Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis US Medical PG Question 1: A scientist is researching the long term effects of the hepatitis viruses on hepatic tissue. She finds that certain strains are oncogenic and increase the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. However, they appear to do so via different mechanisms. Which of the following answer choices correctly pairs the hepatitis virus with the correct oncogenic process?
- A. Hepatitis A virus - chronic inflammation
- B. Hepatitis C virus - chronic inflammation
- C. Hepatitis E virus - integration of viral DNA into host hepatocyte genome
- D. Hepatitis B virus - integration of viral DNA into host hepatocyte genome (Correct Answer)
- E. Hepatitis A virus - integration of viral DNA into host hepatocyte genome
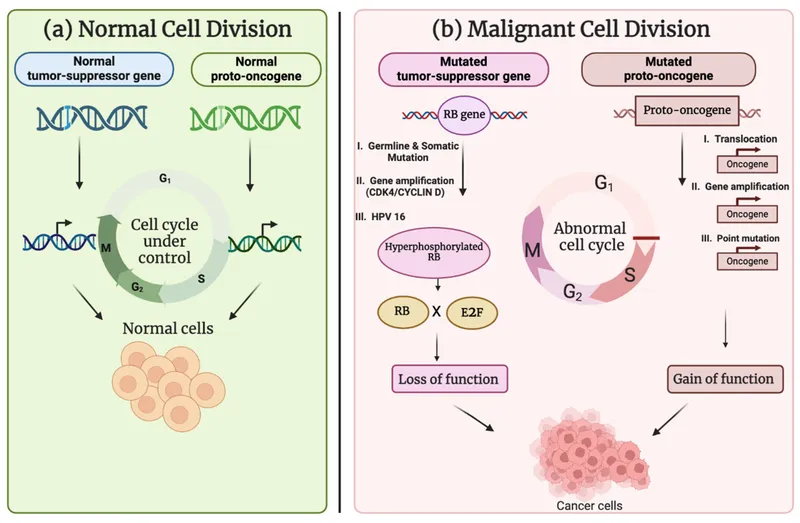
Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis Explanation: ***Hepatitis B virus - integration of viral DNA into host hepatocyte genome***
- **Hepatitis B virus (HBV)** is a **DNA virus** that can integrate its genetic material into the host hepatocyte genome, leading to genomic instability and promoting oncogenesis.
- This integration, along with chronic inflammation and the production of viral regulatory proteins, contributes significantly to the development of **hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)**.
*Hepatitis A virus - chronic inflammation*
- **Hepatitis A virus (HAV)** is an **RNA virus** that causes **acute hepatitis** but does not lead to chronic infection or chronic inflammation.
- Due to its acute and self-limiting nature, HAV is **not associated with hepatocellular carcinoma**.
*Hepatitis C virus - integration of viral DNA into host hepatocyte genome*
- **Hepatitis C virus (HCV)** is an **RNA virus** and therefore does not integrate its DNA into the host genome (as it has no DNA phase).
- HCV causes HCC primarily through **chronic inflammation**, **fibrosis**, and **cirrhosis**, not DNA integration.
*Hepatitis E virus - integration of viral DNA into host hepatocyte genome*
- **Hepatitis E virus (HEV)** is an **RNA virus** that typically causes acute, self-limiting hepatitis and does not integrate its genetic material into the host genome.
- While HEV can cause chronic infection in immunocompromised individuals, it is **not generally recognized as an oncogenic virus** leading to HCC.
*Hepatitis A virus - integration of viral DNA into host hepatocyte genome*
- **Hepatitis A virus (HAV)** is an **RNA virus**, meaning it does not have a DNA stage and therefore cannot integrate DNA into the host genome.
- HAV causes **acute, self-limiting infections** and is definitively **not associated with hepatocellular carcinoma**.
Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis US Medical PG Question 2: A 38-year-old woman makes an appointment with her family physician for a routine check-up after being away due to travel for 1 year. She recently had a screening Pap smear, which was negative for malignancy. Her past medical history is significant for a Pap smear 2 years ago that reported a low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL). A subsequent colposcopy diagnosed high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN2). The patient is surprised by the differences in her diagnostic tests. You explain to her the basis for the difference and reassure her. With this in mind, which of the following HPV serotypes is most likely to be present in the patient?
- A. HPV 33
- B. HPV 16 (Correct Answer)
- C. HPV 6
- D. HPV 31
- E. HPV 18
Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis Explanation: ***HPV 16***
- HPV 16 is the most common **high-risk HPV serotype**, responsible for approximately 50-60% of all **cervical cancers** and a high percentage of **high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN2/3)**. The progression from LSIL to CIN2 in this patient suggests infection with a high-risk type, making HPV 16 the most likely candidate.
- Given the patient's history of CIN2, a lesion of high-grade dysplasia, it is highly probable that she is infected with one of the most oncogenic HPV types, of which HPV 16 is paramount in prevalence.
*HPV 33*
- HPV 33 is a **high-risk HPV type** but is less prevalent than HPV 16 and 18 in causing cervical lesions. While it can cause CIN2, it is not the *most likely* serotype.
- It accounts for a smaller proportion of cervical cancers and high-grade dysplasias compared to HPV 16.
*HPV 6*
- HPV 6 is a **low-risk HPV type** primarily associated with **genital warts (condyloma acuminata)** and **low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSIL)** that typically do not progress to CIN2 or cervical cancer.
- Its presence would be inconsistent with the development of CIN2, as low-risk types are rarely implicated in high-grade dysplasia or malignancy.
*HPV 31*
- HPV 31 is another **high-risk HPV type** capable of causing **CIN2** and cervical cancer. However, it is less common than HPV 16.
- While plausible, HPV 16 remains statistically the most probable cause of CIN2.
*HPV 18*
- HPV 18 is a **high-risk HPV type** and is the second most common cause of **cervical cancer**, particularly **adenocarcinoma**. It is also associated with high-grade squamous lesions.
- While HPV 18 is a strong contender for high-grade lesions like CIN2, HPV 16 is still more frequently implicated in squamous cell carcinoma precursors.
Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis US Medical PG Question 3: A 28-year-old male with a history of HIV infection is found to have a CD4+ T lymphocyte count of 68 cells per microliter. As a consequence of his HIV infection, this patient is at increased risk of malignancy due to which of the following?
- A. Pneumocystis jiroveci
- B. Actinomyces israelii
- C. Helicobacter pylori
- D. HHV-6
- E. Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) (Correct Answer)
Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis Explanation: ***Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)***
- **EBV** is a major cause of **AIDS-related malignancies**, particularly **B-cell lymphomas** including **non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL)** and **primary CNS lymphoma**, which are common in patients with CD4 counts below 100 cells/µL.
- The severe immunosuppression in **HIV/AIDS** allows for unchecked **EBV-driven lymphoproliferative disorders** due to impaired T-cell surveillance of EBV-infected B cells.
- Among the options listed, **EBV** is the only **oncogenic virus** and represents a significant cause of morbidity in advanced AIDS patients.
- **Note:** While HHV-8 (KSHV) causing Kaposi's sarcoma is also a major AIDS-related malignancy, it is not among the listed options.
*Pneumocystis jiroveci*
- **Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PCP)** is a common opportunistic **fungal infection** in HIV patients with CD4 < 200 cells/µL, causing severe respiratory illness.
- **PCP** is not oncogenic and does not increase malignancy risk; it causes acute infection, not cellular transformation.
*Actinomyces israelii*
- **Actinomyces israelii** is a gram-positive **bacterium** causing **actinomycosis**, a chronic suppurative infection with abscess formation and sinus tracts.
- While it can cause opportunistic infections in immunocompromised patients, it is **not oncogenic** and not associated with malignancy risk.
*Helicobacter pylori*
- **H. pylori** is a bacterium associated with **gastric adenocarcinoma** and **gastric MALT lymphoma** in the general population through chronic gastric inflammation.
- However, in the context of advanced HIV/AIDS with CD4 < 100, the predominant malignancy risk is from **oncogenic viruses** (EBV, HHV-8), not gastric pathology from **H. pylori**.
- **H. pylori** is not typically considered an AIDS-defining or AIDS-related malignancy.
*HHV-6*
- **Human Herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6)** causes roseola infantum in children and can reactivate in immunocompromised patients, potentially causing encephalitis or pneumonitis.
- **HHV-6** is **not established as oncogenic** and lacks strong evidence linking it to malignancy in HIV patients, unlike **EBV** (lymphomas) or **HHV-8** (Kaposi's sarcoma).
Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis US Medical PG Question 4: A 63-year-old man presents to his primary care physician because he has been having headaches and hearing loss. In addition, he says that he has been having difficulty opening his jaw to eat and recurrent middle ear infections. Physical exam reveals enlarged neck lymph nodes and a mass in the nasopharynx. Biopsy of the mass reveals undifferentiated squamous epithelial cells. The organism that is most likely associated with this patient's disease is also associated with which of the following disorders?
- A. Kaposi sarcoma
- B. Hepatocellular carcinoma
- C. Adult T-cell lymphoma
- D. Burkitt lymphoma (Correct Answer)
- E. Vulvar carcinoma
Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis Explanation: ***Burkitt lymphoma***
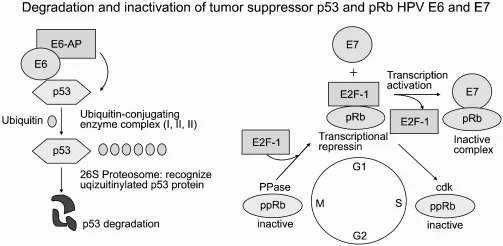
- The patient's symptoms (headaches, hearing loss, difficulty opening jaw, recurrent middle ear infections, nasopharyngeal mass, enlarged neck lymph nodes) and biopsy results (undifferentiated squamous epithelial cells) point to **nasopharyngeal carcinoma**.
- **Nasopharyngeal carcinoma** is strongly associated with the **Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)**. EBV is also a causative agent in **Burkitt lymphoma**.
*Kaposi sarcoma*
- **Kaposi sarcoma** is caused by **Human Herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8)**, not EBV.
- It typically presents as vascular skin lesions and can affect visceral organs, differing from the nasopharyngeal carcinoma described.
*Hepatocellular carcinoma*
- **Hepatocellular carcinoma** is primarily associated with **Hepatitis B virus (HBV)** and **Hepatitis C virus (HCV)** infection, as well as cirrhosis from other causes.
- There is no significant association between EBV and hepatocellular carcinoma.
*Adult T-cell lymphoma*
- **Adult T-cell lymphoma** is caused by the **Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1)**.
- This is a retrovirus distinct from EBV.
*Vulvar carcinoma*
- **Vulvar carcinoma** is most frequently associated with **Human Papillomavirus (HPV)** infection, especially high-risk strains like HPV 16 and 18.
- It is not typically linked to EBV.
Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis US Medical PG Question 5: A 16-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of a lesion that has been growing on his jaw over the past several months. He recently immigrated to the USA from Kenya with his family. Physical examination shows a 3-cm solid mass located above the left mandible. There is cervical lymphadenopathy. Biopsy of the mass shows sheets of lymphocytes and interspersed reactive histiocytes with abundant, clear cytoplasm and phagocytosed debris. Which of the following mechanisms is most likely directly responsible for the malignant transformation of this patient's cells?
- A. Defect in DNA repair
- B. Impairment of receptor function
- C. Inhibition of cell cycle arrest
- D. Integration of viral DNA (Correct Answer)
- E. Activation of transcription
Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis Explanation: **Integration of viral DNA**
- The clinical presentation (rapidly growing jaw mass in a young boy from Kenya) and histological findings (sheets of lymphocytes, "starry sky" appearance due to macrophages) are classic for **endemic Burkitt lymphoma**.
- Endemic Burkitt lymphoma is strongly associated with **Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)** infection. EBV DNA integrates into the host cell genome, promoting the characteristic **t(8;14) translocation** of *MYC* oncogene, leading to its overexpression and uncontrolled cell proliferation.
*Defect in DNA repair*
- While defects in DNA repair can lead to malignancy (e.g., in Lynch syndrome, xeroderma pigmentosum), it is not the primary mechanism of oncogenesis in Burkitt lymphoma.
- The hallmark of Burkitt lymphoma is a specific chromosomal translocation, not a generalized DNA repair defect.
*Impairment of receptor function*
- Impaired receptor function is associated with certain diseases (e.g., some autoimmune conditions, diabetes insipidus) but is not a direct mechanism for malignant transformation in Burkitt lymphoma.
- Malignancy typically arises from uncontrolled cell growth and division, not directly from receptor dysfunction.
*Inhibition of cell cycle arrest*
- While Burkitt lymphoma cells do evade cell cycle arrest, this is a **consequence** of the *MYC* oncogene overexpression, not the primary mechanism of malignant transformation itself.
- The **integration of viral DNA** leading to the *MYC* translocation is the upstream event that *causes* the inhibition of cell cycle arrest.
*Activation of transcription*
- **Activation of transcription** (specifically of the *MYC* oncogene) is a crucial step in the pathogenesis of Burkitt lymphoma, leading to uncontrolled cell growth.
- However, the direct cause of this dysregulated transcriptional activation is the **chromosomal translocation** resulting from viral DNA integration.
Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis US Medical PG Question 6: A 34-year-old man presents to an outpatient clinic with chronic fatigue and bumps on his neck, right axilla, and groin. Upon questioning, he reveals he frequently visits Japan on business and is rather promiscuous on his business trips. He denies use of barrier protection. On examination, there is generalized lymphadenopathy. Routine lab work reveals abnormal lymphocytes on peripheral smear. The serum calcium is 12.2 mg/dL. Which of the following viruses is associated with this patient’s condition?
- A. Hepatitis B virus
- B. Human T-lymphotropic virus 2
- C. Hepatitis C virus
- D. Human T-lymphotropic virus 1 (Correct Answer)
- E. Human immunodeficiency virus
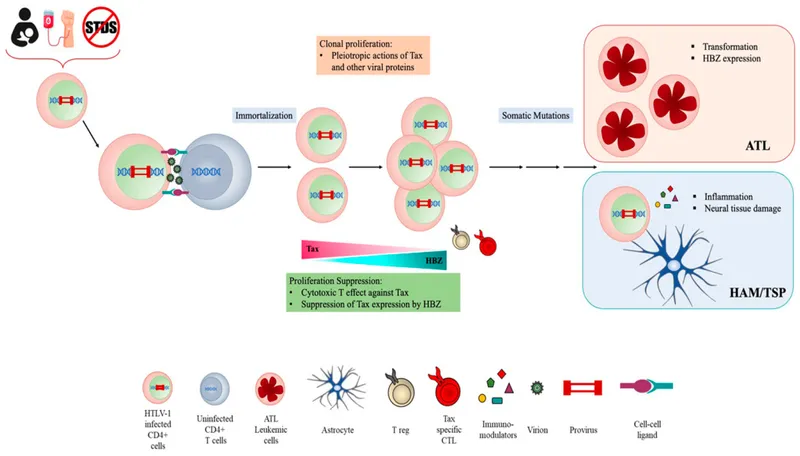
Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis Explanation: ***Human T-lymphotropic virus 1***
- The patient's presentation with **chronic fatigue**, **generalized lymphadenopathy**, **abnormal lymphocytes**, and **hypercalcemia** is highly suggestive of **Adult T-cell Leukemia/Lymphoma (ATLL)**.
- The history of being sexually promiscuous and frequent visits to **Japan**, an endemic area for **HTLV-1**, further supports this diagnosis, as HTLV-1 is the causative agent of ATLL.
*Hepatitis B virus*
- While **Hepatitis B virus (HBV)** can be sexually transmitted, it is primarily associated with **liver disease**, such as **hepatitis**, **cirrhosis**, and **hepatocellular carcinoma**.
- It does not cause **lymphadenopathy**, **atypical lymphocytes**, or **hypercalcemia** as seen in this patient.
*Human T-lymphotropic virus 2*
- **HTLV-2** is endemic in specific populations (e.g., Native Americans, intravenous drug users) and is less clearly linked to severe diseases compared to HTLV-1.
- While it can cause some neurological disorders, it is **not associated with ATLL** or the specific constellation of symptoms presented by this patient, particularly hypercalcemia.
*Hepatitis C virus*
- **Hepatitis C virus (HCV)** is also sexually transmitted but is mainly known for causing **chronic hepatitis**, **cirrhosis**, and some extrahepatic manifestations like **cryoglobulinemia** and **non-Hodgkin lymphoma**.
- It does not typically present with the **generalized lymphadenopathy**, **atypical lymphocytes**, or **hypercalcemia** that are characteristic of ATLL.
*Human immunodeficiency virus*
- **Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)** causes a range of symptoms including **lymphadenopathy** and **fatigue**, progressing to AIDS.
- However, the presence of **hypercalcemia with abnormal lymphocytes** pointing to a specific T-cell malignancy, especially with the epidemiological link to Japan, makes **HTLV-1** a more specific diagnosis than HIV.
Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis US Medical PG Question 7: A study is designed to assess the functions of immune components. The investigator obtains a lymph node biopsy from a healthy subject and observes it under a microscope. A photomicrograph of the cross-section of this lymph node is shown. Which of the following immunologic processes most likely occurs in the region labeled with an arrow?
- A. Isotype switching (Correct Answer)
- B. V(D)J recombination
- C. Macrophage activation
- D. T cell activation
- E. Negative selection
Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis Explanation: ***Isotype switching***
- The arrow points to a **germinal center**, a specialized microenvironment within lymph nodes where B cells undergo **affinity maturation** and **isotype switching**.
- Isotype switching (or class switching) is the process by which B cells change the type of **antibody** they produce, e.g., from IgM to IgG, IgA, or IgE, to mediate different effector functions while retaining antigen specificity.
*V(D)J recombination*
- **V(D)J recombination** is the genetic mechanism by which the diverse repertoires of T cell receptors (TCRs) and immunoglobulins (antibodies) are generated, primarily in the **bone marrow** (for B cells) and **thymus** (for T cells) during their development.
- This process occurs much earlier in lymphocyte development and is largely completed before B cells migrate to secondary lymphoid organs like lymph nodes and form germinal centers.
*Macrophage activation*
- **Macrophage activation** is a process where macrophages acquire enhanced phagocytic and microbicidal activity, often in response to cytokines like **IFN-γ** produced by T helper cells.
- While macrophages are present in lymph nodes and play a role in antigen presentation and immune responses, their primary activation does not specifically occur within germinal centers; the germinal center is mainly a site for B cell maturation.
*T cell activation*
- **T cell activation** primarily occurs in the **T cell zones** (paracortex) of lymph nodes, where **naïve T cells** encounter antigen-presenting cells (APCs) presenting their specific antigen.
- While T follicular helper (Tfh) cells, a type of T cell, are crucial for sustaining germinal center reactions, the germinal center itself is not the primary site for the initial activation of most T cells.
*Negative selection*
- **Negative selection** is a critical process in lymphocyte development, occurring in the **thymus** for T cells and **bone marrow** for B cells, where self-reactive lymphocytes are eliminated.
- This process ensures central tolerance and occurs long before mature lymphocytes populate secondary lymphoid organs like lymph nodes.
Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis US Medical PG Question 8: A 26-year-old woman comes to the physician because of several days of fever, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea. She drank water from a stream 1 week ago while she was hiking in the woods. Abdominal examination shows increased bowel sounds. Stool analysis for ova and parasites shows flagellated multinucleated trophozoites. Further evaluation shows the presence of antibodies directed against the pathogen. Secretion of these antibodies most likely requires binding of which of the following?
- A. CD28 to B7 protein
- B. CD80/86 to CTLA-4
- C. gp120 to CD4
- D. CD8 to MHC I
- E. CD40 to CD40 ligand (Correct Answer)
Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis Explanation: ***CD40 to CD40 ligand***
- The interaction between **CD40 on B cells** and **CD40 ligand (CD40L) on activated T helper cells** is crucial for **T cell-dependent B cell activation** and antibody class switching.
- This binding leads to the maturation of the immune response, including the secretion of **high-affinity antibodies** like IgA, which is especially important for mucosal immunity against pathogens like *Giardia lamblia* (the likely cause of the patient's symptoms).
*CD28 to B7 protein*
- The binding of **CD28 on T cells** to **B7 protein (CD80/86) on antigen-presenting cells (APCs)** provides the **second co-stimulatory signal** required for T cell activation.
- While essential for T cell activation, this interaction primarily supports T cell proliferation and differentiation, rather than directly mediating antibody secretion by B cells.
*CD80/86 to CTLA-4*
- **CTLA-4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4)** is a receptor on T cells that binds to **CD80/86 (B7)** on APCs with higher affinity than CD28.
- This interaction provides an **inhibitory signal** that downregulates T cell activation, serving as a negative feedback mechanism, and does not promote antibody secretion.
*gp120 to CD4*
- The **gp120 glycoprotein** on the surface of **HIV** binds to the **CD4 receptor** on T helper cells, initiating the entry of the virus into the cell.
- This interaction is specific to HIV infection and is not involved in the normal process of antibody secretion in response to other pathogens.
*CD8 to MHC I*
- **CD8** is a co-receptor expressed on **cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs)** that binds to **MHC class I molecules** on target cells.
- This interaction is essential for the recognition of virally infected or cancerous cells by CTLs, leading to their destruction, but it is not directly involved in antibody production.
Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis US Medical PG Question 9: A 12-year-old girl presents to her physician for the evaluation of episodic shortness of breath and cough. These episodes occur more frequently in spring. Her mother has a history of similar complaints. The physical examination reveals bilateral wheezes on chest auscultation. The initial response to pollen consists of the production of IgM; however, over time, antigen-specific IgE becomes predominant. This change from an IgM to an IgE response is caused by which of the following processes?
- A. Junctional diversity
- B. Allelic exclusion
- C. Somatic hypermutation
- D. Isotype switching (Correct Answer)
- E. Affinity maturation
Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis Explanation: ***Isotype switching***
- **Isotype switching** (or class switch recombination) is the process by which a B cell changes the class of antibody it produces from IgM to other classes like IgE, IgG, or IgA, while maintaining the same antigen specificity.
- This process is essential for diversifying the effector functions of antibodies, allowing **IgE** to mediate allergic reactions like the one described.
*Junctional diversity*
- **Junctional diversity** refers to the addition or subtraction of nucleotides at the junctions between V, D, and J gene segments during V(D)J recombination, thereby increasing antibody diversity.
- While it contributes to antigen-binding diversity, it does not explain the change in the **antibody class** (e.g., from IgM to IgE).
*Allelic exclusion*
- **Allelic exclusion** is a mechanism that ensures each B cell produces only one functional heavy chain and one functional light chain of a specific antibody.
- This process prevents the production of multiple antibody specificities by a single B cell, but it does not account for the change in **antibody class**.
*Somatic hypermutation*
- **Somatic hypermutation** introduces point mutations into the variable regions of antibody genes after antigen encounter, leading to changes in antigen-binding affinity.
- This process is crucial for **affinity maturation** but does not directly cause the switch from IgM to IgE production.
*Affinity maturation*
- **Affinity maturation** is the process by which the affinity of antibodies for their specific antigen increases over time due to repeated exposure to the antigen, driven by somatic hypermutation and selection.
- While important for a strong immune response, it describes the refinement of antibody binding, not the change in the **antibody class** itself.
Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis US Medical PG Question 10: A 16-year-old male is brought to the clinic by his mother for the complaints of fever, nonproductive cough, fatigue, lack of appetite, and sore throat for the past 2 months. Several other students at his high school have had similar symptoms. Physical exam shows a whitish membrane in his oropharynx, bilateral enlarged cervical lymphadenopathy, and mild splenomegaly. Which of the following tests is most likely to diagnose his condition?
- A. Monospot test (Correct Answer)
- B. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- C. Throat culture
- D. Urine culture
- E. Chest X-ray
Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis Explanation: ***Monospot test***
- The Monospot test detects **heterophile antibodies**, which are commonly produced during an acute Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, the cause of **infectious mononucleosis**.
- The patient's symptoms (fever, fatigue, nonproductive cough, sore throat, cervical lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly) and the epidemiological context (several other students with similar symptoms) are highly suggestive of **infectious mononucleosis**.
*Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)*
- While ELISA can detect antibodies to various pathogens, including EBV-specific antigens, the **Monospot test** is the more common and rapid initial diagnostic tool for infectious mononucleosis.
- ELISA for EBV-specific antibodies (e.g., VCA-IgM, VCA-IgG) might be used if the Monospot test is negative but clinical suspicion remains high, especially in younger children or atypical presentations.
*Throat culture*
- A throat culture is used to identify bacterial infections, such as **Streptococcus pyogenes** (strep throat).
- Although the patient has a sore throat and a whitish membrane, his other systemic symptoms (fatigue, splenomegaly, lack of appetite for 2 months) are not typical for a bacterial pharyngitis which usually responds to antibiotics. A **nonproductive cough** also makes bacterial pharyngitis less likely.
*Urine culture*
- A urine culture is used to diagnose **urinary tract infections**.
- The patient's symptoms are not indicative of a urinary tract infection.
*Chest X-ray*
- A chest X-ray is used to evaluate the lungs for conditions such as **pneumonia**, **bronchitis**, or other respiratory pathologies.
- While the patient has a nonproductive cough, the predominant systemic symptoms (fever, fatigue, lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly) point towards a systemic viral infection rather than primarily a lung issue that would be definitively diagnosed by a chest X-ray.
More Mechanisms of viral oncogenesis US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.