Antifungal agents US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Antifungal agents. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
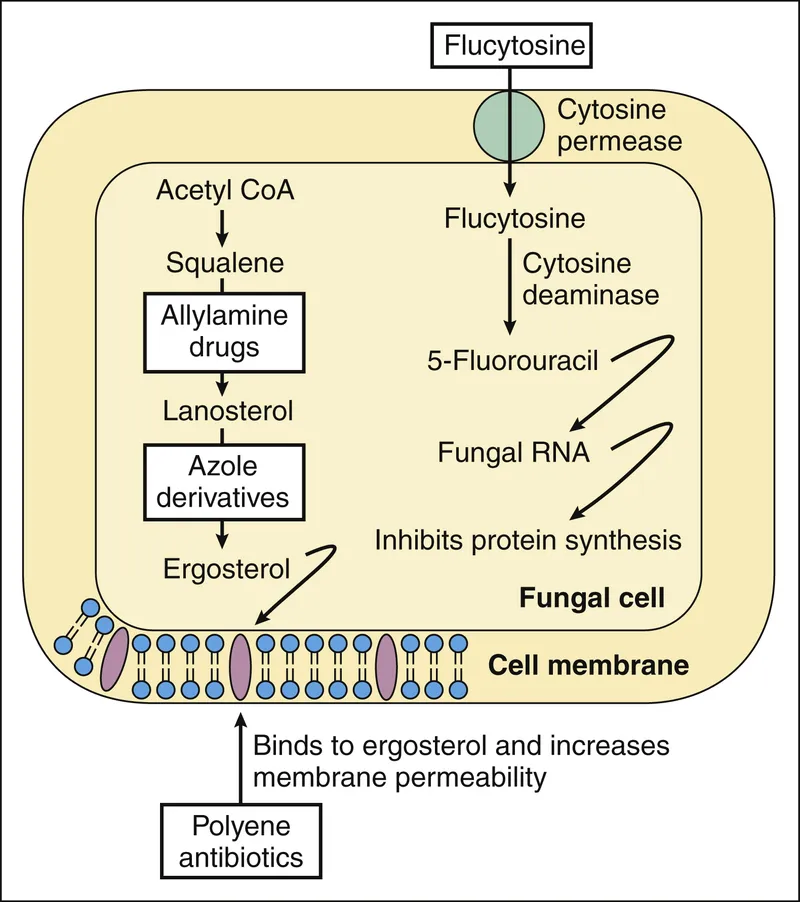
Antifungal agents US Medical PG Question 1: You are taking care of a patient with renal failure secondary to anti-fungal therapy. The patient is a 66-year-old male being treated for cryptococcal meningitis. This drug has a variety of known side effects including acute febrile reactions to infusions, anemia, hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia. What is the mechanism of action of this drug?
- A. Inhibition of squalene epoxidase
- B. Binding of the 50S subunit
- C. Pore formation secondary to ergosterol binding (Correct Answer)
- D. Disruption of microtubule formation
- E. Inhibition of 1,3-beta-glucan synthase
Antifungal agents Explanation: ***Pore formation secondary to ergosterol binding***
- This describes the mechanism of action of **amphotericin B**, the antifungal agent used for cryptococcal meningitis.
- Amphotericin B binds to **ergosterol** in the fungal cell membrane, leading to the formation of pores, disruption of membrane integrity, and ultimately cell death.
- The side effects described—**nephrotoxicity with renal failure, hypokalemia, and hypomagnesemia**—are classic adverse effects of amphotericin B due to its effect on renal tubular cells and electrolyte wasting.
*Inhibition of squalene epoxidase*
- This is the mechanism of action for **terbinafine**, an antifungal primarily used for dermatophyte infections (e.g., onychomycosis), not systemic infections like cryptococcal meningitis.
- Terbinafine inhibits ergosterol synthesis at an earlier step but does not cause the severe nephrotoxicity and electrolyte disturbances described.
*Binding of the 50S subunit*
- This mechanism of action is characteristic of **macrolide antibiotics** like azithromycin or clarithromycin, which are antibacterial agents, not antifungals.
- These drugs inhibit bacterial protein synthesis and are ineffective against fungal infections.
*Disruption of microtubule formation*
- This is the mechanism of action for **griseofulvin**, an antifungal drug used for dermatophyte infections of the skin, hair, and nails.
- Griseofulvin interferes with fungal cell division and is not used for life-threatening systemic infections like cryptococcal meningitis.
*Inhibition of 1,3-beta-glucan synthase*
- This mechanism is associated with **echinocandins** (e.g., caspofungin, micafungin), which inhibit fungal cell wall synthesis.
- While echinocandins are used for some systemic fungal infections (particularly Candida and Aspergillus), they do not typically cause the severe renal failure and electrolyte disturbances characteristic of amphotericin B.
Antifungal agents US Medical PG Question 2: A 45-year-old HIV-positive male presents to his primary care physician complaining of decreased libido. He reports that he has been unable to maintain an erection for the past two weeks. He has never encountered this problem before. He was hospitalized four weeks ago for cryptococcal meningitis and has been on long-term antifungal therapy since then. His CD4 count is 400 cells/mm^3 and viral load is 5,000 copies/ml. He was previously non-compliant with HAART but since his recent infection, he has been more consistent with its use. His past medical history is also notable for hypertension, major depressive disorder, and alcohol abuse. He takes lisinopril and sertraline. His temperature is 98.6°F (37°C), blood pressure is 120/85 mmHg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 18/min. The physician advises the patient that side effects like decreased libido may manifest due to a drug with which of the following mechanisms of action?
- A. Inhibition of beta-glucan synthesis
- B. Formation of pores in cell membrane
- C. Inhibition of ergosterol synthesis (Correct Answer)
- D. Disruption of microtubule formation
- E. Inhibition of pyrimidine synthesis
Antifungal agents Explanation: ***Inhibition of ergosterol synthesis***
- The patient was recently treated for **cryptococcal meningitis** and is likely on an **azole antifungal**, such as fluconazole or itraconazole, for long-term therapy.
- Azole antifungals inhibit **14-alpha-demethylase**, an enzyme crucial for **ergosterol synthesis**, and are known to cause endocrine side effects like **decreased libido** and **erectile dysfunction** due to their impact on steroid hormone synthesis.
*Inhibition of beta-glucan synthesis*
- This mechanism of action belongs to **echinocandins** (e.g., caspofungin, micafungin), which inhibit the synthesis of **1,3-beta-D-glucan**, a key component of the fungal cell wall.
- Echinocandins are typically used for *Candida* infections and are generally not associated with significant endocrine side effects like decreased libido or erectile dysfunction.
*Formation of pores in cell membrane*
- This is the mechanism of action for **polyene antifungals** like **amphotericin B** and **nystatin**, which bind to ergosterol in the fungal cell membrane, creating pores and leading to cell lysis.
- While effective against *Cryptococcus*, amphotericin B is primarily used for acute, severe infections due to its significant toxicity, including nephrotoxicity, and is not typically used for long-term maintenance in this context with libido as the main symptom.
*Disruption of microtubule formation*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **griseofulvin**, an antifungal primarily used for dermatophyte infections of the skin and nails.
- It interferes with **microtubule function** and inhibits fungal mitosis, but it is not used for systemic fungal infections like cryptococcal meningitis, nor is it commonly associated with decreased libido.
*Inhibition of pyrimidine synthesis*
- This mechanism belongs to **flucytosine**, which is converted to **5-fluorouracil** within fungal cells, inhibiting DNA and RNA synthesis.
- Flucytosine is typically used in combination with amphotericin B for severe cryptococcal infections, but it is not known to cause decreased libido as a common or prominent side effect.
Antifungal agents US Medical PG Question 3: A 74-year-old man is admitted to the medical ward after he developed a fungal infection. He has aplastic anemia. The most recent absolute neutrophil count was 450/µL. An anti-fungal agent is administered that inhibits the fungal enzyme, (1→3)-β-D-glucan synthase, and thereby disrupts the integrity of the fungal cell wall. He responds well to the treatment. Although amphotericin B is more efficacious for his condition, it was not used because of the side effect profile. What was the most likely infection?
- A. Invasive aspergillosis
- B. Mucormycosis
- C. Histoplasmosis
- D. Paracoccidioidomycosis
- E. Candidemia (Correct Answer)
Antifungal agents Explanation: ***Candidemia***
- The patient's **neutropenia** (absolute neutrophil count of 450/µL) due to aplastic anemia is a major risk factor for invasive candidiasis, including candidemia.
- The antifungal agent's mechanism of action, targeting **(1→3)-β-D-glucan synthase**, is characteristic of **echinocandins**, which are first-line agents for candidemia, especially in critically ill or neutropenic patients, and often preferred over amphotericin B due to a better side effect profile.
*Invasive aspergillosis*
- While neutropenia is a significant risk factor for invasive aspergillosis, the primary antifungal drugs for this condition are typically **voriconazole** or **isavuconazole**, although echinocandins may be used as salvage therapy or in combination.
- The description of the drug's mechanism specifically targeting **(1→3)-β-D-glucan synthase** does not make aspergillosis the *most likely* infection, as some Aspergillus species may have less β-D-glucan in their cell walls compared to *Candida*.
*Mucormycosis*
- This aggressive fungal infection is often seen in immunocompromised patients, particularly those with **diabetes** or profound neutropenia, but the primary treatment is usually **amphotericin B**.
- Mucorales fungi typically **lack ergosterol** and their cell walls do not contain **(1→3)-β-D-glucan**, making echinocandins ineffective.
*Histoplasmosis*
- This is a dimorphic fungal infection endemic to certain geographic regions, primarily affecting the lungs and disseminating in immunocompromised individuals.
- The drug of choice for severe or disseminated histoplasmosis is **amphotericin B**, followed by azoles; echinocandins are generally not active against *Histoplasma*.
*Paracoccidioidomycosis*
- This is a chronic systemic mycosis found in Latin America, primarily affecting the lungs, skin, and lymph nodes.
- Treatment for severe forms typically involves **amphotericin B**, followed by sulfonamides or azoles for maintenance; echinocandins are not effective against *Paracoccidioides*.
Antifungal agents US Medical PG Question 4: You are treating a neonate with meningitis using ampicillin and a second antibiotic, X, that is known to cause ototoxicity. What is the mechanism of antibiotic X?
- A. It binds the 50S ribosomal subunit and inhibits formation of the initiation complex
- B. It binds the 30S ribosomal subunit and inhibits formation of the initiation complex (Correct Answer)
- C. It binds the 30S ribosomal subunit and reversibly inhibits translocation
- D. It binds the 50S ribosomal subunit and inhibits peptidyltransferase
- E. It binds the 50S ribosomal subunit and reversibly inhibits translocation
Antifungal agents Explanation: ***It binds the 30s ribosomal subunit and inhibits formation of the initiation complex***
- The second antibiotic, X, is likely an **aminoglycoside**, such as **gentamicin** or **amikacin**, which are commonly used in combination with ampicillin for neonatal meningitis and are known to cause ototoxicity.
- Aminoglycosides exert their bactericidal effect by **irreversibly binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit**, thereby **inhibiting the formation of the initiation complex** and leading to misreading of mRNA.
*It binds the 50S ribosomal subunit and inhibits formation of the initiation complex*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **linezolid**, which targets the 50S ribosomal subunit to prevent the formation of the initiation complex.
- While linezolid can cause side effects, **ototoxicity** is less commonly associated with it compared to aminoglycosides, and it is not a primary drug for neonatal meningitis alongside ampicillin.
*It binds the 50S ribosomal subunit and inhibits peptidyltransferase*
- This is the mechanism of action for **chloramphenicol**, which inhibits **peptidyltransferase** activity on the 50S ribosomal subunit, preventing peptide bond formation.
- Although chloramphenicol can cause **ototoxicity** and **aplastic anemia**, its use in neonates is limited due to the risk of **Gray Baby Syndrome**.
*It binds the 30s ribosomal subunit and reversibly inhibits translocation*
- This describes the mechanism of action of **tetracyclines**, which reversibly bind to the 30S ribosomal subunit and prevent the attachment of aminoacyl-tRNA, thereby inhibiting protein synthesis.
- Tetracyclines are **contraindicated in neonates** due to their potential to cause **tooth discoloration** and **bone growth inhibition**, and ototoxicity is not their primary adverse effect.
*It binds the 50s ribosomal subunit and reversibly inhibits translocation*
- This mechanism of reversibly inhibiting translocation by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit is characteristic of **macrolides** (e.g., erythromycin, azithromycin) and **clindamycin**.
- While some macrolides can cause **transient ototoxicity**, they are not typically the second antibiotic of choice for neonatal meningitis in combination with ampicillin, and clindamycin's side effect profile is different.
Antifungal agents US Medical PG Question 5: A potassium hydroxide preparation is conducted on a skin scraping of the hypopigmented area. Microscopy of the preparation shows long hyphae among clusters of yeast cells. Based on these findings, which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy?
- A. Topical corticosteroid
- B. Oral ketoconazole
- C. Topical selenium sulfide (Correct Answer)
- D. Topical nystatin
- E. Oral fluconazole
Antifungal agents Explanation: ***Topical selenium sulfide***
- The presence of **long hyphae** and **clusters of yeast cells** on KOH prep is characteristic of **tinea versicolor**, caused by *Malassezia furfur*.
- **Selenium sulfide** is a common and effective topical antifungal agent for tinea versicolor, available in shampoos and lotions.
*Topical corticosteroid*
- **Corticosteroids** have anti-inflammatory properties but do not treat fungal infections.
- Using corticosteroids alone would only mask symptoms and could potentially worsen the fungal infection.
*Oral ketoconazole*
- While **oral ketoconazole** is an antifungal, it is generally reserved for extensive or recalcitrant cases of tinea versicolor due to potential systemic side effects, such as **hepatotoxicity**.
- **Topical treatments** are preferred as first-line therapy for localized infections like this one.
*Topical nystatin*
- **Nystatin** is an antifungal agent primarily effective against *Candida* species.
- It is **not effective** against *Malassezia furfur*, the causative agent of tinea versicolor.
*Oral fluconazole*
- **Oral fluconazole** is an effective systemic antifungal used for various *Candida* and dermatophyte infections.
- Similar to oral ketoconazole, it is typically reserved for **widespread or recalcitrant cases** of tinea versicolor, with topical therapy being the preferred initial approach.
Antifungal agents US Medical PG Question 6: A 34-year-old woman presents with confusion, drowsiness, and headache. The patient’s husband says her symptoms began 2 days ago and have progressively worsened with an acute deterioration of her mental status 2 hours ago. The patient describes the headaches as severe, localized to the frontal and periorbital regions, and worse in the morning. Review of symptoms is significant for a mild, low-grade fever, fatigue, and nausea for the past week. Past medical history is significant for HIV infection for which she is not currently receiving therapy. Her CD4+ T cell count last month was 250/mm3. The blood pressure is 140/85 mm Hg, the pulse rate is 90/min, and the temperature is 37.7°C (100.0°F). On physical examination, the patient is conscious but drowsy. Papilledema is present. No pain is elicited with extension of the leg at the knee joint. The remainder of the physical examination is negative. Laboratory findings, including panculture, are ordered. A noncontrast CT scan of the head is negative and is followed by a lumbar puncture. CSF analysis is significant for:
Opening pressure 250 mm H2O (70-180 mm H2O)
Glucose 30 mg/dL (40-70 mg/dL)
Protein 100 mg/dL (<40 mg/dL)
Cell count 20/mm3 (0-5/mm3)
Which of the following additional findings would most likely be found in this patient?
- A. Gram-positive diplococci are present on microscopy
- B. CSF shows a positive acid-fast bacillus stain
- C. Multiple ring-enhancing lesions are seen on a CT scan
- D. CSF shows gram negative diplococci
- E. CSF India ink stain shows encapsulated yeast cells (Correct Answer)
Antifungal agents Explanation: ***CSF India ink stain shows encapsulated yeast cells***
- The patient's presentation with **subacute meningitis symptoms** (headache, confusion, low-grade fever) in the setting of **untreated HIV infection** with a low CD4+ count (250/mm3) strongly suggests an opportunistic infection.
- The CSF findings of **elevated opening pressure**, **low glucose**, **high protein**, and **moderate pleocytosis** are classic for **cryptococcal meningitis**, for which the India ink stain is diagnostic for encapsulated yeast cells.
*Gram-positive diplococci are present on microscopy*
- This finding suggests **bacterial meningitis**, specifically caused by organisms like *Streptococcus pneumoniae*.
- While bacterial meningitis presents acutely with severe symptoms, the **subacute course** and moderate pleocytosis are less typical, and the patient's immune status points towards an opportunistic infection.
*CSF shows a positive acid-fast bacillus stain*
- A positive **acid-fast bacillus (AFB) stain** in CSF would indicate **tuberculous meningitis**.
- While tuberculous meningitis can present subacutely with similar CSF findings in HIV patients, it typically involves a more significant lymphocytic pleocytosis and a more pronounced chronic course than suggested by the acute worsening.
*Multiple ring-enhancing lesions are seen on a CT scan*
- **Multiple ring-enhancing lesions** on CT or MRI are characteristic of **Toxoplasma encephalopathy** or **CNS lymphoma** in HIV-positive patients.
- While these are common HIV-related CNS complications, the patient's primary presentation points to **meningitis** (inflammation of meninges with CSF abnormalities) rather than focal brain lesions without meningeal involvement.
*CSF shows gram negative diplococci*
- **Gram-negative diplococci** in CSF suggest **meningococcal meningitis** (*Neisseria meningitidis*).
- This typically presents as an **acute, severe bacterial meningitis** with rapid deterioration, usually in immunocompetent individuals or specific outbreaks, which doesn't align with the subacute onset and specific CSF profile for cryptococcus.
Antifungal agents US Medical PG Question 7: A 32-year-old man is brought to the physician by his wife for a 3-day history of fever, headaches, and myalgias. He returned from a camping trip in Oklahoma 10 days ago. He works as a computer salesman. His temperature is 38.1°C (100.6°F). Neurologic examination shows a sustained clonus of the right ankle following sudden passive dorsiflexion. He is disoriented to place and time but recognizes his wife. Laboratory studies show a leukocyte count of 1,700/mm3 and a platelet count of 46,000/mm3. A peripheral blood smear shows monocytes with intracytoplasmic morulae. Which of the following is the most likely causal organism?
- A. Coxiella burnetii
- B. Rickettsia rickettsii
- C. Anaplasma phagocytophilum
- D. Borrelia burgdorferi
- E. Ehrlichia chaffeensis (Correct Answer)
Antifungal agents Explanation: ***Correct: Ehrlichia chaffeensis***
- The presence of **intracytoplasmic morulae** in **monocytes** is a pathognomonic sign for *Ehrlichia chaffeensis* infection, which causes **human monocytic ehrlichiosis**.
- The patient's symptoms of **fever, headache, myalgias, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia**, and the history of a **camping trip** in an endemic area (Oklahoma) are highly consistent with ehrlichiosis.
*Incorrect: Coxiella burnetii*
- This bacterium causes **Q fever**, characterized by fever, headache, and atypical pneumonia, but it does **not cause intracytoplasmic morulae** in monocytes or frequently lead to the degree of leukopenia and thrombocytopenia seen here.
- While it can be acquired from environments, the **microscopic findings** rule it out in this specific case.
*Incorrect: Rickettsia rickettsii*
- This organism causes **Rocky Mountain spotted fever**, which presents with fever, headache, myalgias, and a characteristic **rash** that is usually present on the palms and soles, none of which are mentioned here.
- It does not form **intracytoplasmic morulae** in monocytes.
*Incorrect: Anaplasma phagocytophilum*
- This bacterium causes **human granulocytic anaplasmosis**, which is clinically similar to ehrlichiosis but forms **morulae in granulocytes** (neutrophils), not monocytes.
- The peripheral blood smear specifically identifies morulae in **monocytes**, directing towards *Ehrlichia*.
*Incorrect: Borrelia burgdorferi*
- This spirochete causes **Lyme disease**, characterized by an **expanding erythematous rash (erythema migrans)**, fever, and musculoskeletal symptoms, but it does not cause leukopenia or thrombocytopenia.
- It does not produce **morulae** in any blood cells.
Antifungal agents US Medical PG Question 8: An 18-year-old man presents to the office, complaining of an itchy patch on his torso that appeared one week ago. The patient is on the college wrestling team and is concerned he will not be able to compete if it gets infected. He has no significant medical history, and his vital signs are within normal limits. On examination, there is an erythematous, scaly plaque with central clearing at approximately the level of rib 6 on the left side of his torso. What diagnostic test would be most appropriate at this time?
- A. Eaton agar
- B. Wood’s lamp examination
- C. Thayer-Martin agar
- D. Sabouraud agar
- E. KOH preparation (Correct Answer)
Antifungal agents Explanation: ***KOH preparation***
- A **KOH (potassium hydroxide) preparation** is the most appropriate initial diagnostic test for suspected **dermatophytosis** (ringworm), a common fungal infection often seen in wrestlers due to skin-to-skin contact.
- The KOH dissolves keratin and cellular debris, allowing for easier visualization of **fungal hyphae** and **spores** under a microscope, confirming the diagnosis.
*Eaton agar*
- **Eaton agar** is a specialized culture medium used for isolating and growing **Mycoplasma pneumoniae**, a bacterium that causes respiratory infections.
- It is not used for diagnosing fungal skin infections.
*Wood’s lamp examination*
- A **Wood's lamp examination** uses ultraviolet light to detect certain dermatophytes (like *Microsporum canis*), which may fluoresce
- However, many common dermatophytes, such as *Trichophyton rubrum*, do not fluoresce, making KOH preparation a more universally effective initial diagnostic tool.
*Thayer-Martin agar*
- **Thayer-Martin agar** is a selective culture medium primarily used for isolating and growing **Neisseria gonorrhoeae** and **Neisseria meningitidis**, bacteria responsible for sexually transmitted infections and meningitis, respectively.
- It is not indicated for diagnosing fungal skin infections.
*Sabouraud agar*
- **Sabouraud agar** is a recognized culture medium specifically designed for the isolation and identification of **fungi**, including dermatophytes.
- While useful for confirmation and species identification, a **KOH preparation** is a quicker and more immediate diagnostic test to confirm the presence of fungal elements in the clinic.
Antifungal agents US Medical PG Question 9: A 19-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with complaints of blurry vision and headaches that started 2 days ago. She reports that she has been experiencing some facial pain, but she thought it was related to her toothache. She is also worried about a black spot that is increasing in size on her face over the last month. She expresses concerns about her frequency of urination. Recently, she had a runny nose and cough that resolved spontaneously. The patient was diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus at 13 years of age. She is a non-smoker and drinks beer occasionally. Her blood pressure is 122/98 mm Hg and temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F). The physical examination is normal with the exception of a black necrotic eschar lateral to the right nasal ala. She lost 2.7 kg (6 lb) since her last visit, which was 6 months ago. A routine urinalysis at the office is positive for glucose and ketones. What is the most likely cause of the patient’s symptoms?
- A. Bacillus anthracis
- B. Mucormycosis (Correct Answer)
- C. Clostridium difficile
- D. Histoplasma capsulatum
- E. Aspergillus fumigatus
Antifungal agents Explanation: ***Mucormycosis***
- This patient, with uncontrolled **Type 1 diabetes** (indicated by frequent urination, weight loss, and glucose/ketones in urine), is at high risk for **mucormycosis**, an opportunistic fungal infection.
- The presence of a **black necrotic eschar** on the face, coupled with eye symptoms (blurry vision) and facial pain, is highly characteristic of **rhino-orbital-cerebral mucormycosis**, which often originates in the sinuses.
*Bacillus anthracis*
- **Cutaneous anthrax** would present as a painless ulcer with a black eschar, but it typically occurs in individuals exposed to infected animals or animal products and is not associated with diabetes or the rhinocerebral symptoms described.
- Systemic symptoms like blurry vision, headaches, and polyuria are not typical for cutaneous anthrax.
*Clostridium difficile*
- This bacterium primarily causes **gastrointestinal infections**, leading to diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever.
- There are no symptoms described that suggest a *C. difficile* infection, and it does not cause facial eschars or rhino-orbital symptoms.
*Histoplasma capsulatum*
- **Histoplasmosis** is a fungal infection typically acquired by inhaling spores, often found in bird or bat droppings, mainly affecting the lungs.
- While it can disseminate in immunocompromised individuals, causing mucocutaneous lesions, it typically doesn't present with a rapid-onset facial eschar or the specific rhino-orbital symptoms seen here.
*Aspergillus fumigatus*
- Although **invasive aspergillosis** can occur in immunocompromised patients, including those with diabetes, it more commonly affects the lungs (e.g., aspergilloma, chronic pulmonary aspergillosis).
- While it can cause sinusitis and, rarely, cutaneous lesions, the rapid progression to a **black necrotic eschar** in the context of uncontrolled diabetes points more strongly towards mucormycosis.
Antifungal agents US Medical PG Question 10: A 58-year-old man presents with a high-grade fever, throbbing left-sided headache, vision loss, and left orbital pain. He says that his symptoms started acutely 2 days ago with painful left-sided mid-facial swelling and a rash, which progressively worsened. Today, he woke up with complete vision loss in his left eye. His past medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus, diagnosed 5 years ago. He was started on an oral hypoglycemic agent which he discontinued after a year. His temperature is 38.9°C (102.0°F), blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, pulse is 120/min, and respiratory rate is 20/min. On examination, there is purulent discharge from the left eye and swelling of the left half of his face including the orbit. Oral examination reveals extensive necrosis of the palate with a black necrotic eschar and purulent discharge. Ophthalmic examination is significant for left-sided ptosis, proptosis, and an absence of the pupillary light reflex. Laboratory findings are significant for a blood glucose level of 388 mg/dL and a white blood cell count of 19,000 cells/mm³. Urinary ketone bodies are positive. Fungal elements are found on a KOH mount of the discharge. Which of the following statements best describes the organism responsible for this patient’s condition?
- A. It appears as a narrow-based budding yeast with a thick capsule
- B. Histopathological examination shows non-septate branching hyphae (Correct Answer)
- C. It produces conidiospores
- D. It has budding and filamentous forms
- E. Histopathological examination shows acute angle branching hyphae
Antifungal agents Explanation: ***Histopathological examination shows non-septate branching hyphae***
- The patient's presentation with **diabetic ketoacidosis**, orbital pain, vision loss, facial swelling, necrotic palatal eschar, and high fever strongly suggests **mucormycosis**, a severe fungal infection.
- Mucormycosis is caused by fungi belonging to **Mucorales order** (e.g., *Rhizopus*, *Mucor*, *Lichtheimia*), which are characterized by **broad, ribbon-like, non-septate hyphae with irregular, wide-angle branching**.
*It appears as a narrow-based budding yeast with a thick capsule*
- This description is characteristic of **Cryptococcus neoformans**, which causes cryptococcosis, often presenting with meningoencephalitis and lung involvement.
- The clinical picture and *KOH mount* findings in this patient are inconsistent with cryptococcosis.
*It produces conidiospores*
- **Conidiospores are asexual spores** produced by many fungi, including *Aspergillus* and *Penicillium*, but this is a general characteristic and not specific enough to definitively identify the pathogen responsible for mucormycosis.
- The *histopathological features* (non-septate hyphae) are the key identifier in mucormycosis.
*It has budding and filamentous forms*
- This description generally refers to **dimorphic fungi** (e.g., *Histoplasma*, *Blastomyces*, *Coccidioides*), which exhibit yeast forms in tissue and mold forms in culture.
- Mucorales are typically **molds** in both environments and are not considered dimorphic, nor do they commonly present with budding forms.
*Histopathological examination shows acute angle branching hyphae*
- This morphological description is characteristic of **Aspergillus species**, which cause aspergillosis, another opportunistic fungal infection.
- *Aspergillus* hyphae are typically **septate** and branch at acute angles (around 45 degrees), unlike the broad, non-septate, wide-angle branching hyphae of Mucorales.
More Antifungal agents US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.