Human T-cell leukemia virus US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Human T-cell leukemia virus. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
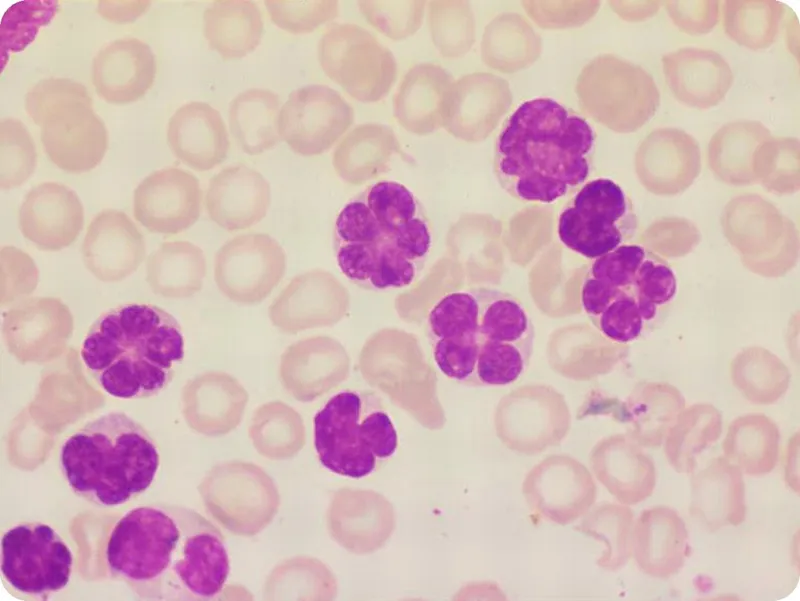
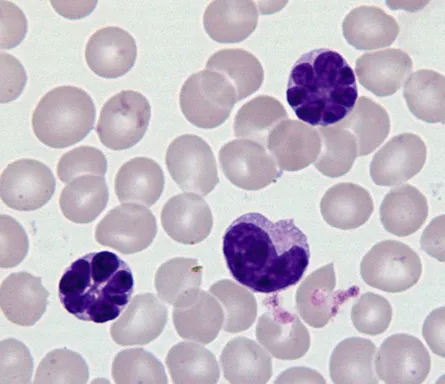
Human T-cell leukemia virus US Medical PG Question 1: A 69-year-old Caucasian man presents for a routine health maintenance examination. He feels well. He has no significant past medical history. He takes aspirin for the occasional headaches that he has had for over several years. He exercises every day and does not smoke. His father was diagnosed with a hematologic malignancy at 79 years old. The patient’s vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. The laboratory test results are as follows:
Hemoglobin 14.5 g/dL
Leukocyte count 62,000/mm3
Platelet count 350,000/mm3
A peripheral blood smear is obtained (shown on the image). Which of the following best explains these findings?
- A. Acute lymphoid leukemia
- B. Hairy cell leukemia
- C. Adult T cell leukemia
- D. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (Correct Answer)
- E. Acute myeloid leukemia
Human T-cell leukemia virus Explanation: ***Chronic lymphocytic leukemia***
- The image displays characteristic **smudge cells** (also known as **basket cells**) and mature-looking lymphocytes with scant cytoplasm and condensed chromatin, which are hallmarks of CLL.
- The patient's age (69 years), elevated leukocyte count (62,000/mm³), and the presence of these particular cells on peripheral smear in an otherwise asymptomatic individual are all highly suggestive of CLL.
*Acute lymphoid leukemia*
- This condition is characterized by a proliferation of **blasts** (immature lymphocytes) in the bone marrow and peripheral blood, which are not depicted in the provided image.
- While it can present with a high leukocyte count, the cellular morphology would show a predominance of immature cells rather than the mature-appearing lymphocytes and smudge cells seen here.
*Hairy cell leukemia*
- This leukemia is characterized by lymphocytes with **fine cytoplasmic projections** (hairy cells) and typically leads to **pancytopenia**, particularly leukopenia, rather than the marked leukocytosis seen in this patient.
- The morphology in the image does not show these cytoplasmic projections.
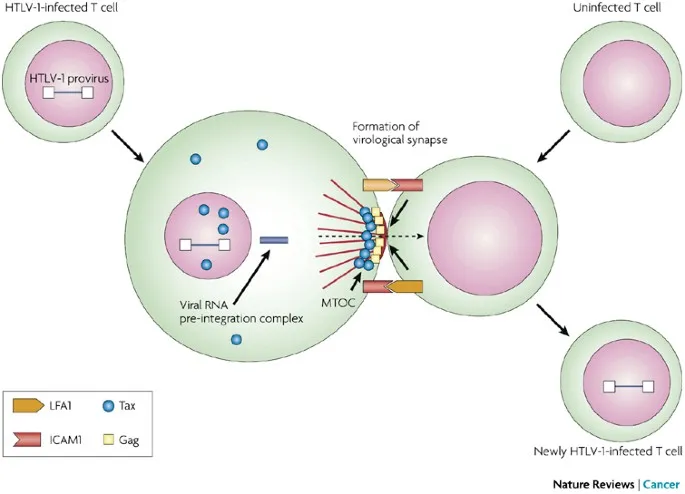
*Adult T cell leukemia*
- This form of leukemia is caused by the **human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1)** and is more prevalent in specific endemic regions (e.g., Japan, Caribbean).
- It usually presents with **atypical pleomorphic T-cells** with convoluted nuclei, often accompanied by skin lesions, hypercalcemia, and lymphadenopathy, none of which are mentioned or depicted.
*Acute myeloid leukemia*
- AML is characterized by an overgrowth of **myeloblasts** (immature myeloid cells) in the bone marrow and peripheral blood, often containing **Auer rods**.
- The cells in the image are clearly lymphoid in origin and do not show features of myeloblasts or Auer rods.
Human T-cell leukemia virus US Medical PG Question 2: A 5-year-old boy presents to his pediatrician with weakness. His father observed that his son seemed less energetic at daycare and kindergarten classes. He was becoming easily fatigued from mild play. His temperature is 98°F (37°C), blood pressure is 90/60 mmHg, pulse is 100/min, and respirations are 20/min. Physical exam reveals pale conjunctiva, poor skin turgor and capillary refill, and cervical and axillary lymphadenopathy with assorted bruises throughout his body. A complete blood count reveals the following:
Leukocyte count: 3,000/mm^3
Segmented neutrophils: 30%
Bands: 5%
Eosinophils: 5%
Basophils: 10%
Lymphocytes: 40%
Monocytes: 10%
Hemoglobin: 7.1 g/dL
Hematocrit: 22%
Platelet count: 50,000/mm^3
The most specific diagnostic assessment would most likely show which of the following?
- A. Bone marrow biopsy with ≥ 20% lymphoblasts (Correct Answer)
- B. Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis with 9:22 translocation
- C. Peripheral blood smear with > 50% lymphoblasts
- D. Flow cytometry with positive terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase staining
- E. Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis with 12:21 translocation
Human T-cell leukemia virus Explanation: ***Bone marrow biopsy with ≥ 20% lymphoblasts***
- The patient's symptoms (weakness, fatigue, pallor, bruising, lymphadenopathy) and blood counts (anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia with relative lymphocytosis) are highly suggestive of **Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)**.
- The most specific diagnostic assessment for ALL involves a **bone marrow biopsy** showing **≥20% lymphoblasts** per WHO 2016 classification, confirming the abnormal proliferation of immature lymphoid cells.
- This is the **gold standard** for diagnosing ALL and distinguishes it from other hematologic disorders.
*Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis with 9:22 translocation*
- The **Philadelphia chromosome (t[9;22])** is characteristic of **Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)**, which is rare in children and presents differently.
- While t(9;22) can occur in 3-5% of childhood ALL and indicates poor prognosis, it is a **prognostic marker**, not the primary diagnostic criterion for ALL itself.
*Peripheral blood smear with > 50% lymphoblasts*
- While lymphoblasts can be seen in the peripheral blood in ALL, a specific percentage threshold in peripheral blood is **not a diagnostic criterion** for ALL.
- The peripheral blood smear can be suggestive, but the **bone marrow blast percentage is the gold standard** for definitive diagnosis.
*Flow cytometry with positive terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase staining*
- **Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)** is a nuclear enzyme expressed in pre-B and pre-T lymphoblasts and is an important marker for ALL.
- Flow cytometry with positive TdT staining helps **characterize and classify the blasts** but does not quantify the blast percentage required for diagnosis, which is provided by the bone marrow biopsy.
*Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis with 12:21 translocation*
- The **t(12;21) [ETV6-RUNX1] translocation** is the most common cytogenetic abnormality in childhood B-cell ALL (20-25% of cases) and is associated with favorable prognosis.
- While its presence is relevant for risk stratification and treatment planning, the primary diagnostic criterion for ALL is the **percentage of lymphoblasts in the bone marrow**.
Human T-cell leukemia virus US Medical PG Question 3: A 4-year-old girl is brought to the physician because of a 3-week history of generalized fatigue and easy bruising. During the past week, she has also had fever and severe leg pain that wakes her up at night. Her temperature is 38.3°C (100.9°F), pulse is 120/min, and respirations are 30/min. Examination shows cervical and axillary lymphadenopathy. The abdomen is soft and nontender; the liver is palpated 3 cm below the right costal margin, and the spleen is palpated 2 cm below the left costal margin. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 10.1 g/dL
Leukocyte count 63,000/mm3
Platelet count 27,000/mm3
A bone marrow aspirate predominantly shows immature cells that stain positive for CD10, CD19, and TdT. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Aplastic anemia
- B. Hodgkin lymphoma
- C. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Correct Answer)
- D. Acute myeloid leukemia
- E. Hairy cell leukemia
Human T-cell leukemia virus Explanation: ***Acute lymphoblastic leukemia***
- The constellation of **generalized fatigue**, **easy bruising** (due to **thrombocytopenia**), fever, **severe leg pain** (bone marrow infiltration), **hepatosplenomegaly**, and **lymphadenopathy** in a child is highly suggestive of **acute leukemia**.
- The laboratory findings of **anemia** (Hb 10.1 g/dL), **thrombocytopenia** (platelet count 27,000/mm³), and a **markedly elevated leukocyte count** (63,000/mm³) with **immature cells** (blasts) in the bone marrow, staining positive for **CD10, CD19, and TdT**, are pathognomonic for **B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)**.
*Aplastic anemia*
- This condition is characterized by **pancytopenia** (low levels of all blood cell types) due to bone marrow failure, but it would not typically present with **lymphadenopathy**, **hepatosplenomegaly**, or an extremely high leukocyte count with immature cells.
- The bone marrow would be **hypocellular** rather than hypercellular with blasts, as seen in this patient.
*Hodgkin lymphoma*
- While Hodgkin lymphoma can cause **lymphadenopathy** and systemic symptoms like fever and fatigue (B symptoms), it is less common in this age group and does not present with **pancytopenia** or an overwhelming presence of immature cells in the bone marrow.
- Diagnosis relies on the identification of **Reed-Sternberg cells** in lymph node biopsy.
*Acute myeloid leukemia*
- **AML** can also present with similar symptoms and pancytopenia with elevated blasts, but the immunophenotype would differ, typically showing markers like **CD13, CD33, and myeloid-specific markers**, not **CD10, CD19, and TdT**.
- **TdT** positivity is characteristic of lymphoid progenitors.
*Hairy cell leukemia*
- This is a rare, **chronic B-cell leukemia** primarily affecting older adults, not children, and is characterized by cells with **"hairy" projections**, **massive splenomegaly**, and typically **pancytopenia** without a high blast count.
- The immunophenotype involves **CD11c, CD25, CD103, and CD123**.
Human T-cell leukemia virus US Medical PG Question 4: A 72-year-old man goes to his primary care provider for a checkup after some blood work showed lymphocytosis 3 months ago. He says he has been feeling a bit more tired lately but doesn’t complain of any other symptoms. Past medical history is significant for hypertension and hyperlipidemia. He takes lisinopril, hydrochlorothiazide, and atorvastatin. Additionally, his right hip was replaced three years ago due to osteoarthritis. Family history is noncontributory. He drinks socially and does not smoke. Today, he has a heart rate of 95/min, respiratory rate of 17/min, blood pressure of 135/85 mm Hg, and temperature of 36.8°C (98.2°F). On physical exam, he looks well. His heartbeat has a regular rate and rhythm and lungs that are clear to auscultation bilaterally. Additionally, he has mild lymphadenopathy of his cervical lymph nodes. A complete blood count with differential shows the following:
Leukocyte count 5,000/mm3
Red blood cell count 3.1 million/mm3
Hemoglobin 11.0 g/dL
MCV 95 um3
MCH 29 pg/cell
Platelet count 150,000/mm3
Neutrophils 40%
Lymphocytes 40%
Monocytes 5%
A specimen is sent for flow cytometry that shows a population that is CD 5, 19, 20, 23 positive. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (Correct Answer)
- B. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura
- C. Aplastic anemia
- D. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- E. Tuberculosis
Human T-cell leukemia virus Explanation: ***Chronic lymphocytic leukemia***
- The patient presents with mild **lymphadenopathy**, a **history of lymphocytosis**, and a **flow cytometry** showing cells positive for **CD5, CD19, CD20, and CD23**, which is pathognomonic for **CLL**.
- While the total leukocyte count is within normal limits due to the absolute neutrophil decrease, the persistent lymphocytosis and characteristic immunophenotype are highly indicative of CLL.
*Immune thrombocytopenic purpura*
- This condition is characterized by **isolated thrombocytopenia** caused by autoantibody-mediated platelet destruction, which is not supported by the patient's normal platelet count (150,000/mm3).
- While it can cause fatigue, it doesn't explain the lymphocytosis or the specific **CD marker profile**.
*Aplastic anemia*
- Aplastic anemia involves **pancytopenia** (decreased red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets) due to bone marrow failure, which is not consistent with the patient's normal-range leukocyte and platelet counts.
- The patient's presentation with lymphocytosis and lymphadenopathy further makes this diagnosis unlikely.
*Acute lymphoblastic leukemia*
- **ALL** typically presents with symptoms related to **bone marrow failure** (anemia, thrombocytopenia, infections) and often very **high blast counts** in the peripheral blood and bone marrow.
- While it involves lymphocytes, the specific **CD5/19/20/23 co-expression** is characteristic of CLL, and ALL usually involves more aggressive symptoms and a different immunophenotype.
*Tuberculosis*
- **Tuberculosis** is an infectious disease that can cause **lymphadenopathy** and systemic symptoms like fatigue, but it is typically associated with a **caseating granulomatous inflammation** and is diagnosed via cultures or PCR rather than flow cytometry.
- It would not explain the specific **B-cell lymphocytosis** with the described immunophenotype.
Human T-cell leukemia virus US Medical PG Question 5: A 72-year-old man presents to the primary care clinic for evaluation of progressive fatigue and weight loss. His past medical history is significant for hypercholesterolemia, type 2 diabetes mellitus, aortic stenosis, and chronic renal insufficiency. He endorses being well-rested after waking from sleep but fatiguing rapidly during the day. In addition, he states that he has lost 15lbs over the previous month. His temperature is 98.3°F (36.8°C), pulse is 100/min, blood pressure is 110/85 mmHg, respirations are 16/min, and oxygen saturation is 96% on room air. Physical exam is notable for conjunctival pallor and scattered areas of ecchymoses. His laboratory results are shown below:
Serum:
Na+: 140 mEq/L
K+: 4.0 mEq/L
Cl-: 101 mEq/L
HCO3-: 22 mEq/L
BUN: 30 mg/dL
Glucose: 160 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1.9 mg/dL
Leukocyte count: 1,100/mm^3
Absolute neutrophil count 920/mm^3
Hemoglobin 8.4 g/dL
Platelet count: 45,000/mm^3
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration: 34%
Red blood cell distribution width: 12.0%
Mean corpuscular volume: 92 µm^3
Lactate dehydrogenase: 456 IU/L
Haptoglobin 120 mg/dL
Fibrinogen 214 mg/dL
A bone marrow biopsy is performed which shows cells that are CD19+, CD20+, CD11c+, and stain with acid phosphatase 5 and tartrate-resistant. Which of the following is the next best step in the treatment of his disorder?
- A. Cyclophosphamide
- B. Hydroxyurea
- C. Cladribine (Correct Answer)
- D. Filgrastim
- E. Doxorubicin
Human T-cell leukemia virus Explanation: ***Cladribine***
- The patient's blood work (pancytopenia: **leukopenia**, **anemia**, **thrombocytopenia**) along with bone marrow biopsy findings (**CD19+, CD20+, CD11c+, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase-positive** cells) are highly indicative of **hairy cell leukemia**.
- **Cladribine** is a purine analog, which is considered the most effective first-line treatment for hairy cell leukemia, often leading to long-lasting remissions.
*Cyclophosphamide*
- This is an **alkylating agent** used in various cancers and autoimmune conditions, but it is not the most effective or preferred first-line treatment for hairy cell leukemia.
- Cyclophosphamide is associated with significant side effects and would likely be reserved for other hematological malignancies.
*Hydroxyurea*
- **Hydroxyurea** is a ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor primarily used in myeloproliferative disorders like **chronic myeloid leukemia** or **polycythemia vera** to reduce cell counts.
- While it can lower white blood cell counts, it is not curative and not the standard primary therapy for hairy cell leukemia.
*Filgrastim*
- **Filgrastim** is a **granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)** used to stimulate neutrophil production, often to counter neutropenia caused by chemotherapy.
- It would not be used to treat hairy cell leukemia itself, and in some cases, can even paradoxically induce leukocytosis, which may not be desired in a condition characterized by abnormal white blood cells.
*Doxorubicin*
- **Doxorubicin** is an **anthracycline antibiotic** used in the treatment of many cancers (e.g., lymphomas, breast cancer, sarcomas) but not hairy cell leukemia.
- Its mechanism of action involves DNA intercalation and inhibition of topoisomerase II, which is not the primary target for hairy cell leukemia therapy.
Human T-cell leukemia virus US Medical PG Question 6: A 29-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of fatigue, weight loss, and multiple painless swellings on his neck and axilla. He reports that his swellings become painful after he drinks alcohol. Physical examination shows nontender cervical and axillary lymphadenopathy. A lymph node biopsy specimen shows giant binucleate cells. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- B. Acute retroviral syndrome
- C. Hodgkin lymphoma (Correct Answer)
- D. Acute lymphocytic leukemia
- E. Adult T-cell lymphoma
Human T-cell leukemia virus Explanation: ***Hodgkin lymphoma***
- The presence of **fatigue, weight loss, and painless lymphadenopathy** (B symptoms) in a young man is highly suggestive of Hodgkin lymphoma.
- The **lymph node biopsy showing giant binucleate cells** (Reed-Sternberg cells) is pathognomonic for Hodgkin lymphoma, and **alcohol-induced lymph node pain** is a classic, though uncommon, symptom.
*Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma*
- This is an **aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma** that can present with rapidly enlarging lymph nodes and B symptoms.
- However, the characteristic **Reed-Sternberg cells** found on biopsy are not seen in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
*Acute retroviral syndrome*
- This syndrome typically presents with **flu-like symptoms, fever, sore throat, and generalized lymphadenopathy** within weeks of HIV infection.
- It is usually **self-limiting** and does not feature the specific histopathology of giant binucleate cells on lymph node biopsy.
*Acute lymphocytic leukemia*
- This is a **hematologic malignancy** characterized by the proliferation of immature lymphoid cells.
- It often presents with symptoms of **bone marrow failure** (anemia, bleeding, infections) and can have lymphadenopathy, but the diagnostic lymph node biopsy features are not consistent with Reed-Sternberg cells.
*Adult T-cell lymphoma*
- This rare lymphoma is associated with **human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infection** and is more common in endemic regions.
- It can present with lymphadenopathy, skin lesions, and hypercalcemia, but the histopathology would show **pleomorphic T-cells**, not Reed-Sternberg cells.
Human T-cell leukemia virus US Medical PG Question 7: A 16-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of a lesion that has been growing on his jaw over the past several months. He recently immigrated to the USA from Kenya with his family. Physical examination shows a 3-cm solid mass located above the left mandible. There is cervical lymphadenopathy. Biopsy of the mass shows sheets of lymphocytes and interspersed reactive histiocytes with abundant, clear cytoplasm and phagocytosed debris. Which of the following mechanisms is most likely directly responsible for the malignant transformation of this patient's cells?
- A. Defect in DNA repair
- B. Impairment of receptor function
- C. Inhibition of cell cycle arrest
- D. Integration of viral DNA (Correct Answer)
- E. Activation of transcription
Human T-cell leukemia virus Explanation: **Integration of viral DNA**
- The clinical presentation (rapidly growing jaw mass in a young boy from Kenya) and histological findings (sheets of lymphocytes, "starry sky" appearance due to macrophages) are classic for **endemic Burkitt lymphoma**.
- Endemic Burkitt lymphoma is strongly associated with **Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)** infection. EBV DNA integrates into the host cell genome, promoting the characteristic **t(8;14) translocation** of *MYC* oncogene, leading to its overexpression and uncontrolled cell proliferation.
*Defect in DNA repair*
- While defects in DNA repair can lead to malignancy (e.g., in Lynch syndrome, xeroderma pigmentosum), it is not the primary mechanism of oncogenesis in Burkitt lymphoma.
- The hallmark of Burkitt lymphoma is a specific chromosomal translocation, not a generalized DNA repair defect.
*Impairment of receptor function*
- Impaired receptor function is associated with certain diseases (e.g., some autoimmune conditions, diabetes insipidus) but is not a direct mechanism for malignant transformation in Burkitt lymphoma.
- Malignancy typically arises from uncontrolled cell growth and division, not directly from receptor dysfunction.
*Inhibition of cell cycle arrest*
- While Burkitt lymphoma cells do evade cell cycle arrest, this is a **consequence** of the *MYC* oncogene overexpression, not the primary mechanism of malignant transformation itself.
- The **integration of viral DNA** leading to the *MYC* translocation is the upstream event that *causes* the inhibition of cell cycle arrest.
*Activation of transcription*
- **Activation of transcription** (specifically of the *MYC* oncogene) is a crucial step in the pathogenesis of Burkitt lymphoma, leading to uncontrolled cell growth.
- However, the direct cause of this dysregulated transcriptional activation is the **chromosomal translocation** resulting from viral DNA integration.
Human T-cell leukemia virus US Medical PG Question 8: A 40-year-old male presents to his primary care physician for a regularly scheduled check-up. Physical examination reveals nontender cervical lymphadenopathy. A biopsy of the lymph node reveals aggregates of follicular architecture, and cytogenic analysis shows a t(14;18) translocation. The protein most likely responsible for the patient’s condition does which of the following:
- A. Regulates passage through the cell cycle
- B. Activates DNA repair proteins
- C. Regulates cell growth through signal transduction
- D. Inhibits apoptosis (Correct Answer)
- E. Provides mitotic cytoskeleton
Human T-cell leukemia virus Explanation: ***Inhibits apoptosis***
- The t(14;18) translocation is characteristic of **follicular lymphoma** and leads to the overexpression of the **BCL-2 protein**.
- **BCL-2** is an anti-apoptotic protein that prevents programmed cell death, allowing abnormal cells to accumulate.
*Regulates passage through the cell cycle*
- Proteins involved in **cell cycle regulation** (e.g., p53, Rb) control progression through different phases, but BCL-2's primary role is in cell survival, not direct cell cycle progression.
- Dysregulation of cell cycle proteins is seen in many cancers, but the specific BCL-2 translocation primarily affects apoptosis.
*Activates DNA repair proteins*
- **DNA repair proteins** (e.g., ATM, BRCA1/2) are crucial for maintaining genomic integrity and correcting DNA damage.
- While important in cancer development, their activation is not the direct function of the BCL-2 protein overexpressed due to the t(14;18) translocation.
*Regulates cell growth through signal transduction*
- **Signal transduction pathways** often involve growth factors and their receptors (e.g., RTKs) that regulate cell proliferation and differentiation.
- While BCL-2 indirectly impacts cell numbers by preventing apoptosis, its direct role is not in initiating or participating in growth-promoting signal transduction cascades.
*Provides mitotic cytoskeleton*
- The **mitotic cytoskeleton**, composed of microtubules, is essential for chromosome segregation during cell division.
- Proteins like tubulin are the primary components, and BCL-2 has no direct role in forming or organizing these structures.
Human T-cell leukemia virus US Medical PG Question 9: A 55-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-day history of decreased urine output, progressively worsening bilateral pedal edema, and fatigue. He has a 4-month history of persistent lower back pain. He has hypercholesterolemia and stable angina pectoris. Current medications include atorvastatin, aspirin, and ibuprofen. His pulse is 80/min, respirations are 16/min, and blood pressure is 150/100 mm Hg. Examination shows periorbital and pedal edema and pallor. There is tenderness of the lumbar spinal vertebrae. Straight leg raise test is negative. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 8.9 g/dl
Serum
Urea nitrogen 20 mg/dl
Creatinine 2.4 mg/dl
Calcium 11.2 mg/dl
Alkaline phosphatase 140 U/L
X-ray of the spine shows diffuse osteopenia and multiple lytic lesions. Which of the following is most likely to confirm the diagnosis?
- A. Bone marrow biopsy (Correct Answer)
- B. Parathyroid hormone levels
- C. Congo red stain of renal tissue
- D. Peripheral blood smear
- E. Skeletal survey
Human T-cell leukemia virus Explanation: ***Bone marrow biopsy***
- This patient presents with signs highly suggestive of **multiple myeloma**, including **anemia**, **renal insufficiency**, **hypercalcemia**, and **lytic bone lesions** and diffuse osteopenia.
- A **bone marrow biopsy** is the most definitive test to confirm multiple myeloma by identifying an increased percentage of **plasma cells** and their clonality.
*Parathyroid hormone levels*
- While **hypercalcemia** is present, increased parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels would indicate **primary hyperparathyroidism**, which typically causes diffuse osteopenia but not multiple lytic lesions in this pattern.
- In multiple myeloma, hypercalcemia results from **bone destruction** by plasma cells, leading to **suppressed PTH levels**.
*Congo red stain of renal tissue*
- A Congo red stain of renal tissue is used to diagnose **amyloidosis**, which can cause renal failure, proteinuria, and sometimes edema.
- Although amyloidosis can be a complication of multiple myeloma, it is not the primary diagnostic test for the underlying myeloma itself, and this patient's presentation with prominent lytic lesions points more directly to myeloma.
*Peripheral blood smear*
- A peripheral blood smear might show **rouleaux formation** (RBCs stacked like coins) and occasionally **plasma cells**, which are suggestive of multiple myeloma.
- However, these findings are not specific or reliably present in all cases, and a bone marrow biopsy is required for definitive diagnosis.
*Skeletal survey*
- A skeletal survey (X-ray series) is crucial for identifying and characterizing the **lytic bone lesions** and diffuse osteopenia, as seen in this patient.
- While it provides strong evidence of bone involvement, it is an imaging study that supports the diagnosis but does not definitively confirm the underlying hematological malignancy like a bone marrow biopsy does.
Human T-cell leukemia virus US Medical PG Question 10: A 63-year-old man presents to his primary care physician because he has been having headaches and hearing loss. In addition, he says that he has been having difficulty opening his jaw to eat and recurrent middle ear infections. Physical exam reveals enlarged neck lymph nodes and a mass in the nasopharynx. Biopsy of the mass reveals undifferentiated squamous epithelial cells. The organism that is most likely associated with this patient's disease is also associated with which of the following disorders?
- A. Kaposi sarcoma
- B. Hepatocellular carcinoma
- C. Adult T-cell lymphoma
- D. Burkitt lymphoma (Correct Answer)
- E. Vulvar carcinoma
Human T-cell leukemia virus Explanation: ***Burkitt lymphoma***
- The patient's symptoms (headaches, hearing loss, difficulty opening jaw, recurrent middle ear infections, nasopharyngeal mass, enlarged neck lymph nodes) and biopsy results (undifferentiated squamous epithelial cells) point to **nasopharyngeal carcinoma**.
- **Nasopharyngeal carcinoma** is strongly associated with the **Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)**. EBV is also a causative agent in **Burkitt lymphoma**.
*Kaposi sarcoma*
- **Kaposi sarcoma** is caused by **Human Herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8)**, not EBV.
- It typically presents as vascular skin lesions and can affect visceral organs, differing from the nasopharyngeal carcinoma described.
*Hepatocellular carcinoma*
- **Hepatocellular carcinoma** is primarily associated with **Hepatitis B virus (HBV)** and **Hepatitis C virus (HCV)** infection, as well as cirrhosis from other causes.
- There is no significant association between EBV and hepatocellular carcinoma.
*Adult T-cell lymphoma*
- **Adult T-cell lymphoma** is caused by the **Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1)**.
- This is a retrovirus distinct from EBV.
*Vulvar carcinoma*
- **Vulvar carcinoma** is most frequently associated with **Human Papillomavirus (HPV)** infection, especially high-risk strains like HPV 16 and 18.
- It is not typically linked to EBV.
More Human T-cell leukemia virus US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.