Merkel cell polyomavirus US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Merkel cell polyomavirus. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Merkel cell polyomavirus US Medical PG Question 1: A 63-year-old woman presents to the outpatient clinic complaining of severe vulvar itching. The pruritus started 1 year ago and became worse over the last several months. She has tried over-the-counter topical steroids without relief. She is not currently sexually active. Her medical history is notable for long-standing lichen sclerosus. The physical examination reveals an ulcerated small nodule on the right labium majus, as well as dry, thin, white lesions encircling the genital and perianal areas. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Squamous cell carcinoma (Correct Answer)
- B. Bartholin gland carcinoma
- C. Melanoma
- D. Bartholin gland cyst
- E. Vulvar Paget's disease
Merkel cell polyomavirus Explanation: ***Squamous cell carcinoma***
- An **ulcerated nodule** on the labium majus, coupled with a history of **long-standing lichen sclerosus** and unremitting pruritus in an elderly woman, is highly suspicious for vulvar squamous cell carcinoma.
- Lichen sclerosus is a **precancerous condition** that increases the risk of vulvar squamous cell carcinoma.
*Bartholin gland carcinoma*
- This is a rare malignancy that typically presents as a **mass deep within the labium majus**, often causing pain or pressure rather than an ulcerated nodule on the surface.
- While it can occur in older women, the ulcerated nodule and history of lichen sclerosus are more indicative of squamous cell carcinoma arising from the vulvar skin.
*Melanoma*
- Vulvar melanoma usually presents as a **pigmented lesion**, which may be raised or ulcerated, but the description of a small, ulcerated nodule in the context of lichen sclerosus points more strongly to squamous cell carcinoma.
- Although possible, the absence of pigmentation makes it less likely than squamous cell carcinoma, especially given the significant risk factor of lichen sclerosus.
*Bartholin gland cyst*
- A Bartholin gland cyst presents as a **smooth, soft, non-tender, fluid-filled mass** usually located at the posterior aspect of the labium majus.
- It would not typically present as an ulcerated nodule or explain the persistent pruritus in the context of lichen sclerosus.
*Vulvar Paget's disease*
- Vulvar Paget's disease typically presents as an **eczematous, erythematous, well-demarcated lesion** with a "crusted" or "velvety" appearance, often with satellite lesions.
- While it can cause pruritus, the description of an **ulcerated small nodule** is less characteristic of Paget's disease and more typical of an invasive squamous cell carcinoma.
Merkel cell polyomavirus US Medical PG Question 2: A 14-month-old boy is brought to the clinic for evaluation of a rash. The rash started on the face and spread to the trunk. He also had a fever and cough for the past 2 days. His mother says that they recently immigrated from Asia and cannot provide vaccination records. The physical examination reveals a maculopapular rash on the face, trunk, and proximal limbs with no lymphadenopathy. Blue-white spots are noted on the oral mucosa and there is bilateral mild conjunctival injection. The causative agent of this condition belongs to which of the following virus families?
- A. ssRNA naked viruses
- B. ssRNA enveloped viruses (Correct Answer)
- C. dsRNA naked viruses
- D. dsRNA enveloped viruses
- E. ssDNA enveloped viruses
Merkel cell polyomavirus Explanation: ***ssRNA enveloped viruses***
- The clinical presentation with **maculopapular rash** spreading from face to trunk, **fever**, **cough**, **conjunctivitis**, and especially **Koplik's spots** (blue-white spots on oral mucosa) is pathognomonic for **measles** (rubeola).
- Measles virus is a **single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) enveloped virus** belonging to the **Paramyxoviridae family**.
- The envelope contains hemagglutinin and fusion proteins that facilitate viral entry.
*ssRNA naked viruses*
- Includes viruses like picornaviruses (rhinovirus, enterovirus) and caliciviruses (norovirus).
- These cause respiratory infections or gastroenteritis, not the classic measles presentation with Koplik's spots.
*dsRNA naked viruses*
- Example: **Rotavirus** (Reoviridae family), which causes gastroenteritis in children.
- Does not present with maculopapular rash or Koplik's spots.
*dsRNA enveloped viruses*
- Extremely rare in human pathology; no common human disease fits this category.
- Not relevant to measles-like presentations.
*ssDNA enveloped viruses*
- Very rare category; most DNA viruses are dsDNA.
- No human disease with maculopapular rash and Koplik's spots is caused by ssDNA enveloped viruses.
Merkel cell polyomavirus US Medical PG Question 3: Researchers are investigating a new strain of a virus that has been infecting children over the past season and causing dermatitis. They have isolated the virus and have run a number of tests to determine its structure and characteristics. They have found that this new virus has an outer coating that is high in phospholipids. Protein targeting assays and immunofluorescence images have shown that the outer layer contains numerous surface proteins. On microscopy, these surface proteins are also expressed around the nucleus of cells derived from the infected tissue of the children. This virus’s structure most closely resembles which of the following?
- A. Adenovirus
- B. Papillomavirus
- C. Herpesvirus (Correct Answer)
- D. Poxvirus
- E. Hepadnavirus
Merkel cell polyomavirus Explanation: ***Herpesvirus***
- The presence of an **outer coating high in phospholipids** indicates an **enveloped virus**. Herpesviruses are large, enveloped DNA viruses.
- The detection of surface proteins expressed around the **nucleus** is a key finding that suggests the virus **buds from the nuclear membrane**, a characteristic feature of **herpesviruses**.
- Many herpesviruses cause dermatitis, including **HSV-1, HSV-2, VZV**, and **HHV-6**.
*Adenovirus*
- Adenoviruses are **non-enveloped viruses**, meaning they lack a lipid outer coating, which contradicts the phospholipid-rich coating described.
- Their replication and assembly occur exclusively in the **nucleus**, but they do not acquire an envelope by budding from the nuclear membrane.
*Papillomavirus*
- Papillomaviruses are also **non-enveloped viruses** with an **icosahedral capsid**, lacking the phospholipid envelope described.
- They replicate and assemble in the nucleus but do not possess the phospholipid-rich outer coating.
*Poxvirus*
- While poxviruses are **enveloped**, they acquire their envelope from the **Golgi apparatus** or **plasma membrane**, not the nuclear membrane.
- They are also distinct from other DNA viruses in that they replicate entirely in the **cytoplasm**, not the nucleus, which does not explain the perinuclear protein expression.
*Hepadnavirus*
- Hepadnaviruses (e.g., **Hepatitis B virus**) are enveloped DNA viruses, but their envelope is acquired by budding through the **endoplasmic reticulum** and **Golgi apparatus**, not the nuclear membrane.
- The perinuclear localization of surface proteins in immunofluorescence is not a characteristic feature of hepadnaviruses.
Merkel cell polyomavirus US Medical PG Question 4: A 65-year-old man with a 40-pack-year smoking history presents with hemoptysis and a persistent cough. Chest CT shows a 3.5 cm centrally located mass in the right main bronchus. Positron emission tomography confirms a malignant nodule. Bronchoscopy with transbronchial biopsy is performed and a specimen sample of the nodule is sent for frozen section analysis. The tissue sample is most likely to show which of the following tumor types?
- A. Carcinoid tumor
- B. Metastasis of colorectal cancer
- C. Small cell lung carcinoma
- D. Large cell carcinoma
- E. Squamous cell carcinoma (Correct Answer)
Merkel cell polyomavirus Explanation: ***Squamous cell carcinoma***
- This is the most likely diagnosis given the **central location** in the main bronchus, **heavy smoking history**, and presentation with **hemoptysis**.
- **Squamous cell carcinoma** accounts for 25-30% of lung cancers and characteristically arises in **central/proximal airways**, making it readily accessible by **bronchoscopy**.
- Histologically, it shows **keratin pearls** and **intercellular bridges** on biopsy.
- The **central endobronchial location** and ability to obtain tissue via transbronchial biopsy strongly favor squamous cell over peripheral tumors.
*Carcinoid tumor*
- **Carcinoid tumors** are **neuroendocrine tumors** that can present as central endobronchial masses and cause hemoptysis.
- However, they are typically **slow-growing** with more indolent presentation, and PET scans show **variable uptake** (often less intense than aggressive carcinomas).
- They represent only **1-2% of lung tumors** and occur more commonly in **younger, non-smoking patients**.
*Metastasis of colorectal cancer*
- While lung is a common site for **colorectal metastases**, these typically present as **multiple peripheral nodules** rather than a solitary central endobronchial mass.
- The clinical presentation strongly suggests **primary lung cancer** rather than metastatic disease.
- Without history of colorectal cancer, this is unlikely.
*Small cell lung carcinoma*
- **Small cell lung carcinoma** (SCLC) represents 15% of lung cancers and typically presents as a **large central mass** with early mediastinal involvement.
- However, SCLC is usually **too extensive at presentation** for transbronchial biopsy alone and often requires mediastinoscopy or CT-guided biopsy.
- Histology shows **small cells with scant cytoplasm**, **salt-and-pepper chromatin**, and **oat-cell morphology**.
- While possible, the single accessible endobronchial mass is more characteristic of squamous cell.
*Large cell carcinoma*
- **Large cell carcinoma** is a **diagnosis of exclusion** made when tumors lack features of adenocarcinoma, squamous cell, or small cell differentiation.
- It typically presents as **large peripheral masses** rather than central endobronchial lesions.
- It represents only **10% of lung cancers** and is less common than squamous cell carcinoma in this clinical scenario.
Merkel cell polyomavirus US Medical PG Question 5: A 28-year-old male with a history of HIV infection is found to have a CD4+ T lymphocyte count of 68 cells per microliter. As a consequence of his HIV infection, this patient is at increased risk of malignancy due to which of the following?
- A. Pneumocystis jiroveci
- B. Actinomyces israelii
- C. Helicobacter pylori
- D. HHV-6
- E. Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) (Correct Answer)
Merkel cell polyomavirus Explanation: ***Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)***
- **EBV** is a major cause of **AIDS-related malignancies**, particularly **B-cell lymphomas** including **non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL)** and **primary CNS lymphoma**, which are common in patients with CD4 counts below 100 cells/µL.
- The severe immunosuppression in **HIV/AIDS** allows for unchecked **EBV-driven lymphoproliferative disorders** due to impaired T-cell surveillance of EBV-infected B cells.
- Among the options listed, **EBV** is the only **oncogenic virus** and represents a significant cause of morbidity in advanced AIDS patients.
- **Note:** While HHV-8 (KSHV) causing Kaposi's sarcoma is also a major AIDS-related malignancy, it is not among the listed options.
*Pneumocystis jiroveci*
- **Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PCP)** is a common opportunistic **fungal infection** in HIV patients with CD4 < 200 cells/µL, causing severe respiratory illness.
- **PCP** is not oncogenic and does not increase malignancy risk; it causes acute infection, not cellular transformation.
*Actinomyces israelii*
- **Actinomyces israelii** is a gram-positive **bacterium** causing **actinomycosis**, a chronic suppurative infection with abscess formation and sinus tracts.
- While it can cause opportunistic infections in immunocompromised patients, it is **not oncogenic** and not associated with malignancy risk.
*Helicobacter pylori*
- **H. pylori** is a bacterium associated with **gastric adenocarcinoma** and **gastric MALT lymphoma** in the general population through chronic gastric inflammation.
- However, in the context of advanced HIV/AIDS with CD4 < 100, the predominant malignancy risk is from **oncogenic viruses** (EBV, HHV-8), not gastric pathology from **H. pylori**.
- **H. pylori** is not typically considered an AIDS-defining or AIDS-related malignancy.
*HHV-6*
- **Human Herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6)** causes roseola infantum in children and can reactivate in immunocompromised patients, potentially causing encephalitis or pneumonitis.
- **HHV-6** is **not established as oncogenic** and lacks strong evidence linking it to malignancy in HIV patients, unlike **EBV** (lymphomas) or **HHV-8** (Kaposi's sarcoma).
Merkel cell polyomavirus US Medical PG Question 6: An investigator is studying the replication of a virus in denucleated embryonic fibroblasts. After the fibroblasts are infected with the virus, viral proteins are directly translated from the virion's genetic material using fibroblast ribosomes. The resultant large polypeptides are then cleaved into smaller peptides by viral proteases to generate mature viral proteins. Finally, the virion's genetic material is replicated using a protein translated from the virion's genetic material. Which of the following is the most likely virus being evaluated in this study?
- A. Parvovirus
- B. Human immunodeficiency virus
- C. Measles virus
- D. Molluscum contagiosum virus
- E. Coxsackievirus (Correct Answer)
Merkel cell polyomavirus Explanation: ***Coxsackievirus***
- The description of **direct translation** from viral genetic material, **polyprotein cleavage by viral proteases**, and replication by a virally encoded protein is characteristic of **positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses** like Coxsackievirus.
- This process mirrors the replication strategy of **picornaviruses**, which include Coxsackievirus, where the genomic RNA acts directly as mRNA.
- Critically, picornaviruses replicate entirely in the **cytoplasm**, allowing them to function in **denucleated cells** as described in the study.
*Parvovirus*
- Parvoviruses are **single-stranded DNA viruses** and require the host cell to be in **S-phase** to replicate their DNA, using host enzymes in the **nucleus**.
- They **cannot replicate in denucleated cells** as they depend on nuclear host cell machinery.
- They do not typically use **polyprotein cleavage** as their primary mechanism for generating mature viral proteins.
*Human immunodeficiency virus*
- HIV is a **retrovirus** (RNA virus) that requires **reverse transcriptase** to convert its RNA genome into DNA, which is then **integrated into the host genome in the nucleus**, before transcription and translation.
- **Cannot replicate in denucleated cells** due to its requirement for nuclear integration.
- While it does use **protease cleavage** of polyproteins, the initial steps of DNA synthesis and integration are distinct from the described mechanism.
*Measles virus*
- Measles is a **negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus**; its genome **cannot be directly translated** into proteins.
- It requires an **RNA-dependent RNA polymerase** to synthesize positive-sense mRNA from its genome before protein synthesis can occur.
- The question specifies that viral proteins are **directly translated** from the virion's genetic material, which is incompatible with negative-sense RNA viruses.
*Molluscum contagiosum virus*
- Molluscum contagiosum virus is a **poxvirus**, which is a **double-stranded DNA virus**.
- While poxviruses uniquely replicate entirely in the **cytoplasm** and could theoretically work in denucleated cells, they do not use **direct translation** of their genome.
- Instead, they employ a complex cascade of gene expression with early, intermediate, and late genes, not the direct genome translation and polyprotein cleavage described in the question.
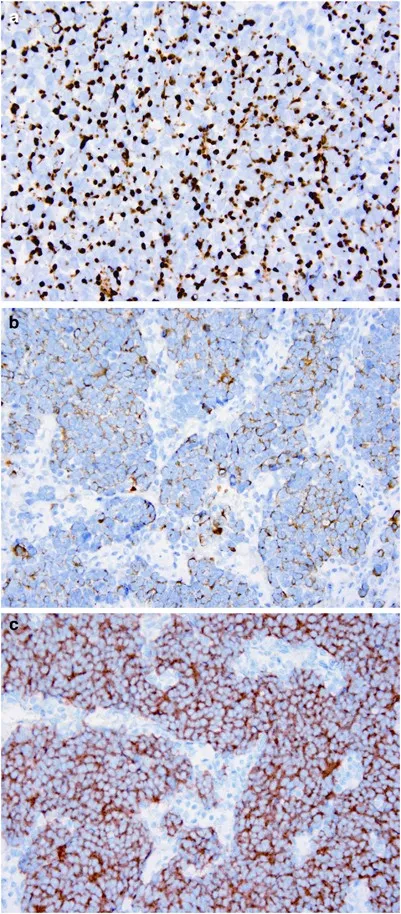
Merkel cell polyomavirus US Medical PG Question 7: A study is designed to assess the functions of immune components. The investigator obtains a lymph node biopsy from a healthy subject and observes it under a microscope. A photomicrograph of the cross-section of this lymph node is shown. Which of the following immunologic processes most likely occurs in the region labeled with an arrow?
- A. Isotype switching (Correct Answer)
- B. V(D)J recombination
- C. Macrophage activation
- D. T cell activation
- E. Negative selection
Merkel cell polyomavirus Explanation: ***Isotype switching***
- The arrow points to a **germinal center**, a specialized microenvironment within lymph nodes where B cells undergo **affinity maturation** and **isotype switching**.
- Isotype switching (or class switching) is the process by which B cells change the type of **antibody** they produce, e.g., from IgM to IgG, IgA, or IgE, to mediate different effector functions while retaining antigen specificity.
*V(D)J recombination*
- **V(D)J recombination** is the genetic mechanism by which the diverse repertoires of T cell receptors (TCRs) and immunoglobulins (antibodies) are generated, primarily in the **bone marrow** (for B cells) and **thymus** (for T cells) during their development.
- This process occurs much earlier in lymphocyte development and is largely completed before B cells migrate to secondary lymphoid organs like lymph nodes and form germinal centers.
*Macrophage activation*
- **Macrophage activation** is a process where macrophages acquire enhanced phagocytic and microbicidal activity, often in response to cytokines like **IFN-γ** produced by T helper cells.
- While macrophages are present in lymph nodes and play a role in antigen presentation and immune responses, their primary activation does not specifically occur within germinal centers; the germinal center is mainly a site for B cell maturation.
*T cell activation*
- **T cell activation** primarily occurs in the **T cell zones** (paracortex) of lymph nodes, where **naïve T cells** encounter antigen-presenting cells (APCs) presenting their specific antigen.
- While T follicular helper (Tfh) cells, a type of T cell, are crucial for sustaining germinal center reactions, the germinal center itself is not the primary site for the initial activation of most T cells.
*Negative selection*
- **Negative selection** is a critical process in lymphocyte development, occurring in the **thymus** for T cells and **bone marrow** for B cells, where self-reactive lymphocytes are eliminated.
- This process ensures central tolerance and occurs long before mature lymphocytes populate secondary lymphoid organs like lymph nodes.
Merkel cell polyomavirus US Medical PG Question 8: A 16-year-old male is brought to the clinic by his mother for the complaints of fever, nonproductive cough, fatigue, lack of appetite, and sore throat for the past 2 months. Several other students at his high school have had similar symptoms. Physical exam shows a whitish membrane in his oropharynx, bilateral enlarged cervical lymphadenopathy, and mild splenomegaly. Which of the following tests is most likely to diagnose his condition?
- A. Monospot test (Correct Answer)
- B. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- C. Throat culture
- D. Urine culture
- E. Chest X-ray
Merkel cell polyomavirus Explanation: ***Monospot test***
- The Monospot test detects **heterophile antibodies**, which are commonly produced during an acute Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, the cause of **infectious mononucleosis**.
- The patient's symptoms (fever, fatigue, nonproductive cough, sore throat, cervical lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly) and the epidemiological context (several other students with similar symptoms) are highly suggestive of **infectious mononucleosis**.
*Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)*
- While ELISA can detect antibodies to various pathogens, including EBV-specific antigens, the **Monospot test** is the more common and rapid initial diagnostic tool for infectious mononucleosis.
- ELISA for EBV-specific antibodies (e.g., VCA-IgM, VCA-IgG) might be used if the Monospot test is negative but clinical suspicion remains high, especially in younger children or atypical presentations.
*Throat culture*
- A throat culture is used to identify bacterial infections, such as **Streptococcus pyogenes** (strep throat).
- Although the patient has a sore throat and a whitish membrane, his other systemic symptoms (fatigue, splenomegaly, lack of appetite for 2 months) are not typical for a bacterial pharyngitis which usually responds to antibiotics. A **nonproductive cough** also makes bacterial pharyngitis less likely.
*Urine culture*
- A urine culture is used to diagnose **urinary tract infections**.
- The patient's symptoms are not indicative of a urinary tract infection.
*Chest X-ray*
- A chest X-ray is used to evaluate the lungs for conditions such as **pneumonia**, **bronchitis**, or other respiratory pathologies.
- While the patient has a nonproductive cough, the predominant systemic symptoms (fever, fatigue, lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly) point towards a systemic viral infection rather than primarily a lung issue that would be definitively diagnosed by a chest X-ray.
Merkel cell polyomavirus US Medical PG Question 9: A 55-year-old Caucasian male presents for a routine colonoscopy. A polyp is found in the patient's transverse colon and is found to be cancerous on histological evaluation. Upon examination, it is found that these cancerous cells have decreased MHC class I expression on their surface. Which immune system cell is most capable of killing these tumor cells?
- A. Cytotoxic T-cells
- B. B-cells
- C. Macrophages
- D. Natural killer cells (Correct Answer)
- E. Eosinophils
Merkel cell polyomavirus Explanation: ***Natural killer cells***
- **Natural killer (NK) cells** are specialized lymphocytes that identify and kill cells with **decreased or absent MHC class I expression**, a common feature of tumor cells and virus-infected cells.
- They provide a rapid, non-specific immune response without prior sensitization.
*Cytotoxic T-cells*
- **Cytotoxic T-cells (CTLs)** recognize and kill target cells by binding to specific **antigens presented by MHC class I molecules**.
- Since these cancer cells have **decreased MHC class I expression**, CTLs would be less effective at recognizing and killing them.
*B-cells*
- **B-cells** are primarily involved in humoral immunity, producing **antibodies** that can neutralize pathogens or mark cells for destruction.
- They do not directly kill target cells, and their activation typically requires specific antigen recognition, often with T-cell help.
*Macrophages*
- **Macrophages** are phagocytic cells that engulf and digest cellular debris, pathogens, and some tumor cells.
- While they can kill tumor cells, their primary mechanism involves **phagocytosis** or antigen presentation, not direct cytotoxicity based on MHC I expression levels.
*Eosinophils*
- **Eosinophils** are granulocytes primarily involved in the defense against **parasitic infections** and in allergic reactions.
- They are not a primary defense mechanism against tumor cells, especially not based on MHC class I expression.
Merkel cell polyomavirus US Medical PG Question 10: A 52-year-old woman presents to a local hospital complaining about a rash on her face and torso, as well as night sweats, low-grade fever, diarrhea, and unintentional weight loss. Her personal history is relevant for homelessness; she also has a history of risky behaviors such as the use and abuse of intravenous drugs, and unprotected intercourse with multiple sexual partners. Upon physical examination, well-demarcated violaceous plaques and papules distributed on her face and back are visible (see image below). Additional findings include fine reticular and interstitial changes on a chest radiograph, a CD4+ count of 50 cells/mm3, and positive HIV serology. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of this patient's dermatological condition?
- A. HHV-6 infection
- B. HHV-5 infection
- C. Human alphaherpesvirus 3 (HHV-3) infection
- D. HHV-8 infection (Correct Answer)
- E. HHV-1 infection
Merkel cell polyomavirus Explanation: ***HHV-8 infection***
- The patient's presentation with **violaceous plaques and papules** on the face and back, coupled with **immunocompromise** (HIV with CD4+ count of 50 cells/mm3), is highly characteristic of **Kaposi's sarcoma**, which is caused by **HHV-8**.
- Systemic symptoms like **night sweats, low-grade fever, diarrhea, and unintentional weight loss** are suggestive of advanced HIV disease and opportunistic infections, supporting the diagnosis of Kaposi's sarcoma in this context.
*HHV-6 infection*
- **HHV-6** is primarily associated with **roseola infantum** (exanthem subitum) in children, characterized by a high fever followed by a truncal rash.
- While HHV-6 can cause opportunistic infections in immunocompromised adults, it typically manifests as **encephalitis** or **bone marrow suppression**, not violaceous skin lesions.
*HHV-5 infection*
- **HHV-5** is also known as **cytomegalovirus (CMV)**. In immunocompromised individuals like this patient, CMV typically causes **retinitis, esophagitis, colitis, or pneumonitis**.
- CMV rarely causes distinct violaceous skin lesions as described in the patient, although **non-specific skin manifestations** can occur.
*Human alphaherpesvirus 3 (HHV-3) infection*
- **HHV-3** is the **varicella-zoster virus (VZV)**, which causes **chickenpox** (varicella) and **shingles** (herpes zoster).
- VZV lesions are typically **vesicular and painful**, distributed in a dermatomal pattern for shingles, which is distinct from the violaceous plaques seen in this patient.
*HHV-1 infection*
- **HHV-1 (Herpes Simplex Virus type 1)** typically causes **oral herpes (cold sores)** or **herpes labialis**.
- While HSV infections can be severe and widespread in immunocompromised patients, they usually present as **vesicular or ulcerative lesions**, not violaceous plaques, and are not typically associated with Kaposi's sarcoma.
More Merkel cell polyomavirus US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.