Opportunistic fungal infections US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Opportunistic fungal infections. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Opportunistic fungal infections US Medical PG Question 1: A 19-year-old man with a history of type 1 diabetes presents to the emergency department for the evaluation of a blood glucose level of 492 mg/dL. Laboratory examination revealed a serum bicarbonate level of 13 mEq/L, serum sodium level of 122 mEq/L, and ketonuria. Arterial blood gas demonstrated a pH of 6.9. He is admitted to the hospital and given bicarbonate and then started on an insulin drip and intravenous fluid. Seven hours later when his nurse is making rounds, he is confused and complaining of a severe headache. Repeat sodium levels are unchanged, although his glucose level has improved. His vital signs include a temperature of 36.6°C (98.0°F), pulse 50/min, respiratory rate 13/min and irregular, and blood pressure 177/95 mm Hg. What other examination findings would be expected in this patient?
- A. Hypoglycemia
- B. Pupillary constriction
- C. Papilledema (Correct Answer)
- D. Pancreatitis
- E. Peripheral edema
Opportunistic fungal infections Explanation: ***Papilledema***
- This patient's symptoms (confusion, severe headache, bradycardia, irregular respiration, hypertension) following treatment for **diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)** are highly suggestive of **cerebral edema**.
- **Papilledema** is a retinal finding resulting from increased intracranial pressure (ICP), which is a characteristic sign of cerebral edema.
*Hypoglycemia*
- While the patient's glucose level has improved, it is not described as being low enough to cause hypoglycemia, and the symptoms are more consistent with **increased ICP**.
- Symptoms of hypoglycemia (e.g., tremors, sweating, hunger, anxiety) are different from the patient's current presentation of confusion and severe headache.
*Pupillary constriction*
- **Pupillary constriction** (miosis) is typically not associated with cerebral edema; instead, **pupillary dilation** (mydriasis) can occur with severe increase in ICP due to uncal herniation.
- The combination of bradycardia, irregular respiration, and hypertension (Cushing's triad) is indicative of increased ICP, which would likely cause pupillary changes related to brainstem compression.
*Pancreatitis*
- Pancreatitis is a known complication of DKA, but it typically presents with **severe abdominal pain**, nausea, and vomiting, rather than cerebral symptoms.
- Although the patient had DKA, the current neurological symptoms point directly to an intracranial process rather than an abdominal issue.
*Peripheral edema*
- **Peripheral edema** results from fluid accumulation in peripheral tissues and is not a direct consequence or expected finding in cerebral edema.
- While fluid administration can cause some peripheral fluid retention, it typically does not lead to the acute neurological deterioration seen in this patient.
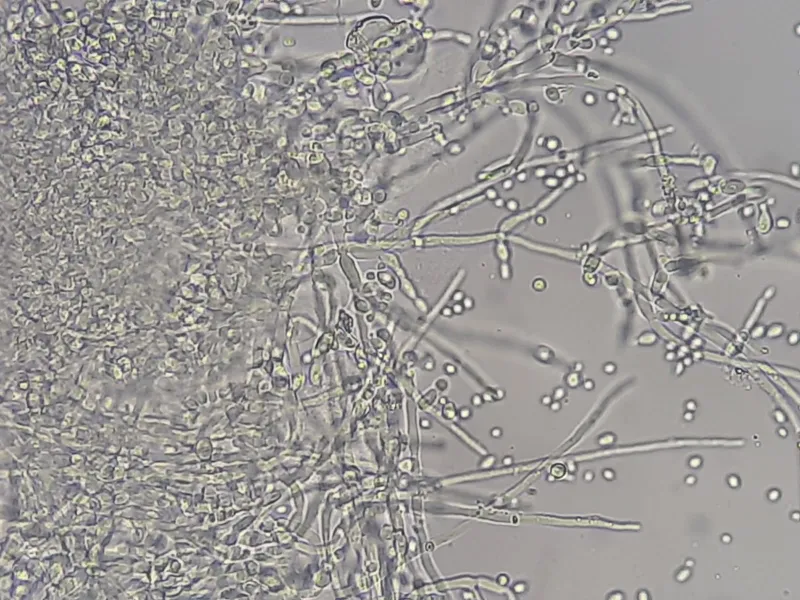
Opportunistic fungal infections US Medical PG Question 2: A 26-year-old man is undergoing a bone marrow transplantation for treatment of a non-Hodgkin lymphoma that has been refractory to several rounds of chemotherapy and radiation over the past 2 years. He has been undergoing a regimen of cyclophosphamide and total body irradiation for the past several weeks in anticipation of his future transplant. This morning, he reports developing a productive cough and is concerned because he noted some blood in his sputum this morning. The patient also reports pain with inspiration. His temperature is 101°F (38.3°C), blood pressure is 115/74 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, respirations are 19/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. A chest radiograph and CT are obtained and shown in Figures A and B respectively. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Streptococcus pneumoniae
- B. Aspergillus fumigatus (Correct Answer)
- C. Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia
- D. Staphylococcus aureus
- E. Mycoplasma pneumonia
Opportunistic fungal infections Explanation: ***Aspergillus fumigatus***
- The patient's immunocompromised state due to **chemotherapy** and **total body irradiation** for lymphoma, combined with the presence of a **productive cough with hemoptysis**, pleuritic pain, and fever, is highly suggestive of an invasive fungal infection.
- **Chest imaging** demonstrating nodules with surrounding ground-glass opacity (the **"halo sign"** on CT) is characteristic of **invasive aspergillosis** in immunocompromised patients, where the ground-glass attenuation represents hemorrhage around a nodular lesion.
*Streptococcus pneumoniae*
- While *S. pneumoniae* can cause pneumonia in immunocompromised patients, it typically presents with **lobar consolidation** on imaging, not the nodular lesions with a halo sign seen here.
- **Hemoptysis**, although possible, is less common as a prominent symptom than in invasive fungal infections in this context.
*Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia*
- *Pneumocystis* pneumonia (PCP) typically presents with **diffuse interstitial infiltrates** on chest imaging, often described as ground-glass opacities, but usually lacks the focal nodular lesions or hemoptysis seen here.
- PCP is more common in patients with **HIV/AIDS** or those undergoing specific immunosuppressive regimens (e.g., high-dose corticosteroids), and while possible, the imaging findings do not directly support it.
*Staphylococcus aureus*
- *S. aureus* pneumonia can cause **abscess formation** and **cavitary lesions**, but the imaging described (nodules with halo sign) is not typical.
- While it can cause severe pneumonia in immunocompromised hosts, **hemoptysis** and the specific imaging findings align less with *S. aureus* and more with invasive mold infections.
*Mycoplasma pneumonia*
- *Mycoplasma pneumoniae* causes **"walking pneumonia"** and typically presents with milder symptoms and **interstitial or patchy infiltrates** on chest imaging.
- Severe symptoms like **hemoptysis** and the imaging findings of nodular lesions with a halo sign are not characteristic of *Mycoplasma* infection.
Opportunistic fungal infections US Medical PG Question 3: A young woman from the Ohio River Valley in the United States currently on corticosteroid therapy for ulcerative colitis presented to a clinic complaining of fever, sweat, headache, nonproductive cough, malaise, and general weakness. A chest radiograph revealed patchy pneumonia in the lower lung fields, together with enlarged mediastinal and hilar lymph nodes. Skin changes suggestive of erythema nodosum (i.e. an acute erythematous eruption) were noted. Because the patient was from a region endemic for fungal infections associated with her symptoms and the patient was in close contact with a person presenting similar symptoms, the attending physician suspected that systemic fungal infection might be responsible for this woman’s illness. Which of the following laboratory tests can the physician use to ensure early detection of the disease, and also effectively monitor the treatment response?
- A. Skin tests
- B. Fungal staining
- C. Antigen detection (Correct Answer)
- D. Culture method
- E. Antibody testing
Opportunistic fungal infections Explanation: ***Antigen detection***
- **Antigen detection assays** (e.g., *Histoplasma galactomannan antigen*) are highly sensitive for **disseminated histoplasmosis**, especially in immunosuppressed patients like this one on corticosteroids.
- They provide **early diagnosis** and are effective for **monitoring treatment response**, as antigen levels typically decrease with successful therapy.
*Skin tests*
- **Skin tests** (e.g., *histoplasmin skin test*) indicate **prior exposure** to the fungus and are not useful for diagnosing active, acute infection.
- A positive skin test does not differentiate between past exposure and current disease, making it unsuitable for early detection or monitoring.
*Fungal staining*
- **Fungal staining** of patient samples (e.g., sputum, biopsy) can reveal fungal elements but has **limited sensitivity** and may not identify the specific pathogen.
- It often requires **invasive procedures** to obtain suitable specimens and is not ideal for routine monitoring of treatment response due to variability.
*Culture method*
- **Fungal cultures** are a **definitive diagnostic method** but can take **several weeks** to yield results, which is too slow for early detection in an acutely ill patient.
- While useful for species identification and susceptibility testing, the **delayed turnaround time** makes it impractical for monitoring rapid treatment changes.
*Antibody testing*
- **Antibody tests** for fungal infections can be useful but may show **false negatives in immunocompromised patients** (like this patient on corticosteroids) due to a blunted immune response.
- Seroconversion or a significant rise in antibody titers can indicate infection, but antibodies may **persist long after resolution**, making them less reliable for monitoring acute treatment efficacy.
Opportunistic fungal infections US Medical PG Question 4: A 65-year-old woman who lives in New York City presents with headache, fever, and neck stiffness. She received a diagnosis of HIV infection 3 years ago and has been inconsistent with her antiretroviral medications. Recent interferon-gamma release assay testing for latent tuberculosis was negative. A computed tomography of her head is normal. A lumbar puncture shows a white blood cell count of 45/mm3 with a mononuclear predominance, the glucose level of 30 mg/dL, and a protein level of 60 mg/dL. A preparation of her cerebrospinal fluid is shown. Which of the following organisms is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
- A. Blastomyces dermatitidis
- B. Cryptococcus neoformans (Correct Answer)
- C. Aspergillus fumigatus
- D. Coccidioides immitis
- E. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Opportunistic fungal infections Explanation: ***Cryptococcus neoformans***
- The patient's presentation with **headache, fever, and neck stiffness** in the setting of **HIV infection with poor medication adherence** (indicating immunosuppression) is highly suggestive of **cryptococcal meningitis**.
- **CSF findings** of **mononuclear pleocytosis**, **low glucose**, and **elevated protein** are classic for fungal meningitis. The provided image, if showing encapsulated yeast cells, would further confirm *Cryptococcus neoformans*.
*Blastomyces dermatitidis*
- This fungus is common in the **southeastern, south-central, and midwestern United States**, not typically associated with New York City as a primary endemic region.
- While it can cause meningitis in immunocompromised patients, it often presents with **pulmonary involvement** or characteristic **skin lesions** as well, which are not mentioned.
*Aspergillus fumigatus*
- *Aspergillus* infections are typically seen in individuals with **severe neutropenia** or those on **high-dose steroids**, rather than primarily in HIV patients with inconsistent ART.
- While it can cause CNS infections, they often manifest as **brain abscesses** or **vasculitis** and are not characterized by the classic meningitis picture with mononuclear pleocytosis.
*Coccidioides immitis*
- This fungus is endemic to the **southwestern United States** and parts of Central and South America, making it geographically unlikely for a patient living in New York City without a travel history.
- While it can cause meningitis in immunocompromised individuals, the geographical context is a significant differentiating factor.
*Mycobacterium tuberculosis*
- Although **tuberculous meningitis** also presents with mononuclear pleocytosis, low glucose, and elevated protein in the CSF, the **negative interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA)** for latent tuberculosis makes this diagnosis less likely.
- Additionally, CT scans may show **basilar meningeal enhancement** or hydrocephalus in tuberculous meningitis, which is not indicated by a normal CT.
Opportunistic fungal infections US Medical PG Question 5: A 74-year-old man is admitted to the medical ward after he developed a fungal infection. He has aplastic anemia. The most recent absolute neutrophil count was 450/µL. An anti-fungal agent is administered that inhibits the fungal enzyme, (1→3)-β-D-glucan synthase, and thereby disrupts the integrity of the fungal cell wall. He responds well to the treatment. Although amphotericin B is more efficacious for his condition, it was not used because of the side effect profile. What was the most likely infection?
- A. Invasive aspergillosis
- B. Mucormycosis
- C. Histoplasmosis
- D. Paracoccidioidomycosis
- E. Candidemia (Correct Answer)
Opportunistic fungal infections Explanation: ***Candidemia***
- The patient's **neutropenia** (absolute neutrophil count of 450/µL) due to aplastic anemia is a major risk factor for invasive candidiasis, including candidemia.
- The antifungal agent's mechanism of action, targeting **(1→3)-β-D-glucan synthase**, is characteristic of **echinocandins**, which are first-line agents for candidemia, especially in critically ill or neutropenic patients, and often preferred over amphotericin B due to a better side effect profile.
*Invasive aspergillosis*
- While neutropenia is a significant risk factor for invasive aspergillosis, the primary antifungal drugs for this condition are typically **voriconazole** or **isavuconazole**, although echinocandins may be used as salvage therapy or in combination.
- The description of the drug's mechanism specifically targeting **(1→3)-β-D-glucan synthase** does not make aspergillosis the *most likely* infection, as some Aspergillus species may have less β-D-glucan in their cell walls compared to *Candida*.
*Mucormycosis*
- This aggressive fungal infection is often seen in immunocompromised patients, particularly those with **diabetes** or profound neutropenia, but the primary treatment is usually **amphotericin B**.
- Mucorales fungi typically **lack ergosterol** and their cell walls do not contain **(1→3)-β-D-glucan**, making echinocandins ineffective.
*Histoplasmosis*
- This is a dimorphic fungal infection endemic to certain geographic regions, primarily affecting the lungs and disseminating in immunocompromised individuals.
- The drug of choice for severe or disseminated histoplasmosis is **amphotericin B**, followed by azoles; echinocandins are generally not active against *Histoplasma*.
*Paracoccidioidomycosis*
- This is a chronic systemic mycosis found in Latin America, primarily affecting the lungs, skin, and lymph nodes.
- Treatment for severe forms typically involves **amphotericin B**, followed by sulfonamides or azoles for maintenance; echinocandins are not effective against *Paracoccidioides*.
Opportunistic fungal infections US Medical PG Question 6: A 27-year-old diabetic male rushes to the emergency department after finding his blood glucose level to be 492 mg/dL which is reconfirmed in the ED. He currently does not have any complaints except for a mild colicky abdominal pain. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), respirations are 15/min, pulse is 67/min, and blood pressure is 122/88 mm Hg. Blood is drawn for labs the result of which is given below:
Serum:
pH 7.0
pCO2 32 mm Hg
HCO3- 15.2 mEq/L
Sodium 122 mEq/L
Potassium 4.8 mEq/L
Urinalysis is positive for ketone bodies. He is admitted to the hospital and given intravenous bicarbonate and then started on an insulin drip and normal saline. 7 hours later, he is found to be confused and complaining of a severe headache. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 50/min, respirations are 13/min and irregular, and blood pressure is 137/95 mm Hg. What other examination findings would be expected in this patient?
- A. Pancreatitis
- B. Pupillary constriction
- C. Hypoglycemia
- D. Peripheral edema
- E. Papilledema (Correct Answer)
Opportunistic fungal infections Explanation: ***Papilledema***
- The patient's presentation with **confusion**, **severe headache**, **bradycardia**, **irregular respirations**, and **elevated blood pressure** (Cushing's triad) 7 hours after treatment for **diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)** suggests increased intracranial pressure due to **cerebral edema**.
- **Papilledema** is a key ophthalmoscopic finding in significant cerebral edema, resulting from increased intracranial pressure transmitted to the optic nerve sheath.
*Pancreatitis*
- Pancreatitis can cause abdominal pain and may be associated with DKA, but the acute neurological deterioration with signs of increased intracranial pressure after initial treatment points away from pancreatitis as the primary expected finding at this stage.
- While initial mild colicky abdominal pain could suggest pancreatitis, the late-onset confusion, headache, and vital sign changes following DKA treatment are not characteristic of pancreatitis, but rather of a severe neurological complication.
*Pupillary constriction*
- **Pupillary constriction** (miosis) can be associated with opioid overdose, pontine lesions, or certain medications, but it is not a direct or expected finding in cerebral edema causing increased intracranial pressure.
- In cerebral edema, pupils are more likely to be dilated or unequal, especially if there is uncal herniation.
*Hypoglycemia*
- While **hypoglycemia** can occur with insulin therapy, leading to confusion and neurological symptoms, the patient's blood pressure is elevated and heart rate is low (bradycardia), which are not typical signs of hypoglycemia.
- Hypoglycemia usually presents with sympathetic activation (tachycardia, diaphoresis) before progressing to bradycardia in severe cases, but the associated hypertension and irregular breathing pattern are more indicative of increased intracranial pressure.
*Peripheral edema*
- **Peripheral edema** is swelling in the extremities and is generally due to fluid overload, heart failure, kidney disease, or liver disease.
- While fluid administration during DKA treatment could potentially lead to some fluid retention, it does not explain the acute neurological deterioration, headache, and vital sign changes (Cushing's triad) seen in this patient, which are far more characteristic of cerebral edema.
Opportunistic fungal infections US Medical PG Question 7: A 43-year-old HIV positive male presents with signs and symptoms concerning for a fungal infection. He is currently not on antiretrovirals and his CD4 count is 98. Which of the following candidal infections could be seen in this patient but would be very rare in an immunocompetent host?
- A. Endocarditis
- B. Intertrigo
- C. Oral thrush
- D. Esophagitis (Correct Answer)
- E. Vaginitis
Opportunistic fungal infections Explanation: ***Esophagitis***
- **Candidal esophagitis** is an **AIDS-defining illness** and is highly suggestive of severe immunosuppression, making it rare in immunocompetent individuals.
- The patient's **CD4 count of 98** indicates advanced HIV disease, placing him at high risk for opportunistic infections like candidal esophagitis.
*Endocarditis*
- While fungal endocarditis can occur in immunocompromised patients, it is more commonly associated with intravenous drug use, prosthetic valves, or central venous catheters, rather than solely with a low CD4 count.
- It is not considered an AIDS-defining illness in the same way as candidal esophagitis.
*Intertrigo*
- **Candidal intertrigo** is a common skin infection that can occur in both immunocompetent and immunocompromised individuals, usually in skin folds where moisture accumulates.
- Its presence does not strongly suggest severe immunosuppression, although it may be more persistent or widespread in HIV patients.
*Oral thrush*
- **Oral candidiasis** is common in HIV-positive patients, especially with lower CD4 counts, but it can also occur in immunocompetent individuals (e.g., due to antibiotic use, steroid inhalers, or diabetes).
- While indicative of some degree of immunosuppression in an HIV patient, it is not as specific for severe immunosuppression as candidal esophagitis.
*Vaginitis*
- **Candidal vaginitis** is a very common infection in women, regardless of immune status, and is not a strong indicator of severe immunosuppression or an AIDS-defining illness.
- Although it can be more frequent or resistant to treatment in HIV-positive women, its mere presence does not signify a condition rare in immunocompetent hosts.
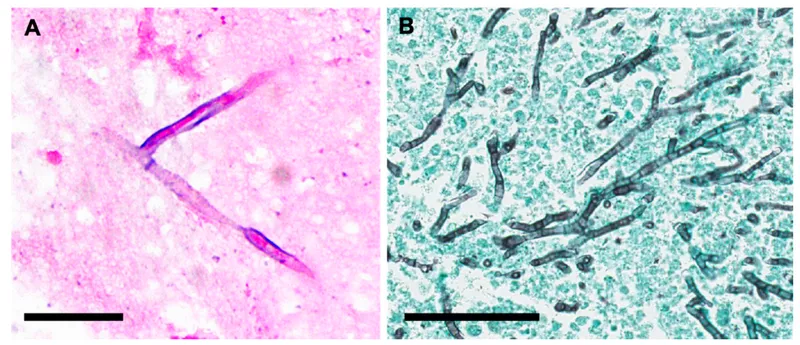
Opportunistic fungal infections US Medical PG Question 8: A 37-year-old man comes to the physician because of fever, night sweats, malaise, dyspnea, and a productive cough with bloody sputum for 4 days. He was diagnosed with HIV infection 15 years ago and has not been compliant with his medication regimen. Physical examination shows diminished breath sounds over the left lung fields. An x-ray of the chest shows an ill-defined lesion in the upper lobe of the left lung. A CT-guided biopsy of the lesion is performed; a photomicrograph of the biopsy specimen stained with mucicarmine is shown. Which of the following is the most likely causal organism?
- A. Histoplasma capsulatum
- B. Coccidioides immitis
- C. Blastomyces dermatitidis
- D. Candida albicans
- E. Cryptococcus neoformans (Correct Answer)
Opportunistic fungal infections Explanation: **Cryptococcus neoformans**
- A **mucicarmine stain** highlights the thick polysaccharide capsule of **Cryptococcus neoformans**, which is a key diagnostic feature for this organism.
- Patients with **HIV infection** who are non-compliant with medication are at high risk for opportunistic infections like **cryptococcosis**, presenting with pulmonary symptoms, night sweats, and ill-defined lung lesions.
*Histoplasma capsulatum*
- This fungus is common in the **Ohio and Mississippi River valleys**; it is diagnosed by demonstrating **small oval yeasts within macrophages** or by antigen detection, not specifically mucicarmine staining.
- While it can cause pulmonary disease in immunosuppressed individuals, its characteristic microscopic appearance and staining differ.
*Coccidioides immitis*
- This dimorphic fungus is endemic to the **Southwestern United States** and is identified by its characteristic **spherules containing endospores** in tissue.
- While it can cause lung lesions in HIV patients, it does not typically stain with mucicarmine.
*Blastomyces dermatitidis*
- This fungus is endemic to the **southeastern and south-central United States** and is characterized by **broad-based budding yeasts** with thick cell walls.
- Like other fungal pathogens, it can cause pulmonary disease, but its diagnostic microscopic features and staining properties differ from those described.
*Candida albicans*
- While a common opportunistic pathogen in HIV patients, **Candida albicans** primarily causes **mucocutaneous infections** (e.g., thrush, esophagitis).
- Although it can cause systemic disease, it does not typically form encapsulated structures that stain with mucicarmine and lung lesions are less common in this presentation.
Opportunistic fungal infections US Medical PG Question 9: A 31-year-old female undergoing treatment for leukemia is found to have a frontal lobe abscess accompanied by paranasal swelling. She additionally complains of headache, facial pain, and nasal discharge. Biopsy of the infected tissue would most likely reveal which of the following?
- A. Yeast with pseudohyphae
- B. Septate hyphae
- C. Irregular non-septate hyphae (Correct Answer)
- D. Spherules containing endospores
- E. Budding yeast with a narrow base
Opportunistic fungal infections Explanation: ***Irregular non-septate hyphae***
- The clinical presentation of a **leukemic patient** with a **frontal lobe abscess** and **paranasal swelling**, along with headache, facial pain, and nasal discharge, strongly suggests **mucormycosis**.
- Mucormycosis is characterized by **broad, ribbon-like, irregular non-septate hyphae** with **right-angle branching** on tissue biopsy, making this the most likely finding.
*Yeast with pseudohyphae*
- This morphology is characteristic of **Candida species**, which can cause opportunistic infections but typically manifest as candidemia, esophagitis, or vulvovaginitis in immunocompromised patients, not usually a frontal lobe abscess with paranasal involvement.
- While Candida can cause severe systemic infections, the specific combination of a frontal lobe abscess and paranasal swelling points away from Candida as the primary cause in this context.
*Septate hyphae*
- **Septate hyphae** are typical of **Aspergillus species**, which can cause invasive aspergillosis, including sinopulmonary infections and CNS involvement in immunocompromised hosts.
- However, Aspergillus hyphae are typically **narrow (3-6 µm)** with **acute-angle (45-degree) branching**, differentiating them from the broad, irregular hyphae seen in mucormycosis.
*Spherules containing endospores*
- This morphology is characteristic of **Coccidioides immitis**, the causative agent of coccidioidomycosis.
- Coccidioidomycosis is geographically restricted to endemic areas (e.g., southwestern US) and typically presents with pulmonary symptoms, disseminated disease, or meningitis, which does not fit the described paranasal and frontal lobe presentation.
*Budding yeast with a narrow base*
- This morphology is characteristic of **Cryptococcus neoformans**, an encapsulated yeast that commonly causes **meningitis** and **pneumonia** in immunocompromised individuals.
- While Cryptococcus can cause CNS infections, the presence of paranasal swelling and the specific description of a frontal lobe abscess make mucormycosis a more fitting diagnosis.
Opportunistic fungal infections US Medical PG Question 10: A 40-year-old farmer from Ohio seeks evaluation at a clinic with complaints of a chronic cough, fevers, and anorexia of several months duration. On examination, he has generalized lymphadenopathy with hepatosplenomegaly. A chest radiograph reveals local infiltrates and patchy opacities involving all lung fields. Fine needle aspiration of an enlarged lymph node shows the presence of intracellular yeast. A fungal culture shows the presence of smooth, thin-walled microconidia and tuberculate macroconidia. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Coccidioidomycosis
- B. Blastomycosis
- C. Cryptococcosis
- D. Histoplasmosis (Correct Answer)
- E. Sporotrichosis
Opportunistic fungal infections Explanation: ***Histoplasmosis***
- **Histoplasmosis** is characterized by the presence of **intracellular yeast** in tissue samples and **tuberculate macroconidia** in fungal cultures, which are key diagnostic findings in this case.
- The patient's presentation with chronic cough, fevers, anorexia, generalized lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and lung infiltrates, along with geographic exposure in **Ohio** (part of the Ohio River Valley endemic area), is highly consistent with disseminated histoplasmosis.
*Coccidioidomycosis*
- While coccidioidomycosis can cause lung infiltrates, it is typically endemic to the **southwestern United States** and Mexico, not Ohio.
- Microscopic examination would reveal **spherules** containing endospores, not intracellular yeast with tuberculate macroconidia.
*Blastomycosis*
- Blastomycosis is also endemic to the Ohio River Valley, but it is characterized by **broad-based budding yeast** in tissue, and its cultures typically do not show tuberculate macroconidia.
- While it causes pulmonary and disseminated disease, the specific microscopic and culture findings differentiate it from histoplasmosis.
*Cryptococcosis*
- Cryptococcosis primarily affects immunocompromised individuals and is characterized by encapsulated yeast, which would be visible with India ink stain.
- It typically presents as **meningitis** or pneumonia, and its culture morphology does not include tuberculate macroconidia.
*Sporotrichosis*
- Sporotrichosis is commonly associated with **cutaneous lesions** following traumatic inoculation of spores from soil or vegetation, and it rarely causes disseminated disease with extensive systemic symptoms like those described.
- The yeast forms in tissue are typically smaller and cigar-shaped, and the culture morphology differs significantly from what is described.
More Opportunistic fungal infections US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.