virus** and **Histoplasma capsulatum** (histoplasmosis from bat guano in caves).
- Neither presents with the characteristic bubonic lymphadenopathy and gram-negative coccobacilli with bipolar staining seen here.
*Dogs*
- **Dogs** are not primary reservoirs for plague, though they can become infected and rarely transmit to humans.
- Dogs are reservoirs for **rabies**, **leptospirosis**, and **Capnocytophaga** infections.
- These do not match the clinical presentation of buboes and the pathognomonic microscopic findings of *Y. pestis*.
*Birds*
- **Birds** are not reservoirs for *Yersinia pestis*.
- Birds can harbor **Chlamydophila psittaci** (causing psittacosis/atypical pneumonia) and **Cryptococcus neoformans** (in pigeon droppings).
- These present with respiratory symptoms, not bubonic lymphadenopathy with bipolar-staining bacteria.
Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases US Medical PG Question 9: A 26-year-old male with no significant past medical history goes camping with several friends in Virginia. Several days after returning, he begins to experience fevers, headaches, myalgias, and malaise. He also notices a rash on his wrists and ankles (Figure A). Which of following should be initiated for treatment of his condition?
- A. Azithromycin
- B. Doxycycline (Correct Answer)
- C. Pyrazinamide
- D. Vancomycin
- E. Praziquantel
Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases Explanation: ***Doxycycline***
- The patient's symptoms (fever, headache, myalgias, rash on wrists and ankles after camping in Virginia) are highly suggestive of **Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF)**, a tick-borne illness.
- **Doxycycline** is the first-line and most effective treatment for RMSF, regardless of age or rash presentation.
*Azithromycin*
- While effective for some bacterial infections, **azithromycin** is not the recommended treatment for RMSF and has shown poor efficacy against *Rickettsia rickettsii*.
- It is typically used for atypical pneumonia, chlamydial infections, and certain strep infections.
*Pyrazinamide*
- **Pyrazinamide** is an antitubercular drug used in combination therapy for **tuberculosis**.
- It has no role in the treatment of tick-borne rickettsial infections like RMSF.
*Vancomycin*
- **Vancomycin** is a glycopeptide antibiotic primarily used for serious **Gram-positive bacterial infections**, especially those resistant to other antibiotics (e.g., MRSA, *C. difficile*).
- It is not effective against rickettsial organisms.
*Praziquantel*
- **Praziquantel** is an anthelmintic medication used to treat **parasitic worm infections**, such as schistosomiasis and tapeworm infections.
- It has no activity against bacterial infections like RMSF.
Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases US Medical PG Question 10: A 24-year-old female comes to the physician because of flu-like symptoms and a new rash for 2 days. She denies contacts with sick individuals or recent travel abroad, but recently went camping in Vermont. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination of the lateral right thigh shows a circular red ring with central clearing. Which of the following is the natural reservoir of the pathogen responsible for this patient's symptoms?
- A. Rat
- B. Rabbit
- C. Tick
- D. Mouse (Correct Answer)
- E. Flea
Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases Explanation: ***Mouse***
- The patient's symptoms, including **flu-like illness** and a **circular red rash with central clearing** (erythema migrans) after camping in Vermont, are classic for **Lyme disease**.
- The causative agent, *Borrelia burgdorferi*, is primarily maintained in **white-footed mice** (genus *Peromyscus*) in its natural reservoir during its larval and nymphal stages.
*Rat*
- While **rats** can carry and transmit various diseases, they are not the primary natural reservoir for *Borrelia burgdorferi*, the pathogen responsible for Lyme disease.
- Diseases associated with rats often include **leptospirosis** and **plague**, which present with different clinical pictures.
*Rabbit*
- **Rabbits** are known reservoirs for diseases like **tularemia** (*Francisella tularensis*), which can cause fever, skin lesions, and lymphadenopathy, but typically not the characteristic **erythema migrans** rash.
- They are not a significant natural reservoir for *Borrelia burgdorferi*.
*Tick*
- The **tick** (specifically *Ixodes scapularis* or **deer tick**) is the **vector** that transmits *Borrelia burgdorferi* to humans, not the natural reservoir.
- The tick acquires the bacteria from infected animal hosts such as mice and deer.
*Flea*
- **Fleas** are vectors for diseases such as **bubonic plague** (*Yersinia pestis*) and **endemic typhus** (*Rickettsia typhi*), which do not manifest with erythema migrans.
- They are not involved in the transmission or natural history of **Lyme disease**.
More Ectoparasites and vector-borne diseases US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.