Pneumocystis jirovecii US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Pneumocystis jirovecii. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Pneumocystis jirovecii US Medical PG Question 1: A 26-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. He was diagnosed with HIV infection 2 weeks ago. His CD4+ T-lymphocyte count is 162/mm3 (N ≥ 500). An interferon-gamma release assay is negative. Prophylactic treatment against which of the following pathogens is most appropriate at this time?
- A. Cytomegalovirus
- B. Toxoplasma gondii
- C. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- D. Aspergillus fumigatus
- E. Pneumocystis jirovecii (Correct Answer)
Pneumocystis jirovecii Explanation: ***Pneumocystis jirovecii***
- This patient's **CD4+ T-lymphocyte count of 162/mm3** is below the threshold of 200/mm3, indicating a significant risk for **Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP)**, an opportunistic infection in HIV.
- Prophylaxis with **trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX)** is highly effective and recommended for HIV patients with CD4 counts less than 200/mm3.
*Cytomegalovirus*
- **CMV prophylaxis** is generally not recommended for all HIV patients, even with low CD4 counts, unless there is evidence of active disease or extremely low CD4 counts (e.g., <50/mm3) with high viral loads.
- While CMV can cause end-organ disease in advanced HIV, routine primary prophylaxis is not standard for this CD4 level.
*Toxoplasma gondii*
- **Toxoplasma prophylaxis** is indicated for HIV patients with **CD4 counts less than 100/mm3** who are also seropositive for *Toxoplasma gondii*.
- The patient's CD4 count is 162/mm3, and there's no mention of *Toxoplasma* serostatus, making it less appropriate than PCP prophylaxis.
*Mycobacterium tuberculosis*
- The patient's **interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA) is negative**, which suggests no **latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI)**, thus making primary prophylaxis unnecessary at this time.
- While HIV patients are at high risk for TB, prophylaxis is typically given for LTBI or as secondary prophylaxis for those who have completed treatment for active TB.
*Aspergillus fumigatus*
- **Aspergillus infections** are typically seen in patients with severe **neutropenia** or those receiving high-dose corticosteroids, not primarily in HIV patients based solely on CD4 count.
- Routine prophylaxis for Aspergillus is not recommended for HIV patients, even with low CD4 counts, unless there is a specific risk factor.
Pneumocystis jirovecii US Medical PG Question 2: A 50-year-old man with a remote history of intravenous drug use and a past medical history of AIDS presents to his primary care provider with several weeks of productive cough and a mild fever. He was in his normal state of health and slowly started to develop these symptoms. He is hoping to be prescribed an antibiotic so he can get back to “normal”. Family history is significant for cardiovascular disease and diabetes. He takes antiviral medication and a multivitamin daily. His heart rate is 90/min, respiratory rate is 19/min, blood pressure is 135/85 mm Hg, and temperature is 38.3°C (100.9°F). On physical examination, he looks uncomfortable. A chest examination reveals consolidation in the right lower lung. Chest radiography confirms right lower lobe pneumonia. Of the following options, which is the most likely cause of the patient’s pneumonia?
- A. Pulmonary sequestration
- B. Pneumocystis pneumonia
- C. Aspiration pneumonia
- D. Community-acquired pneumonia (Correct Answer)
- E. Disseminated cutaneous infection
Pneumocystis jirovecii Explanation: ***Community-acquired pneumonia***
- This patient, despite having AIDS, presents with typical symptoms of **community-acquired pneumonia (CAP)**, including productive cough, fever, and classic consolidation on chest examination and radiography.
- While HIV/AIDS patients are at higher risk for opportunistic infections, CAP caused by common bacterial pathogens like *Streptococcus pneumoniae* is still a frequent cause of pneumonia and should be considered, especially with a **lobar consolidation pattern**.
*Pulmonary sequestration*
- **Pulmonary sequestration** is a rare congenital malformation where a segment of lung tissue is not connected to the tracheobronchial tree and receives systemic blood supply. It typically presents with recurrent infections in the same location or as an asymptomatic mass.
- It would not explain the acute onset of symptoms like fever and productive cough, nor the classic signs of pneumonia like consolidation in an otherwise healthy adult (aside from AIDS).
*Pneumocystis pneumonia*
- **Pneumocystis pneumonia (PJP)**, caused by *Pneumocystis jirovecii*, is a classic opportunistic infection in patients with AIDS, especially those with low CD4 counts.
- However, PJP typically presents with a **subacute onset** of dyspnea, non-productive cough, and diffuse interstitial infiltrates on chest radiography, not focal consolidation.
*Aspiration pneumonia*
- **Aspiration pneumonia** occurs when foreign material, often gastric contents or oral flora, is inhaled into the lungs, leading to inflammation and infection.
- There is no clinical indication of aspiration in this patient (e.g., dysphagia, impaired consciousness, reflux), and the history does not suggest risk factors for aspiration.
*Disseminated cutaneous infection*
- A **disseminated cutaneous infection** involves widespread skin lesions caused by an infection.
- This patient's symptoms are localized to the respiratory system (productive cough, lung consolidation) and do not suggest a primary cutaneous infection.
Pneumocystis jirovecii US Medical PG Question 3: A 33-year-old HIV-positive male is seen in clinic for follow-up care. When asked if he has been adhering to his HIV medications, the patient exclaims that he has been depressed, thus causing him to not take his medication for six months. His CD4+ count is now 33 cells/mm3. What medication(s) should he take in addition to his anti-retroviral therapy?
- A. Azithromycin and fluconazole
- B. Azithromycin, dapsone, and fluconazole
- C. Dapsone
- D. Fluconazole
- E. Azithromycin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Correct Answer)
Pneumocystis jirovecii Explanation: ***Azithromycin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole***
- With a **CD4+ count of 33 cells/mm3**, this patient is at high risk for **Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP)** and **Toxoplasma gondii encephalitis**, for which **trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX)** is the prophylaxis of choice.
- He is also at very high risk for **Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infection**, for which **azithromycin** is the recommended preventative treatment when the CD4 count is below 50 cells/mm3.
*Azithromycin and fluconazole*
- While **azithromycin** is indicated for MAC prophylaxis, **fluconazole** is typically used for **cryptococcal meningitis** or **candidiasis**, which are not the primary, immediate prophylactic concerns at this specific CD4 count unless there's evidence of these infections.
- The most critical opportunistic infections to prevent at a CD4 count of 33 cells/mm3 are PJP, Toxoplasmosis, and MAC.
*Azithromycin, dapsone, and fluconazole*
- **Dapsone** can be used as an alternative for **PJP prophylaxis** if TMP-SMX is contraindicated, but it is not the first-line choice and does not cover toxoplasmosis as effectively as TMP-SMX alone.
- **Fluconazole** again is not a primary prophylactic agent at this CD4 count in the absence of specific indications.
*Dapsone*
- **Dapsone** is an alternative for **PJP prophylaxis** and can also prevent **Toxoplasma gondii encephalitis** when combined with pyrimethamine, but it is not the first-line recommendation.
- It does not provide coverage against **MAC infection**, which is a significant risk at this CD4 count.
*Fluconazole*
- **Fluconazole** is primarily used for **fungal infections** like **candidiasis** or **cryptococcosis**.
- It does not prevent **PJP, Toxoplasmosis, or MAC**, which are the most critical prophylactic concerns for a patient with a CD4 count of 33 cells/mm3.
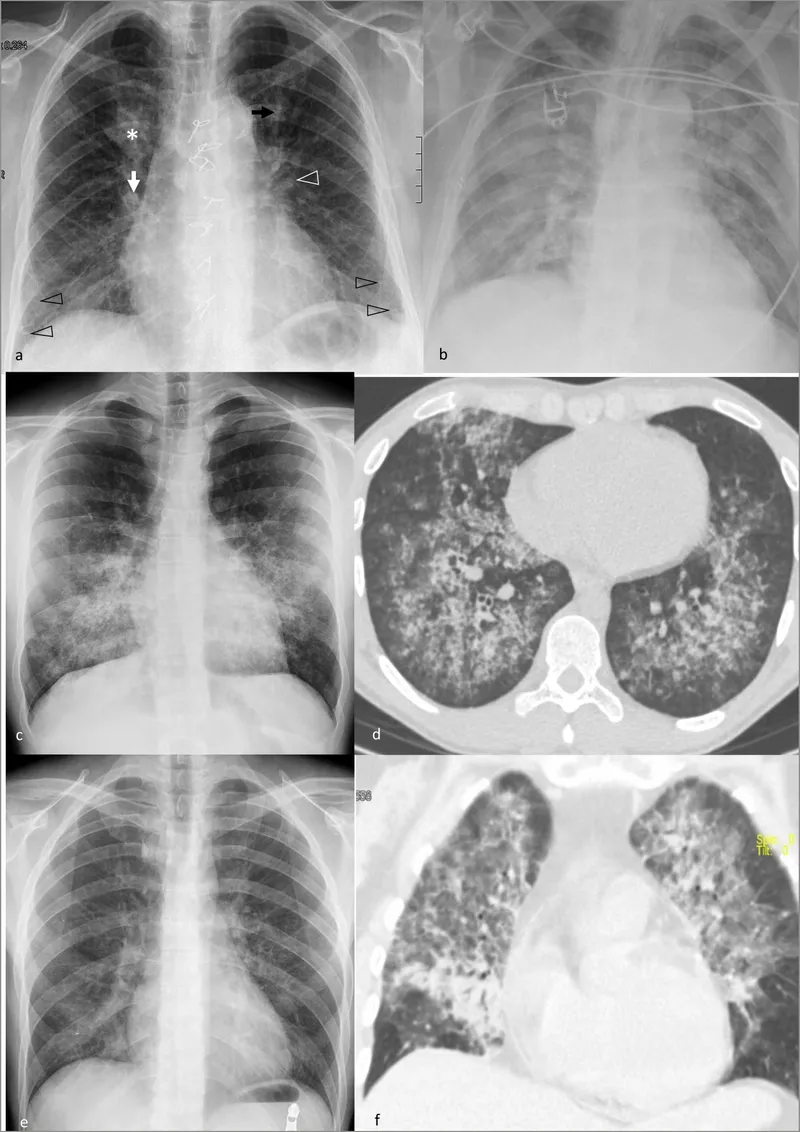
Pneumocystis jirovecii US Medical PG Question 4: A 26-year-old man is undergoing a bone marrow transplantation for treatment of a non-Hodgkin lymphoma that has been refractory to several rounds of chemotherapy and radiation over the past 2 years. He has been undergoing a regimen of cyclophosphamide and total body irradiation for the past several weeks in anticipation of his future transplant. This morning, he reports developing a productive cough and is concerned because he noted some blood in his sputum this morning. The patient also reports pain with inspiration. His temperature is 101°F (38.3°C), blood pressure is 115/74 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, respirations are 19/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. A chest radiograph and CT are obtained and shown in Figures A and B respectively. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Streptococcus pneumoniae
- B. Aspergillus fumigatus (Correct Answer)
- C. Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia
- D. Staphylococcus aureus
- E. Mycoplasma pneumonia
Pneumocystis jirovecii Explanation: ***Aspergillus fumigatus***
- The patient's immunocompromised state due to **chemotherapy** and **total body irradiation** for lymphoma, combined with the presence of a **productive cough with hemoptysis**, pleuritic pain, and fever, is highly suggestive of an invasive fungal infection.
- **Chest imaging** demonstrating nodules with surrounding ground-glass opacity (the **"halo sign"** on CT) is characteristic of **invasive aspergillosis** in immunocompromised patients, where the ground-glass attenuation represents hemorrhage around a nodular lesion.
*Streptococcus pneumoniae*
- While *S. pneumoniae* can cause pneumonia in immunocompromised patients, it typically presents with **lobar consolidation** on imaging, not the nodular lesions with a halo sign seen here.
- **Hemoptysis**, although possible, is less common as a prominent symptom than in invasive fungal infections in this context.
*Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia*
- *Pneumocystis* pneumonia (PCP) typically presents with **diffuse interstitial infiltrates** on chest imaging, often described as ground-glass opacities, but usually lacks the focal nodular lesions or hemoptysis seen here.
- PCP is more common in patients with **HIV/AIDS** or those undergoing specific immunosuppressive regimens (e.g., high-dose corticosteroids), and while possible, the imaging findings do not directly support it.
*Staphylococcus aureus*
- *S. aureus* pneumonia can cause **abscess formation** and **cavitary lesions**, but the imaging described (nodules with halo sign) is not typical.
- While it can cause severe pneumonia in immunocompromised hosts, **hemoptysis** and the specific imaging findings align less with *S. aureus* and more with invasive mold infections.
*Mycoplasma pneumonia*
- *Mycoplasma pneumoniae* causes **"walking pneumonia"** and typically presents with milder symptoms and **interstitial or patchy infiltrates** on chest imaging.
- Severe symptoms like **hemoptysis** and the imaging findings of nodular lesions with a halo sign are not characteristic of *Mycoplasma* infection.
Pneumocystis jirovecii US Medical PG Question 5: A 10-year-old boy is brought to the physician by his mother because of a 2-day history of fever and productive cough. He has had similar episodes sporadically in the past with frequent episodes of thick, discolored nasal discharge. Physical examination shows diffuse crackles and rhonchi. The most likely cause of recurrent infections in this patient is a dysfunction of which of the following cell types?
- A. Type I pneumocytes
- B. Club cells
- C. Alveolar macrophages
- D. Type II pneumocytes
- E. Ciliated columnar cells (Correct Answer)
Pneumocystis jirovecii Explanation: ***Ciliated columnar cells***
- The patient's presentation with **recurrent respiratory infections**, productive cough, and thick nasal discharge suggests a defect in mucociliary clearance, which is primarily mediated by **ciliated columnar cells**.
- Conditions like **primary ciliary dyskinesia** involve dysfunctional cilia unable to clear mucus and pathogens, leading to chronic infections.
*Type I pneumocytes*
- These cells are responsible for **gas exchange** in the alveoli due to their thin, flat structure.
- Dysfunction of type I pneumocytes would primarily lead to **respiratory distress** and impaired oxygenation, not recurrent infections.
*Club cells*
- **Club cells** (formerly Clara cells) are found in the bronchioles and secrete components of the surfactant and detoxify harmful substances.
- While they contribute to airway defense, their primary role is not mucociliary clearance, and their dysfunction is less likely to cause recurrent productive cough and thick nasal discharge.
*Alveolar macrophages*
- **Alveolar macrophages** are crucial for phagocytosing inhaled particles and pathogens within the alveoli.
- Dysfunction of these cells would likely result in increased susceptibility to **pneumonia** and more severe lower respiratory tract infections, but is not typically associated with chronic productive cough and nasal discharge suggesting a primary mucociliary defect.
*Type II pneumocytes*
- **Type II pneumocytes** produce **surfactant** to reduce alveolar surface tension and are progenitors for type I pneumocytes.
- Dysfunction primarily leads to **atelectasis** and reduced lung compliance, not recurrent bacterial infections associated with impaired clearance.
Pneumocystis jirovecii US Medical PG Question 6: A 35-year-old man comes to the emergency department with fever, chills, dyspnea, and a productive cough. His symptoms began suddenly 2 days ago. He was diagnosed with HIV 4 years ago and has been on triple antiretroviral therapy since then. He smokes one pack of cigarettes daily. He is 181 cm (5 ft 11 in) tall and weighs 70 kg (154 lb); BMI is 21.4 kg/m2. He lives in Illinois and works as a carpenter. His temperature is 38.8°C (101.8°F), pulse is 110/min, respirations are 24/min, and blood pressure is 105/74 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 92%. Examinations reveals crackles over the right lower lung base. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 11.5 g/dL
Leukocyte count 12,800/mm3
Segmented neutrophils 80%
Eosinophils 1%
Lymphocytes 17%
Monocytes 2%
CD4+ T-lymphocytes 520/mm3(N ≥ 500)
Platelet count 258,000/mm3
Serum
Na+ 137 mEq/L
Cl- 102 mEq/L
K+ 5.0 mEq/L
HCO3- 22 mEq/L
Glucose 92 mg/dL
An x-ray of the chest shows a right lower-lobe infiltrate of the lung. Which of the following is the most likely causal organism?
- A. Streptococcus pneumoniae (Correct Answer)
- B. Legionella pneumophila
- C. Pneumocystis jirovecii
- D. Staphylococcus aureus
- E. Cryptococcus neoformans
Pneumocystis jirovecii Explanation: ***Streptococcus pneumoniae***
- This patient presents with **fever, chills, productive cough, dyspnea, leukocytosis with neutrophilia, and a lobar infiltrate on chest X-ray**, which are classic signs of **community-acquired bacterial pneumonia**.
- Although the patient is **HIV-positive**, his CD4+ count is >500/mm3 and he is on antiretroviral therapy, indicating relatively preserved immune function, making *S. pneumoniae* the most common cause of pneumonia even in HIV-infected individuals with controlled disease.
*Legionella pneumophila*
- While *Legionella* can cause pneumonia with fever and dyspnea, it is often associated with **gastrointestinal symptoms** (e.g., diarrhea) and **hyponatremia**, which are not present here.
- Exposure to contaminated water sources is a common risk factor, and the lobar infiltrate is less typical than diffuse or patchy infiltrates.
*Pneumocystis jirovecii*
- *Pneumocystis pneumonia (PJP)* is typically seen in **HIV patients with severely suppressed immune systems (CD4+ count <200/mm3)**.
- The patient's CD4+ count (520/mm3) is above this threshold, and PJP usually presents with diffuse interstitial infiltrates rather than a lobar infiltrate.
*Staphylococcus aureus*
- *S. aureus* pneumonia often occurs in the context of recent **influenza infection, intravenous drug use, or hospitalization**, or can present rapidly with **necrotizing pneumonia** or **empyema**.
- While possible, the absence of these specific risk factors or severe features makes it less likely than *S. pneumoniae* in this specific presentation.
*Cryptococcus neoformans*
- *Cryptococcus neoformans* is an opportunistic fungus that typically causes **pulmonary or central nervous system infections**, especially in severely immunocompromised patients (CD4+ count usually <100/mm3).
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis often manifests as **nodules or cavitary lesions**, or can be asymptomatic, which differs from the acute lobar pneumonia presented.
Pneumocystis jirovecii US Medical PG Question 7: A 26-year-old man with HIV and a recent CD4+ count of 800 presents to his PCP with fever, cough, and dyspnea. He notes that he recently lost his job as a construction worker and has not been able to afford his HAART medication. His temperature is 102.6°F (39.2°C), pulse is 75/min, respirations are 24/min, and blood pressure is 135/92 mmHg. Physical exam reveals a tachypneic patient with scattered crackles in both lungs, and labs show a CD4+ count of 145 and an elevated LDH. The chest radiography is notable for bilateral diffuse interstitial infiltrates. For definitive diagnosis, the physician obtains a sputum sample. Which stain should he use to visualize the most likely responsible organism?
- A. Periodic acid schiff stain
- B. Silver stain (Correct Answer)
- C. Ziehl-Neelsen stain
- D. India ink stain
- E. Carbol fuchsin stain
Pneumocystis jirovecii Explanation: ***Silver stain***
- The patient's presentation with **fever, cough, dyspnea, bilateral diffuse interstitial infiltrates**, and a **CD4+ count of 145** (indicating severe immunosuppression) is highly suggestive of ***Pneumocystis jirovecii*** **pneumonia (PCP)**, formerly known as ***Pneumocystis carinii***.
- ***Pneumocystis jirovecii*** **cysts** and **trophozoites** are best visualized using **silver-based stains** (e.g., Gomori methenamine silver stain) which stain the fungal cell walls dark brown or black.
*Periodic acid schiff stain*
- **PAS stain** is used to identify **glycogen, mucus, and fungal elements** like those of *Candida* or *Aspergillus*, by staining polysaccharides a magenta color.
- While it can stain some fungal organisms, it is **not the primary or most effective stain** for *Pneumocystis jirovecii*.
*Ziehl-Neelsen stain*
- The **Ziehl-Neelsen stain** (also known as acid-fast stain) is used to identify **acid-fast bacilli**, such as *Mycobacterium tuberculosis* or *Nocardia*.
- Although **tuberculosis** is common in HIV patients, the clinical presentation and CXR findings (diffuse interstitial infiltrates rather than cavitary lesions or granulomas) **do not strongly suggest tuberculosis** as the primary diagnosis here.
*India ink stain*
- The **India ink stain** is primarily used to visualize the **capsule of *Cryptococcus neoformans*** in cerebrospinal fluid or other body fluids, appearing as a halo around the yeast cells.
- This patient's symptoms are respiratory, and the likely pathogen is *Pneumocystis*, making India ink stain **inappropriate** for this suspected diagnosis.
*Carbol fuchsin stain*
- **Carbol fuchsin stain** is a component of the **acid-fast staining** procedure (like Ziehl-Neelsen), used as the primary stain to identify acid-fast organisms.
- As with Ziehl-Neelsen, this stain is for **mycobacteria** and would **not effectively visualize** ***Pneumocystis jirovecii***.
Pneumocystis jirovecii US Medical PG Question 8: A 41-year-old male with a history of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia is found to have multiple ring-enhancing lesions on brain CT. Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's abnormal scan?
- A. Protozoa (Correct Answer)
- B. Virus
- C. Neoplasm
- D. Bacteria
- E. Prion
Pneumocystis jirovecii Explanation: ***Protozoa***
- The patient's history of **Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia** (PJP) suggests an **immunocompromised state**, likely due to HIV/AIDS.
- In such patients, **ring-enhancing brain lesions** are highly characteristic of **cerebral toxoplasmosis**, an opportunistic infection caused by the protozoan *Toxoplasma gondii*.
*Virus*
- While viruses like **CMV** or **JC virus** (causing PML) can affect the brain in immunocompromised patients, they typically present with different imaging features (e.g., non-enhancing lesions in PML) and are less likely to cause multiple ring-enhancing lesions.
- Though HIV can cause **HIV encephalopathy**, it typically involves **diffuse atrophy** and **white matter changes**, rather than distinct ring-enhancing lesions.
*Neoplasm*
- **Primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL)** can present with ring-enhancing lesions, especially in HIV-positive individuals.
- However, given the association with PJP, **infectious etiologies** like toxoplasmosis are generally more common as the initial diagnosis for multiple ring-enhancing lesions in this patient population.
*Bacteria*
- **Bacterial brain abscesses** can cause ring-enhancing lesions but are less common in disseminated opportunistic infections in HIV/AIDS compared to protozoal or fungal infections.
- They also typically present with a more **acute inflammatory picture** and may be preceded by a source of bacterial infection (e.g., endocarditis, sinusitis) not mentioned here.
*Prion*
- **Prion diseases** (e.g., Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease) cause rapidly progressive dementia and characteristic EEG and MRI findings (e.g., cortical ribboning, basal ganglia hyperintensity) that do not typically include multiple ring-enhancing lesions.
- They are also not associated with the immunocompromised state indicated by PJP.
Pneumocystis jirovecii US Medical PG Question 9: A 3-month-old girl is brought to the emergency department because of a 2-day history of progressive difficulty breathing and a dry cough. Five weeks ago, she was diagnosed with diffuse hemangiomas involving the intrathoracic cavity and started treatment with prednisolone. She appears uncomfortable and in moderate respiratory distress. Her temperature is 38°C (100.4°F), pulse is 150/min, respirations are 50/min, and blood pressure is 88/50 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 87%. Oral examination shows a white plaque covering the tongue that bleeds when scraped. Chest examination shows subcostal and intercostal retractions. Scattered fine crackles and rhonchi are heard throughout both lung fields. Laboratory studies show a leukocyte count of 21,000/mm3 and an increased serum beta-D-glucan concentration. An x-ray of the chest shows symmetrical, diffuse interstitial infiltrates. Which of the following is most likely to confirm the diagnosis?
- A. Tuberculin skin test
- B. Urine antigen test
- C. CT scan of the chest
- D. Bronchoalveolar lavage (Correct Answer)
- E. DNA test for CFTR mutation
Pneumocystis jirovecii Explanation: ***Bronchoalveolar lavage***
- The patient, an infant on **prednisolone** (immunosuppression) with **diffuse interstitial infiltrates**, **uncomfortable appearance**, **respiratory distress**, and **oral thrush (white plaque that bleeds when scraped)**, points to **Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP)**.
- **Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL)** is the gold standard for diagnosing PCP by identifying **Pneumocystis jirovecii cysts** or **trophozoites** using special stains (e.g., Giemsa, methenamine silver).
*Tuberculin skin test*
- The **tuberculin skin test** is used to diagnose **tuberculosis**, which typically presents with **granulomas** and **cavitary lesions** on chest X-ray, not diffuse interstitial infiltrates.
- While tuberculosis can cause respiratory symptoms, the presence of oral thrush and immunosuppression suggests an opportunistic fungal infection like PCP rather than TB.
*Urine antigen test*
- A **urine antigen test** is commonly used for diagnosing **Legionnaires' disease** or **pneumococcal pneumonia** in adults, and is not applicable for PCP.
- It does not detect *Pneumocystis jirovecii*, which is the suspected pathogen in this immunosuppressed infant.
*CT scan of the chest*
- A **CT scan of the chest** would show **diffuse ground-glass opacities** characteristic of PCP but is a **radiological finding**, not a definitive diagnostic test for the pathogen itself.
- While it can further characterize the pulmonary findings, it cannot identify the causative organism, which is crucial for targeted treatment.
*DNA test for CFTR mutation*
- A **DNA test for CFTR mutation** is used to diagnose **cystic fibrosis**, a genetic disorder affecting mucus production, and is not relevant in this acute presentation of respiratory distress and immunosuppression.
- Cystic fibrosis typically presents with recurrent respiratory infections, pancreatic insufficiency, and failure to thrive, not primarily with opportunistic infections like PCP.
Pneumocystis jirovecii US Medical PG Question 10: A 44-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-week history of productive cough, fever, and lethargy. He also has several skin lesions over his body. His symptoms began 3 weeks after he returned from a camping trip in Kentucky. Three years ago, he underwent kidney transplantation for polycystic kidney disease. Current medications include sirolimus and prednisone. His temperature is 38°C (100.4°F). Diffuse crackles are heard over the lung fields. There are 4 white, verrucous skin patches over his chest and upper limbs. A photomicrograph of a skin biopsy specimen from one of the lesions is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Coccidioidomycosis
- B. Mucormycosis
- C. Blastomycosis (Correct Answer)
- D. Cryptococcosis
- E. Histoplasmosis
Pneumocystis jirovecii Explanation: ***Blastomycosis***
- The patient's history of **camping in Kentucky**, along with the presence of **pulmonary symptoms** (productive cough, fever, crackles) and **verrucous skin lesions**, are classic for blastomycosis.
- The photomicrograph showing **broad-based budding yeast** is pathognomonic for *Blastomyces dermatitidis*.
*Coccidioidomycosis*
- This is typical in the **Southwestern United States and parts of Mexico**, not Kentucky.
- Microscopic examination would reveal **spherules containing endospores**, which are not seen in the provided image.
*Mucormycosis*
- This infection is characterized by **irregular, broad, non-septate hyphae** with **wide-angle branching**, often invading blood vessels, leading to tissue necrosis.
- It primarily affects immunocompromised patients but typically presents as **rhinocerebral** or **pulmonary infection**, less commonly with verrucous skin lesions of this type.
*Cryptococcosis*
- Primarily affects the **lungs and central nervous system**, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
- Microscopy typically shows **encapsulated yeast** cells, which would be visible with India ink stain, and are not represented by the broad-based budding in the image.
*Histoplasmosis*
- Prevalent in the **Ohio and Mississippi River Valleys**, which includes Kentucky, and is often associated with **bird or bat droppings**.
- On microscopy, it presents as **small intracellular yeast** within macrophages, which is morphologically distinct from the large, broad-based budding yeast shown.
More Pneumocystis jirovecii US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.