Candida species US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Candida species. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
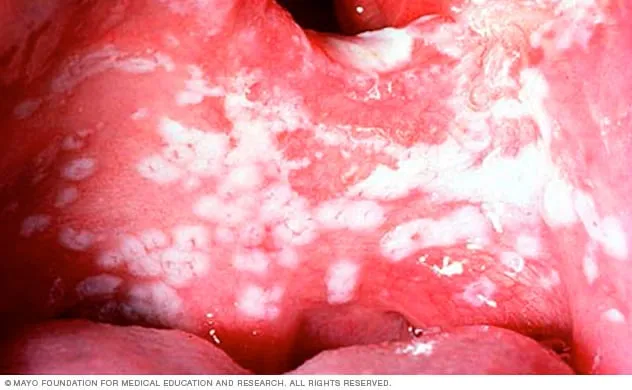
Candida species US Medical PG Question 1: A 28-year-old homeless male with a past medical history significant for asthma comes to your clinic complaining of a chronic rash on his scalp and feet. He describes the rash as “dry and flaky,” and reports it has been present for at least a year. He was using a new dandruff shampoo he got over the counter, with little improvement. The patient reports it is extremely itchy at night, to the point that he can't sleep. On exam, you note a scaly patch of alopecia, enlarged lymph glands along the posterior aspect of his neck, and fine scaling in between his toes and on the heel and sides of his foot. His temperature is 99°F (37°C), blood pressure is 118/78 mmHg, and pulse is 81/min. Which of the following is the most accurate test for the suspected diagnosis?
- A. KOH preparation of scalp scraping (Correct Answer)
- B. Wood's lamp
- C. Skin biopsy with histopathological examination
- D. CBC and total serum IgE
- E. Culture on Sabouraud dextrose agar
Candida species Explanation: ***KOH preparation of scalp scraping***
- The patient's presentation with **chronic, itchy, scaly scalp rash** (alopecia and enlarged lymph glands) and **fungal-like rash on feet** (scaling between toes, heel, and sides) strongly suggests a dermatophyte infection (**tinea capitis** and **tinea pedis**).
- A **KOH preparation** allows for direct visualization of **fungal hyphae and spores**, confirming the presence of a fungal infection quickly and accurately.
- This is the **most accurate rapid diagnostic test** for dermatophyte infections.
*Wood's lamp*
- A Wood's lamp is useful for certain types of **tinea capitis** (e.g., those caused by *Microsporum* species) that **fluoresce**, but it is not accurate for all dermatophyte infections (e.g., *Trichophyton* species do not fluoresce).
- It is a screening tool but **not a definitive diagnostic test** for all fungal infections, as it doesn't confirm the presence of fungi directly.
*Skin biopsy with histopathological examination*
- While a **skin biopsy** can identify fungal elements on histopathology (especially with PAS stain), it is **invasive, expensive, and unnecessary** for a straightforward clinical presentation of dermatophyte infection.
- Biopsy is typically reserved for cases where the diagnosis is unclear or when malignancy or other inflammatory conditions need to be ruled out.
*CBC and total serum IgE*
- A **CBC (complete blood count)** and **total serum IgE** would be helpful in diagnosing allergic conditions or parasitic infections, but are not direct diagnostic tools for fungal infections.
- While asthma (an allergic condition) is in the patient's history, the rash description is more consistent with a **fungal etiology** rather than an allergic one alone.
*Culture on Sabouraud dextrose agar*
- **Fungal culture** on Sabouraud dextrose agar is a confirmatory test that identifies the specific species of dermatophyte and can guide treatment if initial therapies fail.
- However, it takes **2-4 weeks** for results, making it less practical for initial diagnosis compared to a **KOH preparation**, which provides rapid results within minutes.
Candida species US Medical PG Question 2: An investigator is studying growth patterns of various fungal pathogens. Incubation of an isolated fungus at 25°C shows branching hyphae with rosettes of conidia under light microscopy. After incubation at 37°C, microscopic examination of the same organism instead shows smooth, white colonies with rounded, elongated cells. Infection with the investigated pathogen is most likely to cause which of the following conditions?
- A. Pityriasis versicolor
- B. Candidiasis
- C. Cryptococcosis
- D. Sporotrichosis (Correct Answer)
- E. Coccidioidomycosis
Candida species Explanation: ***Sporotrichosis***
- The description of a fungal pathogen exhibiting **thermal dimorphism** (different forms at 25°C and 37°C) is characteristic of **Sporothrix schenckii**.
- At 25°C, it typically grows as **mold with branching hyphae and conidia in rosettes**, and at 37°C, it grows as **yeast-like cells (cigar-shaped bodies in tissue)**, which can appear rounded and elongated.
*Pityriasis versicolor*
- Caused by **Malassezia globosa**, which is a **lipophilic yeast** and does not exhibit thermal dimorphism described here.
- Characterized by **hypo- or hyperpigmented skin patches**, not deep tissue infection with dimorphic growth.
*Candidiasis*
- Caused by **Candida species**, which are **opportunistic yeasts** that can form pseudohyphae and true hyphae but do not display the specific dimorphism with rosettes of conidia at 25°C.
- Infections range from superficial mucocutaneous to systemic, but the fungal morphology described does not fit.
*Cryptococcosis*
- Caused by **Cryptococcus neoformans** or **Cryptococcus gattii**, which are **encapsulated yeasts** and do not exhibit dimorphism (mold at 25°C, yeast at 37°C).
- Primarily causes **meningoencephalitis** or pulmonary disease, and is identified by its capsule and yeast form.
*Coccidioidomycosis*
- Caused by **Coccidioides immitis** or **Coccidioides posadasii**, which are **thermally dimorphic fungi**, but their morphology differs from the description.
- At 25°C, they grow as molds with **arthroconidia**, and at 37°C, they form **spherules containing endospores** in tissue, not smooth, white colonies with rounded, elongated cells.
Candida species US Medical PG Question 3: An 11-year-old boy with HIV and esophageal candidiasis is being treated with caspofungin. What is the mechanism of action of this drug?
- A. Pore formation in cell membranes
- B. Inhibition of ergosterol synthesis
- C. Inhibition of 1,3-Beta-glucan synthase (Correct Answer)
- D. Inhibition of squalene epoxidase
- E. Inhibition of pyrimidine synthesis
Candida species Explanation: ***Inhibition of 1,3-Beta-glucan synthase***
- **Caspofungin** is an **echinocandin** antifungal agent that works by inhibiting **1,3-beta-D-glucan synthase**.
- This enzyme is crucial for the synthesis of **glucan**, a vital component of the **fungal cell wall**, leading to cell wall disruption and fungal cell death.
*Pore formation in cell membranes*
- This mechanism of action is characteristic of **polyene antifungals** like **amphotericin B**.
- These drugs bind to **ergosterol** in the fungal cell membrane, forming pores that lead to leakage of cellular contents.
*Inhibition of ergosterol synthesis*
- This is the mechanism of action for **azole antifungals** (e.g., fluconazole, itraconazole) and **allylamines** (e.g., terbinafine).
- Azoles inhibit **14-alpha-demethylase**, an enzyme involved in converting lanosterol to ergosterol, while allylamines inhibit **squalene epoxidase**.
*Inhibition of squalene epoxidase*
- This is the specific mechanism for **allylamine antifungals** like **terbinafine**.
- Inhibition of **squalene epoxidase** prevents the synthesis of **ergosterol**, primarily used for superficial fungal infections.
*Inhibition of pyrimidine synthesis*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **flucytosine**, an antifungal pro-drug.
- Flucytosine is converted to **5-fluorouracil** within fungal cells, which then inhibits fungal DNA and RNA synthesis.
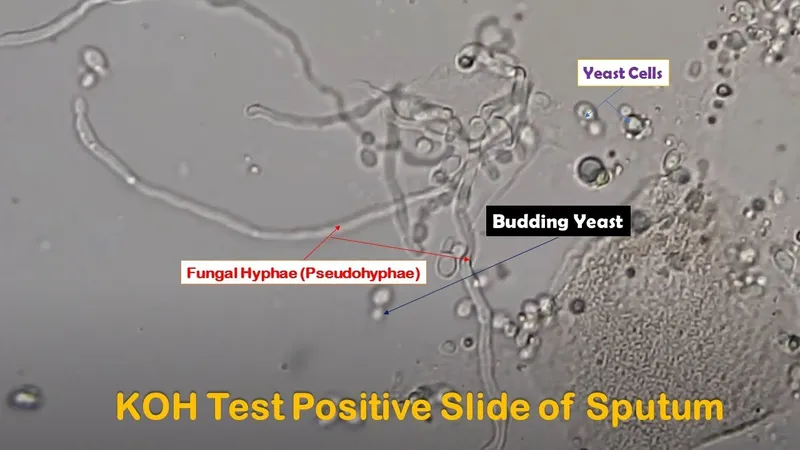
Candida species US Medical PG Question 4: A 32-year-old woman presents with three-days of vaginal burning, itching, and pain with intercourse. She is in a monogamous relationship with her husband and has an intrauterine device for contraception. Her past medical history is unremarkable, except for recently being treated with antibiotics for sinusitis. Pelvic exam is remarkable for vulvar excoriations, vaginal wall edema, and thick, white discharge in the vault. Wet mount with KOH staining reveals budding filaments with pseudohyphae and hyphae. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment?
- A. Voriconazole
- B. Posaconazole
- C. Metronidazole
- D. Itraconazole
- E. Fluconazole (Correct Answer)
Candida species Explanation: ***Fluconazole***
- The patient's symptoms (vaginal burning, itching, pain with intercourse, thick, white discharge) and **wet mount findings (budding filaments with pseudohyphae and hyphae)** are classic for **vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC)**, often precipitated by recent antibiotic use.
- **Fluconazole** is a highly effective and commonly prescribed oral antifungal for uncomplicated VVC due to its convenience and excellent therapeutic profile.
*Voriconazole*
- **Voriconazole** is a broad-spectrum triazole antifungal primarily used for invasive fungal infections, such as **invasive aspergillosis** and candidemia, and is not a first-line treatment for uncomplicated VVC.
- Its use is typically reserved for more severe or refractory systemic fungal infections, and it has a more significant side effect profile than fluconazole.
*Posaconazole*
- **Posaconazole** is another extended-spectrum triazole antifungal primarily used for the prophylaxis and treatment of **invasive fungal infections** in immunocompromised patients, particularly those unresponsive to other antifungals.
- It is not indicated for the treatment of uncomplicated vulvovaginal candidiasis.
*Metronidazole*
- **Metronidazole** is an antibiotic and antiprotozoal agent used to treat bacterial vaginosis and trichomoniasis, both of which are common causes of vaginitis.
- It is **ineffective against fungal infections**, and the patient's symptoms and wet mount findings rule out bacterial vaginosis and trichomoniasis.
*Itraconazole*
- **Itraconazole** is an antifungal drug effective against superficial and systemic fungal infections, but it is typically used for more severe or recurrent VVC, or in cases of non-albicans Candida species.
- While effective, **fluconazole** is generally preferred as the first-line oral treatment for uncomplicated VVC due to its single-dose efficacy and established safety profile for this indication.
Candida species US Medical PG Question 5: A 72-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus comes to the physician because she is concerned about the appearance of her toenails. Examination shows yellowish discoloration of all toenails on both feet. The edges of the toenails are lifted, and there is subungual debris. Potassium hydroxide preparation of scrapings from the nails shows multiple branching septate hyphae. Treatment with oral terbinafine is begun. Which of the following is the primary mechanism of action of this drug?
- A. Inhibition of squalene epoxidase (Correct Answer)
- B. Formation of pores in cell membrane
- C. Inhibition of β-glucan synthesis
- D. Interference with mitosis during metaphase
- E. Prevention of lanosterol to ergosterol conversion
Candida species Explanation: ***Inhibition of squalene epoxidase***
- **Terbinafine** is an **allylamine** antifungal that inhibits the enzyme **squalene epoxidase**, an early step in fungal ergosterol synthesis
- This inhibition leads to the accumulation of **squalene**, which is toxic to the fungal cell, and a deficiency of **ergosterol**, disrupting cell membrane integrity and function
- Terbinafine is highly effective for **onychomycosis** (fungal nail infections) caused by dermatophytes
*Formation of pores in cell membrane*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **polyene antifungals** like **amphotericin B** and **nystatin**
- These drugs bind to **ergosterol** in the fungal cell membrane, creating pores that lead to leakage of intracellular contents and cell death
*Inhibition of β-glucan synthesis*
- This is the primary mechanism of action for **echinocandin** antifungals, such as **caspofungin**, **micafungin**, and **anidulafungin**
- These drugs inhibit **(1,3)-β-D-glucan synthase**, which is essential for the synthesis of glucan, a major component of the fungal cell wall
*Interference with mitosis during metaphase*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **griseofulvin**, another antifungal agent used for dermatophyte infections
- **Griseofulvin** interferes with **microtubule function**, disrupting mitotic spindle formation and preventing fungal cell division
*Prevention of lanosterol to ergosterol conversion*
- This mechanism is associated with **azole antifungals** (e.g., fluconazole, itraconazole), which inhibit fungal **cytochrome P450-dependent 14-α-demethylase**
- This enzyme is responsible for the conversion of **lanosterol** to **ergosterol**, leading to ergosterol depletion and accumulation of toxic sterol precursors
Candida species US Medical PG Question 6: A 27-year-old female presents to her primary care physician because she is concerned about lighter colored patches on her skin. She recently went sunbathing and noticed that these areas also did not tan. Her doctor explains that she has a fungal infection of the skin that damages melanocytes by producing acids. She is prescribed selenium sulfide and told to follow-up in one month. Which of the following describes the appearance of the most likely infectious organism under microscopy?
- A. Broad based budding yeast
- B. "Captain's wheel" yeast
- C. Germ tube forming fungus
- D. Branching septate hyphae
- E. "Spaghetti and meatballs" fungus (Correct Answer)
Candida species Explanation: ***"Spaghetti and meatballs" fungus***
- The "spaghetti and meatballs" appearance on microscopy, referring to a mixture of short, septate hyphae and spherical yeast forms, is characteristic of **Malassezia globosa** or other *Malassezia* species, which cause **tinea versicolor**.
- **Tinea versicolor** presents as hypopigmented patches, especially after sun exposure, because the fungus produces **azelaic acid** that inhibits melanin synthesis.
*Broad based budding yeast*
- This description is characteristic of **Blastomyces dermatitidis**, which causes **blastomycosis**, a deep fungal infection.
- Blastomycosis typically manifests as pulmonary disease or disseminated lesions, not superficial hypopigmented skin patches.
*"Captain's wheel" yeast*
- The "captain's wheel" or multi-budding yeast appearance is characteristic of **Paracoccidioides brasiliensis**, the causative agent of **paracoccidioidomycosis**.
- This is a systemic mycosis primarily affecting the lungs and mucocutaneous areas, not a superficial skin infection like tinea versicolor.
*Germ tube forming fungus*
- The formation of **germ tubes** when incubated in serum at 37°C is a characteristic feature used to identify **Candida albicans**.
- *Candida* most commonly causes mucocutaneous candidiasis (e.g., thrush, vaginitis) or invasive infections, not hypopigmented skin patches that fail to tan.
*Branching septate hyphae*
- **Branching septate hyphae** are a general microscopic feature seen in many filamentous fungi, including dermatophytes like *Trichophyton* and *Microsporum*, which cause **tinea corporis** or **tinea pedis**.
- While dermatophytes cause skin infections, they typically result in erythematous, scaly, and often pruritic lesions and do not usually present as hypopigmented patches that fail to tan due to melanin inhibition, as seen in tinea versicolor.
Candida species US Medical PG Question 7: A 43-year-old HIV positive male presents with signs and symptoms concerning for a fungal infection. He is currently not on antiretrovirals and his CD4 count is 98. Which of the following candidal infections could be seen in this patient but would be very rare in an immunocompetent host?
- A. Endocarditis
- B. Intertrigo
- C. Oral thrush
- D. Esophagitis (Correct Answer)
- E. Vaginitis
Candida species Explanation: ***Esophagitis***
- **Candidal esophagitis** is an **AIDS-defining illness** and is highly suggestive of severe immunosuppression, making it rare in immunocompetent individuals.
- The patient's **CD4 count of 98** indicates advanced HIV disease, placing him at high risk for opportunistic infections like candidal esophagitis.
*Endocarditis*
- While fungal endocarditis can occur in immunocompromised patients, it is more commonly associated with intravenous drug use, prosthetic valves, or central venous catheters, rather than solely with a low CD4 count.
- It is not considered an AIDS-defining illness in the same way as candidal esophagitis.
*Intertrigo*
- **Candidal intertrigo** is a common skin infection that can occur in both immunocompetent and immunocompromised individuals, usually in skin folds where moisture accumulates.
- Its presence does not strongly suggest severe immunosuppression, although it may be more persistent or widespread in HIV patients.
*Oral thrush*
- **Oral candidiasis** is common in HIV-positive patients, especially with lower CD4 counts, but it can also occur in immunocompetent individuals (e.g., due to antibiotic use, steroid inhalers, or diabetes).
- While indicative of some degree of immunosuppression in an HIV patient, it is not as specific for severe immunosuppression as candidal esophagitis.
*Vaginitis*
- **Candidal vaginitis** is a very common infection in women, regardless of immune status, and is not a strong indicator of severe immunosuppression or an AIDS-defining illness.
- Although it can be more frequent or resistant to treatment in HIV-positive women, its mere presence does not signify a condition rare in immunocompetent hosts.
Candida species US Medical PG Question 8: A 4-month-old boy is brought to the physician by his father because of a progressively worsening rash on his buttocks for the last week. He cries during diaper changes and is more fussy than usual. Physical examination of the boy shows erythematous papules and plaques in the bilateral inguinal creases, on the scrotum, and in the gluteal cleft. Small areas of maceration are also present. A diagnosis is made, and treatment with topical clotrimazole is initiated. Microscopic examination of skin scrapings from this patient's rash is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Round yeast surrounded by budding yeast cells
- B. Oval, budding yeast with pseudohyphae (Correct Answer)
- C. Broad-based budding yeast
- D. Fruiting bodies with septate, acute-angle hyphae
- E. Narrow budding, encapsulated yeast
Candida species Explanation: ***Oval, budding yeast with pseudohyphae***
- This morphology is characteristic of *Candida albicans*, which commonly causes **diaper rash** due to the warm, moist environment in the diaper area.
- The rash described, with **erythematous papules and plaques** in the inguinal creases, scrotum, and gluteal cleft, along with **maceration**, is typical of candidal diaper dermatitis.
*Round yeast surrounded by budding yeast cells*
- This description ("wagon wheel" appearance) is characteristic of *Malasseella globosa*, the causative agent of **tinea versicolor**.
- Tinea versicolor typically presents with hypo- or hyperpigmented patches, not the erythematous, macerated rash seen in this infant.
*Broad-based budding yeast*
- This morphology is characteristic of **Blastomycosis**, caused by *Blastomyces dermatitidis*.
- This infection typically causes **pulmonary disease** or **cutaneous lesions** that are often verrucous or ulcerative, not a diaper rash.
*Fruiting bodies with septate, acute-angle hyphae*
- This describes the microscopic appearance of *Aspergillus* species.
- *Aspergillus* typically causes **invasive pulmonary disease** in immunocompromised individuals or **allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis**, not diaper dermatitis.
*Narrow budding, encapsulated yeast*
- This is the characteristic microscopic appearance of *Cryptococcus neoformans*.
- *Cryptococcus* commonly causes **meningitis** or **pulmonary infections**, particularly in immunocompromised patients, and is not associated with diaper rash.
Candida species US Medical PG Question 9: A 31-year-old female undergoing treatment for leukemia is found to have a frontal lobe abscess accompanied by paranasal swelling. She additionally complains of headache, facial pain, and nasal discharge. Biopsy of the infected tissue would most likely reveal which of the following?
- A. Yeast with pseudohyphae
- B. Septate hyphae
- C. Irregular non-septate hyphae (Correct Answer)
- D. Spherules containing endospores
- E. Budding yeast with a narrow base
Candida species Explanation: ***Irregular non-septate hyphae***
- The clinical presentation of a **leukemic patient** with a **frontal lobe abscess** and **paranasal swelling**, along with headache, facial pain, and nasal discharge, strongly suggests **mucormycosis**.
- Mucormycosis is characterized by **broad, ribbon-like, irregular non-septate hyphae** with **right-angle branching** on tissue biopsy, making this the most likely finding.
*Yeast with pseudohyphae*
- This morphology is characteristic of **Candida species**, which can cause opportunistic infections but typically manifest as candidemia, esophagitis, or vulvovaginitis in immunocompromised patients, not usually a frontal lobe abscess with paranasal involvement.
- While Candida can cause severe systemic infections, the specific combination of a frontal lobe abscess and paranasal swelling points away from Candida as the primary cause in this context.
*Septate hyphae*
- **Septate hyphae** are typical of **Aspergillus species**, which can cause invasive aspergillosis, including sinopulmonary infections and CNS involvement in immunocompromised hosts.
- However, Aspergillus hyphae are typically **narrow (3-6 µm)** with **acute-angle (45-degree) branching**, differentiating them from the broad, irregular hyphae seen in mucormycosis.
*Spherules containing endospores*
- This morphology is characteristic of **Coccidioides immitis**, the causative agent of coccidioidomycosis.
- Coccidioidomycosis is geographically restricted to endemic areas (e.g., southwestern US) and typically presents with pulmonary symptoms, disseminated disease, or meningitis, which does not fit the described paranasal and frontal lobe presentation.
*Budding yeast with a narrow base*
- This morphology is characteristic of **Cryptococcus neoformans**, an encapsulated yeast that commonly causes **meningitis** and **pneumonia** in immunocompromised individuals.
- While Cryptococcus can cause CNS infections, the presence of paranasal swelling and the specific description of a frontal lobe abscess make mucormycosis a more fitting diagnosis.
Candida species US Medical PG Question 10: A 28-year-old woman with a past history of type 1 diabetes presents to your office with a 2-week history of vaginal itching and soreness accompanied by a white, clumpy vaginal discharge which she says resembles cheese curds. Her last HbA1c from a month ago was 7.8%, and her last cervical cytology from 10 months ago was reported as normal. She has a blood pressure of 118/76 mmHg, respiratory rate of 14/min, and heart rate of 74/min. Pelvic examination reveals multiple small erythematous lesions in the inguinal and perineal area, vulvar erythema, and excoriations. Inspection demonstrates a normal cervix and a white, adherent, thick, non-malodorous vaginal discharge. Which of the following is most likely to be present in a saline wet mount from the vaginal discharge of this patient?
- A. Clue cells on saline smear
- B. Gram-negative diplococci
- C. Hyphae (Correct Answer)
- D. Motile flagellates
- E. Multinucleated giant cells
Candida species Explanation: ***Hyphae***
- The patient's symptoms of **vaginal itching**, soreness, and a **white, clumpy discharge resembling cheese curds** are classic for **vulvovaginal candidiasis** (yeast infection).
- A **saline wet mount** in such cases typically reveals **hyphae** and **budding yeast forms** of *Candida albicans*.
*Clue cells on saline smear*
- **Clue cells** are characteristic of **bacterial vaginosis**, which is typically associated with a **thin, grayish discharge** and a **fishy odor** (amine odor), neither of which are described here.
- The discharge in this patient is described as **thick and non-malodorous**, which is inconsistent with bacterial vaginosis.
*Gram-negative diplococci*
- **Gram-negative diplococci** are the hallmark of **gonorrhea**, caused by *Neisseria gonorrhoeae*.
- Gonorrhea often presents with **purulent discharge** and cervical inflammation, or it can be asymptomatic; it does not typically cause the **clumpy discharge** and intense itching seen in this patient.
*Motile flagellates*
- **Motile flagellates** are characteristic of **trichomoniasis**, caused by *Trichomonas vaginalis*.
- This infection usually presents with a **frothy, yellow-green discharge**, a **fishy odor**, and cervical petechiae (strawberry cervix), which are not a feature of this patient's presentation.
*Multinucleated giant cells*
- **Multinucleated giant cells** are indicative of **herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection**, particularly when found on a **Tzanck smear** of a lesion.
- While the patient has erythematous lesions, the primary complaint of **vaginal discharge** and itching points away from herpes as the main cause of the discharge.
More Candida species US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.