Parasites/Fungi

On this page
🦠 The Parasitic Arsenal: Mastering Nature's Most Cunning Invaders
Parasites and fungi wage silent wars inside human hosts, exploiting immune blind spots and hijacking cellular machinery with strategies honed over millions of years. You'll master how these organisms invade, evade, and persist-then learn to recognize their clinical fingerprints, deploy precise diagnostics, and execute evidence-based treatments that save lives. From molecular mechanisms to bedside decision-making, this lesson transforms complex pathogen behavior into actionable clinical expertise you'll use across every system and practice setting.
The parasitic kingdom operates through three fundamental invasion strategies: vector-borne transmission (40% of parasitic diseases), direct penetration (35% of infections), and ingestion cycles (25% of cases). Each strategy demands specific diagnostic approaches and targeted therapeutic interventions.
📌 Remember: VIP - Vector-borne (malaria, filariasis), Ingestion (helminths, protozoa), Penetration (schistosomes, hookworms). Vector-borne diseases affect >1 billion people globally, with 90% concentrated in tropical regions.
Parasitic Classification Matrix
| Category | Transmission | Primary Sites | Diagnostic Window | Treatment Duration | Resistance Patterns |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protozoa | Vector/Ingestion | Blood/GI/CNS | 7-21 days | 3-14 days | 15-30% resistance |
| Helminths | Ingestion/Penetration | GI/Tissue/Blood | 2-8 weeks | 1-3 days | <5% resistance |
| Fungi | Inhalation/Contact | Lung/Skin/CNS | 1-4 weeks | 2-52 weeks | 10-25% resistance |
| Ectoparasites | Direct Contact | Skin/Hair | 1-7 days | 1-2 applications | 5-15% resistance |
- Single-celled organisms with complex lifecycles
- Intracellular replication in 60% of species
- Plasmodium: 48-72 hour replication cycles
- Toxoplasma: 6-8 hour division time
- Leishmania: 12-24 hour generation time
- Vector dependency in 75% of pathogenic species
- Helminthic Infections
- Multicellular worms with tissue-specific tropism
- Chronic infections lasting 5-20 years without treatment
- Soil-transmitted: 1-2 billion people infected
- Schistosomiasis: 240 million cases globally
- Lymphatic filariasis: 120 million affected
- Eosinophilia >500 cells/μL in 80% of tissue infections
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Eosinophil count >1000 cells/μL suggests tissue-invasive helminths in 85% of cases. Combined with travel history and specific IgE elevation, this triad achieves 95% diagnostic accuracy for parasitic infections.
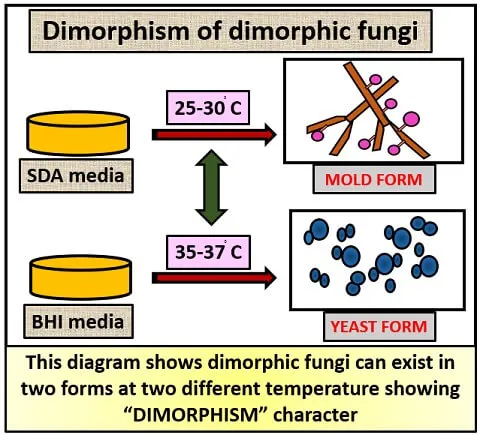
Fungal pathogens demonstrate thermal dimorphism in 70% of systemic species, existing as molds at 25°C (environmental) and yeasts at 37°C (human body temperature). This adaptation enables environmental survival and human pathogenicity.
💡 Master This: Geographic distribution patterns predict 90% of endemic fungal infections. Histoplasma (Ohio/Mississippi valleys), Coccidioides (Southwest US), Blastomyces (Great Lakes region) each show >95% correlation with specific soil conditions and climate patterns.
The diagnostic timeline varies dramatically: acute parasitic infections present within 1-4 weeks, while chronic helminthic diseases may remain asymptomatic for months to years. Fungal infections show biphasic patterns - acute pulmonary symptoms within 2-3 weeks, followed by potential dissemination after 6-12 months in immunocompromised hosts.
Understanding these temporal patterns enables precise diagnostic timing and prevents missed diagnoses. The next section reveals how these pathogens execute their cellular invasion strategies through sophisticated molecular mechanisms.
🦠 The Parasitic Arsenal: Mastering Nature's Most Cunning Invaders
⚔️ Invasion Mechanics: The Molecular Warfare Arsenal

Parasitic Invasion Strategies
-
Receptor-Mediated Entry
- Plasmodium sporozoites target hepatocyte CD81 receptors
- Binding affinity: Kd = 10⁻⁹ M (extremely high specificity)
- >95% hepatocyte invasion success rate
- 48-hour liver stage development
- 30,000+ merozoites released per infected hepatocyte
- Toxoplasma utilizes moving junction complex
- 2-20 second invasion timeline
- Active penetration independent of host cell endocytosis
-
Enzymatic Barrier Degradation
- Hookworm larvae secrete metalloproteinases
- Skin penetration within 5-10 minutes of contact
- Hyaluronidase degrades dermal matrix
- Collagenase creates migration pathways
- Success rate: 60-80% depending on skin thickness
- Schistosome cercariae release elastase and chondroitinase
📌 Remember: HELP - Hyaluronidase (spreads infection), Elastase (vessel penetration), Lipase (membrane disruption), Protease (tissue degradation). These four enzyme classes account for >90% of parasitic tissue invasion mechanisms.
Fungal Pathogenesis Mechanisms
| Species | Primary Virulence Factor | Target Tissue | Invasion Time | Success Rate | Host Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Candida albicans | Hyphal transformation | Mucosa/Blood | 2-6 hours | 70-90% | Neutrophil recruitment |
| Aspergillus fumigatus | Conidial germination | Lung alveoli | 6-12 hours | 40-60% | Macrophage activation |
| Cryptococcus neoformans | Capsule formation | CNS/Lung | 12-24 hours | 80-95% | Minimal inflammation |
| Histoplasma capsulatum | Intracellular survival | Macrophages | 1-4 hours | 85-95% | Granuloma formation |
| Mucor species | Angioinvasion | Blood vessels | 4-8 hours | 60-80% | Thrombosis/necrosis |
- Temperature-sensitive morphogenesis at 37°C
- Histoplasma: yeast form survives phagolysosomal fusion
- pH tolerance: 4.5-6.0 (phagolysosome range)
- Iron acquisition through siderophore production
- Intracellular replication every 8-12 hours
- Coccidioides: spherule formation with >200 endospores
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Angioinvasive fungi (Aspergillus, Mucor) cause vessel thrombosis within 24-48 hours, leading to tissue necrosis in >80% of cases. Early recognition of black eschar or rapid tissue death demands immediate antifungal therapy and surgical debridement.
Immune Evasion Sophistication reaches extraordinary levels in chronic parasites. Trypanosoma brucei employs variant surface glycoprotein (VSG) switching, generating >1000 different surface antigens during single infections. This antigenic variation occurs every 7-10 days, staying ahead of adaptive immune responses.
💡 Master This: Cryptococcal capsule thickness correlates directly with virulence and immune evasion capacity. Capsules >2 μm thick show >90% resistance to phagocytosis, while thin capsules (<0.5 μm) demonstrate <20% survival in macrophages. India ink preparation reveals capsule thickness for rapid virulence assessment.
Molecular Mimicry enables pathogens to exploit host recognition systems. Schistosoma adults acquire host blood group antigens on their surface, achieving immunological invisibility for 5-30 years. This explains why chronic schistosomiasis shows minimal inflammatory responses despite massive worm burdens.
The precision of these invasion mechanisms determines infection probability, disease severity, and treatment requirements. Understanding molecular pathogenesis enables targeted therapeutic interventions and explains why certain populations show differential susceptibility patterns. Next, we explore how these mechanisms translate into recognizable clinical presentation patterns.
⚔️ Invasion Mechanics: The Molecular Warfare Arsenal
🎯 Pattern Recognition Mastery: Clinical Presentation Blueprints
Geographic-Pathogen Correlation Matrix
-
Sub-Saharan Africa
- Malaria: >90% of global deaths
- African trypanosomiasis: 36 endemic countries
- T.b. gambiense: West/Central Africa (98% of cases)
- T.b. rhodesiense: East Africa (2% of cases)
- Schistosomiasis: S. haematobium (urogenital, 54 countries)
- Onchocerciasis: 31 countries, >99% of global cases
-
Latin America
- Chagas disease: 21 endemic countries
- Leishmaniasis: Cutaneous (90% of cases), Visceral (10%)
- Brazil: >50% of visceral cases globally
- Peru/Bolivia: >60% of mucocutaneous cases
- Soil-transmitted helminths: >200 million infected
📌 Remember: SAFE travel history - Sub-Saharan Africa (malaria, trypanosomiasis), Asia (dengue, Japanese encephalitis), Fresh water exposure (schistosomiasis), Endemic fungi (histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis). >95% of imported parasitic diseases correlate with specific geographic exposure patterns.
Temporal Pattern Recognition Framework
| Onset Timeline | Primary Pathogens | Key Clinical Features | Diagnostic Priority | Mortality Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <1 week | Malaria, Dengue | Fever, headache, myalgia | Blood smear STAT | High (>10%) |
| 1-4 weeks | Typhoid, Rickettsial | Fever, rash, GI symptoms | Blood culture, serology | Moderate (2-5%) |
| 1-3 months | Hepatitis, Schistosomiasis | Hepatomegaly, eosinophilia | Liver enzymes, eosinophil count | Low (<1%) |
| >3 months | Tuberculosis, Leishmaniasis | Weight loss, chronic symptoms | Tissue biopsy, culture | Variable |
- Malaria: Fever every 48-72 hours (depending on species)
- P. falciparum: Irregular fever, cerebral complications
- P. vivax/ovale: 48-hour cycles, relapse potential
- P. malariae: 72-hour cycles, nephritis risk
- Dengue: Biphasic fever with 3-7 day initial phase
- Critical phase: Days 4-6 with capillary leak
- Thrombocytopenia <100,000/μL in >80% of cases
- Subacute Presentations (2-8 weeks)
- Katayama syndrome (acute schistosomiasis)
- Eosinophilia >20% with fever and hepatosplenomegaly
- 4-8 weeks post-freshwater exposure
- IgE elevation >1000 IU/mL in >90% of cases
- Acute Chagas disease
- Romaña's sign (unilateral periorbital edema)
- Chagoma at inoculation site
- Parasitemia detectable for 4-8 weeks
- Katayama syndrome (acute schistosomiasis)
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Fever + eosinophilia + travel history suggests tissue-invasive helminths in >85% of cases. Eosinophil count >1500/μL with recent travel demands immediate stool examination, serology, and imaging for larva migrans syndromes.
Organ System-Specific Recognition Patterns
-
Central Nervous System Involvement
- Cerebral malaria: Altered consciousness + retinal hemorrhages
- Glasgow Coma Scale <11 in severe cases
- Mortality rate: 15-20% despite treatment
- Neurocysticercosis: Seizures in 70-90% of cases
- Ring-enhancing lesions on MRI
- Most common cause of acquired epilepsy in endemic areas
- Cryptococcal meningitis: Headache + minimal neck stiffness
- Opening pressure >25 cmH₂O in >80% of cases
- Cerebral malaria: Altered consciousness + retinal hemorrhages
-
Gastrointestinal Manifestations
- Giardiasis: Chronic diarrhea + malabsorption
- Steatorrhea with foul-smelling stools
- Weight loss >10% in chronic cases
- Amebiasis: Bloody diarrhea + liver abscess
- Right upper quadrant pain in >90% of liver cases
- Anchovy paste appearance of abscess contents
- Giardiasis: Chronic diarrhea + malabsorption
💡 Master This: Eosinophilia patterns provide diagnostic clues: >20% suggests acute tissue invasion (Katayama, larva migrans), 10-20% indicates chronic helminth infection, <10% with symptoms points toward protozoan or fungal causes. Normal eosinophil count does NOT exclude parasitic disease.
Pattern Recognition Drill Framework: For any febrile traveler, systematically assess geographic exposure (endemic diseases), timeline (incubation periods), symptom constellation (organ involvement), and laboratory patterns (eosinophilia, anemia, thrombocytopenia). This approach identifies >90% of imported parasitic diseases within 24-48 hours of presentation.
The systematic recognition of these clinical blueprints enables rapid diagnostic focus and prevents delayed treatment of life-threatening infections. Next, we examine how to systematically differentiate between similar presentations using quantitative discriminators.
🎯 Pattern Recognition Mastery: Clinical Presentation Blueprints
🔬 Diagnostic Discrimination: The Laboratory Detective Arsenal
Microscopic Identification Mastery
| Pathogen | Size Range (μm) | Key Morphological Features | Diagnostic Sensitivity | Time to Result | Cost Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. falciparum | 12-15 | Banana-shaped gametocytes | >95% (thick smear) | 15-30 minutes | High |
| P. vivax | 15-20 | Enlarged RBCs, Schüffner dots | >90% (thick smear) | 15-30 minutes | High |
| Giardia lamblia | 10-14 x 6-8 | Falling leaf motility | 60-80% (single stool) | 10-15 minutes | High |
| Entamoeba histolytica | 15-25 | Ingested RBCs visible | 50-70% (single stool) | 10-15 minutes | Moderate |
| Schistosoma eggs | 112-170 x 40-70 | Terminal/lateral spines | >85% (concentrated) | 20-30 minutes | High |
- Parasitemia quantification: >5% suggests severe falciparum malaria
- Ring forms: P. falciparum shows multiple rings per RBC
- Appliqué forms (rings at RBC periphery)
- Double chromatin dots in >20% of rings
- Gametocytes: Banana-shaped (falciparum) vs round (other species)
- Mature gametocytes appear 7-10 days after initial infection
- RBC morphology: Enlarged cells with Schüffner dots (vivax/ovale)
- Helminth Egg Identification
- Schistosoma species discrimination:
- S. haematobium: Terminal spine, 112-170 μm length
- S. mansoni: Lateral spine, 114-180 μm length
- S. japonicum: No spine, 70-100 μm length
- Soil-transmitted helminths:
- Ascaris: Mammillated coat, 45-75 μm diameter
- Trichuris: Barrel-shaped with polar plugs
- Hookworm: Thin shell, segmented embryo
- Schistosoma species discrimination:
📌 Remember: SPINES for schistosome ID - S. haematobium (Terminal spine), S. mansoni (Lateral spine), S. japonicum (No spine). Egg size and spine position provide 100% species differentiation when properly measured.
Serological and Molecular Diagnostics
-
Antigen Detection Systems
- Malaria rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs):
- HRP-2 detection: >95% sensitivity for P. falciparum
- pLDH detection: Pan-species reactivity
- False negative rate: <5% at >100 parasites/μL
- Cryptococcal antigen (CrAg):
- Sensitivity >95% in CSF and serum
- Titer >1:1024 predicts poor prognosis
- Remains positive for weeks to months after treatment
- Malaria rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs):
-
Molecular Diagnostics (PCR)
- Species-specific identification: >99% accuracy
- Quantitative PCR: Parasite load assessment
- Malaria: <1000 copies/μL suggests low-grade parasitemia
- Leishmaniasis: >10⁶ copies/mL indicates active disease
- Drug resistance markers:
- pfk13 mutations: Artemisinin resistance (P. falciparum)
- dhfr/dhps mutations: Sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine resistance
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Negative microscopy with positive RDT suggests recent treatment or low-level parasitemia. Positive microscopy with negative RDT indicates non-falciparum species or HRP-2 deletion mutants (emerging in 5-10% of P. falciparum isolates).

Fungal Diagnostic Discrimination
-
Direct Microscopy Techniques
- KOH preparation: 10-20% KOH dissolves cellular debris
- Sensitivity: 40-80% depending on specimen quality
- Dermatophytes: Septate hyphae with arthroconidia
- Candida: Budding yeasts with pseudohyphae
- Calcofluor white staining: Enhanced visualization
- Fluorescent chitin in fungal cell walls
- Sensitivity increase: 15-25% over KOH alone
- KOH preparation: 10-20% KOH dissolves cellular debris
-
Culture-Based Identification
- Sabouraud dextrose agar: Standard fungal medium
- Growth time: 2-4 weeks for dimorphic fungi
- Temperature testing: 25°C vs 37°C for dimorphism
- Chromogenic media: Species-specific color reactions
- CHROMagar Candida: Species identification within 48 hours
- Accuracy >90% for common Candida species
- Sabouraud dextrose agar: Standard fungal medium
💡 Master This: Galactomannan antigen (Aspergillus) shows optical density >0.5 in >80% of invasive aspergillosis cases. Serial monitoring with increasing titers predicts treatment failure, while decreasing levels correlate with therapeutic response in >85% of cases.
Laboratory Integration Strategy: Combine multiple diagnostic modalities for optimal accuracy. Microscopy provides immediate results, antigen detection offers rapid confirmation, and molecular methods deliver definitive identification. Sequential testing based on clinical probability maximizes cost-effectiveness while ensuring diagnostic precision.
Understanding these quantitative discriminators enables confident pathogen identification and appropriate treatment selection. The next section explores evidence-based treatment algorithms that translate diagnostic precision into therapeutic success.
🔬 Diagnostic Discrimination: The Laboratory Detective Arsenal
⚡ Therapeutic Command Center: Evidence-Based Treatment Algorithms
Antimalarial Treatment Protocols
| Clinical Scenario | First-Line Therapy | Dosing Regimen | Treatment Duration | Success Rate | Resistance Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uncomplicated P. falciparum | Artemether-lumefantrine | 20/120 mg BID x 3 days | 3 days | >95% | pfk13 mutations |
| Severe malaria | IV Artesunate | 2.4 mg/kg at 0, 12, 24h | 3+ days | 85-90% | Parasite clearance time |
| P. vivax/ovale | Chloroquine + Primaquine | 25 mg/kg + 0.5 mg/kg x 14d | 3 + 14 days | >90% | G6PD status required |
| Prevention (high risk) | Atovaquone-proguanil | 250/100 mg daily | Duration + 7 days | >98% | Geographic resistance |
- IV Artesunate: Superior to quinine (15% mortality reduction)
- Parasite clearance: <24 hours in >80% of cases
- Neurological recovery: 48-72 hours typical timeline
- Delayed hemolysis: 7-21 days post-treatment (10-15% incidence)
- Supportive care protocols:
- Glucose monitoring: <70 mg/dL in >30% of severe cases
- Fluid management: Avoid overload (pulmonary edema risk)
- Seizure prophylaxis: Not routinely recommended
- Resistance Pattern Recognition
- Artemisinin resistance: Delayed parasite clearance >72 hours
- pfk13 mutations: C580Y most common (Southeast Asia)
- Ring-stage survival assay: >1% survival indicates resistance
- Chloroquine resistance: >95% of P. falciparum globally
- pfcrt K76T mutation: Primary resistance marker
- Still effective for P. vivax in most regions
- Artemisinin resistance: Delayed parasite clearance >72 hours
📌 Remember: ACTS for malaria treatment - Artesunate (severe cases), Coartem (uncomplicated falciparum), Test for G6PD (before primaquine), Support (glucose, fluids, monitoring). Artesunate reduces mortality by 15% compared to quinine in severe malaria.
Antifungal Therapeutic Strategies
-
Invasive Aspergillosis Treatment
- Voriconazole: First-line therapy for invasive disease
- Loading dose: 6 mg/kg IV q12h x 2 doses
- Maintenance: 4 mg/kg IV q12h or 200 mg PO BID
- Therapeutic levels: 1-5.5 μg/mL (trough)
- Response rate: 60-70% in immunocompromised hosts
- Alternative agents:
- Isavuconazole: Similar efficacy, fewer side effects
- Amphotericin B: Salvage therapy (40-50% response)
- Caspofungin: Combination therapy for refractory cases
- Voriconazole: First-line therapy for invasive disease
-
Cryptococcal Meningitis Protocol
- Induction phase (2 weeks):
- Amphotericin B: 0.7-1.0 mg/kg/day IV
- Flucytosine: 100 mg/kg/day PO (divided q6h)
- CSF sterilization: >80% by day 14
- Consolidation phase (8 weeks):
- Fluconazole: 400 mg daily PO
- Maintenance phase (≥1 year):
- Fluconazole: 200 mg daily PO
- Immune reconstitution: CD4 >100 for >6 months
- Induction phase (2 weeks):
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Therapeutic drug monitoring is essential for voriconazole due to >10-fold inter-patient pharmacokinetic variability. Trough levels <1 μg/mL correlate with treatment failure, while >5.5 μg/mL increases hepatotoxicity risk by >3-fold.
Helminth Treatment Algorithms
-
Soil-Transmitted Helminths
- Albendazole: 400 mg single dose (broad spectrum)
- Efficacy: >90% for Ascaris, >80% for hookworm
- Mebendazole alternative: 500 mg single dose
- Mass drug administration: Annual or biannual in endemic areas
- Strongyloides treatment:
- Ivermectin: 200 μg/kg daily x 2 days
- Cure rate: >95% for uncomplicated infection
- Hyperinfection syndrome: Extended therapy (7-14 days)
- Albendazole: 400 mg single dose (broad spectrum)
-
Schistosomiasis Management
- Praziquantel: 40 mg/kg single dose (S. mansoni/haematobium)
- 60 mg/kg for S. japonicum/mekongi
- Cure rate: >85% with single treatment
- Egg reduction: >90% in responding patients
- Treatment timing: >6 weeks post-exposure
- Acute schistosomiasis: Corticosteroids + delayed praziquantel
- Praziquantel: 40 mg/kg single dose (S. mansoni/haematobium)
💡 Master This: Ivermectin resistance in Strongyloides remains <5% globally, but treatment failure occurs in 10-15% of immunocompromised patients. Extended therapy (7-14 days) and combination with albendazole improves cure rates to >95% in difficult cases.
Treatment Monitoring Framework: Clinical response assessment at 48-72 hours (acute infections), 1-2 weeks (subacute), and 4-6 weeks (chronic infections). Parasitological cure requires negative testing at 4-6 weeks post-treatment, with species-specific follow-up protocols for relapse detection.
Understanding these evidence-based algorithms enables optimal therapeutic outcomes while minimizing resistance development and adverse effects. The next section integrates these treatment principles with multi-system complications and advanced management strategies.
⚡ Therapeutic Command Center: Evidence-Based Treatment Algorithms
🌐 Integration Nexus: Multi-System Complications and Advanced Management
Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome (IRIS)
-
Pathophysiology and Risk Factors
- Immune system recovery triggers excessive inflammation against residual pathogens
- Incidence rates: 10-30% in cryptococcal meningitis, 15-25% in histoplasmosis
- CD4 count <50 cells/μL at diagnosis increases risk 3-fold
- Rapid CD4 recovery (>100 cells/μL increase/month) correlates with IRIS development
- Timeline: 2-8 weeks after antiretroviral therapy initiation
- Paradoxical IRIS: Worsening of known infection
- Unmasking IRIS: New presentation of subclinical infection
-
Clinical Manifestations by System
- Central Nervous System:
- Increased intracranial pressure: >25 cmH₂O in >80% of cryptococcal IRIS
- New neurological deficits: Focal seizures, cranial nerve palsies
- Imaging changes: New enhancing lesions despite negative cultures
- Pulmonary System:
- Respiratory failure: PaO₂/FiO₂ ratio <200 in severe cases
- Mediastinal lymphadenopathy: >2cm increase in lymph node size
- Pleural effusions: New or worsening in 40-60% of cases
- Central Nervous System:
📌 Remember: IRIS criteria - Immune recovery (CD4 increase), Residual pathogen (positive cultures/antigens), Inflammatory response (fever, elevated CRP), Symptom worsening (despite pathogen control). Corticosteroids reduce symptom duration by 50-70% but don't affect mortality.
Cardiovascular Complications
| Pathogen | Cardiac Manifestation | Incidence Rate | Diagnostic Method | Treatment Approach | Mortality Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T. cruzi | Chronic cardiomyopathy | 20-30% of chronic cases | Echo, ECG, Holter | Benznidazole + supportive | Variable |
| Aspergillus | Endocarditis | <5% of invasive disease | TEE, blood cultures | Voriconazole + surgery | >80% |
| Candida | Endocarditis | 10-15% of candidemia | TEE, ophthalmology | Echinocandin + surgery | 40-60% |
| Schistosoma | Pulmonary hypertension | 5-10% of chronic cases | Right heart cath | Praziquantel + vasodilators | Progressive |
- Antiparasitic therapy: Benznidazole (5-7 mg/kg/day x 60 days)
- Parasitological cure: 60-80% in chronic phase
- Cardiac progression: Slowed but not reversed
- Side effects: Dermatitis (30%), peripheral neuropathy (10%)
- Heart failure management:
- ACE inhibitors: First-line for systolic dysfunction
- Beta-blockers: Carvedilol preferred (mortality benefit)
- Amiodarone: Ventricular arrhythmia control
- ICD placement: EF <35% with optimal medical therapy
- Fungal Endocarditis Protocols
- Diagnostic criteria: Modified Duke criteria with fungal modifications
- Positive blood cultures: >2 sets with same organism
- Echocardiographic evidence: Vegetation >10mm or new regurgitation
- Ophthalmologic examination: Candida endophthalmitis in >30%
- Surgical indications:
- Vegetation size >10mm with embolic events
- Heart failure due to valve dysfunction
- Persistent fungemia despite >72 hours appropriate therapy
- Diagnostic criteria: Modified Duke criteria with fungal modifications
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Fungal endocarditis requires combined medical-surgical therapy in >80% of cases. Medical therapy alone shows <20% cure rate, while combined approach achieves 60-70% success. Early surgical consultation within 48-72 hours improves outcomes significantly.

Hepatosplenic Complications
-
Schistosomal Hepatic Fibrosis
- Periportal fibrosis: Pipestem appearance on ultrasound
- Portal hypertension: >12 mmHg gradient
- Splenomegaly: >15 cm in >90% of advanced cases
- Esophageal varices: Grade 2-3 in 60-80% of patients
- Management strategies:
- Praziquantel: Prevents progression but doesn't reverse fibrosis
- Endoscopic therapy: Variceal banding for bleeding prevention
- TIPS procedure: Refractory portal hypertension
- Periportal fibrosis: Pipestem appearance on ultrasound
-
Visceral Leishmaniasis Complications
- Pancytopenia: Universal finding in active disease
- Hemoglobin <8 g/dL: >80% of cases
- Platelet count <50,000/μL: >90% of cases
- Neutropenia <1000/μL: Secondary infection risk
- Post-kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis (PKDL):
- Incidence: 5-10% in Indian subcontinent, >50% in East Africa
- Timeline: 6 months to 3 years post-treatment
- Reservoir potential: Maintains transmission in elimination programs
- Pancytopenia: Universal finding in active disease
💡 Master This: Hepatosplenic schistosomiasis shows preserved liver function despite severe portal hypertension. Normal albumin and bilirubin with massive splenomegaly and varices characterizes schistosomal vs cirrhotic portal hypertension. Liver biopsy shows periportal fibrosis without hepatocyte necrosis.
Advanced Therapeutic Integration
- Combination Therapy Strategies
- Invasive aspergillosis: Voriconazole + anidulafungin
- Improved survival: >15% compared to monotherapy
- Faster clinical response: Median 7 vs 12 days
- Reduced resistance emergence: <5% vs 15% with monotherapy
- Severe malaria: Artesunate + supportive care optimization
- Exchange transfusion: Parasitemia >30% or severe complications
- Renal replacement therapy: Acute kidney injury in >25% of cases
- Mechanical ventilation: ARDS develops in 10-15% of severe cases
- Invasive aspergillosis: Voriconazole + anidulafungin
Multi-System Monitoring Framework: Daily assessment of organ function (renal, hepatic, cardiac), immune status (CD4, inflammatory markers), and treatment response (pathogen clearance, clinical improvement). Early recognition of system dysfunction enables proactive intervention and prevents cascade failures.
Understanding these complex interactions enables comprehensive patient management that addresses both pathogen elimination and host system optimization. The final section synthesizes these concepts into practical clinical mastery tools.
🌐 Integration Nexus: Multi-System Complications and Advanced Management
🎖️ Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Rapid Assessment and Decision Tools
The FEVER-TRAVEL Rapid Assessment Protocol
📌 Master Framework: FEVER-TRAVEL - Fever pattern, Eosinophilia, Vector exposure, Endemic regions, Recent travel (<6 months), Timeline of symptoms, Risk activities, Animal contact, Vaccination status, Exposure history, Laboratory abnormalities. This 11-point assessment identifies >95% of imported parasitic diseases.
| Assessment Component | Key Discriminators | High-Risk Indicators | Immediate Actions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fever Pattern | Periodicity, severity, response | Tertian/quartan cycles | Malaria smear STAT |
| Eosinophilia | Absolute count, percentage | >1000 cells/μL | Stool O&P x3, serology |
| Geographic Risk | Endemic diseases, season | Sub-Saharan Africa | Malaria RDT + smear |
| Timeline | Incubation period matching | <2 weeks | Blood cultures, PCR |
| Exposure History | Water, food, vectors, soil | Freshwater swimming | Schistosomiasis serology |
- Fever + Recent Africa Travel: Malaria until proven otherwise
- Thick/thin smears within 1 hour of presentation
- Rapid diagnostic test if microscopy delayed
- Empirical treatment if high clinical suspicion and delayed results
- Eosinophilia + Travel History: Tissue-invasive helminths
- Stool examination x3 over alternate days
- Serology panel: Strongyloides, Schistosoma, Filaria
- Imaging studies: Chest X-ray, abdominal ultrasound
Essential Clinical Thresholds Arsenal
⭐ Critical Numbers Mastery: Parasitemia >5% (severe malaria), Eosinophils >1000/μL (tissue invasion), CSF opening pressure >25 cmH₂O (cryptococcal meningitis), CD4 <100 (opportunistic risk), Platelet count <50,000 (visceral leishmaniasis). These five thresholds guide >80% of critical parasitic decisions.
-
Malaria Severity Indicators
- Parasitemia thresholds: >2% (moderate), >5% (severe), >20% (exchange transfusion)
- Clinical severity markers:
- Glasgow Coma Scale <11: Cerebral malaria
- Creatinine >3.0 mg/dL: Acute kidney injury
- Hemoglobin <7 g/dL: Severe anemia
- Platelet count <50,000/μL: Bleeding risk
- Lactate >4 mmol/L: Tissue hypoxia
-
Fungal Infection Risk Stratification
- Neutropenia severity: <500 cells/μL for >10 days = high risk
- Galactomannan levels: >0.5 optical density = probable aspergillosis
- Cryptococcal antigen titers: >1:1024 = poor prognosis
- CD4 count thresholds: <200 (PCP risk), <100 (cryptococcal risk), <50 (MAC risk)
💡 Clinical Pearl Integration: Negative malaria smear with positive RDT suggests recent treatment or submicroscopic parasitemia. Repeat smears q12h x3 and consider PCR confirmation. False-negative RDTs occur with HRP-2 deletion mutants (emerging 5-10% of P. falciparum).
Rapid Treatment Decision Matrix
-
Emergency Protocols (Life-Threatening)
- Severe malaria: IV artesunate 2.4 mg/kg immediately
- No delay for species confirmation
- Supportive care: Glucose monitoring, fluid balance, seizure precautions
- Invasive aspergillosis: Voriconazole loading dose within 6 hours
- 6 mg/kg IV q12h x2, then 4 mg/kg q12h
- Therapeutic drug monitoring within 48-72 hours
- Cryptococcal meningitis: Amphotericin B + flucytosine within 24 hours
- Lumbar puncture for opening pressure management
- Severe malaria: IV artesunate 2.4 mg/kg immediately
-
Outpatient Management Criteria
- Uncomplicated malaria: Oral artemether-lumefantrine
- Reliable follow-up within 24-48 hours
- No vomiting, able to take oral medications
- Parasitemia <2%, no severity indicators
- Intestinal parasites: Single-dose therapy for most helminths
- Albendazole 400 mg for soil-transmitted helminths
- Praziquantel 40 mg/kg for schistosomiasis
- Uncomplicated malaria: Oral artemether-lumefantrine
Monitoring and Follow-Up Protocols
📌 Follow-Up Framework: 24-48 hours (acute infections), 1 week (subacute), 4-6 weeks (parasitological cure), 3-6 months (relapse monitoring). Species-specific protocols ensure optimal outcomes and resistance prevention.
- Treatment Response Assessment
- Malaria: Parasite clearance by 72 hours, fever resolution by 48 hours
- Fungal infections: Clinical improvement by 5-7 days, biomarker reduction by 2 weeks
- Helminth infections: Symptom resolution by 2-4 weeks, negative stool by 4-6 weeks
Clinical Mastery Integration: These rapid assessment tools enable systematic evaluation of complex parasitic presentations while minimizing diagnostic delays and optimizing therapeutic outcomes. Regular practice with these frameworks develops expert-level pattern recognition and clinical decision-making capabilities.
🎖️ Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Rapid Assessment and Decision Tools
Practice Questions: Parasites/Fungi
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 22-year-old man presents with abdominal cramps and diarrhea over the last few weeks. He notes that several of his bowel movements have a small amount of blood. Past medical history is significant for an intermittent cough that has been persistent since returning from Mexico last month. The patient takes no current medications. On physical examination, there is diffuse tenderness to palpation. Which of the following medications is indicated for this patient’s condition?













